- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 8th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 8th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.

8th Standard CBSE Subjects
8th standard cbse study materials.


Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 8th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
A to Z Classes
Cbse, ncert and icse solution online, class 8 science case study question, case study question class 8 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 8 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 8 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 8 Science.
There are total 18 chapter Crop Production and Management, Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
, Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Materials: Metals and Non-Metals, Coal and Petroleum, Combustion and Flame, Conservation of Plants and Animals, Cell – Structure and Functions, Reproduction in Animals, Reaching the Age of Adolescence, Force and Pressure, Friction, Sound, Chemical Effects of Electric Current, Some Natural Phenomena, Light, Stars and the Solar System, Pollution of Air and Water
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 8 Science Case Study Question
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum Case Study Question
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Case Study Question
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions Case Study Question
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence Case Study Question
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure Case Study Question
- Chapter 12 Friction Case Study Question
- Chapter 13 Sound Case Study Question
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Case Study Question
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Case Study Question
- Chapter 16 Light Case Study Question
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Case Study Question
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions For Class 8 Science
CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Science
CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Science help students face the exams confidently. As the exam nears, they should complete the syllabus and start with the revision. The CBSE Important Questions for Class 8 Science will help them revise the subject quickly. Here, we have compiled the important questions for all the chapters of the CBSE Class 8 Science subject. By solving them, students will understand the types of questions asked in the exam. All types of questions are provided for students’ practice from basic to high level. CBSE Class 8 Science is a fascinating subject and includes interesting topics, thus providing basic knowledge about light, current, force, human beings, etc. Solving these CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions is the best way to revise the major concepts of the subject.
The subject experts created the questions based exclusively from the exam perspective. Students must start solving them at least 20 days before the annual exam. By doing so, they will be able to analyse their weak areas and work on them. Practising the CBSE Important Questions will improve their performance and overall score in CBSE Class 8 Science exam.
There is a total of 18 chapters in NCERT Class 8 Science book. In the table below, we have provided the Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science for all the chapters. We have also included all types of questions, i.e. very short, short and long answers. These questions will cover all the crucial topics and the CBSE Class 8 Science syllabus.
How to Practise the CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions
- Practise the question of a particular chapter in one go.
- Refrain from looking for the answer while solving the questions.
- Allocate a time duration for solving the questions and try to finish it accordingly.
- After completing all the questions, do a self-evaluation.
- Go through those questions again that could not be solved.
We, at BYJU’S, also provide other study materials such as CBSE Class 8 Science sample papers , notes, exemplars, solutions, etc.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Byjus app was super
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Extra Questions and Answers are provided here. We prepared these extra questions based on the latest NCERT Class 8 Science Book. CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Extra Questions will help you to properly understand a particular concept of the chapter.
Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Extra Questions
Very short answer type question.
Question 1: Name the plastic whose sheets are used for packing liquids.
Answer: Polythene
Question 2: Name one naturally occurring polymer.
Answer: Cellulose
Question 3: Name the fibre used for making parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
Answer: Nylon
Question 4: Which synthetic fiber is known as artificial silk?
Answer: Rayon fiber is known as artificial silk.
Question 5: Which is the first fully synthetic fibre?
Answer: Nylon is the first fully synthetic fibre.
Question 6: Write one disadvantage of synthetic fibre.
Answer: Synthetic fibres melt on heating.
Question 7: What are esters?
Answer: Esters are the chemicals which give fruits their smell.
Question 8: What are the 4 R in waste management? Or What are the 4 R’s principles of plastic?
Answer: 4 R principles mean Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover.
Question 9: What are the advantages of nylon?
Answer: Nylon fibre is strong, elastic and light. It is lustrous and easy to wash.
Question 10: Write uses of bakelite.
Answer: It is used for making electrical switches, handles of various utensils, etc.
Question 11: Write uses of melamine.
Answer: It is used for making floor tiles, kitchenware and fabrics which resist fire.
Question 12: How is rayon different from synthetic fibres?
Answer: Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because it is obtained from a natural source, wood pulp.
Question 13: Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Answer: Nylon fibres are very strong as it is used to make parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
Question 14: What is polythene?
Answer: Polythene (Poly + ethene) is a type of plastic that is used for making commonly used polythene bags.
Question 15: Is plastic bag non-biodegradable? Why?
Answer: Plastic bag is non-biodegradable because it takes several years to degenerate.
Question 16: Can we store jams and pickles in plastic containers? Give reason.
Answer: We can store jams and pickles in plastic containers because plastics do not react with water and air and do not get corroded easily.
Question 17: Do all plastics have same type of arrangement of units?
Answer: All plastics do not have the same type of arrangement of units. In some it is linear, whereas in others it is cross-linked.
Question 18: Why nylon is called fully synthetic fibre?
Answer: Nylon is called fully synthetic fibre because it is prepared from coal, water and air.
Question 19: What is polyester?
Answer: Polyester (Poly+ ester) is actually made up of the repeating units of a chemical called an ester.
Question 20: Write one use of acrylic.
Answer: Acrylic is used as a substitute of natural wool for knitting sweaters, shawls, blankets etc.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1: Why is nylon used for making parachutes and ropes for rock climbing?
Answer: Nylon is used for making parachutes and ropes for rock climbing because nylon fibre is strong and can hold heavy weight.
Question 2: What is polymer?
Answer: Synthetic fibres and plastics, like natural fibres, are made of very large units called polymers. Polymers are made up of many smaller units.
Question 3: Define petrochemicals.
Answer: All the synthetic fibres are prepared by a number of processes using raw materials of petroleum origin, called petrochemicals.
Question 4: Why should we use a cotton carry bag or jute bag while going for shopping?
Answer: We should use cotton or jute bags while going for shopping in order to minimise the use of plastic bags.
Question 5: Why plastic articles are available in all shape and size?
Answer: Plastic articles are available in all possible shapes and sizes because plastic is easily mouldable i.e. can be shaped in any form.
Question 6: Why is Teflon used for nonstick coating on cookware? Or Which material is used for coating non-stick kitchen wares and why?
Answer: Teflon is used for nonstick coating on cookwares because it is a special plastic on which oil and water do not stick.
Question 7: Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Answer: Plastic containers are favoured for storing food because of their light weight, lower price, good strength and easy handling.
Question 8: What is PET? Write its uses.
Answer: PET is a very familiar form of polyester. It is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires and many other useful products.
Question 9: Give the composition of Polycot and Polywool.
Answer: Polycot is a mixture of polyester and cotton.
Polywool is a mixture of polyester and wool.
Question 10: “Tin, aluminium and other metal can are considered non-biodegradable.” Give reason.
Answer: Tin, aluminium and other metal can are considered non-biodegradable because they approximately take 100 to 500 years to degenerate.
Question 11: Give two uses of rayon.
- It is mixed with cotton to make bed sheets.
- It is mixed with wool to make carpets.
Question 12: Suggest some ways in which we can contribute towards reducing the use of plastic materials?
Answer: Ways to reduce use of plastic materials are
- Avoid the use of plastics as far as possible.
- Make use of bags made of cotton or jute when you go for shopping.
Question 13: Give examples to show that plastics are noncorrosive in nature. Or Why are the chemicals in the laboratory stored in plastic containers? Or Why are plastic containers used to store chemicals in labs?
Answer: Plastics do not react with water and air. They are not corroded easily. That is why they are used to store various kinds of material, including many chemicals.
Question 14: What type of cookware is used in microwave oven and why?
Answer: Special plastic cookware is used in microwave ovens for cooking food. In microwave ovens, the heat cooks the food but does not affect the plastic vessel.
Question 15: How is plastic useful in healthcare industry?
Answer: Plastics find extensive use in the health-care industry. Some examples of their use are the packaging of tablets, threads used for stitching wounds, syringes, doctors’ gloves and a number of medical instruments.
Question 16: Why is melamine used for making floor tiles, kitchenware and fabrics which resist fire?
Answer: Melamine is a versatile material. It resists fire and can tolerate heat better than other plastics. It is used for making floor tiles, kitchenware and fabrics which resist fire.
Question 17: Why electrical wires have plastic covering, and handles of screw drivers are made of plastic?
Ans. Plastics are poor conductors of heat and electricity. That is why electrical wires have plastic covering, and handles of screw drivers are made of plastic.
Question 18: Why should recycled plastic not be used for the storage of food? Or Why is recycled plastic not suitable for storage of food items? Or Can recycled plastics be used in food containers? Why or why not?
Answer: Most of the thermoplastics can be recycled. However, during recycling certain colouring agents are added. This limits its usage especially for storage of food.
Question 19: Why plastic finds such a variety of uses?
