Reference management. Clean and simple.

How to start your research paper [step-by-step guide]
1. Choose your topic
2. find information on your topic, 3. create a thesis statement, 4. create a research paper outline, 5. organize your notes, 6. write your introduction, 7. write your first draft of the body, 9. write your conclusion, 10. revise again, edit, and proofread, frequently asked questions about starting your research paper, related articles.
Research papers can be short or in-depth, but no matter what type of research paper, they all follow pretty much the same pattern and have the same structure .
A research paper is a paper that makes an argument about a topic based on research and analysis.
There will be some basic differences, but if you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Below is a step-by-step guide to starting and completing your research paper.
Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
- make sure your topic is not too broad
- narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general
Academic search engines are a great source to find background information on your topic. Your institution's library will most likely provide access to plenty of online research databases. Take a look at our guide on how to efficiently search online databases for academic research to learn how to gather all the information needed on your topic.
Tip: If you’re struggling with finding research, consider meeting with an academic librarian to help you come up with more balanced keywords.
If you’re struggling to find a topic for your thesis, take a look at our guide on how to come up with a thesis topic .
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing. It can be defined as a very brief statement of what the main point or central message of your paper is. Our thesis statement guide will help you write an excellent thesis statement.
In the next step, you need to create your research paper outline . The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
Then, fill out your outline with the following components:
- the main ideas that you want to cover in the paper
- the types of evidence that you will use to support your argument
- quotes from secondary sources that you may want to use
Organizing all the information you have gathered according to your outline will help you later on in the writing process. Analyze your notes, check for accuracy, verify the information, and make sure you understand all the information you have gathered in a way that you can communicate your findings effectively.
Start with the introduction. It will set the direction of your paper and help you a lot as you write. Waiting to write it at the end can leave you with a poorly written setup to an otherwise well-written paper.
The body of your paper argues, explains or describes your topic. Start with the first topic from your outline. Ideally, you have organized your notes in a way that you can work through your research paper outline and have all the notes ready.
After your first draft, take some time to check the paper for content errors. Rearrange ideas, make changes and check if the order of your paragraphs makes sense. At this point, it is helpful to re-read the research paper guidelines and make sure you have followed the format requirements. You can also use free grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .
Tip: Consider reading your paper from back to front when you undertake your initial revision. This will help you ensure that your argument and organization are sound.
Write your conclusion last and avoid including any new information that has not already been presented in the body of the paper. Your conclusion should wrap up your paper and show that your research question has been answered.
Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit, and proofread your paper.
Tip: Take a break from your paper before you start your final revisions. Then, you’ll be able to approach your paper with fresh eyes.
As part of your final revision, be sure to check that you’ve cited everything correctly and that you have a full bibliography. Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize your research and to create accurate citations.
The first step to start writing a research paper is to choose a topic. Make sure your topic is not too broad; narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general.
The format of your research paper will vary depending on the journal you submit to. Make sure to check first which citation style does the journal follow, in order to format your paper accordingly. Check Getting started with your research paper outline to have an idea of what a research paper looks like.
The last step of your research paper should be proofreading. Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit and proofread your paper.
There are plenty of software you can use to write a research paper. We recommend our own citation software, Paperpile , as well as grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .

Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads
Product updates
Dovetail retro: our biggest releases from the past year
Tips and tricks
How to affinity map using the canvas

Dovetail in the Details: 21 improvements to influence, transcribe, and store
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms, including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies, or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data, conducting interviews, or doing field research.
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research. Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research. Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 September 2023
Last updated: 14 February 2024
Last updated: 17 February 2024
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2024
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Latest articles
Related topics.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
How to Start a Research Paper

Beginning is always the hardest part of an assignment. The introduction should not be the first thing you begin to write when starting to work on an essay. First, tons of research should be conducted — in order for your paper to be good. Only then you will be able to extract the main points of your work, and introduce them to your readers. A good introduction will also include your personal opinion of the problem, and, therefore, will make the writing easier overall. Let's dive into the details with admission essay writing services .
What Is a Research Paper?
A research paper is a type of writing in which the author does an independent analysis of the topic and describes the findings from that investigation. Furthermore, one will have to identify the weaknesses and strengths of the subject and evaluate them accordingly.
Don't Know How to Start Your Research Paper?
Head on over to Pro. Our research paper writing service can assist you with writing and polishing up any of the work that you write.
A good way to write an introduction for a research paper is to introduce your reader to the topic by telling them what you are writing about. Then, make sure you include an interesting fact, or some surprising statistical data, so that your reader will be hooked and will continue to read your research paper. Treat your essay introduction like an advertisement for a product you want to sell—if your advertisement is bad, the sales won’t be great. The same goes for a bad introduction; if it does not intrigue readers, they might lose interest in your paper.
The beginning is always the hardest part of an assignment. Regardless of if you are writing a small resume education section or a full-blown research paper - following the correct steps is very important . The introduction should not be the first thing you begin to write when starting to work on an essay.
You might also be interested in getting more info about HOW TO WRITE A RESEARCH PAPER
Introduction Paragraph Outline

Present Your Essay Topic
The base of every essay is its topic. What you are writing about should always be a reflection of your topic. Simply start off your introduction by telling your readers, in a simple and accessible language, what it is you are writing your research paper about. Although, we suggest you include a “trigger” when introducing the topic of your paper. A personal reference, or a story that relates to the essay topic, are options for a good way to link plain text to people’s emotions. So, feel free to write sincerely, as if you were talking to a friend.
The best strategy to start your introduction is by writing a broad topic presentation, then gradually narrow it down to what you would like to focus on exactly. It will put your topic into perspective for readers’ general understanding. When writing your research paper, make sure to include your opinion on the issue in your introduction. This will make your topic sound more personal and it will likely become more important to your audience as well.
Provide Background Information and Context
The topic you begin writing about is likely very familiar to you, as it is expected that you have done plenty of research. But what about your readers? For the most part, the amount of context is determined by what your audience already knows—though, let’s focus on a bigger assortment of readers, to make sure everyone’s needs are met. Imagine that you are part of your audience. Read the information you provided in the introduction. Is this sufficient? Does it leave gaps and unanswered questions in your research? Your job as a writer is to provide the perfect background to your topic, which gives readers just enough information to be able to grasp your topic and enjoy your research paper to the fullest. Another extreme you should avoid is giving too much context—consequently making the audience feel bored right from the introduction. Write your essay as something that you would enjoy reading yourself, like a story, but not an academic research paper.
Explain the Importance of Your Research
There is no doubt that after plenty of research you are an expert in your field. But what about your readers? In the introduction you need to showcase the extent of your research and write about the work you have completed. This will also help your readers understand that your ideas are supported by other scholars, and you share their views in your paper.
Make sure to write about all the works you have studied in order to persuade readers of your expertise. For your introduction, simply use the names you are referencing, or their most important works, so that the audience does not feel overwhelmed. It is also necessary to cite all your sources—in order to avoid academic plagiarism.
Looking to Have Your Work Proofread or Interested in Our Service?
Simply chat with our academic writer to pay for essay .
Make Your Rationale Work
Rationale is the most important part of the beginning of your paper. Explain to readers the reasoning behind your research paper—the importance of this is a guarantee that they will keep reading and appreciate your topic. In the introduction, you need to write an explanation of how your paper fits into all the research that has already been done in that field; this shows your audience the importance of your essay and the role your research plays in the field overall.
Show the Significance of Your Research
You, and only you, understand how important your research is. The next step of your introduction is to prove to your audience how important it is. Include the basic, and the most important literature, you support your ideas with. This will show the readers your solid analytical skills, your writing capabilities, and your ability to sort out information to deliver the most important points for your paper. And the final part of the introduction is to simply explain why your research is important to the field, to society, to the whole world, and, most importantly, to the readers. When a person can relate to an idea, it is almost always a guarantee that your argument will be persuasive and have a positive outcome.
Make Sure Your Thesis Is Clear
A research paper introduction uses primary sources and data to support its thesis statement. A research paper’s thesis statement has a lot in common with a thesis for an essay, or other non-research assignment. The difference lies in the fact that in a research thesis, you gather evidence from valid sources to prove your perspective on a topic. Despite the fact that you support your thoughts by sources, the idea for your thesis in your introduction should be original and your own, as it reflects the way you think.
Here is a quick checklist for writing a thesis statement:
- Remember, the thesis is your argument. Make sure it sounds assertive.
- Write two to three versions of your thesis and choose the best one.
- Share your thesis with a neutral person—to get a different point of view.
- Discuss your thesis with others; they might have good ideas as well.
- It should appear in your introduction, and be restated in your conclusion.
If you're looking to free yourself from the burden of academic writing, consider our research papers for sale , offering a convenient solution to meet your scholarly needs efficiently.
Research Paper Title Page
Mla title page.
Here are some tips from our writing team on how to format your research paper MLA title page:
- The title page is double spaced and the text needs to be centred.
- Write the name of your university or college.
- Skip about one-third of the page down and type your research paper title—include a subtitle if you have one.
- Skip several lines down and type your name, your course name and number, your instructor’s name, and your paper’s due date.

APA Title Page
- Place a running head in your page’s header:
- Use the label “Running head:” then, put your shortened title (IN UPPERCASE LETTERS), and align it all to the left.
- Place the page number in this same header, but align it to the right, and begin with page number 1.
- The header should be 1 inch from the top. Some teachers say 1/2 inch is okay as well.
- Place your paper’s title in the upper half of the page, centred. Capitalize the first letter of all of the important words in your title.
- Place your University’s name below your name, double-spaced.

Read also our research proposal example APA .
Final Thoughts
Congratulations on finishing your research paper! Answer these questions to avoid careless mistakes.
- Are all of your quotations, paraphrases, and summaries accurate?
- Are all of your references accurate?
- Is your format the proper format assigned by your instructor?
- Are all the concepts defined and easily understood by an average reader?
- Is your “hook” good enough for the reader to become interested?
- Is there a structure to your introduction that is easy to navigate for the reader?
- Does your introduction give a good idea of what your paper is about?
And here are several tips for your help:

If you need, you can hire a coursework, buy research paper or other specialist at our service. All you need to do is just leave us a notice like ' write my paper for me ' or something else.
Research Paper Introduction Example
Now that you have a solid idea about the introduction of a research paper, let’s take a look at some examples from our writers. They will help you see how all of the rules we presented above work in practice.
Research Paper Introduction Example: Should Parents Be Held Accountable for the Criminal Acts of Their Children? Recently, youth gang connected attacks have been occurring in an increasing prevalence, with some even causing deaths, such as the killing of a college student at Suburbs East. Such occurrences have made a lot of people to wonder about the origin of those violent actions, with much of the extent of guilt being put on the parents of such adolescents. In any event, one has to question whether the parents should be penalized for the offenses of their kids. Some people believe that parents should be held responsible for the criminal acts of their offspring because parents are mostly accountable for the education and upbringing of their kids, and frequently impact the actions and behavior of their children until they become mature and independent. This is because they are almost always the ones that raise their kids after birth. As such, it is believed that parents start to influence the ethical range of their children from a young age, and one’s ethics are critically impacted by the way parents act and their personalities (Gratz, 169). This logic can make parents responsible for their children if they do wrong later on — because they are understood to not have raised their child in the right way. Furthermore, there is an argument that children are virtually completely controlled by their parents, as they are apt to want to make their parents happy, and they would, therefore, listen to whatever they are told to do or how they are told to behave (Michael, Andrew and Michael, 4). This, in turn, makes many people think that parents should always be the ones to be blamed for the criminal acts of their children, as they believe that they have the power to warn and control them.
Need Some Help with Your Research Paper?
A research paper is a very challenging task to complete. The introduction is a crucial piece of it: it ensures that the reader is interested and will enjoy your paper. If you are still struggling with any part of your essay, remember that you can always pay for a research paper . We are always here to give you a helping hand to make your life easier.
Related Articles
%20(1).webp)
Starting Your Research Paper: Writing an Introductory Paragraph
- Choosing Your Topic
- Define Keywords
- Planning Your Paper
- Writing an Introductory Paragraph
The Dreaded Introductory Paragraph
Writing the introductory paragraph can be a frustrating and slow process -- but it doesn't have to be. If you planned your paper out, then most of the introductory paragraph is already written. Now you just need a beginning and an end.
Here's an introductory paragraph for a paper I wrote. I started the paper with a factoid, then presented each main point of my paper and then ended with my thesis statement.
Breakdown:
- << Previous: Planning Your Paper
- Last Updated: Feb 12, 2024 12:16 PM
- URL: https://libguides.astate.edu/papers

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Yale J Biol Med
- v.84(3); 2011 Sep