Answer: The fact is that plastic is easily mouldable i.e. can be shaped in any form. Plastic can be recycled, reused, coloured, melted, rolled into sheets or made into wires. That is why it finds such a variety of uses.
Question 20: Should the handle and bristles of a tooth brush be made of the same material? Explain your answer.
Answer: The handle and bristle of a toothbrush should not be made of same material as the handle of the toothbrush should be hard and strong while the bristle should be soft and flexible.
Question 21: List the characteristics of synthetic fibres which make them popular dress materials. Or What are characteristics of synthetic Fibres? Or Mention the general characteristics of synthetic plastics.
Answer: Synthetic fibres possess unique characteristics which make them popular dress materials. They dry up quickly, are durable, less expensive, readily available and easy to maintain.
Question 22: Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Answer: Rana should buy cotton shirts for summer because cotton absorbs sweats away from the body and helps eliminate moisture buildup between clothes and skin in order to keep the body dry.
Question 23: How is rayon made? Write two advantages of using rayon. Or What are the advantages of artificial silk over natural silk?
Answer: Rayon is obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp.
Advantages of Rayon are:
- It is cheaper than silk and can be woven like silk fibres.
- It can also be dyed in a wide variety of colours.
Question 24: Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics.
(a) Saucepan handles
(b) Electric plugs/switches/plug boards
Answer: (a) Saucepan handles are made of thermosetting plastics because it is a poor conductor of heat.
(b) Electric plugs/switches/plug boards are made of thermosetting plastics because it is a poor conductor of heat and electricity.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1: Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
Answer: Some fibres are called synthetic because they are made by human beings by chemical processing. Such fibre is made up of small units that join together to form long chains. Each small unit is actually a chemical substance.
Question 2: Give three advantages of polythene over natural materials.
Answer: Three advantages of polythene over natural materials are:
- It is light, strong and durable.
- It can be rolled into sheets.
- It does not react with water and air.
Question 4: ‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping conservation of forests’. Comment
Answer: Natural fibres are obtained from plants and animals, which means cutting off lots of trees. This leads to deforestation. But synthetic fibres are obtained by chemical processing of petrochemicals and hence help in conservation of forests.
Question 5: What properties of plastics make them so useful?
Answer: Characteristic properties of plastics as follows
- Plastic is non-reactive
- Plastic is light, strong and durable
- Plastics are poor conductors
Question 6: Why is a plastic bucket preferred over an iron bucket?
Answer: Plastic bucket preferred over an iron bucket because
Question 7: What are some uses of nylon?
Answer: Uses of Nylon
- Nylon is used to make articles such as socks, ropes, tents, toothbrushes, car seat belts, sleeping bags, curtains etc.
- It is also used for making parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
Question 8: Why is acrylic fibre more popular than wool?
Answer: Acrylic fibre is more popular than wool because
- Clothes made from acrylic are relatively cheaper.
- They are available in a variety of colours.
- Synthetic fibres are more durable.
Question 9: Name two polyester fabrics and write their uses.
Answer: Terylene is a popular polyester. It can be drawn into very fine fibres that can be woven like any other yarn.
PET is a very familiar form of polyester. It is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires and many other useful products.
Question 10: Why should we not wear synthetic clothes while working in in the kitchen or in a laboratory?
Answer: Synthetic fibres melt on heating. If the clothes catch fire, it can be disastrous. The fabric melts and sticks to the body of the person wearing it. We should, therefore, not wear synthetic clothes while working in in the kitchen or in a laboratory.
Question 11: Differentiate between natural and synthetic fibres.
Answer: Difference between natural and synthetic fibres
Question 12: “Even though plastics are very useful, they are not environment friendly.” Justify the statement.
Answer: Since plastic takes several years to decompose, it is not environment friendly. It causes environmental pollution. Besides, the burning process in the synthetic material is quite slow and it does not get completely burnt easily. In the process it releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution.
Question 13: ‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice.
Answer: Since plastic takes several years to decompose, it is not environment friendly. It causes environmental pollution. Besides, the burning process in the synthetic material is quite slow and it does not get completely burnt easily. In the process it releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution. Thus, we should avoid plastic as far as possible.
Question 14: Suggest some ways to solve plastic pollution. Or How can pollution due to plastics be solved?
Answer: Ways to solve plastic pollution
- The biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes should be collected separately and disposed off separately.
- Recycle the plastic waste.
Question 15: Explain the difference between the thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Question 16: Why we should not throw polybags in the water bodies or on the road?
Answer: We should not throw polybags in the water bodies or on the road because:
- Cow while eating garbage waste food items swallow the polythene bags and wrappers of food. The plastic material chokes the respiratory system of these animals, or forms a lining in their stomachs and can be the cause of their death.
- The polybags carelessly thrown here and there are responsible for clogging the drains, too.
Question 17: Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’: Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ball point pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Question 18: Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Answer: In order to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity, we will design a circuit. For that, we need a bulb, some wires, a battery, a piece of metal and a plastic pipe. After switching on the current, the bulb glows in the former case. In the latter case, the bulb does not glow. Hence a plastic pipe (which is a thermoplastic) is shown to be a poor conductor of electricity.
Question 19: Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials.
Answer: Difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials
At Study Path, you can also learn more about Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics by accessing the free exhaustive list of study materials and resources related to the chapter such as NCERT Solutions, Notes, Important Questions, and MCQ.
Question 1:
Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
There are some fibres that are prepared by man by using chemicals. These are called synthetic fibres. These are made of small units that join together to form long chains. Examples of synthetic fibres are rayon, nylon, polyester, acrylic, etc.
Page No 41:
Question 2:.
Mark ( &mnTick; ) the correct answer.
Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because
(a) it has a silk-like appearance.
(b) it is obtained from wood pulp.
(c) its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres.
(b) it is obtained from wood pulp. (correct)
Question 3:
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
(a) Synthetic fibres are also called _______ __ or _______ __ fibres.
(b) Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw materials called _______ __ .
(c) Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a _______ __ .
(a) Synthetic fibres are also called __artificial__ or __man-made__ fibres.
(b) Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw materials called __petrochemicals__ .
(c) Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a __polymer__ .
Question 4:
Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Nylon fibres are very strong. It is used for making ropes used for climbing rocks and for making parachutes. Their usage shows that nylon fibres have high tensile strength.
Question 5:
Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
The characteristics that make plastics favourable for storing food items are:
(i) Light weight
(ii) Lower price
(iii) Good strength
(iv) Easy handling
Question 6:
Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
There ar e two types of plastics: Thermosetting plastics and Thermoplastics.
Question 7:
Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics.
(a) Saucepan handles
(b) Electric plugs/switches/plug boards
( a) Saucepan handles are made of thermosetting plastics because these plastics do not get softened on heating. Also, thermosetting plastics such as bakelite are poor conductors of heat.
( b) Thermosetting plastics such as bakelite are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Therefore, they are used for making electric plugs, switches, plug boards, etc.
Question 8:
Categorize the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’.
Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ball point pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Question 9:
Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Rana should buy shirts made from cotton. This is because cotton is a good absorber of water. It can soak the sweat coming out of our body and expose it to the environment. Thus, it helps in evaporating the liquid (sweat), thereby cooling our body.
Question 10:
Give examples to show that plastics are non -corrosive in nature.
Plastics are not corroded even if they come in contact with strong chemicals. This is because of their non-reactive nature with most materials. For example, the cleansing chemicals that we use at home are stored in plastic bottles, instead of metal containers.
Question 11:
Should the handle and bristles of a tooth brush be made of the same material? Explain your answer.
No. T he handle and bristles of a tooth brush should be made of different materials. The handle of a toothbrush should be hard and strong, while the bristles should be soft and flexible.
Question 12:
‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice.
Plastics are non -biodegradable. Once introduced into the environment, they take several years to decompose. Plastics add to the environmental pollution. They cannot be burnt as when burnt, they release poisonous gases. Plastic bags thrown in the garbage dump are swallowed by animals like cows. These plastic bags choke their respiratory system and can even prove fatal. Therefore, we should avoid plastics as far as possible.
Page No 42:
Question 13:.
Match the terms of column A correctly with the phrases given in column B.
Question 14:
‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping conservation of forests’. Comment.
R aw materials for natural fibres are mainly derived from plants and this means cutting a lot of trees. This leads to deforestation. But raw materials of synthetic materials are mainly petrochemicals. Hence, manufacturing synthetic fibres helps in the conservation of forests.