Focus: Education — Career Advice
How to write your first research paper.
Writing a research manuscript is an intimidating process for many novice writers in the sciences. One of the stumbling blocks is the beginning of the process and creating the first draft. This paper presents guidelines on how to initiate the writing process and draft each section of a research manuscript. The paper discusses seven rules that allow the writer to prepare a well-structured and comprehensive manuscript for a publication submission. In addition, the author lists different strategies for successful revision. Each of those strategies represents a step in the revision process and should help the writer improve the quality of the manuscript. The paper could be considered a brief manual for publication.
It is late at night. You have been struggling with your project for a year. You generated an enormous amount of interesting data. Your pipette feels like an extension of your hand, and running western blots has become part of your daily routine, similar to brushing your teeth. Your colleagues think you are ready to write a paper, and your lab mates tease you about your “slow” writing progress. Yet days pass, and you cannot force yourself to sit down to write. You have not written anything for a while (lab reports do not count), and you feel you have lost your stamina. How does the writing process work? How can you fit your writing into a daily schedule packed with experiments? What section should you start with? What distinguishes a good research paper from a bad one? How should you revise your paper? These and many other questions buzz in your head and keep you stressed. As a result, you procrastinate. In this paper, I will discuss the issues related to the writing process of a scientific paper. Specifically, I will focus on the best approaches to start a scientific paper, tips for writing each section, and the best revision strategies.
1. Schedule your writing time in Outlook
Whether you have written 100 papers or you are struggling with your first, starting the process is the most difficult part unless you have a rigid writing schedule. Writing is hard. It is a very difficult process of intense concentration and brain work. As stated in Hayes’ framework for the study of writing: “It is a generative activity requiring motivation, and it is an intellectual activity requiring cognitive processes and memory” [ 1 ]. In his book How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing , Paul Silvia says that for some, “it’s easier to embalm the dead than to write an article about it” [ 2 ]. Just as with any type of hard work, you will not succeed unless you practice regularly. If you have not done physical exercises for a year, only regular workouts can get you into good shape again. The same kind of regular exercises, or I call them “writing sessions,” are required to be a productive author. Choose from 1- to 2-hour blocks in your daily work schedule and consider them as non-cancellable appointments. When figuring out which blocks of time will be set for writing, you should select the time that works best for this type of work. For many people, mornings are more productive. One Yale University graduate student spent a semester writing from 8 a.m. to 9 a.m. when her lab was empty. At the end of the semester, she was amazed at how much she accomplished without even interrupting her regular lab hours. In addition, doing the hardest task first thing in the morning contributes to the sense of accomplishment during the rest of the day. This positive feeling spills over into our work and life and has a very positive effect on our overall attitude.
Rule 1: Create regular time blocks for writing as appointments in your calendar and keep these appointments.
2. start with an outline.
Now that you have scheduled time, you need to decide how to start writing. The best strategy is to start with an outline. This will not be an outline that you are used to, with Roman numerals for each section and neat parallel listing of topic sentences and supporting points. This outline will be similar to a template for your paper. Initially, the outline will form a structure for your paper; it will help generate ideas and formulate hypotheses. Following the advice of George M. Whitesides, “. . . start with a blank piece of paper, and write down, in any order, all important ideas that occur to you concerning the paper” [ 3 ]. Use Table 1 as a starting point for your outline. Include your visuals (figures, tables, formulas, equations, and algorithms), and list your findings. These will constitute the first level of your outline, which will eventually expand as you elaborate.
The next stage is to add context and structure. Here you will group all your ideas into sections: Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion/Conclusion ( Table 2 ). This step will help add coherence to your work and sift your ideas.
Now that you have expanded your outline, you are ready for the next step: discussing the ideas for your paper with your colleagues and mentor. Many universities have a writing center where graduate students can schedule individual consultations and receive assistance with their paper drafts. Getting feedback during early stages of your draft can save a lot of time. Talking through ideas allows people to conceptualize and organize thoughts to find their direction without wasting time on unnecessary writing. Outlining is the most effective way of communicating your ideas and exchanging thoughts. Moreover, it is also the best stage to decide to which publication you will submit the paper. Many people come up with three choices and discuss them with their mentors and colleagues. Having a list of journal priorities can help you quickly resubmit your paper if your paper is rejected.
Rule 2: Create a detailed outline and discuss it with your mentor and peers.
3. continue with drafts.
After you get enough feedback and decide on the journal you will submit to, the process of real writing begins. Copy your outline into a separate file and expand on each of the points, adding data and elaborating on the details. When you create the first draft, do not succumb to the temptation of editing. Do not slow down to choose a better word or better phrase; do not halt to improve your sentence structure. Pour your ideas into the paper and leave revision and editing for later. As Paul Silvia explains, “Revising while you generate text is like drinking decaffeinated coffee in the early morning: noble idea, wrong time” [ 2 ].
Many students complain that they are not productive writers because they experience writer’s block. Staring at an empty screen is frustrating, but your screen is not really empty: You have a template of your article, and all you need to do is fill in the blanks. Indeed, writer’s block is a logical fallacy for a scientist ― it is just an excuse to procrastinate. When scientists start writing a research paper, they already have their files with data, lab notes with materials and experimental designs, some visuals, and tables with results. All they need to do is scrutinize these pieces and put them together into a comprehensive paper.
3.1. Starting with Materials and Methods
If you still struggle with starting a paper, then write the Materials and Methods section first. Since you have all your notes, it should not be problematic for you to describe the experimental design and procedures. Your most important goal in this section is to be as explicit as possible by providing enough detail and references. In the end, the purpose of this section is to allow other researchers to evaluate and repeat your work. So do not run into the same problems as the writers of the sentences in (1):
1a. Bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation. 1b. To isolate T cells, lymph nodes were collected.
As you can see, crucial pieces of information are missing: the speed of centrifuging your bacteria, the time, and the temperature in (1a); the source of lymph nodes for collection in (b). The sentences can be improved when information is added, as in (2a) and (2b), respectfully:
2a. Bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation at 3000g for 15 min at 25°C. 2b. To isolate T cells, mediastinal and mesenteric lymph nodes from Balb/c mice were collected at day 7 after immunization with ovabumin.
If your method has previously been published and is well-known, then you should provide only the literature reference, as in (3a). If your method is unpublished, then you need to make sure you provide all essential details, as in (3b).
3a. Stem cells were isolated, according to Johnson [23]. 3b. Stem cells were isolated using biotinylated carbon nanotubes coated with anti-CD34 antibodies.
Furthermore, cohesion and fluency are crucial in this section. One of the malpractices resulting in disrupted fluency is switching from passive voice to active and vice versa within the same paragraph, as shown in (4). This switching misleads and distracts the reader.
4. Behavioral computer-based experiments of Study 1 were programmed by using E-Prime. We took ratings of enjoyment, mood, and arousal as the patients listened to preferred pleasant music and unpreferred music by using Visual Analogue Scales (SI Methods). The preferred and unpreferred status of the music was operationalized along a continuum of pleasantness [ 4 ].
The problem with (4) is that the reader has to switch from the point of view of the experiment (passive voice) to the point of view of the experimenter (active voice). This switch causes confusion about the performer of the actions in the first and the third sentences. To improve the coherence and fluency of the paragraph above, you should be consistent in choosing the point of view: first person “we” or passive voice [ 5 ]. Let’s consider two revised examples in (5).
5a. We programmed behavioral computer-based experiments of Study 1 by using E-Prime. We took ratings of enjoyment, mood, and arousal by using Visual Analogue Scales (SI Methods) as the patients listened to preferred pleasant music and unpreferred music. We operationalized the preferred and unpreferred status of the music along a continuum of pleasantness. 5b. Behavioral computer-based experiments of Study 1 were programmed by using E-Prime. Ratings of enjoyment, mood, and arousal were taken as the patients listened to preferred pleasant music and unpreferred music by using Visual Analogue Scales (SI Methods). The preferred and unpreferred status of the music was operationalized along a continuum of pleasantness.
If you choose the point of view of the experimenter, then you may end up with repetitive “we did this” sentences. For many readers, paragraphs with sentences all beginning with “we” may also sound disruptive. So if you choose active sentences, you need to keep the number of “we” subjects to a minimum and vary the beginnings of the sentences [ 6 ].
Interestingly, recent studies have reported that the Materials and Methods section is the only section in research papers in which passive voice predominantly overrides the use of the active voice [ 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. For example, Martínez shows a significant drop in active voice use in the Methods sections based on the corpus of 1 million words of experimental full text research articles in the biological sciences [ 7 ]. According to the author, the active voice patterned with “we” is used only as a tool to reveal personal responsibility for the procedural decisions in designing and performing experimental work. This means that while all other sections of the research paper use active voice, passive voice is still the most predominant in Materials and Methods sections.
Writing Materials and Methods sections is a meticulous and time consuming task requiring extreme accuracy and clarity. This is why when you complete your draft, you should ask for as much feedback from your colleagues as possible. Numerous readers of this section will help you identify the missing links and improve the technical style of this section.
Rule 3: Be meticulous and accurate in describing the Materials and Methods. Do not change the point of view within one paragraph.
3.2. writing results section.
For many authors, writing the Results section is more intimidating than writing the Materials and Methods section . If people are interested in your paper, they are interested in your results. That is why it is vital to use all your writing skills to objectively present your key findings in an orderly and logical sequence using illustrative materials and text.
Your Results should be organized into different segments or subsections where each one presents the purpose of the experiment, your experimental approach, data including text and visuals (tables, figures, schematics, algorithms, and formulas), and data commentary. For most journals, your data commentary will include a meaningful summary of the data presented in the visuals and an explanation of the most significant findings. This data presentation should not repeat the data in the visuals, but rather highlight the most important points. In the “standard” research paper approach, your Results section should exclude data interpretation, leaving it for the Discussion section. However, interpretations gradually and secretly creep into research papers: “Reducing the data, generalizing from the data, and highlighting scientific cases are all highly interpretive processes. It should be clear by now that we do not let the data speak for themselves in research reports; in summarizing our results, we interpret them for the reader” [ 10 ]. As a result, many journals including the Journal of Experimental Medicine and the Journal of Clinical Investigation use joint Results/Discussion sections, where results are immediately followed by interpretations.
Another important aspect of this section is to create a comprehensive and supported argument or a well-researched case. This means that you should be selective in presenting data and choose only those experimental details that are essential for your reader to understand your findings. You might have conducted an experiment 20 times and collected numerous records, but this does not mean that you should present all those records in your paper. You need to distinguish your results from your data and be able to discard excessive experimental details that could distract and confuse the reader. However, creating a picture or an argument should not be confused with data manipulation or falsification, which is a willful distortion of data and results. If some of your findings contradict your ideas, you have to mention this and find a plausible explanation for the contradiction.
In addition, your text should not include irrelevant and peripheral information, including overview sentences, as in (6).
6. To show our results, we first introduce all components of experimental system and then describe the outcome of infections.
Indeed, wordiness convolutes your sentences and conceals your ideas from readers. One common source of wordiness is unnecessary intensifiers. Adverbial intensifiers such as “clearly,” “essential,” “quite,” “basically,” “rather,” “fairly,” “really,” and “virtually” not only add verbosity to your sentences, but also lower your results’ credibility. They appeal to the reader’s emotions but lower objectivity, as in the common examples in (7):
7a. Table 3 clearly shows that … 7b. It is obvious from figure 4 that …
Another source of wordiness is nominalizations, i.e., nouns derived from verbs and adjectives paired with weak verbs including “be,” “have,” “do,” “make,” “cause,” “provide,” and “get” and constructions such as “there is/are.”
8a. We tested the hypothesis that there is a disruption of membrane asymmetry. 8b. In this paper we provide an argument that stem cells repopulate injured organs.
In the sentences above, the abstract nominalizations “disruption” and “argument” do not contribute to the clarity of the sentences, but rather clutter them with useless vocabulary that distracts from the meaning. To improve your sentences, avoid unnecessary nominalizations and change passive verbs and constructions into active and direct sentences.
9a. We tested the hypothesis that the membrane asymmetry is disrupted. 9b. In this paper we argue that stem cells repopulate injured organs.
Your Results section is the heart of your paper, representing a year or more of your daily research. So lead your reader through your story by writing direct, concise, and clear sentences.
Rule 4: Be clear, concise, and objective in describing your Results.
3.3. now it is time for your introduction.
Now that you are almost half through drafting your research paper, it is time to update your outline. While describing your Methods and Results, many of you diverged from the original outline and re-focused your ideas. So before you move on to create your Introduction, re-read your Methods and Results sections and change your outline to match your research focus. The updated outline will help you review the general picture of your paper, the topic, the main idea, and the purpose, which are all important for writing your introduction.
The best way to structure your introduction is to follow the three-move approach shown in Table 3 .
Adapted from Swales and Feak [ 11 ].
The moves and information from your outline can help to create your Introduction efficiently and without missing steps. These moves are traffic signs that lead the reader through the road of your ideas. Each move plays an important role in your paper and should be presented with deep thought and care. When you establish the territory, you place your research in context and highlight the importance of your research topic. By finding the niche, you outline the scope of your research problem and enter the scientific dialogue. The final move, “occupying the niche,” is where you explain your research in a nutshell and highlight your paper’s significance. The three moves allow your readers to evaluate their interest in your paper and play a significant role in the paper review process, determining your paper reviewers.
Some academic writers assume that the reader “should follow the paper” to find the answers about your methodology and your findings. As a result, many novice writers do not present their experimental approach and the major findings, wrongly believing that the reader will locate the necessary information later while reading the subsequent sections [ 5 ]. However, this “suspense” approach is not appropriate for scientific writing. To interest the reader, scientific authors should be direct and straightforward and present informative one-sentence summaries of the results and the approach.
Another problem is that writers understate the significance of the Introduction. Many new researchers mistakenly think that all their readers understand the importance of the research question and omit this part. However, this assumption is faulty because the purpose of the section is not to evaluate the importance of the research question in general. The goal is to present the importance of your research contribution and your findings. Therefore, you should be explicit and clear in describing the benefit of the paper.
The Introduction should not be long. Indeed, for most journals, this is a very brief section of about 250 to 600 words, but it might be the most difficult section due to its importance.
Rule 5: Interest your reader in the Introduction section by signalling all its elements and stating the novelty of the work.
3.4. discussion of the results.
For many scientists, writing a Discussion section is as scary as starting a paper. Most of the fear comes from the variation in the section. Since every paper has its unique results and findings, the Discussion section differs in its length, shape, and structure. However, some general principles of writing this section still exist. Knowing these rules, or “moves,” can change your attitude about this section and help you create a comprehensive interpretation of your results.
The purpose of the Discussion section is to place your findings in the research context and “to explain the meaning of the findings and why they are important, without appearing arrogant, condescending, or patronizing” [ 11 ]. The structure of the first two moves is almost a mirror reflection of the one in the Introduction. In the Introduction, you zoom in from general to specific and from the background to your research question; in the Discussion section, you zoom out from the summary of your findings to the research context, as shown in Table 4 .
Adapted from Swales and Feak and Hess [ 11 , 12 ].
The biggest challenge for many writers is the opening paragraph of the Discussion section. Following the moves in Table 1 , the best choice is to start with the study’s major findings that provide the answer to the research question in your Introduction. The most common starting phrases are “Our findings demonstrate . . .,” or “In this study, we have shown that . . .,” or “Our results suggest . . .” In some cases, however, reminding the reader about the research question or even providing a brief context and then stating the answer would make more sense. This is important in those cases where the researcher presents a number of findings or where more than one research question was presented. Your summary of the study’s major findings should be followed by your presentation of the importance of these findings. One of the most frequent mistakes of the novice writer is to assume the importance of his findings. Even if the importance is clear to you, it may not be obvious to your reader. Digesting the findings and their importance to your reader is as crucial as stating your research question.
Another useful strategy is to be proactive in the first move by predicting and commenting on the alternative explanations of the results. Addressing potential doubts will save you from painful comments about the wrong interpretation of your results and will present you as a thoughtful and considerate researcher. Moreover, the evaluation of the alternative explanations might help you create a logical step to the next move of the discussion section: the research context.
The goal of the research context move is to show how your findings fit into the general picture of the current research and how you contribute to the existing knowledge on the topic. This is also the place to discuss any discrepancies and unexpected findings that may otherwise distort the general picture of your paper. Moreover, outlining the scope of your research by showing the limitations, weaknesses, and assumptions is essential and adds modesty to your image as a scientist. However, make sure that you do not end your paper with the problems that override your findings. Try to suggest feasible explanations and solutions.
If your submission does not require a separate Conclusion section, then adding another paragraph about the “take-home message” is a must. This should be a general statement reiterating your answer to the research question and adding its scientific implications, practical application, or advice.
Just as in all other sections of your paper, the clear and precise language and concise comprehensive sentences are vital. However, in addition to that, your writing should convey confidence and authority. The easiest way to illustrate your tone is to use the active voice and the first person pronouns. Accompanied by clarity and succinctness, these tools are the best to convince your readers of your point and your ideas.
Rule 6: Present the principles, relationships, and generalizations in a concise and convincing tone.
4. choosing the best working revision strategies.
Now that you have created the first draft, your attitude toward your writing should have improved. Moreover, you should feel more confident that you are able to accomplish your project and submit your paper within a reasonable timeframe. You also have worked out your writing schedule and followed it precisely. Do not stop ― you are only at the midpoint from your destination. Just as the best and most precious diamond is no more than an unattractive stone recognized only by trained professionals, your ideas and your results may go unnoticed if they are not polished and brushed. Despite your attempts to present your ideas in a logical and comprehensive way, first drafts are frequently a mess. Use the advice of Paul Silvia: “Your first drafts should sound like they were hastily translated from Icelandic by a non-native speaker” [ 2 ]. The degree of your success will depend on how you are able to revise and edit your paper.
The revision can be done at the macrostructure and the microstructure levels [ 13 ]. The macrostructure revision includes the revision of the organization, content, and flow. The microstructure level includes individual words, sentence structure, grammar, punctuation, and spelling.
The best way to approach the macrostructure revision is through the outline of the ideas in your paper. The last time you updated your outline was before writing the Introduction and the Discussion. Now that you have the beginning and the conclusion, you can take a bird’s-eye view of the whole paper. The outline will allow you to see if the ideas of your paper are coherently structured, if your results are logically built, and if the discussion is linked to the research question in the Introduction. You will be able to see if something is missing in any of the sections or if you need to rearrange your information to make your point.
The next step is to revise each of the sections starting from the beginning. Ideally, you should limit yourself to working on small sections of about five pages at a time [ 14 ]. After these short sections, your eyes get used to your writing and your efficiency in spotting problems decreases. When reading for content and organization, you should control your urge to edit your paper for sentence structure and grammar and focus only on the flow of your ideas and logic of your presentation. Experienced researchers tend to make almost three times the number of changes to meaning than novice writers [ 15 , 16 ]. Revising is a difficult but useful skill, which academic writers obtain with years of practice.
In contrast to the macrostructure revision, which is a linear process and is done usually through a detailed outline and by sections, microstructure revision is a non-linear process. While the goal of the macrostructure revision is to analyze your ideas and their logic, the goal of the microstructure editing is to scrutinize the form of your ideas: your paragraphs, sentences, and words. You do not need and are not recommended to follow the order of the paper to perform this type of revision. You can start from the end or from different sections. You can even revise by reading sentences backward, sentence by sentence and word by word.
One of the microstructure revision strategies frequently used during writing center consultations is to read the paper aloud [ 17 ]. You may read aloud to yourself, to a tape recorder, or to a colleague or friend. When reading and listening to your paper, you are more likely to notice the places where the fluency is disrupted and where you stumble because of a very long and unclear sentence or a wrong connector.
Another revision strategy is to learn your common errors and to do a targeted search for them [ 13 ]. All writers have a set of problems that are specific to them, i.e., their writing idiosyncrasies. Remembering these problems is as important for an academic writer as remembering your friends’ birthdays. Create a list of these idiosyncrasies and run a search for these problems using your word processor. If your problem is demonstrative pronouns without summary words, then search for “this/these/those” in your text and check if you used the word appropriately. If you have a problem with intensifiers, then search for “really” or “very” and delete them from the text. The same targeted search can be done to eliminate wordiness. Searching for “there is/are” or “and” can help you avoid the bulky sentences.
The final strategy is working with a hard copy and a pencil. Print a double space copy with font size 14 and re-read your paper in several steps. Try reading your paper line by line with the rest of the text covered with a piece of paper. When you are forced to see only a small portion of your writing, you are less likely to get distracted and are more likely to notice problems. You will end up spotting more unnecessary words, wrongly worded phrases, or unparallel constructions.
After you apply all these strategies, you are ready to share your writing with your friends, colleagues, and a writing advisor in the writing center. Get as much feedback as you can, especially from non-specialists in your field. Patiently listen to what others say to you ― you are not expected to defend your writing or explain what you wanted to say. You may decide what you want to change and how after you receive the feedback and sort it in your head. Even though some researchers make the revision an endless process and can hardly stop after a 14th draft; having from five to seven drafts of your paper is a norm in the sciences. If you can’t stop revising, then set a deadline for yourself and stick to it. Deadlines always help.
Rule 7: Revise your paper at the macrostructure and the microstructure level using different strategies and techniques. Receive feedback and revise again.
5. it is time to submit.
It is late at night again. You are still in your lab finishing revisions and getting ready to submit your paper. You feel happy ― you have finally finished a year’s worth of work. You will submit your paper tomorrow, and regardless of the outcome, you know that you can do it. If one journal does not take your paper, you will take advantage of the feedback and resubmit again. You will have a publication, and this is the most important achievement.
What is even more important is that you have your scheduled writing time that you are going to keep for your future publications, for reading and taking notes, for writing grants, and for reviewing papers. You are not going to lose stamina this time, and you will become a productive scientist. But for now, let’s celebrate the end of the paper.
- Hayes JR. In: The Science of Writing: Theories, Methods, Individual Differences, and Applications. Levy CM, Ransdell SE, editors. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 1996. A new framework for understanding cognition and affect in writing; pp. 1–28. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silvia PJ. How to Write a Lot. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Whitesides GM. Whitesides’ Group: Writing a Paper. Adv Mater. 2004; 16 (15):1375–1377. [ Google Scholar ]
- Soto D, Funes MJ, Guzmán-García A, Warbrick T, Rotshtein T, Humphreys GW. Pleasant music overcomes the loss of awareness in patients with visual neglect. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009; 106 (14):6011–6016. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hofmann AH. Scientific Writing and Communication. Papers, Proposals, and Presentations. New York: Oxford University Press; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zeiger M. Essentials of Writing Biomedical Research Papers. 2nd edition. San Francisco, CA: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Martínez I. Native and non-native writers’ use of first person pronouns in the different sections of biology research articles in English. Journal of Second Language Writing. 2005; 14 (3):174–190. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodman L. The Active Voice In Scientific Articles: Frequency And Discourse Functions. Journal Of Technical Writing And Communication. 1994; 24 (3):309–331. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tarone LE, Dwyer S, Gillette S, Icke V. On the use of the passive in two astrophysics journal papers with extensions to other languages and other fields. English for Specific Purposes. 1998; 17 :113–132. [ Google Scholar ]
- Penrose AM, Katz SB. Writing in the sciences: Exploring conventions of scientific discourse. New York: St. Martin’s Press; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Swales JM, Feak CB. Academic Writing for Graduate Students. 2nd edition. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hess DR. How to Write an Effective Discussion. Respiratory Care. 2004; 29 (10):1238–1241. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Belcher WL. Writing Your Journal Article in 12 Weeks: a guide to academic publishing success. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Single PB. Demystifying Dissertation Writing: A Streamlined Process of Choice of Topic to Final Text. Virginia: Stylus Publishing LLC; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Faigley L, Witte SP. Analyzing revision. Composition and Communication. 1981; 32 :400–414. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flower LS, Hayes JR, Carey L, Schriver KS, Stratman J. Detection, diagnosis, and the strategies of revision. College Composition and Communication. 1986; 37 (1):16–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Young BR. In: A Tutor’s Guide: Helping Writers One to One. Rafoth B, editor. Portsmouth, NH: Boynton/Cook Publishers; 2005. Can You Proofread This? pp. 140–158. [ Google Scholar ]
Research Paper Writing Guides
How To Start A Research Paper
Last updated on: Jan 15, 2024
The Definitive Guide on How to Start a Research Paper
By: Donna C.
Reviewed By: Leanne R.
Published on: Jan 1, 2024

Writing a research paper can feel overwhelming, especially when you do not know where to start.
There's a ton of information out there, and it can be challenging to put it in a coherent manner, leaving many researchers unsure of where to begin.
Deciding on a topic, creating a clear thesis, and keeping your audience interested can be a real task. The excitement of discovering something new is great, but there's also a fear of getting lost in a sea of information.
No need to worry!
In this step by step guide, we will help you to tackle the challenging first steps of your research paper. We will tell you what prep work you have to do and how to start your research paper efficiently.
So, why wait? Let’s dive right into it!
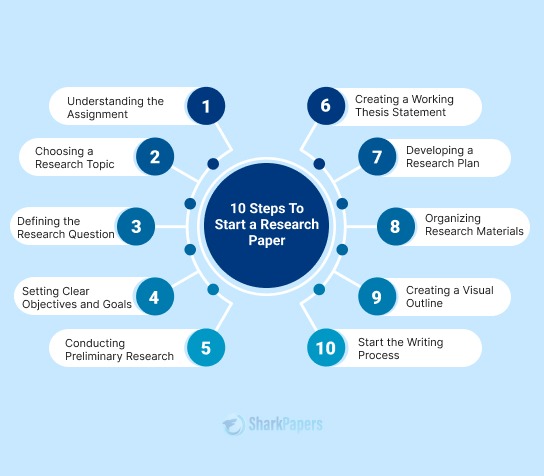
On this Page

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How To Start a Research Paper
The first step of writing a research paper is to do the groundwork. Knowing how to start a research paper gives you an edge in writing a thorough and academically sound research paper.
Here is a step-by-step breakdown for how to start a research paper leading to an outstanding research paper introduction.
Step 1: Understanding the Research Topic
Before you learn how to write a research paper, carefully review the research problem.
Identify key components such as the required length, formatting style (APA, MLA, etc.), and any specific expectations required by your publisher or journal.
This step lays the foundation for tailoring your research approach to meet the journal’s unique criteria.
Step 2: Choosing a Research Topic
The importance of choosing the right research paper topic cannot be overstated, as it forms the basis for your entire research paper. Consider your personal interests, ensuring they align with the assignment guidelines.
Go for a topic that helps and facilitates existing research, and make sure there is enough literature about it.
Take the time to explore various options, ensuring that readers understand your chosen topic and it also aligns with both your academic and personal objectives.
Step 3: Defining the Research Question
Refining your chosen topic involves writing a clear and specific research question leading to a well-crafted abstract.
This question serves as the guiding force throughout your research, ensuring a focused and purposeful exploration of the chosen subject.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself before starting a research paper:
- What is the main purpose or objective of my research paper?
- Who is my target audience, and what level of knowledge do they have on the topic?
- What is the key message or argument I want to convey in my paper?
- What evidence or data do I need to support my claims or arguments?
- What are the potential counterarguments or opposing views that I should address?
- What is the significance of my research, and why should readers care about it?
Step 4: Setting Clear Objectives and Goals
When you're working on a research paper, setting clear objectives and goals helps you know exactly what you want to achieve and where you're headed with your study.
Objectives outline the specific achievements or outcomes you aim to attain through your research. They provide a clear and measurable focus, guiding your efforts toward answering the overarching research question.
Goals , on the other hand, provide the research with direction and purpose, offering a sense of the intended impact or contribution.
Section 5: Conducting Preliminary Research
Preliminary research involves gathering background information on your topic from credible and scholarly sources. This step helps you grasp existing knowledge, identify research gaps, and refine the direction of your study.
For conducting the research, make sure to follow these steps:
- Utilize academic databases and libraries
- Existing literature review
- Use online resources and websites
- Take detailed notes
- Identify key concepts and keywords
- Consider multiple perspectives
- Evaluate source credibility
- Cite your sources properly
- Refine your research question
- Establish a solid foundation
Utilize academic databases and scholarly articles to collect information on the current state of research related to your chosen topic. This foundational step informs the subsequent stages of your investigation.
Step 6: Creating a Working Thesis Statement
Develop an introductory thesis that concisely conveys the main point or argument of your research.
Recognize that this statement may evolve as your understanding of the topic deepens throughout the research process.
Step 7: Developing a Research Plan
Craft a detailed research plan outlining the steps and timeline for each phase of your project.
This plan serves as a roadmap, helping you stay organized and ensuring a systematic progression from initial exploration to the final draft.
Step 8: Organizing Research Materials
Systematically organize your research materials to facilitate easy access and reference during the writing phase.
Categorize articles, notes, and references based on themes, supporting evidence, or relevance to specific sections of your research paper.
You can utilize folders, digital tools, or citation management software to categorize and label materials effectively.
Here are some popular citation management software tools:
Step 9: Creating a Visual Outline
Develop a visual representation of your research structure using a research paper outline.
This visual plan helps you write an introduction and see how different ideas, supporting points, and important parts of your research paper are connected.
Step 10: Start the Writing Process
Now that you've gathered information and figured out what you want to study, it's time to start writing. This means turning what you know into a clear and organized research paper.
Start with writing an introduction for your research paper emphasizing the main topic, followed by methodology, discussion, and results.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How To Start Research Paper - Examples
After following these steps, you should have a better understanding of how to start a research paper.
When beginning a research paper, consider consulting the following examples to ensure you start your paper in the right way!
How To Start A Research Paper About A Person
How To Start A Research Paper Intro Example
Tips on How To Start a Research Paper
Starting a research paper can be exciting and a bit challenging. To make sure you do well, here are some simple tips to keep in mind:
- Create a Timeline
Develop a realistic timeline for your research project. This helps in managing tasks efficiently and ensures you have sufficient time for each stage of the process.
- Consider Ethical Considerations
Think about the ethical aspects of your research, especially if it involves human subjects.
- Stay Flexible in Your Approach
Be prepared to adapt your research plan as needed. Research is an evolving process, and staying flexible allows you to navigate unexpected challenges.
- Use Primary and Secondary Sources Wisely
Distinguish between different types of sources and understand their respective roles in your research.
- Stay Updated on Research Trends
Keep yourself informed about recent developments and trends in your field. This knowledge will enhance the relevance and timeliness of your research.
All in all, starting a research paper requires thoughtful planning and a smart approach to existing literature. This guide is here to give you the tools to start your academic journey confidently.
But if you need expert help, turn to our paper writing service .
At SharkPapers.com , our dedicated team is here to guide you 24/7, making sure your academic journey goes well.
So, don’t waste time!
Place your order and work together with experts to turn your ideas into impactful research!
Frequently Asked Questions
How to start a research paper thesis.
Begin your research paper thesis by clearly stating the main point or argument you will explore. Craft a concise and focused thesis statement that outlines the purpose and direction of your research.
How to Start a Research Paper with a Quote?
Introduce your research paper with a relevant and impactful quote that sets the tone for your topic.
Ensure the quote relates directly to your research and adds value to the parts of the introduction, providing a perspective.