Question 15:
Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
View NCERT Solutions for all chapters of Class 8
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals
Please refer to Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals
Case/Passage – 1
Metals are electropositive elements. They can easily lose electrons to form ions. Metals show distinguished physical as well as chemical properties. Generally most of the metals are ductile and malleable with exception such as mercury. These properties make them valuable for commercial as well as domestic uses. Reaction of a metal with water is one of important chemical property. Metals like sodium and potassium reacts with cold water while magnesium reacts with hot water. Metals like aluminium, zinc do not react with hot/cold water but they easily react with steam. When a metal react with hot/cold water the products are metal hydroxide and hydrogen,and when it react with steam, the product are metal oxide and hydrogen. Some metals like sodium, potassium react violently with water.
Question: When zinc reacts with steam it produces: (a) Zn(OH) 2 (b) ZnO (c) O 2 (d) ZnO 2
Question: During the reaction of calcium with water, pieces of metal start floating due to the formation of: (a) Ca(OH) 2 (b) CO2 (c) H 2 (d) none of these
Question: Consider the reactions: Na(s) + H 2 O (l) → NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) ……….(i) Ca(s) + H 2 O (l) → Ca(OH) 2 (aq) + H 2 (g) ………(ii) (a) Reaction (i) is endothermic reaction. (b) Reaction (ii) is endothermic reaction. (c) Reaction (ii) is more exothermic than reaction (i). (d) Reaction (i) is more exothermic than reaction (ii).
Question: Most ductile metal among the following is: (a) Au (b) Ag (c) Cu (d) Al
Question: Metals can be converted into thin sheet by hammering.This property is known as: (a) Ductility (b) Sonorous (c) Malleability (d) Both (a) and (c)
Case/Passage – 2
Elements can be classified as metals or non-metals on the basis of their properties. The easiest way to start grouping substances is by comparing their physical properties. Metals, in their pure state, have a shining surface. This property is called metallic luster. metals are generally hard. The hardness varies from metal to metal. some metals are used for making cooking vessels.
Question: The most abundant metal in the earth’s crust is – (a) iron (b) copper (c) aluminium (d) mercury
Question: The metal that reacts with cold water is – (a) mercury (b) sodium (c) zinc (d)tungsten
Question: Metal present in chloroplast is (a) Iron (b) Copper (c) Magnesium (d) Cobalt
Question: Metals generally are (a) reducing agents (b) oxidising agent (c) both oxidising and reducing agents (d) None of these
Question: Which of the following metal(s) catch fire on reaction with water? (a) Sodium (b) Potassium (c) Magnesium (d) both (a) and (b)
Case/Passage – 3
The huge annual loss due to corrosion is a national waste and should be minimized. Following are some methods which are helpful to prevent corrosion
(i) Coating the iron surface with paint or oil or grease prevents moist oxygen from coming in contact with the metal and thus effectively prevents rusting of iron. (ii) Galvanisation : Iron is blasted with fine sand to make the surface rough dipped in molten zinc and then cooled. A thin layer of zinc forms on the iron surface. Since zinc is more reactive than iron, it acts as a sacrificial metal and is preferentially oxidised thus preventing oxidation of iron. (iii) Electroplating with tin, nickel or chromium also prevents rusting. (iv) Alloying (mixing iron in its molten state with other metals) prevents rusting. Stainless steel is an alloy of iron with Cr or Ni.
Question: The most convenient method to protect the bottom of ship made of iron is : (a) coating it with red lead oxide. (b) white tin plating. (c) connecting it with Mg block. (d) connecting it with Pb block.
Question: The best way to prevent rusting of iron is : (a) making it cathode (b) putting in saline water (c) both of these (d) none of these
Question: The most durable metal plating on iron to protect against corrosion is : (a) nickel plating (b) copper plating (c) tin plating (d) zinc plating
Case/Passage – 4
Some metals are chemically very reactive, whereas others are less reactive or unreactive. On the basis of vigourness of reactions of various metals with oxygen, water and acids, as well as displacement reactions, the metals have been arranged in a group or series according to their chemical reactivity. The arrangement of metals in a vertical column in the order of decreasing reactivities is called reactivity series of metals (or activity series of metals). In reactivity series, the most reactive metal is placed at the top whereas the least reactive metal is placed at the bottom. As we come down in the series, the chemical reactivity of metals decreases. Since the metals placed at the bottom of the reactivity series (like silver and gold) are less reactive, so they are usually found in free state (native state) in nature.
Question: Copper sulphate solution can be safely kept in a container made of : (a) aluminium (b) lead (c) silver (d) zinc
Question: When metal Z is added to dilute HCl solution, there is no evolution of gas. Metal is : (a) K (b) Na (c) Ag (d) Zn
Question: Metal always found in free state is : (a) gold (b) silver (c) copper (d) sodium

Related Posts

Case Study Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce

Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science Notes And Questions

CBSE Class 10 English The Trees Summary
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 3
Home » NCERT Solutions » NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 3

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3: Synthetic Fibres and Plastic
Science is an exciting subject, and it plays a vital role in a student’s life as it offers various concepts that can appear in the following classes. Class 8 also holds equal importance for the students as it prepares them for their future career options in Science and Engineering. Hence it is a transition phase for any student who wishes to take Science as a significant subject.
Class 8 Science Chapter 3 is about synthetic fibers and plastic. First, it introduces the various types of synthetic fibers and their characteristics. Here, students learn about fiber, polymer, natural fiber, silk, and nylon. In addition, they will understand how thermoplastic is formed and its characteristics. Furthermore, students can understand the key difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials.
Students can benefit from our website and access NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3. Our solutions help the students to get detailed notes, illustrations, and examples, and it also has previous years’ papers. The students will be able to gain confidence in the Science subject with the help of the solutions.
Extramarks is a leading online learning platform that provides students with the best study material and solutions. The solution tries to build the skills which are essential for enhanced learning. It helps to build a foundation on all the concepts prescribed in the NCERT curriculum and CBSE Class 8 Science.

Our NCERT solution guide covers important subtopics such as the uses of synthetic fibers, different types of synthetic fibers, characteristics of plastics, and the effect of plastics on the environment. It also elaborates on the role and contribution of other synthetic fibers such as Rayon, Nylon, Polyester, and acrylic.
Students can visit the Extramarks website for current updates and notifications about the NCERT syllabus and its exam-related updates. Further, students can access other class solutions, including NCERT solutions Class 9, NCERT solutions Class 10, and NCERT solutions Class 11.

Key Topics Covered In NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3
Class 8 Science Chapter 3 solutions maintain quality by following the guidelines and syllabus for Class 8. Our NCERT solutions are easy to understand with elaborative illustrations and diagrams so that students rarely face any difficulty in learning the answers. The Science teachers have written NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 in a very simplistic and easy-to-understand manner to clarify their concepts and help them excel in their academics. .
The sub-topic covered in Extramarks NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 are given below:
What are synthetic fibers?
Synthetic fiber is an artificial fiber that is prepared by using raw materials. The materials predominantly originated from petroleum which is also known as petrochemicals. Besides, there are several processes involved in the preparation of fiber. Some of the standard synthetic fibers are rayon, polyester, and nylon.
The fibers are made up of tiny chemical units known as monomers. They are joined together to form a chain, and these chains are called polymers. Synthetic fibers are also obtained by the chemical processing of petrochemicals, unlike natural fibers made from animal and plant sources. In our Extramarks NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3, we have elaborated on the processing of the petrochemicals in detail.
Types of synthetic fibers
The classification of synthetic fibers is based on the chemicals used in their manufacturing. Therefore, every fiber differs in its nature of burning, affordability, availability, water absorption, etc. The different types of synthetic fibers discussed in NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 are listed below:
- Rayon: It is artificial silk known as viscose-rayon regenerated cellulose. The cellulose is obtained from the natural source of wood pulp. Besides, it is also manufactured fiber made in the laboratory by chemical treatment of wood pulp. It is dyed in various colors, and it can also be woven like silk fibers. Rayon is used to making fabrics, bedsheets, carpets, and car upholstery.
- Acrylic: It is a monomer also known as polyacrylonitrile. Acrylic fiber is similar to wool used to make sweaters, blankets, shawls, etc. Therefore, it is affordable, cheap, and durable compared to natural woolen fibers. In addition, acrylics are light, soft, warm, and resistant to chemicals, moths, and sunlight.
- Polyester: It is also a monomer ester and manufactured fiber. Polyester offers a brilliant wrinkle-free quality and remains crisp, and it is easy to wash. Therefore, it is used for dresses, suits, rainwear, etc. In addition, a type of polyester known as PET or Polyethylene terephthalate is trendy for making kitchen products, wires, bottles, etc.
- Nylon is different from other fabric types; it is a polymer of adipic acid hexamethylenediamine. Nylon is the first fiber made from coal, water, and air. They are light, elastic, strong, durable, and lustrous. This property makes it a good choice for fabrics, and it also dries up quickly. Nylon is used in car seats, belts, ropes, curtains, and toothbrushes.