Donna writes on a broad range of topics, but she is mostly passionate about social issues, current events, and human-interest stories. She has received high praise for her writing from both colleagues and readers alike. Donna is known in her field for creating content that is not only professional but also captivating.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Learning How to Write a Research Paper: Step-by-Step Guide

- Best 300+ Ideas For Research Paper Topics in 2024

- A Complete Guide to Help You Write a Research Proposal

- How To Write An Introduction For A Research Paper - A Complete Guide
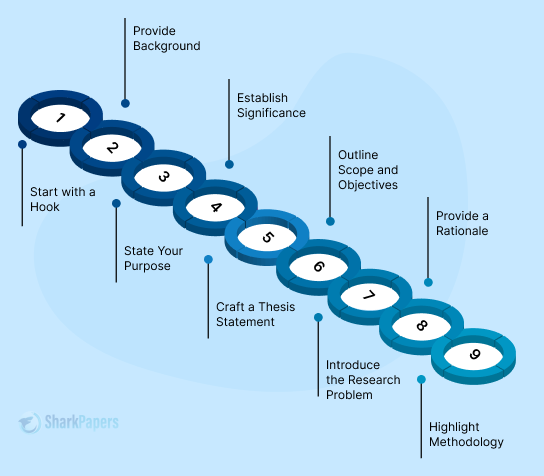
- Learn How To Write An Abstract For A Research Paper with Examples and Tips

- How to Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | A Complete Guide

- How To Write The Methods Section of A Research Paper

- How to Write a Research Paper Thesis: A Detailed Guide

- How to Write a Research Paper Title That Stands Out

- A Detailed Guide on How To Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

- How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Tips

- How to Problem Statement for a Research Paper: An Easy Guide

- How to Find Credible Sources for a Research Paper

- A Detailed Guide: How to Write a Discussion for a Research Paper
)
- How To Write A Hypothesis In A Research Paper - A Simple Guide

- Learn How To Cite A Research Paper in Different Formats: The Basics

- The Ultimate List of Ethical Research Paper Topics in 2024
- 150+ Controversial Research Paper Topics to Get You Started

- How to Edit Research Papers With Precision: A Detailed Guide

- A Comprehensive List of Argumentative Research Paper Topics
- A Detailed List of Amazing Art Research Paper Topics

People Also Read
- press release
- analytical essay outline
- qualitative research
- opinion essay
- rhetorical analysis essay
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
© 2024 - All rights reserved
2000+ SATISFIED STUDENTS
95% Satisfaction RATE
30 Days Money Back GUARANTEE
95% Success RATE
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Contact Us
© 2021 SharkPapers.com(Powered By sharkpapers.com). All rights reserved.
© 2022 Sharkpapers.com. All rights reserved.
LOGIN TO YOUR ACCOUNT
SIGN UP TO YOUR ACCOUNT
- Your phone no.
- Confirm Password
- I have read Privacy Policy and agree to the Terms and Conditions .
FORGOT PASSWORD
- SEND PASSWORD
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Start a Research Paper
Last Updated: March 10, 2024 References
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. There are 16 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 313,205 times.
A research paper employs primary sources/data to support a thesis statement. It is a type of persuasive essay used frequently in science, literature, and history curricula. Regardless of your level of education and chosen field, you'll need to follow a few simple steps to get your research paper off the ground. You'll need to decide on a topic, formulate a thesis statement, conduct research, organize your findings, and then set pen to paper or fingers to keyboard.
Sample Research Papers

Deciding on a Topic

- For example, if you are writing a research paper for a college course, you should know how long it should be, what sources can be used, the topics you can choose from, and the deadline to turn it in. Once you understand the parameters, you can set out a schedule to complete the paper on time. [2] X Research source

- For example, if you are taking an American history course and you want to write a research paper on the origins of the American Revolution, you'd probably want to begin by reading other books on the subject. You'll soon realize that historians have discussed the Revolution's origins primarily in political and economic terms, but have given less attention to the social dimensions of the revolutionary experience. So you decide to focus — broadly — on the social origins of the American Revolution.

- Let's return to the social origins of the American Revolution. You might be able to cover this topic in 500 pages, but if you are writing a 20-page research paper for a class, you'll need to focus your topic further. What social group or groups will you focus on in order to address the social origins of the American Revolution? Break down the "social" into categories — women, racial minorities, farmers, city-dwellers, writers, travelers, businessmen, or children. There are numerous different angles you can take. See what hasn't been written before and then write on that subject.

- Let's say that you've decided to focus on the role of farmers and the American Revolution. Try to formulate a question based on your narrowed field such as: What role did farmers play in the origins of the American Revolution?
Constructing a Thesis

- For example, you could answer the above question (i.e., What role did farmers play in the origins of the American Revolution?) in several ways. Farmers directly participated in public riots against British officers. Farmers refused to sell their crops to British contingents. Farmers refused to quarter British soldiers in their homes. Farmers refused to pay taxes on their goods.
- It is a good idea to start with several hypothetical thesis statements. If one proves to be false or isn't supported by enough evidence, you can start in a new direction quickly.

- For example: The quartering of British soldiers in the homes of poor farmers caused them to protest British taxes and to attack British troops.
- This is a single sentence thesis statement that addresses both why the farmers chose to revolt and how they did so.

- If your professor wanted to you to focus on the political causes of the American Revolution, she might stop you from researching farmers. This would save you time in the long run.
Performing Research

- For our paper on the role of farmers and the American Revolution, we might need to visit local archives and the U.S. National Archives and Records Administration to get the necessary documents.
- If you're feeling overwhelmed by the volume of research, see if your library has appointments with a research librarian. Librarians stay up to date with current trends in scholarship and can help guide your search. [10] X Research source

- Include author, title, and publication information in your notes, so that you can type up a reference list at the end of your research paper. You can also use a program such as EndNote, RefWorks, or LaTEX to help you manage your citations.
- Create a note sheet of quotations that you may want to use in your research paper. It is better to gather more than you need at this point, since you will need evidence from reputable sources to support your thesis.

- For web sources, use sources from peer-reviewed journals, government institutions and organizations, and public archives first. Blogs and other non-authoritative web sources are usually inappropriate for a research paper.
- Organize your notes. Put your notes/data in a logical order that backs up your thesis statement. Organize them so they flow from one to the next. For our imaginary project, it would be best to put your notes on quartered British troops before notes on farmer's revolutionary actions. Since our argument is that quartered troops angered farmers into action, we need to discuss them in that order. [13] X Research source

- For example, if you discovered that farmers were primarily unhappy quartering British soldiers because they ate all their food, you'd want to include that information in your thesis statement.
- Quartered British troops consumed large quantities of food while housed with poor farmers. Because they couldn't feed themselves and quarter troops, these farmers chose to protest British taxes and to attack British troops. As such, farmers played a significant role in the origins of the American Revolution.
Starting Your Research Paper

- Consider composing an outline as a list of questions you would like to answer. Start with your thesis at the beginning, then break it down into sections that back up your argument. Write questions like "Why is this research important?" and "What studies support my thesis?" Then insert information you found while researching into your outline that answers these questions.
- You can also write a prose outline, instead of a question-based outline. Place headers that are the subjects of each paragraph or section of your research paper. Add quotes and other notes in bullets below the subject. You can begin your composition directly from a prose-based outline.
- Continue researching if you need to fill holes in your outline. Be sure to gather bibliographic information as you go.

- This is how most people begin their research papers. They don't want to make their subject seem too obscure, so they write about larger points before jumping head first into their topic. [16] X Research source
- Just make sure that your broad statement is related to your thesis statement. And make sure that everyone can agree with your broad statement. You don't want to have your readership criticizing your argument from the beginning. You need to build a certain degree of trust.
- By all means, avoid the "Throughout history" or "In modern society" types of opening lines. These are so overused that they have become hackneyed, and they will damage your credibility as a writer before your reader has looked at another word. [17] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- For example, if you want to write a research paper on philately (stamp collecting), you should probably begin by defining your key term. But don't go for the standard "Webster's Dictionary defines philately as..." opening. See if you can make your opening line attention-grabbing or intriguing. [19] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- By setting up this story at the beginning, you'd be able to return to it periodically over the course of your paper to illustrate points and to re-assert your thesis statement. [20] X Research source
- Interesting anecdotes or surprising facts can be a good way to hook your readers and lead in to your thesis statement. [21] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- If you aren't sure about how to start your essay, have a look at some published works in your subject. They'll be a lot fancier than your paper needs to be, but they can give you a sense of that subject's conventions.
Drafting Your Research Paper

- Some writers find it helpful to write the body of the text and then return and write the introduction and conclusion. This gives them a better sense of what exactly they want to argue.

- Be sure to give the author credit. You don't want to be accused of plagiarism. [22] X Research source

- In general, bibliographies should be organized by type of source and by alphabetical order.

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://gustavus.edu/writingcenter/handoutdocs/getting_started_research.php
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/688/01/
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Sociology Professor, Stanford University. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/658/03/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/545/01/
- ↑ https://www.esc.edu/online-writing-center/resources/research/research-paper-steps/developing-thesis/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/552/01/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/559/1/
- ↑ http://www.aresearchguide.com/1steps.html
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/553/03/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/544/01/
- ↑ http://libguides.astate.edu/c.php?g=14501&p=78098
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/introductions/
- ↑ http://docs.lib.purdue.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1063&context=ijpbl
- ↑ http://www.plagiarism.org/citing-sources/cite-sources/
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/reading-aloud/
About this article

To start a research paper, start by crafting a broad, factual statement about your subject to pull readers in before introducing your thesis. For example, if you’re writing about the role of famers in the American Revolution, make a blanket statement about the complex causes of the revolutionary movement. Alternatively, begin with a true story, such as an attack by a family on a British soldier quartered with them for eating all their bread. Then, return to the story periodically throughout your paper to illustrate the key points of your thesis. For more tips from our English co-author, including how to decide on a topic and formulate a thesis, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
Reader Success Stories
Lanka Ranasinghe
May 11, 2017
Did this article help you?
Nov 14, 2016
Jan 30, 2017
Shruti Parulekar
Jan 22, 2017

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
How to Start a Research Paper

Now when you know what is a research paper it’s time to know how to start a research paper. Research paper writing begins with a writing assignment the instructor gives you. This assignment may be specific, or it may be general. It may assign you a research topic and point you in the direction the research should take. Or it may offer a great deal of flexibility, allowing you to pick your topic and stage your own research. The assignment serves as a road map to what you must do. It is your first clue to what your professor expects of you. If you have a thorough understanding of the assignment, you will be better able to deliver what is expected of you.
Tackling a research paper is, in many ways, like preparing to run a race.You have no hope of finishing among the leaders if you have no idea where the finishing line is or how to get there. That may sound sophomoric but the vast majority of research papers that end in failure do so because the writer proceeded with no clear understanding of what was expected and delivered something off the mark.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
The first step you take in tackling the paper should point you in the direction of a successful finish. You need to know what is expected of you and how to prepare to deliver it. By understanding where you need to end up, you will spare yourself a lot of trial and error in writing.
First Steps in Writing a Research Paper:
- Interpret the assignment given.
- Identify your instructor’s the expectations and grading criteria.
- Analyze the audience of your paper.
- Choose a topic.
- Write a thesis statement.
- Write a proposal.
Step 1: Interpreting the Assignment
Knowing precisely what you need to produce is the first step to producing a perfect paper. Not only will it spare you the frustration of assembling material that may not be appropriate to the assignment, but it will assure you of a better grade. One of the first questions on an instructor’s mind is: Did this student understand the assignment? A student’s ability to deliver what the assignment requests shows the teacher or professor that the student possesses the skills to properly interpret instructions and identify expectations.
Research papers typically begin with an assignment that identifies your teacher’s expectations and provides the information you need to know to complete the assignment.
What You Should Know before You Start
What is the purpose of the assignment? What does your instructor expect you to learn?
- Is there an assigned topic? Can you choose your own?
- What kinds of sources should you use?
- How many sources should you use?
- Are print and online sources equally acceptable?
- When is the paper due?
- How long should it be?
- How should the paper be formatted?
- How should bibliographic information be presented?
- What are the qualities of a paper that gets an A, B, C, or D?
You cannot produce a good research paper if you do not know what “goodness”means to your professor or instructor who will be evaluating it. More important are those expectations that actually tell you what you are supposed to do. Writing assignments are often written very deliberately to test how well students read, interpret, and respond to the expectations that are outlined. Your professor may want to know how well you can summarize new ideas and complex material, or whether you can present a logical argument to support an opinion or advocate an idea. Another assignment might spell out how you should conduct your research by specifying the types of sources you should consult. Other instructors may use words like analyze, discuss, or investigate to describe what is expected. Students should not take these words lightly because they have specific meanings. You must learn to recognize the goals and expectations in an assignment.
When you receive a research paper assignment, read it thoroughly and be prepared to ask your professor about anything that is unclear to you. Make a list of the stated goals and expectations. Though you already have these on the assignment sheet but writing them down will make them concreted in your mind and help you to remember them. If you receive the criteria for how your research paper will be graded, examine them as closely as you do the assignment to determine what you are expected to do in order to achieve the grade you want. If your instructor does not provide the grading criteria, ask what they are. An example of typical university grading criteria appears below:
Step 2: Identifying Grade Criteria
A Grade: A research paper that merits an A demonstrates a generally high degree of competence and control of language. Typically, such a paper meets all of the following criteria:
- Responds to the assignment thoroughly, thoughtfully, and with insight or originality.
- Demonstrates strong reading comprehension of the assigned texts.
- Is well-developed and supports analysis with effective textual evidence, reasons, examples, and details.
- Is well-focused and well-organized, demonstrating strong control over the conventions of analytical writing.
- Demonstrates facility with language, using effective vocabulary and sentence variety.
- Demonstrates strong control of grammar, the rules of usage, and mechanics of standard English but may have minor errors.
B Grade: A research paper that receives a B is written in a clearly competent manner and displays generally consistent control of language. Typically, such a paper meets all of the following criteria:
- Responds to all elements of the assignment competently and thoughtfully.
- Demonstrates an adequate understanding of the readings.
- Is adequately developed, using appropriate textual evidences, reasons, examples, and details.
- Is focused and effectively organized, demonstrating control of the conventions of analytical writing.
- Demonstrates strong language competence and uses appropriate vocabulary and sentence variety.
- Shows good control of grammar, the rules of usage, and mechanics of standard English, although it may have some errors and minor lapses in quality.
C Grade: A research paper that earns a grade of C demonstrates some competence but is limited in one or more of the following ways:
- Does not address all parts of the writing assignment.
- Does not demonstrate an adequate understanding of the readings.
- Is thinly developed, often relying on assertions with little textual evidence or few relevant reasons, examples, and details.
- Is adequately focused and/or adequately organized, but connections between the parts could be more explicit.
- Demonstrates limited facility with language and minimal sentence variety.
- Demonstrates inconsistent control of grammar, usage, and the mechanics of writing.
Grade of D: A research paper receives a grade of D if it has one or more of the following flaws:
- Is unclear and/or seriously limited in its response to the writing assignment.
- Demonstrates a limited reading or misreading of the texts.
- Is unfocused and/or disorganized, demonstrating little control of the conventions of analytical writing.
- Demonstrates serious errors in the use of language, which may interfere with meaning.
- Demonstrates serious errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics, which may interfere with meaning.
Grade of F: A research paper receives a grade of F when it:
- Demonstrates little or no ability to develop an organized response to the writing assignment.
- Contains severe writing errors that persistently obscure meaning.
Make sure to note any specific information or ideas that the assignment asks you to discuss in your research paper. It helps to ask any questions you may have, and take notes. Any information you receive will help you in your pursuit of the “perfect” research paper.
Make every effort to ensure that you understand what your professor is requesting. That way, you know what to deliver.
Types of Writing Assignments
Writing assignments in schools and universities are not created equal. The approach you take to receive an A in a paper written for one class will not necessary work well for you in another. You should expect that any research paper assignment, whether it is given at the high school or college level, will differ according to the class you are taking and the expectations of your professor. Even within a class, a professor’s expectations are likely to change from one assignment to another. Getting a good grade is not a function of “psyching out” your professor. It is a function of understanding the assignment and what you are being expected to do.
High School Research Paper
On a high school level, research papers are generally assigned to test an ability to look up information and explain it adequately in student’s own words. Here is a list of the kinds of assignments typically given in high school and what they mean:
- Summary : An abbreviated account of a larger article, book, or other work. Examples: Book report,movie review, or a summary of something you read in the news or saw on TV.
- Description : A detailed account of what things look like. Descriptions that help readers “see” what you are talking about are especially useful to clarify events, conditions, or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the reader. Good descriptions make appropriate use of adjectives and adverbs, metaphors, similes, and examples to build readers’ understanding. Examples: A history report about life in another time or a geography report about the culture and industries in another country.
- Explanation : A description that tells why certain conditions exist or certain events occur. Explanations attempt to identify the cause or causes that create an effect. They attempt to answer the question,“Why”? Examples: A science report.
- Process : A description of conditions that must exist and actions that must be taken to produce an outcome. Examples: Instructions someone should follow to do something successfully, such as following the steps in an experiment, or directions to a destination.
- Narrative : A story about something that happened. Narratives are often told in chronological order with a beginning, middle, and end. Examples:“What I Did on My Summer Vacation”

College and University Research Paper
At the college and university levels, a much more is expected from students. Writing assignments become more complex. Instead of simply asking you to summarize or describe something, the assignment typically will present you with a challenge. Often, too, the assignment is not even called an “assignment.” Instead, it is called a “writing prompt,” meaning that the purpose of the assignment is to “prompt” your thinking and elicit a thorough written response from you. Writing prompts usually call upon the writer to use a combination of the approaches learned in high school (those listed above), as well as employ other approaches and strategies to advance new ideas, opinions, and arguments about the topic under discussion.
The path to producing a perfect research paper begins with understanding what those goals are and how to identify them in the assignment. Below is a list of terms that professors often use in writing prompts and what they mean:
- Analyze relationships among facts, trends, theories, and issues. Point out their significant likes and differences and tell why they are meaningful.
- Argue in defense of (or against) a concept, opinion, position, thesis, or point of view. Strong arguments apply logic and point out fallacies, errors, and “fuzzy” thinking.
- Categorize or classify items, concepts, or events by sorting them in sets of predefined qualities or conditions according to their similarities.
- Compare and contrast two or more events, ideas, or opinions by identifying their similarities and/or differences.
- Define the meaning of an unfamiliar term, phrase, or concept by describing the concept behind it.
- Discuss the implications of your research or various points of view on your topic by looking at different sides of the issue and pointing out their merits.
- Examine a topic in minute detail by describing it as if it were under a microscope.
- Illustrate a concept by using many significant details to describe it.
- Interpret a set of facts or events by explaining their significance and importance to your reader, or to other audiences with other needs or interests.
- Give your opinion by telling what you think about the topic and provide an explanation about why you think it.
- Reason (the verb, not the noun) by presenting the logical thought process required to support a specific conclusion.
- Synthesize information from a variety of sources to support a single thesis, opinion, or conclusion.
- Theorize by presenting your own hypothesis, or best guess, about why things are the way they are.
Step 3: Analyzing the Audience
A key test of a good research paper is how well it resonates with your audience. It is useful, before you begin, to create a profile of a theoretical reader.
Rather than focus on your professor as your audience, assume you are writing for intelligent people of the same age and educational level as yourself. Assume that they have not read the material you have researched and that you will need to provide enough background to ensure that your audience will understand and respond to your arguments. You will determine how to present your information and ideas according to the effect you hope they will have on the reader.
What You Should Know about Members of Your Audience
- Approximate age.
- Approximate educational level.
- Experiences they have in common.
- Why they would be interested in your topic.
- How much the average reader should already know about your topic.
- What questions a reader is likely to have.
- How that reader might react to your arguments.
Step 4: Choosing a Topic
Topics for some research papers will be assigned to you by your instructor, along with very specific requirements that you must follow in completing the paper. Others allow you to choose the topic you will research.
Many writing assignments are deliberately open-ended, allowing students to pick their own topics and pursue their own research. If your assignment is open-ended,you will have lots of latitude to research a topic that interests you, based on whatever guidelines or parameters your instructor specifies. The challenge then becomes finding a good research paper topic and devising a thesis and arguments to support it.
Below is an example of an open-ended writing assignment from a freshman English Composition class. It was designed to determine how effectively students can identify a topic, construct their own thesis statements, find sources to support the thesis, and use that research to present arguments their audience would find convincing.
Example open-ended assignment:
Pick an issue that interests you and find at least three newspaper articles or editorials from different sources that express differing points of view on the issue.Produce a five-page paper, including four pages plus a Works Cited page, that analyzes the various points of view.What appears to be the best course of action, based on the merits of the arguments that the articles present? Be sure to use arguments from each of your sources as you explore the issue. Paraphrase, summarize, and quote them accurately and be sure to cite them according to MLA style.
Open-ended writing assignments can be fun. They allow you to pursue your own topics of interest but they can also be frustrating because they require you to make decisions that your instructors make for you in specific assignments. Students often get lost and don’t know what to write about, or they spend a lot of time gathering research on vague topics that do not address their thesis.
The task becomes much easier if you already have a topic, one that is specific and focused and offers something to say. Coming up with one is the challenge but it is not as difficult as it sounds. Most of us know more—a lot more—than we think we know about the world around us and the subjects studied in schools colleges, and universities. At a minimum, people usually hold opinions about what is happening in our world, and, whether they realize it or not, they formed those opinions based on information and experience we gathered somewhere. If you find yourself stuck for a good research paper topic, ask yourself a few questions. You will find you have a lot more to say about those topics that you are involved with or that captured your interest than topics others might suggest, including your instructor.
Here are some things to consider when choosing a research paper topic:
- Your hobbies and special interests.
- Class discussions that caught your attention and aroused your interest.
- Things you have read that caught your attention and aroused your interest.
- True stories you have heard about on the radio or saw on TV that provoked a reaction from you and made you happy, sad, angry, or disgusted.
- Things you have overheard that you would like to know more about.
- Your hopes for the future.
- Your worries about the future.
- Things you dream about.
- Issues you think someone should do something about.
Make a list of everything that comes to mind. You can use this list to begin brainstorming. You can even make games you play a starting point of your research paper: people playing Total War series can be interested in some period in history, like Ancient Rome or Napoleonic Wars, the fans of Fallout games may find it interesting to research technologies, nuclear weapons, or the physics of radioactive materials. Just write whatever comes to you.
When you have finished the list, pick the topic that most interests you—one that you actually want to write about and that you feel you would have a lot to say about. Open-ended writing assignments tend to be large, even massive, projects. They are often assigned weeks ahead of when they are due in order to give you plenty of time to find sources to support your arguments. See our collection of research paper topics, maybe you’ll find something interesting.
After you have picked a research paper topic, begin to focus it by writing down anything you can think about the topic of your choice.Things to consider as you narrow your topic:
- Your opinion about it.
- Interesting things you have heard about it.
- Things you have read about it.
- Others’ observations on it.
- Any facts, assumptions, rumors,myths, and even the misrepresentations you have heard about it.
If you are assigned a research topic, you do not have a lot of flexibility. If the assignment requires you to write about a specific topic, simply write about it. Never stray from an assignment and head off in a direction all your own unless you first get approval from your professor. One of the best ways to ensure a bad grade is to write a research paper on a topic that in no way resembles the one you were assigned. No matter how perfect your research or how brilliant your style, you will most likely receive an F if you fail to produce what the assignment requests.
Instructors usually construct writing assignments with learning goals in mind. A student’s failure to correctly respond to an assignment means that he or she has not met those learning goals. Moreover, it raises a red flag to the instructor who may question whether the student understood the assignment or, worse, whether the student got lazy and desperate and found a well-written essay on the Internet and decided to submit it instead.
If you want to research a topic that was not assigned, ask your instructor if you can. Often, an instructor will be happy to let you follow your interests and conduct your own research, but always ask permission before you do.
Step 5: Developing a Working Thesis
A thesis statement is a claim that you intend to prove using sound, well-reasoned arguments drawn from careful research. It will be the central statement in your research paper when you actually sit down to write. Usually, your working thesis will not be the one that you actually present in your paper.
A working thesis simply aims to get you started on writing your research paper. You need it as an idea to guide you. Professors and writing instructors often refer to this process of developing an idea into a working thesis as “invention.” When you have finished this “invention” stage, you will find that you have the basis for a thesis statement and a good sense of direction in identifying the research you will need to support it.
The working thesis should be aimed at helping you narrow and manage your paper topic. A working thesis that is phrased in the form of a question can help guide your research. A good working thesis makes the job more manageable. Keep it focused and avoid making it too general. Theses that are too general often ramble and result in research papers that lose focus and therefore earn low grades.
Here are some examples of questions for working theses that are general and not well focused:
- Should more money be spent on education?
- How can the government balance the budget?
- Why should we study art?
- What should we do about global warming?
- How can we eliminate poverty?
- How should we respond to the energy crisis?
The following examples, however, are focused on specific issues that can be more easily researched:
- Should more government-backed student loans be made available?
- Should cuts in military spending be enacted before cutting domestic spending to balance the national budget?
- Should the study of art history or the creative arts receive greater emphasis in America’s high schools?
- Is wind energy a viable alternative to fossil fuels?
- Will the extension of unemployment benefits improve life for the nation’s unemployed?
- Will the sale of electric vehicles reduce American dependence on foreign oil?
Step 6: Writing a Proposal
Research proposals are only occasionally required in high school courses, sometimes in freshman-level college courses, and often in upper-level college business and science courses. However, even if your research paper assignment does not require you to submit a proposal, it is a good idea to develop one for your own purposes. A proposal helps you to organize ideas that can guide the research process. Research proposals allow you to start the thought process needed to focus your ideas. A good research proposal will identify the topic, present a working thesis, and offer a plan to prove it.
Think of your research proposal as an outline for how you will pursue your investigation and structure your research paper.
- Your proposal should:
- Identify your topic.
- Present a working thesis.
- Identify how you will conduct your research.
- Present a hypothesis for what you expect to prove.
Having completed these 6 steps we can proceed to the main part in research paper writing – doing your research .
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...
- Page Content
- Sidebar Content
- Main Navigation
- Quick links
- All TIP Sheets
- Choosing and Using a Dictionary
- How to Use a Thesaurus
How to Start (and Complete) a Research Paper
- Using the Butte College Library
- Evaluating Websites
TIP Sheet HOW TO START (AND COMPLETE) A RESEARCH PAPER
You are a re-entry student and it's been fourteen years since you've written a paper. You coasted through high school on your charm and good looks and never actually wrote a research paper. You have written research papers, but every time is like the first time, and the first time was like a root canal. How do you start? Here is a step-by-step approach to starting and completing a research paper.
- Choose a topic.
- Read and keep records.
- Form a thesis.
- Create a mind map or outline.
- Read again.
- Rethink your thesis.
- Draft the body.
- Add the beginning and end.
- Proofread and edit.
You may read this TIP Sheet from start to finish before you begin your paper, or skip to the steps that are causing you the most grief.
1. Choosing a topic: Interest, information, and focus Your job will be more pleasant, and you will be more apt to retain information if you choose a topic that holds your interest. Even if a general topic is assigned ("Write about impacts of GMO crops on world food supply"), as much as possible find an approach that suits your interests. Your topic should be one on which you can find adequate information; you might need to do some preliminary research to determine this. Go to the Reader's Guide to Periodical Literature in the reference section of the library, or to an electronic database such as Proquest or Wilson Web, and search for your topic. The Butte College Library Reference Librarians are more than happy to assist you at this (or any) stage of your research. Scan the results to see how much information has been published. Then, narrow your topic to manageable size:
Once you have decided on a topic and determined that enough information is available, you are ready to proceed. At this point, however, if you are having difficulty finding adequate quality information, stop wasting your time; find another topic.
2. Preliminary reading & recordkeeping Gather some index cards or a small notebook and keep them with you as you read. First read a general article on your topic, for example from an encyclopedia. On an index card or in the notebook, record the author, article and/or book title, and all publication information in the correct format (MLA or APA, for example) specified by your instructor. (If you need to know what publication information is needed for the various types of sources, see a writing guide such as S F Writer .) On the index cards or in your notebook, write down information you want to use from each identified source, including page numbers. Use quotation marks on anything you copy exactly, so you can distinguish later between exact quotes and paraphrasing. (You will still attribute information you have quoted or paraphrased.)
Some students use a particular index card method throughout the process of researching and writing that allows them great flexibility in organizing and re-organizing as well as in keeping track of sources; others color-code or otherwise identify groups of facts. Use any method that works for you in later drafting your paper, but always start with good recordkeeping.
3. Organizing: Mind map or outline Based on your preliminary reading, draw up a working mind map or outline. Include any important, interesting, or provocative points, including your own ideas about the topic. A mind map is less linear and may even include questions you want to find answers to. Use the method that works best for you. The object is simply to group ideas in logically related groups. You may revise this mind map or outline at any time; it is much easier to reorganize a paper by crossing out or adding sections to a mind map or outline than it is to laboriously start over with the writing itself.
4. Formulating a thesis: Focus and craftsmanship Write a well defined, focused, three- to five-point thesis statement, but be prepared to revise it later if necessary. Take your time crafting this statement into one or two sentences, for it will control the direction and development of your entire paper.
For more on developing thesis statements, see the TIP Sheets "Developing a Thesis and Supporting Arguments" and "How to Structure an Essay."
5. Researching: Facts and examples Now begin your heavy-duty research. Try the internet, electronic databases, reference books, newspaper articles, and books for a balance of sources. For each source, write down on an index card (or on a separate page of your notebook) the publication information you will need for your works cited (MLA) or bibliography (APA) page. Write important points, details, and examples, always distinguishing between direct quotes and paraphrasing. As you read, remember that an expert opinion is more valid than a general opinion, and for some topics (in science and history, for example), more recent research may be more valuable than older research. Avoid relying too heavily on internet sources, which vary widely in quality and authority and sometimes even disappear before you can complete your paper.
Never copy-and-paste from internet sources directly into any actual draft of your paper. For more information on plagiarism, obtain from the Butte College Student Services office a copy of the college's policy on plagiarism, or attend the Critical Skills Plagiarism Workshop given each semester.
6. Rethinking: Matching mind map and thesis After you have read deeply and gathered plenty of information, expand or revise your working mind map or outline by adding information, explanations, and examples. Aim for balance in developing each of your main points (they should be spelled out in your thesis statement). Return to the library for additional information if it is needed to evenly develop these points, or revise your thesis statement to better reflect what you have learned or the direction your paper seems to have taken.
7. Drafting: Beginning in the middle Write the body of the paper, starting with the thesis statement and omitting for now the introduction (unless you already know exactly how to begin, but few writers do). Use supporting detail to logically and systematically validate your thesis statement. For now, omit the conclusion also.
For more on systematically developing a thesis statement, see TIP sheets "Developing a Thesis and Supporting Arguments" and "How to Structure an Essay."
8. Revising: Organization and attribution Read, revise, and make sure that your ideas are clearly organized and that they support your thesis statement. Every single paragraph should have a single topic that is derived from the thesis statement. If any paragraph does not, take it out, or revise your thesis if you think it is warranted. Check that you have quoted and paraphrased accurately, and that you have acknowledged your sources even for your paraphrasing. Every single idea that did not come to you as a personal epiphany or as a result of your own methodical reasoning should be attributed to its owner.
For more on writing papers that stay on-topic, see the TIP Sheets "Developing a Thesis and Supporting Arguments" and "How to Structure an Essay." For more on avoiding plagiarism, see the Butte College Student Services brochure, "Academic Honesty at Butte College," or attend the Critical Skills Plagiarism Workshop given each semester.
9. Writing: Intro, conclusion, and citations Write the final draft. Add a one-paragraph introduction and a one-paragraph conclusion. Usually the thesis statement appears as the last sentence or two of the first, introductory paragraph. Make sure all citations appear in the correct format for the style (MLA, APA) you are using. The conclusion should not simply restate your thesis, but should refer to it. (For more on writing conclusions, see the TIP Sheet "How to Structure an Essay.") Add a Works Cited (for MLA) or Bibliography (for APA) page.
10. Proofreading: Time and objectivity Time permitting, allow a few days to elapse between the time you finish writing your last draft and the time you begin to make final corrections. This "time out" will make you more perceptive, more objective, and more critical. On your final read, check for grammar, punctuation, correct word choice, adequate and smooth transitions, sentence structure, and sentence variety. For further proofreading strategies, see the TIP Sheet "Revising, Editing, and Proofreading."
Home | Calendars | Library | Bookstore | Directory | Apply Now | Search for Classes | Register | Online Classes | MyBC Portal MyBC -->
Butte College | 3536 Butte Campus Drive, Oroville CA 95965 | General Information (530) 895-2511
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The pages in this section provide detailed information about how to write research papers including discussing research papers as a genre, choosing topics, and finding sources.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.
How To Write A Research Paper
Research Paper Thesis