To understand the properties of synthetic fibers in detail, students can register on the Extramarks website and access NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3.
Characteristics of synthetic fibers
- Synthetic fibers dry up quickly, are durable, and are less expensive. In addition, it is readily available and easy to maintain.
- Synthetic fibers melt on heating and can catch fire which can be disastrous.
- The fibers are strong, elastic, and light.
Many people use plastic in their everyday life. Plastic is also a polymer like synthetic fibers. Further, there are various forms and uses of plastic. It can be recycled, reused, colored, melted or made into wires. The plastic can be deformed easily by heating and made easily known as “Thermoplastic”.
Besides, there are some plastics that, when molded once, cannot be softened by heating, called “Thermosetting” plastic. Bakelite and melamine are two examples of the thermosetting plastic. Whereas bakelite is a poor conductor of heat and electricity, melamine is a versatile material. Students can refer to our NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3, where we have elaborated on the various properties of plastic.
Plastic as a material of choice
Various food items such as water, milk, pickles, and dry food are primarily stored in plastic containers. They are lightweight, strong, durable, have good strength, and are easy to handle. On the other hand, metals like iron rust over time and when exposed to moisture. Yet, it is different from plastic materials. Plastic can easily be molded into various shapes and sizes.
Plastic is a lot cheaper than metals. Further, it is used in many industries such as health care, fire industry, IT industry, and wrapping industry. Plastic has a lot to offer as a material. Therefore, students can register on our Extramarks website or refer to NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3. We have explained the critical role of plastic in different industries in detail.
Plastics and Environment
Plastic as a material is not environmentally friendly as it accumulates in the environment over the years without disintegrating. When we burn plastics, it releases toxic gases into the atmosphere, which pose a health hazard for humans, animals, and plants; further, plastic is not biodegradable. It means that plastic cannot be decomposed naturally by the action of bacteria.
When plastic bags are not disposed of properly, they can clog the drains and can lead to choking on animals. There are five R principles: Reduce, Recycle, Reuse, Recover, and Refuse to keep our environment safe. It can contribute to cleaning our environment. There are also some eco-friendly ways, such as cloth bags, steel utensils, and paper bags.
Students can access NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 on our website to understand plastic and its impact on nature.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3: Exercises & Solutions
Extramarks NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 offers students all the solved answers to questions from the textbook chapters. The answers are written in a descriptive and detailed manner, which helps in answering the question and clears all the doubts while responding to similar questions while revising and in exams.
Besides, students can take advantage and start with a trial account by registering on our website. Our NCERT solutions have proven fruitful for many students in primary and secondary classes. The solutions cover all the sub-topics in Chapter 3, synthetic fibers and plastic. All the essential topics are explained in a simple and easy-to-understand language which helps students score well in the Science exams.
Students can click on the link below to access the exercise-specific questions and their solutions which are covered in Extramarks NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3:
- Chapter 3: Exercise 3.1 Solutions: 14 Questions
Our NCERT solutions are also available for other primary and secondary classes on our Extramarks website. Students can click on the links given below:
NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Science
Science is a subject of curiosity about the nature and behavior of natural things. It demands a high level of understanding to grasp the concepts. To increase the knowledge of such concepts, solving different equations is always beneficial. It helps to clear the doubt and develop a strong understanding of the topics.
NCERT Exemplars are designed in the same manner to help the students to enhance their knowledge of the topic. It has various types of questions with varying levels of difficulty such as multiple-choice questions; fill in the blanks and match the following questions. It also contains objective, concise answer type, short-answer type, and long-answer-type questions in Chapter 3, Class 8. With the daily practice of the exemplar, students can expect good results in the examination. In other words, an effort has been made to ensure that nothing is left in the process.
Our NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 offer questions from exemplars covering the topics of synthetic fibers and plastic. Here, students will explore different sub-topics, including characteristics of plastics, thermoplastics, thermosetting plastic, and acrylic fiber. In addition, students will understand the critical difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials. It will ensure that even the minutest doubt is resolved and the students develop an interest in learning and mastering the topic with ease.
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter-wise List
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3
Extramarks has an in-house dedicated team of subject experts who prepare accurate, up-to-date, and authentic solutions for each topic and each section covered in the chapter. Some Students find it difficult to answer the textbook questions and they should follow the answers on our Extramarks website to get an overall idea about the chapter to help them achieve excellent scores.
Some of the prominent characteristics of our NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 are as follows:
- The solutions help clarify students’ queries that arise while learning the chapter.
- The answers are prepared in an understandable language, making it easy for students to learn complicated definitions.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 strictly adhere to the CBSE syllabus and guidelines for students to prepare for the exam more rigorously so that they don’t have to look for any help elsewhere.
- The subject experts frame each answer in the solution with utmost care to encourage and enable reading abilities among students to study independently and master the topic with ease.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
Ans. Man-made fibres are called synthetic fibres. These fibres are prepared from petrochemicals with the help of various processes. Examples of some synthetic fibres are nylon, rayon, polyester, acrylic, etc.
Q.2 Mark (✓) the correct answer.
Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because
- it has a silk-like appearance.
- it is obtained from wood pulp.
- its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres.
Ans. Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because
- it is obtained from wood pulp. (✓)
Q.3 Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
- Synthetic fibres are also called ______ or ______ fibres.
- Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw materials called _________.
- Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a ________.
- artificial, man-made
- petrochemicals
Q.4 Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Ans. Nylon fibres are strong, elastic and light. In fact they are stronger than steel wire. They are used in making ropes for rock climbing and parachutes. This usage indicates that nylon fibres are very strong.
Q.5 Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Ans. The plastic containers are favoured for storing food because plastic is non-reactive, corrosion resistant, cheap, durable, strong and light in weight.
Q.6 Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Q.7 Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics.
- Saucepan handles
- Electric plugs/switches/plug boards
- Saucepan handles are made of thermosetting plastics because these plastics do not soften on heating.
- Thermosetting plastics are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Therefore, they are used in making electric plugs, switches, plug boards, etc.
Q.8 Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’.
Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ball point pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Q.9 Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Ans. Rana should buy cotton shirts. This is because cotton is a good absorber of water. Therefore, it absorbs the sweat (mainly water having dissolved salts) and exposes it to the environment. With the help of atmospheric heat, water present in sweat is evaporated. During evaporation water is lost and this water takes away heat with it. Thus, it helps in evaporating the water (sweat), thereby cooling our body.
Q.10 Give examples to show that plastics are noncorrosive in nature.
Ans. Plastics are non-reactive and noncorrosive in nature. They are not corroded even by strong chemicals. That is why various kind of chemicals are stored in plastics bottles.
Q.11 Should the handle and bristles of a tooth brush be made of the same material? Explain your answer.
Ans. Handle and bristle of a tooth brush should not be made of the same material. This is because handle of brush is strong and hard, while bristles are soft and flexible.
Q.12 ‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice.
Ans. Plastics are non-biodegradable, i.e. they are not decomposed by micro-organisms. Once introduced into the environment they may take several years to decompose. Plastics when burnt produce poisonous gases. They are dangerous to animals like cows, which swallow these bags from garbage. These bags choke the respiratory system of the animals or form a lining in their stomach and may cause their death. Hence, we should avoid plastics as far as possible.
Q.13 Match the terms of column A correctly with the phrases given in column B.
Q.14 ‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping in conservation of forests’. Comment.
Ans. Raw material used for making natural fibres is mainly derived from plants. It requires cutting of lots of trees leading to deforestation. On the other hand raw materials required for synthetic fibres are mainly obtained from petrochemicals. It means for manufacturing of synthetic fibres, cutting of trees is not needed. Hence, it can be said that ‘manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping in conservation of forest’.
Q.15 Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Ans. We can set two circuits to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity. For this we need two bulbs, wires, two batteries, a piece of metal and a pipe made of thermoplastic.
Set up the circuits with metal and plastic pipe separately as shown below.
When you turn the switch on the current flows and the bulb glows in the first circuit (circuit with metal) while, bulb does not glow in the second circuit (circuit with plastic).
This activity confirms that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Please register to view this section
Faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. what are the different types of questions in class 8 science chapter 3.
Students will come across multiple-choice questions and explanatory answers, fill in the blanks and match the following question in the chapter. They will get to solve different types of questions, which will help them to strengthen their knowledge of synthetic fibre and plastic.
2. How many subtopics are included in Chapter 3 of NCERT solutions for Class 8?
The students will get to learn the following sub-topics in the NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3:
- What are synthetic fibres?