How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
12 min read
Published on: Mar 6, 2024
Last updated on: Mar 5, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How to Write an Abstract That Captivates Your Readers
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
Share this article
Creating a strong thesis for a research paper can be tough for researchers and scholars. Despite their expertise, condensing complex ideas into a clear thesis statement is a common struggle.
This concise element encapsulates the core arguments or points of the piece. Notably, a thesis statement serves various roles, prominently addressing the research question.
This guide offers a step-by-step approach for researchers and scholars to learn thesis writing. From choosing a solid topic to balancing academic standards, each step aims to empower you in creating a thesis that meets scholarly criteria and resonates widely.
This guide ensures you develop a strong thesis, making your research paper stand out in academic circles.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a concise sentence that presents the main point or argument of a research paper or an essay.
According to the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill's Writing Center , a thesis statement is defined as, "a concise, declarative statement that encapsulates the central argument or main point of an academic paper or essay. It serves as a guidepost for the reader, outlining the focus and direction of the piece"
In a standard academic essay writing or research paper , the thesis statement is typically placed at the end of the introduction. It serves as a roadmap for the reader, providing a concise summary of the main point or argument that the paper will explore.
The structure of an introduction often follows a general pattern:
- Hook/Attention Grabber
- Background Information/Context
- Thesis Statement
There is no strict rule regarding the length of a thesis statement, as it can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the scope of the paper. However, as a general guideline, a thesis statement is typically one or two sentences long.
Qualities of a Good Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement possesses several key qualities that contribute to its effectiveness:
- Clarity and Precision : Clearly conveys the main idea without unnecessary complexity, avoiding vague language.
- Debatable and Focused : Presents a claim open to interpretation, requiring support and evidence, and maintains a narrow focus.
- Assertive and Defensible: Takes a clear position, avoiding indecisiveness, and is defensible through logical reasoning and evidence.
- Relevance to the Topic : Directly relates to the subject matter, avoiding irrelevant or off-topic statements.
- Scope Limitation : Defines the paper's scope, avoiding broad, sweeping statements to maintain focus.
- Analytical and Thought-Provoking : Goes beyond stating facts, presenting an argument that requires analysis and thought, encouraging consideration of multiple perspectives.
- Coherent and Well-Structured : Well-crafted with a logical structure, serving as a roadmap to guide the reader through the main points of the research paper.
How To Write a Thesis Statement in 5 Steps
Writing a thesis statement involves several key steps to ensure that it is clear, concise, and effectively conveys the main idea of your essay or research paper. Here's a guide with steps and examples:
Step 1. Understand the Assignment
Before diving into writing a thesis statement, thoroughly understand the assignment's requirements, including the topic, length, and specific guidelines provided by your instructor or the prompt.
Step 2. Narrow Down Your Topic
Choose a specific aspect or angle within your broader topic that you can effectively address in your paper. This helps in focusing your research and drafting a more precise thesis.
Example : If your original topic is "Global warming," narrow it down to "The impact of deforestation on global warming."
Step 3. Conduct Research
Gather relevant information and evidence from reputable sources to support your thesis. A well-researched thesis is more likely to be compelling and convincing.
Example : Find studies, scientific articles, or statistics that demonstrate the connection between deforestation and increased carbon emissions.
Step 4. Identify Your Position or Claim
Determine your stance on the narrowed topic. What is the main argument or point you want to make?
Example : Decide that your position is that "Deforestation contributes significantly to the acceleration of global warming."

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Step 5. Craft a Concise Thesis Statement
Summarize your main argument in a clear, specific, and concise sentence. This will be the central point around which your entire paper revolves.
Example : "The rampant deforestation observed globally is a primary driver of increased carbon emissions, leading to a substantial acceleration of global warming."
Step 6. Make It Arguable
Ensure that your thesis statement is debatable. Avoid stating facts that everyone would agree with; instead, present a claim that invites discussion.
Example : "While some argue that deforestation has minimal impact on global warming, the overwhelming evidence supports the assertion that it plays a significant role."
Step 7. Consider Counterarguments
Anticipate potential counterarguments and address them within your thesis. This shows that you've considered different perspectives and strengthens your overall position.
Example : "While some contend that other factors contribute to global warming, the undeniable link between deforestation and increased carbon emissions cannot be ignored."
Step 8. Ensure Clarity and Specificity
Avoid vague language and make sure your thesis clearly communicates the main point of your paper. Provide enough detail to guide your reader.
Example : "Deforestation's impact on global warming is a complex issue that demands immediate attention."
Step 9. Review and Revise
Critically evaluate your thesis for clarity, relevance, and strength. Revise as needed to ensure it encapsulates your main argument effectively.
The final Thesis Statement may look like this:
Types of Thesis Statements
Thesis statements serve as the core of a research paper, providing the main argument or purpose of the work. Here are a few types of thesis statements with examples:
Argumentative Thesis Statement
Argumentative thesis statements assert a specific stance on an issue and provide reasons or evidence to support that viewpoint. They aim to persuade the reader of a particular perspective.
Here is a thesis statement example for argumentative essay :
Analytical Thesis Statement
Analytical thesis statements break down a topic into its constituent parts, examining it critically to understand its components or significance. They don't argue a point but rather analyze and interpret.
Expository Thesis Statement
Expository thesis statements present factual information or explain a topic without expressing opinions or arguments. They aim to inform and elucidate.
Comparative Thesis Statement
Comparative thesis statements highlight similarities and differences between two or more subjects, offering an evaluation or analysis of their relationship.
Cause and Effect Thesis Statement
Cause and effect thesis statements outline the relationship between events or phenomena, indicating how one factor influences another and the resulting consequences.
Research Paper Thesis Template
A useful guideline for creating a thesis statement is to follow a three-part structure that includes the topic, the main point or claim, and the supporting reasons or evidence. This formula can be expressed as:
Topic + Claim + Reasons/Evidence
Here's a breakdown of each component:
Follow the steps above and use this research paper thesis statement template to develop a useful thesis.
Thesis For a Research Paper Examples
Here are a few thesis statement examples for research papers:
Research Paper Thesis Examples
Thesis For a Research Paper Middle School
College thesis statement examples, thesis for a research report, thesis statement for a research paper in apa format.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Thesis For a History Research Paper
Thesis statements for personal essays, examples of weak and strong thesis statements.
Here's a table with examples of weak and strong thesis statements across three different subjects:
Tips for Writing Strong Thesis Statements
Here are some tips for developing strong thesis statements:
- Challenge conventional wisdom or commonly held beliefs in your thesis.
- Use powerful and vivid words to evoke emotions or curiosity in your thesis.
- Introduce a fresh perspective or angle that hasn't been widely discussed.
- Offer a glimpse into potential solutions or broader implications of your thesis.
- Pose a thought-provoking question or a startling fact to engage the reader.
- Highlight the contemporary relevance or timeliness of your thesis statement.
- Appeal to the reader's emotions or personal experiences to make a connection.
- Emphasize the importance of exploring contradictions or complexities in your topic.
- Encourage the reader to contemplate the deeper implications of your thesis.
- Highlight how your thesis reflects personal growth or a change in perspective over time.
Thesis Statement Assessment Checklist
So, you may be wondering, how do I know if my thesis is strong? Use the checklist below to assess the strength of your thesis statement:
Summit it Up!
Crafting a strong thesis for a research paper involves precision, specificity, and a clear position. Remember to regularly revisit and refine your thesis as you progress through the writing process.
If you find yourself struggling to formulate the perfect thesis statement, worry not! The professionals at CollegeEssay.org are here to provide expert assistance.
Our professional writing service can guide you through the process, ensuring a compelling and impactful thesis statement.
Get custom research paper today and elevate the quality of your academic work.
Commonly Asked Questions
How does a research hypothesis differ from a thesis statement.
A research hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about the outcome of a research study. On the other hand, a thesis statement is a broader statement summarizing the main argument of a paper.
Can a thesis statement change during the research process?
Yes, as you conduct research and refine your understanding of the topic, it's common for your thesis statement to evolve or be adjusted.
How does the thesis statement relate to the research methodology?
The thesis statement may hint at the research approach but focuses more on the main argument. The methodology is detailed separately in the research paper to explain how the study was conducted.
How do I choose the right tone for my thesis statement?
Tailor the tone to match the nature of your research. It can be analytical, argumentative, or explanatory, depending on the purpose and style of your paper.
Cathy A. (Marketing, Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024
It’s time for a generative AI (gen AI) reset. The initial enthusiasm and flurry of activity in 2023 is giving way to second thoughts and recalibrations as companies realize that capturing gen AI’s enormous potential value is harder than expected .
With 2024 shaping up to be the year for gen AI to prove its value, companies should keep in mind the hard lessons learned with digital and AI transformations: competitive advantage comes from building organizational and technological capabilities to broadly innovate, deploy, and improve solutions at scale—in effect, rewiring the business for distributed digital and AI innovation.
About QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey
QuantumBlack, McKinsey’s AI arm, helps companies transform using the power of technology, technical expertise, and industry experts. With thousands of practitioners at QuantumBlack (data engineers, data scientists, product managers, designers, and software engineers) and McKinsey (industry and domain experts), we are working to solve the world’s most important AI challenges. QuantumBlack Labs is our center of technology development and client innovation, which has been driving cutting-edge advancements and developments in AI through locations across the globe.
Companies looking to score early wins with gen AI should move quickly. But those hoping that gen AI offers a shortcut past the tough—and necessary—organizational surgery are likely to meet with disappointing results. Launching pilots is (relatively) easy; getting pilots to scale and create meaningful value is hard because they require a broad set of changes to the way work actually gets done.
Let’s briefly look at what this has meant for one Pacific region telecommunications company. The company hired a chief data and AI officer with a mandate to “enable the organization to create value with data and AI.” The chief data and AI officer worked with the business to develop the strategic vision and implement the road map for the use cases. After a scan of domains (that is, customer journeys or functions) and use case opportunities across the enterprise, leadership prioritized the home-servicing/maintenance domain to pilot and then scale as part of a larger sequencing of initiatives. They targeted, in particular, the development of a gen AI tool to help dispatchers and service operators better predict the types of calls and parts needed when servicing homes.
Leadership put in place cross-functional product teams with shared objectives and incentives to build the gen AI tool. As part of an effort to upskill the entire enterprise to better work with data and gen AI tools, they also set up a data and AI academy, which the dispatchers and service operators enrolled in as part of their training. To provide the technology and data underpinnings for gen AI, the chief data and AI officer also selected a large language model (LLM) and cloud provider that could meet the needs of the domain as well as serve other parts of the enterprise. The chief data and AI officer also oversaw the implementation of a data architecture so that the clean and reliable data (including service histories and inventory databases) needed to build the gen AI tool could be delivered quickly and responsibly.
Our book Rewired: The McKinsey Guide to Outcompeting in the Age of Digital and AI (Wiley, June 2023) provides a detailed manual on the six capabilities needed to deliver the kind of broad change that harnesses digital and AI technology. In this article, we will explore how to extend each of those capabilities to implement a successful gen AI program at scale. While recognizing that these are still early days and that there is much more to learn, our experience has shown that breaking open the gen AI opportunity requires companies to rewire how they work in the following ways.
Figure out where gen AI copilots can give you a real competitive advantage
The broad excitement around gen AI and its relative ease of use has led to a burst of experimentation across organizations. Most of these initiatives, however, won’t generate a competitive advantage. One bank, for example, bought tens of thousands of GitHub Copilot licenses, but since it didn’t have a clear sense of how to work with the technology, progress was slow. Another unfocused effort we often see is when companies move to incorporate gen AI into their customer service capabilities. Customer service is a commodity capability, not part of the core business, for most companies. While gen AI might help with productivity in such cases, it won’t create a competitive advantage.
To create competitive advantage, companies should first understand the difference between being a “taker” (a user of available tools, often via APIs and subscription services), a “shaper” (an integrator of available models with proprietary data), and a “maker” (a builder of LLMs). For now, the maker approach is too expensive for most companies, so the sweet spot for businesses is implementing a taker model for productivity improvements while building shaper applications for competitive advantage.
Much of gen AI’s near-term value is closely tied to its ability to help people do their current jobs better. In this way, gen AI tools act as copilots that work side by side with an employee, creating an initial block of code that a developer can adapt, for example, or drafting a requisition order for a new part that a maintenance worker in the field can review and submit (see sidebar “Copilot examples across three generative AI archetypes”). This means companies should be focusing on where copilot technology can have the biggest impact on their priority programs.
Copilot examples across three generative AI archetypes
- “Taker” copilots help real estate customers sift through property options and find the most promising one, write code for a developer, and summarize investor transcripts.
- “Shaper” copilots provide recommendations to sales reps for upselling customers by connecting generative AI tools to customer relationship management systems, financial systems, and customer behavior histories; create virtual assistants to personalize treatments for patients; and recommend solutions for maintenance workers based on historical data.
- “Maker” copilots are foundation models that lab scientists at pharmaceutical companies can use to find and test new and better drugs more quickly.
Some industrial companies, for example, have identified maintenance as a critical domain for their business. Reviewing maintenance reports and spending time with workers on the front lines can help determine where a gen AI copilot could make a big difference, such as in identifying issues with equipment failures quickly and early on. A gen AI copilot can also help identify root causes of truck breakdowns and recommend resolutions much more quickly than usual, as well as act as an ongoing source for best practices or standard operating procedures.
The challenge with copilots is figuring out how to generate revenue from increased productivity. In the case of customer service centers, for example, companies can stop recruiting new agents and use attrition to potentially achieve real financial gains. Defining the plans for how to generate revenue from the increased productivity up front, therefore, is crucial to capturing the value.
Upskill the talent you have but be clear about the gen-AI-specific skills you need
By now, most companies have a decent understanding of the technical gen AI skills they need, such as model fine-tuning, vector database administration, prompt engineering, and context engineering. In many cases, these are skills that you can train your existing workforce to develop. Those with existing AI and machine learning (ML) capabilities have a strong head start. Data engineers, for example, can learn multimodal processing and vector database management, MLOps (ML operations) engineers can extend their skills to LLMOps (LLM operations), and data scientists can develop prompt engineering, bias detection, and fine-tuning skills.
A sample of new generative AI skills needed
The following are examples of new skills needed for the successful deployment of generative AI tools:
- data scientist:
- prompt engineering
- in-context learning
- bias detection
- pattern identification
- reinforcement learning from human feedback
- hyperparameter/large language model fine-tuning; transfer learning
- data engineer:
- data wrangling and data warehousing
- data pipeline construction
- multimodal processing
- vector database management
The learning process can take two to three months to get to a decent level of competence because of the complexities in learning what various LLMs can and can’t do and how best to use them. The coders need to gain experience building software, testing, and validating answers, for example. It took one financial-services company three months to train its best data scientists to a high level of competence. While courses and documentation are available—many LLM providers have boot camps for developers—we have found that the most effective way to build capabilities at scale is through apprenticeship, training people to then train others, and building communities of practitioners. Rotating experts through teams to train others, scheduling regular sessions for people to share learnings, and hosting biweekly documentation review sessions are practices that have proven successful in building communities of practitioners (see sidebar “A sample of new generative AI skills needed”).
It’s important to bear in mind that successful gen AI skills are about more than coding proficiency. Our experience in developing our own gen AI platform, Lilli , showed us that the best gen AI technical talent has design skills to uncover where to focus solutions, contextual understanding to ensure the most relevant and high-quality answers are generated, collaboration skills to work well with knowledge experts (to test and validate answers and develop an appropriate curation approach), strong forensic skills to figure out causes of breakdowns (is the issue the data, the interpretation of the user’s intent, the quality of metadata on embeddings, or something else?), and anticipation skills to conceive of and plan for possible outcomes and to put the right kind of tracking into their code. A pure coder who doesn’t intrinsically have these skills may not be as useful a team member.
While current upskilling is largely based on a “learn on the job” approach, we see a rapid market emerging for people who have learned these skills over the past year. That skill growth is moving quickly. GitHub reported that developers were working on gen AI projects “in big numbers,” and that 65,000 public gen AI projects were created on its platform in 2023—a jump of almost 250 percent over the previous year. If your company is just starting its gen AI journey, you could consider hiring two or three senior engineers who have built a gen AI shaper product for their companies. This could greatly accelerate your efforts.
Form a centralized team to establish standards that enable responsible scaling
To ensure that all parts of the business can scale gen AI capabilities, centralizing competencies is a natural first move. The critical focus for this central team will be to develop and put in place protocols and standards to support scale, ensuring that teams can access models while also minimizing risk and containing costs. The team’s work could include, for example, procuring models and prescribing ways to access them, developing standards for data readiness, setting up approved prompt libraries, and allocating resources.
While developing Lilli, our team had its mind on scale when it created an open plug-in architecture and setting standards for how APIs should function and be built. They developed standardized tooling and infrastructure where teams could securely experiment and access a GPT LLM , a gateway with preapproved APIs that teams could access, and a self-serve developer portal. Our goal is that this approach, over time, can help shift “Lilli as a product” (that a handful of teams use to build specific solutions) to “Lilli as a platform” (that teams across the enterprise can access to build other products).
For teams developing gen AI solutions, squad composition will be similar to AI teams but with data engineers and data scientists with gen AI experience and more contributors from risk management, compliance, and legal functions. The general idea of staffing squads with resources that are federated from the different expertise areas will not change, but the skill composition of a gen-AI-intensive squad will.
Set up the technology architecture to scale
Building a gen AI model is often relatively straightforward, but making it fully operational at scale is a different matter entirely. We’ve seen engineers build a basic chatbot in a week, but releasing a stable, accurate, and compliant version that scales can take four months. That’s why, our experience shows, the actual model costs may be less than 10 to 15 percent of the total costs of the solution.
Building for scale doesn’t mean building a new technology architecture. But it does mean focusing on a few core decisions that simplify and speed up processes without breaking the bank. Three such decisions stand out:
- Focus on reusing your technology. Reusing code can increase the development speed of gen AI use cases by 30 to 50 percent. One good approach is simply creating a source for approved tools, code, and components. A financial-services company, for example, created a library of production-grade tools, which had been approved by both the security and legal teams, and made them available in a library for teams to use. More important is taking the time to identify and build those capabilities that are common across the most priority use cases. The same financial-services company, for example, identified three components that could be reused for more than 100 identified use cases. By building those first, they were able to generate a significant portion of the code base for all the identified use cases—essentially giving every application a big head start.
- Focus the architecture on enabling efficient connections between gen AI models and internal systems. For gen AI models to work effectively in the shaper archetype, they need access to a business’s data and applications. Advances in integration and orchestration frameworks have significantly reduced the effort required to make those connections. But laying out what those integrations are and how to enable them is critical to ensure these models work efficiently and to avoid the complexity that creates technical debt (the “tax” a company pays in terms of time and resources needed to redress existing technology issues). Chief information officers and chief technology officers can define reference architectures and integration standards for their organizations. Key elements should include a model hub, which contains trained and approved models that can be provisioned on demand; standard APIs that act as bridges connecting gen AI models to applications or data; and context management and caching, which speed up processing by providing models with relevant information from enterprise data sources.
- Build up your testing and quality assurance capabilities. Our own experience building Lilli taught us to prioritize testing over development. Our team invested in not only developing testing protocols for each stage of development but also aligning the entire team so that, for example, it was clear who specifically needed to sign off on each stage of the process. This slowed down initial development but sped up the overall delivery pace and quality by cutting back on errors and the time needed to fix mistakes.
Ensure data quality and focus on unstructured data to fuel your models
The ability of a business to generate and scale value from gen AI models will depend on how well it takes advantage of its own data. As with technology, targeted upgrades to existing data architecture are needed to maximize the future strategic benefits of gen AI:
- Be targeted in ramping up your data quality and data augmentation efforts. While data quality has always been an important issue, the scale and scope of data that gen AI models can use—especially unstructured data—has made this issue much more consequential. For this reason, it’s critical to get the data foundations right, from clarifying decision rights to defining clear data processes to establishing taxonomies so models can access the data they need. The companies that do this well tie their data quality and augmentation efforts to the specific AI/gen AI application and use case—you don’t need this data foundation to extend to every corner of the enterprise. This could mean, for example, developing a new data repository for all equipment specifications and reported issues to better support maintenance copilot applications.
- Understand what value is locked into your unstructured data. Most organizations have traditionally focused their data efforts on structured data (values that can be organized in tables, such as prices and features). But the real value from LLMs comes from their ability to work with unstructured data (for example, PowerPoint slides, videos, and text). Companies can map out which unstructured data sources are most valuable and establish metadata tagging standards so models can process the data and teams can find what they need (tagging is particularly important to help companies remove data from models as well, if necessary). Be creative in thinking about data opportunities. Some companies, for example, are interviewing senior employees as they retire and feeding that captured institutional knowledge into an LLM to help improve their copilot performance.
- Optimize to lower costs at scale. There is often as much as a tenfold difference between what companies pay for data and what they could be paying if they optimized their data infrastructure and underlying costs. This issue often stems from companies scaling their proofs of concept without optimizing their data approach. Two costs generally stand out. One is storage costs arising from companies uploading terabytes of data into the cloud and wanting that data available 24/7. In practice, companies rarely need more than 10 percent of their data to have that level of availability, and accessing the rest over a 24- or 48-hour period is a much cheaper option. The other costs relate to computation with models that require on-call access to thousands of processors to run. This is especially the case when companies are building their own models (the maker archetype) but also when they are using pretrained models and running them with their own data and use cases (the shaper archetype). Companies could take a close look at how they can optimize computation costs on cloud platforms—for instance, putting some models in a queue to run when processors aren’t being used (such as when Americans go to bed and consumption of computing services like Netflix decreases) is a much cheaper option.
Build trust and reusability to drive adoption and scale
Because many people have concerns about gen AI, the bar on explaining how these tools work is much higher than for most solutions. People who use the tools want to know how they work, not just what they do. So it’s important to invest extra time and money to build trust by ensuring model accuracy and making it easy to check answers.
One insurance company, for example, created a gen AI tool to help manage claims. As part of the tool, it listed all the guardrails that had been put in place, and for each answer provided a link to the sentence or page of the relevant policy documents. The company also used an LLM to generate many variations of the same question to ensure answer consistency. These steps, among others, were critical to helping end users build trust in the tool.
Part of the training for maintenance teams using a gen AI tool should be to help them understand the limitations of models and how best to get the right answers. That includes teaching workers strategies to get to the best answer as fast as possible by starting with broad questions then narrowing them down. This provides the model with more context, and it also helps remove any bias of the people who might think they know the answer already. Having model interfaces that look and feel the same as existing tools also helps users feel less pressured to learn something new each time a new application is introduced.
Getting to scale means that businesses will need to stop building one-off solutions that are hard to use for other similar use cases. One global energy and materials company, for example, has established ease of reuse as a key requirement for all gen AI models, and has found in early iterations that 50 to 60 percent of its components can be reused. This means setting standards for developing gen AI assets (for example, prompts and context) that can be easily reused for other cases.
While many of the risk issues relating to gen AI are evolutions of discussions that were already brewing—for instance, data privacy, security, bias risk, job displacement, and intellectual property protection—gen AI has greatly expanded that risk landscape. Just 21 percent of companies reporting AI adoption say they have established policies governing employees’ use of gen AI technologies.
Similarly, a set of tests for AI/gen AI solutions should be established to demonstrate that data privacy, debiasing, and intellectual property protection are respected. Some organizations, in fact, are proposing to release models accompanied with documentation that details their performance characteristics. Documenting your decisions and rationales can be particularly helpful in conversations with regulators.
In some ways, this article is premature—so much is changing that we’ll likely have a profoundly different understanding of gen AI and its capabilities in a year’s time. But the core truths of finding value and driving change will still apply. How well companies have learned those lessons may largely determine how successful they’ll be in capturing that value.