- Types of synthetic fibres
- Characteristics of synthetic fibres
- Plastics and environment
3. Why should we study from NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3?
Sometimes, it isn’t easy for students to understand the definitions and concepts in the chapter. Therefore, Extramarks NCERT solutions offer answers for all the topics present in the exercises. In addition, the solutions contain explanations for each step to help understand the concepts without difficulty.
NCERT Solutions Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
CBSE Papers, Questions, Answers, MCQ ...
Blog provides NCERT solutions, CBSE, NTSE, Olympiad study material, model test papers, important Questions and Answers asked in CBSE examinations. References to Educational Sites and resources.
- CareerAfter12
- Syllabus 2017-18
- Entrance Exams
Thursday 15 December 2022
Cbse class 8 - physics - sound - case study based question #class8science #sound #physics #eduvictors.
CBSE Class 8 - Physics - Sound - Case Study Based Question

Q1. Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Sound is a form of energy that is produced when air molecules vibrate in a particular pattern called waves. Hence, the sound is a wave. Sound is produced by vibrating objects. Vibration can be described as to and fro motion of an objects. Sound cannot be produced without any vibrations. Sound always requires a medium to travel from the source of its production to the receiver end. Speed of the sound is maximum in solids and minimum in gases.
(i) The audible frequency range of a human ear is:
(a) The range of audible frequency of human ear is 20 to 200 Hz
(b) The range of audible frequency of human ear is 2 Hz to 20 Hz
(c)The range of audible frequency of human ear is 200 to 2000Hz.
(d) The range of audible frequency of human ear is 20 to 20,000Hz
(ii) Ria used a device to measure the loudness of a machine. She recorded her observation as given below. Which of the following represents the correct measurement of loudness?
(iii) Arrange the speed of sounds in solids, liquids and gases in an ascending order:
(a) Gas < Liquid < Solid
(b) Liquid > Gas > Solid
(c) Liquid < Solid < Gas
(d) Solid > Liquid > Gas
(iv) The number of vibrations made by a vibrating body in one second is:
(a) frequency
(c) loudness
1. (d) The range of audible frequency of human ear is 20 to 20,000Hz
2. (c) 80 dB
3. (a) Gas < Liquid < Solid
4. (a) frequency
Ch 13 - Sound (Q & A) Ch 13 - Sound (MCQs) Ch 13 - Sound (Worksheet) Ch 13 - Sound (Question Bank) Ch 13 - Sound (Worksheet)
CBSE All In One NCERT Based Science Class 8 2022-23 Edition

No comments:
Post a comment.
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.
Ad-Blocker Detected!
Please turn off the ad blocker. This is only way that we can earn some penny. Please support us by trun off the ad blocker. Thank you!!

Case Study Questions Class 8 Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Case study questions class 8 science chapter 2 microorganisms: friend and foe.
CBSE Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe. Important Case Study Questions for Class 8 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Microorganisms: Friend and Foe.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Case study 1.
You have seen several kinds ofplants and animals. However,there are other living organismsaround us which we normally cannotsee. These are called microorganismsor microbes. For example, you mighthave observed that during the rainyseason moist bread gets spoilt and itssurface gets covered with greyish whitepatches. Observe these patches througha magnifying glass. You will see tiny,black rounded structures. Do you knowwhat these structures are and where dothese come from? Waterand soil are full of tiny organisms,though not all of them fall into thecategoryofmicrobes.Thesemicroorganisms or microbes are sosmall in size that they cannot be seenwith the unaided eye. Some of these,such as the fungus that grows on bread,can be seen with a magnifying glass.Others cannot be seen without the helpof a microscope. That is why these arecalled microorganisms or microbes.Microorganisms are classified intofour major groups. These groups arebacteria, fungi, protozoa and somealgae. Viruses are also microscopic but aredifferent from other microorganisms.They, however, reproduce only inside thecells of the host organism, which may bea bacterium, plant or animal. Commonailments like cold, influenza (flu) andmost coughs are caused by viruses.Serious diseases like polio and chickenpox are also caused by viruses.Diseases like dysentery and malariaare caused by protozoa(protozoans)whereas typhoid and tuberculosis (TB)are bacterial diseases.You have learnt about some ofthese microorganisms in Classes VIand VII.Microorganisms may be single-celledlike bacteria, some algae and protozoa,or multicellular, such as many algae andfungi. They live in all types of environments, ranging from ice coldclimate to hot springs; and deserts tomarshy lands. They are also foundinside the bodies of animals includinghumans. Some microorganismsgrow on other organisms while othersexist freely.
Que. 1) ……………………………………………………………………………. only reproduce inside the cells of host organisms like bacteria, plants or animals.
(a) Microbes
(b) Viruses
(d) Bacillus
Que. 2) Which among the following is an example of disease caused by bacteria?
(b) Malaria
(c) Tuberculosis
(d) Covid 19
Que. 3) During rainy season moist bread gets spoilt and are covered with greyish white patches. What are these greyish white patches?
(a) Bacteria
Que. 4) Define microorganisms and state its major groups of classification.
Que. 5) Explain in detail where are microorganisms commonly found.
Que. 1) (b) Viruses
Que. 2) (c) Tuberculosis
Que. 3) (d) Fungus
Que. 4) Answer: Microorganisms are tiny living organisms that cannot be seen with our naked eyes. Microorganisms are classified into four major groups namely bacteria, fungi, protozoa and some algae.
Que. 5) Answer: Microorganisms are present in all types of environments ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs, deserts and marshy lands. They can also be seen inside the bodies of animals. Some microorganisms exist freely and some grow on other organisms.
Case study 2
Microorganisms are used for variouspurposes. They are used in thepreparation of curd, bread and cake.Microorganisms have been used forthe production of alcohol since ages.They are also used in cleaning upof the environment. For example, theorganic wastes (vegetable peels, remainsof animals, faeces, etc.) are brokendown into harmless and usablesubstances by bacteria. Recall thatbacteria are also used in thepreparation of medicines. In agriculturethey are used to increase soil fertilityby fixing nitrogen.You have learnt in Class VII that milk isturned into curd by bacteria.Curd contains several micro-organisms. Of these, the bacterium,Lactobacillus promotes the formationof curd. It multiplies in milk andconverts it into curd. Bacteria are alsoinvolved in the making of cheese,pickles and many other food items. Animportant ingredient of rava (sooji )idlis and bhaturas is curd. Can youguess why? Bacteria and yeast are alsohelpful for fermentation of rice idlisand dosa batter. Kneading of Yeast and sugar into the flour causes the flour to rise and double in size. Yeast reproduces rapidly andproduces carbon dioxide duringrespiration. Bubbles of the gas fill thedough and increase its volume.This is the basis of the use of yeast inthe baking industry for making breads,pastries and cakes.Commercial Use of Microorganisms:Microorganisms are used for the large-scale production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid(vinegar).
Yeast is used for commercialproduction of alcohol and wine. For this purpose, yeast is grown on natural sugarspresent in grains like barley, wheat, rice,crushed fruit juices, etc. Adding a spoon full of yeast powder into sugar solution gives out a characteristic smell after few hours.This is the smell of alcohol as sugarhas been converted into alcohol by yeast.This process of conversion of sugar intoalcohol is known as fermentation.Louis Pasteurdiscoveredfermentationin 1857.
Que. 1) In the process of fermentation the sugar is converted into …………………………………………………………………………………………. .
(a) Vinegar
(d) Alcohol
Que. 2) Name the bacterium which when added to milk, multiplies in it and converts milk into curd?
(a) Lactobacillus
(b) Streptococcus
(c) Salmonella
Que. 3) Louis Pasteur a French chemist in 1857 discovered the process of ……………………………………………………………………………………. ?
(a) Fermentation
(b) Pollination
(c) Saturation
(d) Composting
Que. 4) Explain the process of doubling of flour after addition of yeast into it.
Que. 5) Name some of the common uses of microorganisms.
Que. 1) (d) Alcohol
Que. 2) (a) Lactobacillus
Que. 3) (a) Fermentation
Que. 4) Answer: After adding yeast and sugar into the flour, the yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of gas fill the dough and hence the volume of dough is doubled in size.
Que. 5) Answer: Microorganisms are useful in various purposes like in the preparation of curd, bread and cake. It is used in the production of alcohol as well as medicines. These are also used to increase the fertility of soil.
Case study 3
Whenever you fall ill the doctor may give you some antibiotic tablets, capsules or injections such as of penicillin. The source of these medicines is microorganisms. These medicines kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microorganisms. Such medicines are called antibiotics. These days a number of antibiotics are being produced from bacteria and fungi. Streptomycin, tetracycline and erythromycin are some of thecommonly known antibiotics which are made from fungi and bacteria. The antibiotics are manufactured by growing specific microorganisms and are used to cure a variety of diseases. Antibiotics are even mixed with the feed of livestock and poultry to check microbial infection in animals. They are also used to control many plant diseases.In 1929, Alexander Fleming was working on a culture of disease- causing bacteria. Suddenly he found the spores of a little green mould in one of his culture plates. He observed that the presence of mould prevented the growth of bacteria. In fact, it also killed many of these bacteria. From this the mould penicillin was prepared.When a disease-carrying microbe enters our body, the body produces antibodies to fight the invader. The body also remembers how to fight the microbe if it enters again. If dead or weakened microbes are introduced into a healthy body, the body fights and kills the invading bacteria by producing suitable antibodies. The antibodies remain in the body and we are protected from the disease-causing microbes for ever. This is how a vaccine works. Several diseases, including cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination.Edward Jenner discovered the vaccine for small- pox in 1798.In your childhood, you must have been given injections to protect yourself against several diseases. Can you prepare a list of these diseases? You may take help from your parents.
It is essential to protect all children against these diseases. Necessary vaccines are available in the nearby hospitals. You might have seen the advertisement on TV and newspapers regarding protection of children against polio under the Pulse Polio Programme. Polio drops given to children are actually a vaccine. A worldwide campaign against smallpox has finally led to its eradication from most parts of the world. These days vaccines are made on a large scale from microorganisms to protect humans and other animals from several diseases.
Que. 1) Which among the following scientist discovered the vaccine for Small pox in 1798?
(a) Edward Jenner
(b) Alexander Fleming
(c) Carl Linnaeus
(d) Rosalind Franklin
Que. 2) When a disease carrying microbe enters our body, the body produces ……………………………………………………………………………… to fight against it.
(a) Soldiers
(b) Antibodies
(c) Viruses
(d) Bacteria
Que. 3) In which year did Alexander Fleming a Scottish Physician discover penicillin?
Que. 4) Define antibiotics and give their uses.
Que. 5) Name some of the diseases that can be prevented by taking vaccination.
Que. 1) (a) Edward Jenner
Que. 2) (b) Antibodies
Que. 3) (d) 1929
Que. 4) Answer: Antibiotics are medicines produced from microorganisms that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms. Some common examples include Streptomycin, Tetracycline and erythromycin. They are used to cure a variety of human and plant diseases and also to check microbial infection in animals.
Que. 5) Answer: Some diseases that can be prevented by taking vaccination are Cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox, and hepatitis.
Case study 4
Microorganisms are harmful in manyways. Some of the microorganismscause diseases in human beings, plantsand animals. Such disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens.Some microorganisms spoil food,clothing and leather. Let us study moreabout their harmful activities.Pathogens enter our body through theair we breathe, the water we drink orthe food we eat. They can also gettransmitted by direct contact with aninfected person or carried by an animal.Microbial diseases that can spread froman infected person to a healthy personthrough air, water, food or physicalcontact are called communicablediseases. Examples of such diseasesinclude cholera, common cold, chickenpox and tuberculosis.When a person suffering fromcommon cold sneezes, fine droplets ofmoisture carrying thousands of virusesare spread in the air. The virus may enterthe body of a healthy person whilebreathing and cause infection.There are some insects and animalswhich act as carriers of disease-causing microbes. Housefly is one suchcarrier. The flies sit on the garbage andanimal excreta. Pathogens stick to theirbodies. When these flies sit on uncoveredfood, they may transfer the pathogens.Whoever eats the contaminated food islikely to get sick. So, it is advisable toalways keep food covered. Avoidconsuming uncovered items of food.Another example of a carrier is thefemale Anopheles mosquito,which carries the parasite of malaria(Plasmodium). Female Aedes mosquitoacts as carrier of dengue virus.How can we control the spread of malariaor dengue?All mosquitoes breed in water. Hence,one should not let water collectanywhere, in coolers, tyres, flower pot,etc. By keeping the surroundings cleanand dry we can prevent mosquitoes frombreeding. Try to make a list of measureswhich help to avoid the spread ofmalaria.Several microorganisms not only causediseases in humans and plants, but alsoin other animals. For example, anthraxis a dangerous human and cattledisease caused by a bacterium. Footand mouth disease of cattle is causedby a virus.RobertKöch(1876)discovered the bacterium(Bacillus anthracis) whichcauses anthrax disease.Severalmicroorganismscausediseases in plants like wheat, rice, potato,sugarcane, orange, apple and others.The diseases reduce the yield of crops. They can be controlled by theuse of certain chemicals which kill themicrobes.
Que. 1) Disease causing microorganisms are called as …………………………………………………………………………………………. .
(a) Antibodies
(b) Macrophages
(c) Pathogens
(d) Eosinophils
Que. 2) Which among the following insect acts as the carrier of dengue virus?
(a) Female Anopheles
(b) Female Aedes
(c) Female Culex
(d) Ochlerotatus
Que. 3) Robert Koch in 1876 discovered the bacterium (Bacillus anthracis) which causes …………………………………………………………………………………….. disease.
(a) Anthrax
(c) Chikungunya
(d) Cholera
Que. 4) Define the term “communicable diseases” with some examples.
Que. 5) How can we control the spread of diseases caused by mosquitoes?
Que. 1) (c) Pathogens
Que. 2) (b) Female Aedes
Que. 3) (a) Anthrax
Que. 4) Answer: Microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through air, water, food or physical contact are called communicable diseases. Cholera, common cold, chicken pox, and tuberculosis are some of the examples.
Que. 5) Answer: Breeding of mosquitoes occur in water. Therefore, by not letting water to collect in our surroundings like in coolers, tyres, flower pot, etc and keeping the surrounding clean and dry, we can control the spread of such diseases.
Case study 5
How do we preserve cooked foodat home? You know that bread leftunused under moist conditions isattacked by fungus. Microorganismsspoil our food. Spoiled food emits badsmell and has a bad taste and changedcolour. Is spoiling of food a chemicalreaction?Paheli bought some mangoes but shecould not eat them for a few days. Latershe found that they were spoilt androtten. But she knows that the mango picklesthat her grandmother makes does notspoil for a long time. She is confused.Let us study the common methodsof preserving food in our homes. Wehave to save it from the attack ofmicroorganisms.Chemical Method:Salts and edible oils are the commonchemicals generally used to check thegrowth of microorganisms. Therefore, they are called preservatives. We addsalt or acid preservatives to pickles toprevent the attack of microbes. Sodiumbenzoate and sodium metabisulphite arecommon preservatives. These are alsoused in jams and squashes to checktheir spoilage.Preservation by Common Salt:Common salt has been used to preservemeat and fish for ages. Meat and fishare covered with dry salt to checkthe growth of bacteria. Salting is alsoused to preserve amla, raw mangoes,tamarind, etc.Preservation by Sugar:Jams, jellies and squashes are preservedby sugar. Sugar reduces the moisturecontent which inhibits the growth ofbacteria which spoil food.Preservation by Oil and Vinegar:Use of oil and vinegar prevents spoilageof pickles because bacteria cannot livein such an environment. Vegetables,fruits, fish and meat are often preservedby this method.Heat and Cold Treatments: You must have observed your motherboiling milk before it is stored or used.Boiling kills many microorganisms.Similarly, we keep our food in the refrigerator. Low temperature inhibits the growth of microbes.Pasteurised milk can be consumed without boiling as it is free from harmful microbes.
The milk is heated to about 700C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. By doing so, it prevents the growth of microbes. This process was discovered by Louis Pasteur. It is called pasteurisation. Storage and Packing: These days dry fruits and even vegetables are sold in sealed air tight packets to prevent the attack of microbes.
Que. 1) Which of the following is NOT an example of chemical method of preservation?
(b) Heating
(c) Sodium Benzoate
(d) Sodium Metabisulphite
Que. 2) ………………………………………………………………………………. of milk before storing is done to kill many microorganisms.
(b) Distilling
(d) Boiling
Que. 3) Pasteurisation technique was discovered by which of the following scientist?
(a) Louis Pasteur
(b) Fanny Hesse
(c) Ronald Ross
(d) Harold Ginsberg
Que. 4) Explain the process of Pasteurization in detail.
Que. 5) Name some of the common methods of food preservation at your home.
Que. 1) (b) Heating
Que. 2) (d) Boiling
Que. 3) (a) Louis Pasteur
Que. 4)Answer: In the pasteurisation process the milk is heated to about 700°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. This process prevents the growth of microbes.
Que. 5) Answer: Some common methods of preservation include: Adding common salt to pickles, meat and fish. Using sugar as well as oil and vinegar are also some of the preservation methods.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell Structure and Functions

Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 Important Questions with Solutions: Free PDF Download
Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions with solutions have been created by experts at Vedantu. The important questions PDF will be available for free of cost on the Vedantu site and it covers topic-wise important questions. Cell structure and function Class 8 important questions will help the student to assume the type of questions asked in the exam in chapter 8.
The main concept behind the creation of important questions is that the students should not struggle to prioritise the topics while their exam preparation. and the important questions are created following the recent CBSE guidelines. For better preparations for the examination, students can opt for Class 8 Science tuition available online at Vedantu and can also download other study materials from there.
Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths students who are looking for better solutions can download Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Topics Covered in Class 8 Science Chapter 8
Study important questions for class 8 science chapter 8 – the cell structures and functions.
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Which one of the following is NOT a part of the nucleus?
ribosome
nucleolus
chromosome
Ans: A. ribosome
2. Which one of the following is a unicellular organism?
amoeba and paramecium
human
mouse
Ans: A. amoeba and paramecium
3. The basic structural and functional unit of an organ is ________.
red blood corpuscle (RBC)
kidney
renal tubule
Ans: B. cell
4. The green colour of leaves is due to the presence of the pigment _______.
chlorophyll
ribosomes
mitochondria
chloroplast
Ans: A. chlorophyll
5. Who among the following discovered cell?
Robert Hooke
Matthias Schleiden
Theodor Schwann
Rudolf Virchow
Ans: A. Robert Hooke
6. All the multicellular organisms start their life as a ___________.
single cell
double cell
triple cell
without a cell
Ans: A. single cell
7. Give any two examples of multicellular organisms.
Ans: Human, elephant, etc.
8. Name any two cell organelles.
Ans: Nucleus, ribosome
9. What is the substance used to see a cell under the microscope?
Ans: Stain or dye
10. What does the amoeba use for locomotion?
Ans: Pseudopodia
Short Answer Question (3 Marks)
1. Define genes and their function.
Ans: The basic physical and functional unit of heredity is the gene. They aid in character inheritance or transfer from parents to offspring.
2. What is a tissue?
Ans: Tissue is a collection of related cells that perform a specific job. Muscle tissue, for example, is made up of muscle cells.
3. What is a nucleus? State the importance of the nucleus.
Ans: The nucleus is the primary dense circular body at the centre. The transport of materials into and out of the cell is regulated by the nucleus. It also regulates the cell's metabolic activity.
4. What is the function of the nuclear membrane?
Ans: The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear membrane. It also allows materials to flow between the cytoplasm and the nucleus' interior.
5. Why is the cell wall present in plant cells and not in animal cells?
Ans: Plant cells have a cell wall, but animal cells do not, since plants require protection. Plant cells require protection against extremes in temperature, strong wind speeds, and atmospheric moisture, among other things. Because humans are unable to migrate like animals for protection, they are subjected to these changes.
6. What is chloroplast? Define the functions of the chloroplast.
Ans: Chloroplasts are plastids that are green in colour. They give the leaves a bluish-green hue. Photosynthesis requires chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of leaves.
7. Draw a diagram of Onion peel, as observed under a microscope, and label its basic components.
Ans: Diagram of onion peel
8. Draw a labelled diagram of an animal cell.
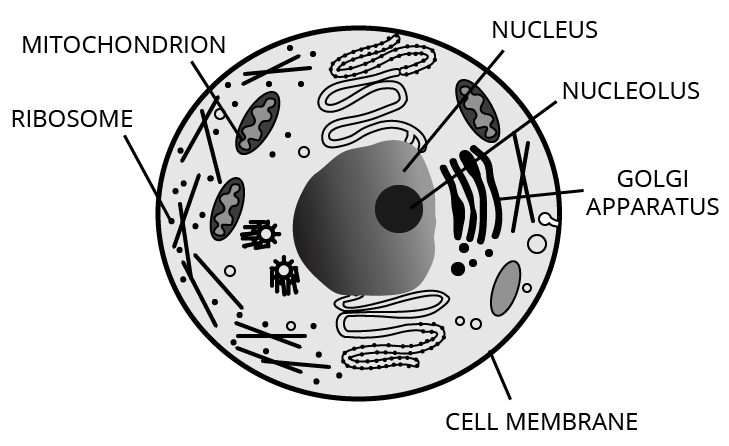
9. Why is a cell membrane important to a cell?
Ans: The cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus are the three basic components of a cell. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, encloses the cytoplasm and nucleus. Cells are separated from one another by membranes, which also separate the cell from the surrounding liquid. The plasma membrane is permeable, allowing substances or materials to pass across it both inward and outward.
10. Draw a labelled diagram of a human cheek cell.
Ans: Diagram of human cheek cell
11. Define Plastids.
Ans: Plastids are coloured bodies found in a plant's cytoplasm. They are available in a range of colours.
Long Answer Question (5 Marks)
1. Define a cell. Explain the variation in cell number, shape and size.
Ans: A cell is an organism's structural and functional unit.
Cell Number: Multicellular organisms are organisms made up of more than one cell. The fact that smaller creatures have fewer cells has no bearing on the organisms' ability to operate. Unicellular organisms are organisms with only one cell. A single-celled creature can carry out all of the functions that multicellular organisms can.
The Shape of Cells: Cells can have an irregular shape, such as an amoeba, or a well-defined shape, such as an RBC. Cells that may change their form include amoeba and WBC. The form of cells might be circular, spherical, or elongated. Some cells are lengthy and have two pointed ends. They have a spindle form to them. Cells can be pretty lengthy at times. Some, like a nerve cell or a neuron, are branching.
Size of Cells: Cells in living things can be as small as a millionth of a metre (micrometre or micron) or as huge as several centimetres. The majority of the cells, however, are minute and invisible to the naked eye. A microscope is required to enlarge or magnify them. In bacteria, the smallest cell measures 0.1 to 0.5 micrometres. The ostrich egg is the biggest cell, measuring 170 mm by 130 mm. The size of the cells has no bearing on the size of the animal or plant's body. The function of a cell is related to its size. For example, the nerve cells of the elephant and rat are lengthy and branching. They both do the same thing: they send and receive messages.
2. Write short notes on the following:
Cytoplasm
Ans: The cytoplasm is a jelly-like material that exists between the cell and the nucleus. The cytoplasm possesses a variety of cell organelles. Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, lysosomes, chloroplast, and other cell organelles are examples.
Ans: This is a spherical structure found inside the cell, usually near the cell's centre. A nuclear membrane is a double-layered membrane that encloses the nucleus. Inside the nucleus is a dot-like structure known as the nucleolus. Chromosomes appear as thread-like structures which are found in the nucleus. The transport of materials into and out of the cell is regulated by the nucleus. It also regulates the cell's metabolic activity.
3. State any three differences between plant and animal cells.
Ans: The difference between plant and animal cell is as given below,
What Is Cell in Class 8 Science Chapter 8?
The cell is the basic unit of life. It is a small membrane-bound compartment which contains all the chemicals and molecules that help to support an organism's life. Understanding the structure and function of cells is one of the basic steps to comprehend the complex cellular interactions, which produces life.
There are two types of cells, namely unicellular and multicellular organisms. Both the organisms have their own uniqueness and functions. Like unicellular organisms have the capability to sustain their life on their own. All the organisms are made up of cells, but the cell differs from one organism to others like from plants to animals. To understand the chapter more in-depth, go through the NCERT solutions of Class 8 Science Chapter 8.
What Are the Benefits of Referring to the Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8?
Solving important questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 can be helpful for students in the following ways:
Students can develop time management skills while solving these questions.
These important questions covered in the pdf are frequently asked in the Class 8 exam.
Practising these questions will give the students a brief idea of how to present the answer in the exam, eventually helping them to fetch more marks.
Solving the different types of questions will help students to revise the chapter thoroughly and efficiently a day before the exam.
Extra Important Questions for Practice
Very short answer type questions.
Who discovered the slices of cork under a simple magnifying device?
Are the cells present in the eggs of a hen can be seen through the naked eyes?
Write one example of a single cell which can change its shape.
What is pseudopodia?
Are the cells in elephants larger than cells in rats?
Short Answer Type Questions
What are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
What is the shape and size of a cell?
Why is there a change in the shape of a cell?
What is cytoplasm?
Who first discovered the cell and when?
Long Answer Type Questions
Explain the structure of the cell.
What are single cells, unicellular cells, and multicellular cells?
Write a short paragraph on the nucleus.
Tips to Study Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Better
The following suggested tips will help you to prepare for the Science Chapter 8 better:
Understand all the concepts of the chapter covered in the NCERT textbook thoroughly.
Practice the important questions given in this article after understanding the chapter concepts.
Practice all the questions of this chapter that are asked in the NCERT textbook.
Attend test series to check your knowledge and to gain confidence.
Why are Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell Structure and Functions Necessary?
Vedantu’s Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell Structure and Functions are the finest material to understand and practice the topics in the best way.
The material carries all the information in detail and pointwise.
All the cases of the material are solved in the simplest way which explains the term clearly.
Vedantu’s Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell Structure and Functions provides all the main topics so that the student can focus on it and prepare for the exam.
Class 8 Science cell structure and function important questions provide self-confidence to the student in their preparation for the exam. Vedantu provides one of the best study materials free of cost PDF, which helps students in learning all the basics about the chapter.
Important questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 cell structure and functions help the student to write short notes on the various parts of the cell such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, etc. The solution given will help us to understand the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Students will also get knowledge about chromosomes, their location, and other interesting topics.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell Structure and Functions
Q1. What are the most important concepts in Chapter 8 of Class 8 Science?
Chapter 8 of Class 8 Science talks about the structure and functions of cells. Vedantu provides students with important questions that are taken from important topics and concepts from this chapter. The solutions for these important questions are given by subject experts making the students understand the solutions in an easy-going way. The important questions PDF are available for free on Vedantu(vedantu.com) chapter-wise and topic-wise. These important questions will even give an idea to the students about the type of questions that can be asked. These solutions can be downloaded from Vedantu mobile app as well.
Q2. Who discovered the cell?
Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1655. He came across this while exploring and examining a cork which is a part of the bark of a tree. Hook observed thin slices of cork under a microscope that he designed himself. Under that, he observed that there were several tiny compartments and partitioned boxes just like a honeycomb. Upon further notice, he could see that each compartment and box are divided from each other by a wall. He later termed all the single compartments and boxes as "cells".
Q3. What are the basics of Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions of Class 8 Science?
Cell Structure and Functions is an important chapter for Class 8 Science. This chapter starts by explaining how cells were discovered for the first time. It then moves on to the structure of the cell and its characteristics. This chapter even focuses on the different types of cells and the different number of cells available in the animal and human body as well as in plants. Therefore, it is important to understand this chapter as it will help Students create a fundamental base for similar chapters.
Q4. What are cells?
Cells are generally considered to be the basic unit of life as they are the building blocks of all living matter. It contains many molecules and chemicals. There are two types of cells found. These include multicellular and unicellular organisms. Both these cells have their own unique characteristics and functions. A cell has three main parts namely the nucleus, the cell membrane, and the cytoplasm. Although all living organisms are made up of cells, one cell can differ from another.
Q5. What is the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell?
The main difference between a plant cell and an animal cell is that in an animal cell the cell wall is absent, whereas a plant cell has a rigid cell wall. A plant cell comprises chloroplasts while animal cells don’t have chloroplasts in them. Since an animal cell does not have a cell wall, it comprises a Centrosome that is present near the nucleus. A centrosome refers to a cell organelle which divides the cells. The Centrosome in a plant cell is absent.
Chapterwise Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science
Cbse study materials.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms-Friend and Foe
Here we are providing case study questions for CBSE Class 8 science Chapter 2 Microorganisms-Friend and Foe.
Case Study Questions
Question 1:
Daksh lived in delhi and he loves to play football. But as of now his half yearly exams were going on so his mother didn’t allow him to go out and play. She promised Daksh that as soon as his exams are over he can go and play. Post exams he went out to play football with his friends in the park. Suddenly a mosquito bit him under his left knee. He came home and everything was normal that time. The next day his health started getting affected. His Parents rushed him to the doctor. The doctor prescribed some medicines and some medical tests. The next day parents went to the doctor with Daksh’s medical report. In that report the platelet counts were very low. The doctor diagnosed him with Dengue fever. Daksh was hospitalised for some time and followed a strict diet to recover as early as possible. And eventually some days passed and he recovered.
Q. 1. Organisms which cannot be seen by naked eye. (a) Plants (b) Animals (c) Microorganisms (d) None of these
Q. 2. The causative organisms of dengue is (a) Anopheles mosquito (b) Aedes aegypti mosquito (c) Dengue virus (d) None of these
Q. 3. How does dengue virus spread?
Q. 4. Write any three preventive measures for dengue fever.
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE Class 8 Science Case Study Question. Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question. Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question. Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question. Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question.
CBSE 8th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 8th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and ...
Students have to read Chapter 3 very carefully as they can get important questions from this Chapter in the final exam. Students can study the important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 3 from Vedantu. All concepts are given in simple and easy-to-understand language that can help students to score well in their Class 8 Science exam.
Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question. Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question. Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question. Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question. Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum Case Study Question. Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Case Study Question.
Answer Key. Que. 1) (a) Kharif. Que. 2) (d) Mustard. Que. 3) (c) Literacy. Que. 4) Answer: When plants of same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale in order to provide food for a large population, it is called a crop. Que. 5) Answer: Rabi crops are grown in winter season mainly from October to March.
Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 1- Crop Production and Management. Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 - Microorganisms: Friend and Foe. Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 3 - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics. Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 - Materials: Metals and Non-Metals.
Answer: Synthetic fibres and plastics, like natural fibres, are made of very large units called polymers. Polymers are made up of many smaller units. Question 3: Define petrochemicals. Answer: All the synthetic fibres are prepared by a number of processes using raw materials of petroleum origin, called petrochemicals.
Therefore, practising questions and answers from Extramarks question bank Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 3 will benefit students massively by providing them stepwise solutions to every question. Science Class 8 Chapter 3 important questions covers all aspects of the chapter and bring a complete set of questions per the latest CBSE ...
The NCERT Science book class 8 solutions have been provided below: Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management. Chapter 2 - Microorganisms : Friend and Foe. Chapter 3 - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics. Chapter 4 - Materials : Metals and Non-Metals. Chapter 5 - Coal and Petroleum. Chapter 6 - Combustion and Flame. Chapter 7 ...
Question 1: Explain why some fibres are called synthetic. There are some fibres that are prepared by man by using chemicals. These are called synthetic fibres. These are made of small units that join together to form long chains. Examples of synthetic fibres are rayon, nylon, polyester, acrylic, etc.
CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions with Answer PDF. Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management. Chapter 2 - Microorganisms : Friend and Foe. Chapter 3 - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics. Chapter 4 - Materials : Metals and Non-Metals. Chapter 5 - Coal and Petroleum.
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Science NCERT Textbook Questions. Question 1. Explain why some fibres are called synthetic. Answer: Some fibres are called synthetic fibres because they are made by man using chemicals. Question 2. Mark ( ) the correct answer. Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because.
These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations. Case Study Questions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals. Case/Passage - 1. Metals are electropositive elements. They can easily lose electrons to form ions.
Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science History Chapter 3 Ruling the Countryside Here we are providing case study questions for class 8 social science History Chapter 3 Ruling the Countryside. Case Study Questions Question 1: Being a plant of the temperate zones, woad was more easily available in Europe. It was grown in … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social ...
Download the NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Solutions PDF Here! NCERT Solutions of Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Coal and Petroleum. Let us now explore NCERT Solutions of Class 8 Science Chapter 3 to get answers to all writing questions in the lesson Coal and Petroleum. Exercise Questions. 1. What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels ...
Class 8 Science Chapter 3 is about synthetic fibers and plastic. First, it introduces the various types of synthetic fibers and their characteristics. Here, students learn about fiber, polymer, natural fiber, silk, and nylon. In addition, they will understand how thermoplastic is formed and its characteristics.
CBSE Class 8 - Physics - Sound - Case Study Based Question #class8Science #Sound #Physics #eduvictors ... CBSE All In One NCERT Based Science Class 8 2022-23 Edition. Posted by www.eduvictors.in at Thursday, December 15, ... Case Study-Based Questions Chapter: Chemical Effects of Current Directions : Read the following and answer the questio ...
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Extra Questions Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions Question 1. Name a natural fibre. Answer: Cotton Question 2. Name the basic component of animal fibres. Answer: Protein Question 3. Name some artificial fibres. Answer: Nylon, terylene, PET, acrylic, teflon, etc. […]
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Science Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case study 1. You have seen several kinds ofplants and ...
Vedantu provides one of the best study materials free of cost PDF, which helps students in learning all the basics about the chapter. Important questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 cell structure and functions help the student to write short notes on the various parts of the cell such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, etc.
Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management. Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs.
October 19, 2023 October 19, 2023 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources. ... What is Case Study Question in Class 8 Social Science? Case study questions typically present a specific scenario or case related to a historical event, geographical issue, or ...
Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms-Friend and Foe Here we are providing case study questions for CBSE Class 8 science Chapter 2 Microorganisms-Friend and Foe. Case Study Questions Question 1: Daksh lived in delhi and he loves to play football. But as of now his half yearly exams were going on … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 ...