The authors wish to thank Michael Chui, Juan Couto, Ben Ellencweig, Josh Gartner, Bryce Hall, Holger Harreis, Phil Hudelson, Suzana Iacob, Sid Kamath, Neerav Kingsland, Kitti Lakner, Robert Levin, Matej Macak, Lapo Mori, Alex Peluffo, Aldo Rosales, Erik Roth, Abdul Wahab Shaikh, and Stephen Xu for their contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Barr Seitz, an editorial director in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier

Rewired to outcompete

Meet Lilli, our generative AI tool that’s a researcher, a time saver, and an inspiration
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved March 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Remarks of President Joe Biden — State of the Union Address As Prepared for Delivery
The United States Capitol
Good evening.
Mr. Speaker. Madam Vice President. Members of Congress. My Fellow Americans.
In January 1941, President Franklin Roosevelt came to this chamber to speak to the nation.
He said, “I address you at a moment unprecedented in the history of the Union.”
Hitler was on the march. War was raging in Europe.
President Roosevelt’s purpose was to wake up the Congress and alert the American people that this was no ordinary moment.
Freedom and democracy were under assault in the world.
Tonight I come to the same chamber to address the nation.
Now it is we who face an unprecedented moment in the history of the Union.
And yes, my purpose tonight is to both wake up this Congress, and alert the American people that this is no ordinary moment either.
Not since President Lincoln and the Civil War have freedom and democracy been under assault here at home as they are today.
What makes our moment rare is that freedom and democracy are under attack, both at home and overseas, at the very same time.
Overseas, Putin of Russia is on the march, invading Ukraine and sowing chaos throughout Europe and beyond.
If anybody in this room thinks Putin will stop at Ukraine, I assure you, he will not.
But Ukraine can stop Putin if we stand with Ukraine and provide the weapons it needs to defend itself. That is all Ukraine is asking. They are not asking for American soldiers.
In fact, there are no American soldiers at war in Ukraine. And I am determined to keep it that way.
But now assistance for Ukraine is being blocked by those who want us to walk away from our leadership in the world.
It wasn’t that long ago when a Republican President, Ronald Reagan, thundered, “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall.”
Now, my predecessor, a former Republican President, tells Putin, “Do whatever the hell you want.”
A former American President actually said that, bowing down to a Russian leader.
It’s outrageous. It’s dangerous. It’s unacceptable.
America is a founding member of NATO the military alliance of democratic nations created after World War II to prevent war and keep the peace.
Today, we’ve made NATO stronger than ever.
We welcomed Finland to the Alliance last year, and just this morning, Sweden officially joined NATO, and their Prime Minister is here tonight.
Mr. Prime Minister, welcome to NATO, the strongest military alliance the world has ever known.
I say this to Congress: we must stand up to Putin. Send me the Bipartisan National Security Bill.
History is watching.
If the United States walks away now, it will put Ukraine at risk.
Europe at risk. The free world at risk, emboldening others who wish to do us harm.
My message to President Putin is simple.
We will not walk away. We will not bow down. I will not bow down.
History is watching, just like history watched three years ago on January 6th.
Insurrectionists stormed this very Capitol and placed a dagger at the throat of American democracy.
Many of you were here on that darkest of days.
We all saw with our own eyes these insurrectionists were not patriots.
They had come to stop the peaceful transfer of power and to overturn the will of the people.
January 6th and the lies about the 2020 election, and the plots to steal the election, posed the gravest threat to our democracy since the Civil War.
But they failed. America stood strong and democracy prevailed.
But we must be honest the threat remains and democracy must be defended.
My predecessor and some of you here seek to bury the truth of January 6th.
I will not do that.
This is a moment to speak the truth and bury the lies.
And here’s the simplest truth. You can’t love your country only when you win.
As I’ve done ever since being elected to office, I ask you all, without regard to party, to join together and defend our democracy!
Remember your oath of office to defend against all threats foreign and domestic.
Respect free and fair elections! Restore trust in our institutions! And make clear –political violence
has absolutely no place in America!
And history is watching another assault on freedom.
Joining us tonight is Latorya Beasley, a social worker from Birmingham, Alabama. 14 months ago tonight, she and her husband welcomed a baby girl thanks to the miracle of IVF.
She scheduled treatments to have a second child, but the Alabama Supreme Court shut down IVF treatments across the state, unleashed by the Supreme Court decision overturning Roe v. Wade.
She was told her dream would have to wait.
What her family has gone through should never have happened. And unless Congress acts, it could happen again.
So tonight, let’s stand up for families like hers!
To my friends across the aisle, don’t keep families waiting any longer. Guarantee the right to IVF nationwide!
Like most Americans, I believe Roe v. Wade got it right. And I thank Vice President Harris for being an incredible leader, defending reproductive freedom and so much more.
But my predecessor came to office determined
to see Roe v. Wade overturned.
He’s the reason it was overturned. In fact, he brags about it.
Look at the chaos that has resulted.
Joining us tonight is Kate Cox, a wife and mother
from Dallas.
When she became pregnant again, the fetus had a fatal condition.
Her doctors told Kate that her own life and her ability to have children in the future were at risk if she didn’t act.
Because Texas law banned abortion, Kate and her husband had to leave the state to get the care she needed.
What her family has gone through should never have happened as well. But it is happening to so many others.
There are state laws banning the right to choose, criminalizing doctors, and forcing survivors of rape and incest to leave their states as well to get the care they need.
Many of you in this Chamber and my predecessor are promising to pass a national ban on reproductive freedom.
My God, what freedoms will you take away next?
In its decision to overturn Roe v. Wade the Supreme Court majority wrote, “Women are not without –
electoral or political power.”
No kidding.
Clearly, those bragging about overturning Roe v. Wade have no clue about the power of women in America.
They found out though when reproductive freedom
was on the ballot and won in 2022, 2023, and they will find out again, in 2024.
If Americans send me a Congress that supports the right to choose, I promise you, I will restore Roe v. Wade as the law of the land again!
America cannot go back. I am here tonight to show the way forward. Because I know how far we’ve come.
Four years ago next week, before I came to office, our country was hit by the worst pandemic and the worst economic crisis in a century.
Remember the fear. Record job losses. Remember the spike in crime. And the murder rate.
A raging virus that would take more than 1 million American lives and leave millions of loved ones behind.
A mental health crisis of isolation and loneliness.
A president, my predecessor, who failed the most basic duty. Any President owes the American people the duty to care.
That is unforgivable.
I came to office determined to get us through one of the toughest periods in our nation’s history.
And we have. It doesn’t make the news but in thousands of cities and towns the American people are writing the greatest comeback story never told.
So let’s tell that story here and now.
America’s comeback is building a future of American possibilities, building an economy from the middle out and the bottom up, not the top down, investing in all of America, in all Americans to make sure everyone has a fair shot and we leave no one behind!
The pandemic no longer controls our lives. The vaccines that saved us from COVID are now being used to help beat cancer.
Turning setback into comeback.
That’s America!
I inherited an economy that was on the brink. Now our economy is the envy of the world!
15 million new jobs in just three years – that’s a record!
Unemployment at 50-year lows.
A record 16 million Americans are starting small businesses and each one is an act of hope.
With historic job growth and small business growth for Black, Hispanic, and Asian-Americans.
800,000 new manufacturing jobs in America and counting.
More people have health insurance today than ever before.
The racial wealth gap is the smallest it’s been in 20 years.
Wages keep going up and inflation keeps coming down!
Inflation has dropped from 9% to 3% – the lowest in the world!
And trending lower.
And now instead of importing foreign products and exporting American jobs, we’re exporting American products and creating American jobs – right here in America where they belong!
And the American people are beginning to feel it.
Consumer studies show consumer confidence is soaring.
Buy American has been the law of the land since the 1930s.
Past administrations including my predecessor failed to Buy American.
Not any more.
On my watch, federal projects like helping to build American roads bridges and highways will be made with American products built by American workers creating good-paying American jobs!
Thanks to my Chips and Science Act the United States is investing more in research and development than ever before.
During the pandemic a shortage of semiconductor chips drove up prices for everything from cell phones to automobiles.
Well instead of having to import semiconductor chips, which America invented I might add, private companies are now investing billions of dollars to build new chip factories here in America!
Creating tens of thousands of jobs many of them paying over $100,000 a year and don’t require a college degree.
In fact my policies have attracted $650 Billion of private sector investments in clean energy and advanced manufacturing creating tens of thousands of jobs here in America!
Thanks to our Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, 46,000 new projects have been announced across your communities – modernizing our roads and bridges, ports and airports, and public transit systems.
Removing poisonous lead pipes so every child can drink clean water without risk of getting brain damage.
Providing affordable high speed internet for every American no matter where you live.
Urban, suburban, and rural communities — in red states and blue.
Record investments in tribal communities.
Because of my investments, family farms are better be able to stay in the family and children and grandchildren won’t have to leave home to make a living.
It’s transformative.
A great comeback story is Belvidere, Illinois. Home to an auto plant for nearly 60 years. Before I came to office the plant was on its way to shutting down.
Thousands of workers feared for their livelihoods. Hope was fading.
Then I was elected to office and we raised Belvidere repeatedly with the auto company knowing unions make all the difference.
The UAW worked like hell to keep the plant open and get those jobs back. And together, we succeeded!
Instead of an auto factory shutting down an auto factory is re-opening and a new state-of-the art battery factory is being built to power those cars.
Instead of a town being left behind it’s a community moving forward again!
Because instead of watching auto jobs of the future go overseas 4,000 union workers with higher wages will be building that future, in Belvidere, here in America!
Here tonight is UAW President, Shawn Fain, a great friend, and a great labor leader.
And Dawn Simms, a third generation UAW worker in Belvidere.
Shawn, I was proud to be the first President in American history to walk a picket line.
And today Dawn has a job in her hometown providing stability for her family and pride and dignity.
Showing once again, Wall Street didn’t build this country!
The middle class built this country! And unions built the middle class!
When Americans get knocked down, we get back up!
We keep going!
That’s America! That’s you, the American people!
It’s because of you America is coming back!
It’s because of you, our future is brighter!
And it’s because of you that tonight we can proudly say the State of our Union is strong and getting stronger!
Tonight I want to talk about the future of possibilities that we can build together.
A future where the days of trickle-down economics are over and the wealthy and biggest corporations no longer get all the breaks.
I grew up in a home where not a lot trickled down on my Dad’s kitchen table.
That’s why I’m determined to turn things around so the middle class does well the poor have a way up and the wealthy still does well.
We all do well.
And there’s more to do to make sure you’re feeling the benefits of all we’re doing.
Americans pay more for prescription drugs than anywhere else.
It’s wrong and I’m ending it.
With a law I proposed and signed and not one Republican voted for we finally beat Big Pharma!
Instead of paying $400 a month for insulin seniors with diabetes only have to pay $35 a month!
And now I want to cap the cost of insulin at $35 a month for every American who needs it!
For years people have talked about it but I finally got it done and gave Medicare the power to negotiate lower prices for prescription drugs just like the VA does for our veterans.
That’s not just saving seniors money.
It’s saving taxpayers money cutting the federal deficit by $160 Billion because Medicare will no longer have to pay exorbitant prices to Big Pharma.
This year Medicare is negotiating lower prices for some of the costliest drugs on the market that treat everything from heart disease to arthritis.
Now it’s time to go further and give Medicare the power to negotiate lower prices for 500 drugs over the next decade.
That will not only save lives it will save taxpayers another $200 Billion!
Starting next year that same law caps total prescription drug costs for seniors on Medicare at $2,000 a year even for expensive cancer drugs that can cost $10,000, $12,000, $15,000 a year.
Now I want to cap prescription drug costs at $2,000 a year for everyone!
Folks Obamacare, known as the Affordable Care Act is still a very big deal.
Over one hundred million of you can no longer be denied health insurance because of pre-existing conditions.
But my predecessor and many in this chamber want to take that protection away by repealing the Affordable Care Act I won’t let that happen!
We stopped you 50 times before and we will stop you again!
In fact I am protecting it and expanding it.
I enacted tax credits that save $800 per person per year reducing health care premiums for millions of working families.
Those tax credits expire next year.
I want to make those savings permanent!
Women are more than half of our population but research on women’s health has always been underfunded.
That’s why we’re launching the first-ever White House Initiative on Women’s Health Research, led by Jill who is doing an incredible job as First Lady.
Pass my plan for $12 Billion to transform women’s health research and benefit millions of lives across America!
I know the cost of housing is so important to you.
If inflation keeps coming down mortgage rates will come down as well.
But I’m not waiting.
I want to provide an annual tax creditthat will give Americans $400 a month for the next two years as mortgage rates come down to put toward their mortgage when they buy a first home or trade up for a little more space.
My Administration is also eliminating title insurance fees for federally backed mortgages.
When you refinance your home this can save you $1,000 or more.
For millions of renters, we’re cracking down on big landlords who break antitrust laws by price-fixing and driving up rents.
I’ve cut red tape so more builders can get federal financing, which is already helping build a record 1.7 million housing units nationwide.
Now pass my plan to build and renovate 2 million affordable homes and bring those rents down!
To remain the strongest economy in the world we need the best education system in the world.
I want to give every child a good start by providing access to pre-school for 3- and 4-year-olds.
Studies show that children who go to pre-school are nearly 50% more likely to finish high school and go on to earn a 2- or 4-year degree no matter their background.
I want to expand high-quality tutoring and summer learning time and see to it that every child learns to read by third grade.
I’m also connecting businesses and high schools so students get hands-on experience and a path to a good-paying job whether or not they go to college.
And I want to make college more affordable.
Let’s continue increasing Pell Grants for working- and middle-class families and increase our record investments in HBCUs and Hispanic and Minority-serving Institutions
I fixed student loan programs to reduce the burden of student debt for nearly 4 Million Americans including nurses firefighters and others in public service like Keenan Jones a public-school educator in Minnesota who’s here with us tonight.
He’s educated hundreds of students so they can go to college now he can help his own daughter pay for college.
Such relief is good for the economy because folks are now able to buy a home start a business even start a family.
While we’re at it I want to give public school teachers a raise!
Now let me speak to a question of fundamental fairness for all Americans.
I’ve been delivering real results in a fiscally responsible way.
I’ve already cut the federal deficit by over one trillion dollars.
I signed a bipartisan budget deal that will cut another trillion dollars over the next decade.
And now it’s my goal to cut the federal deficit $3 trillion more by making big corporations and the very wealthy finally pay their fair share.
Look, I’m a capitalist.
If you want to make a million bucks – great!
Just pay your fair share in taxes.
A fair tax code is how we invest in the things –
that make a country great, health care, education, defense, and more.
But here’s the deal.
The last administration enacted a $2 Trillion tax cut that overwhelmingly benefits the very wealthy and the biggest corporations and exploded the federal deficit.
They added more to the national debt than in any presidential term in American history.
For folks at home does anybody really think the tax code is fair?
Do you really think the wealthy and big corporations need another $2 trillion in tax breaks?
I sure don’t. I’m going to keep fighting like hell to make it fair!
Under my plan nobody earning less than $400,000 will pay an additional penny in federal taxes.
Nobody. Not one penny.
In fact the Child Tax Credit I passed during the pandemic cut taxes for millions of working families and cut child poverty in HALF.
Restore the Child Tax Credit because no child should go hungry in this country!
The way to make the tax code fair is to make big corporations and the very wealthy finally pay their share.
In 2020 55 of the biggest companies in America made $40 Billion in profits and paid zero in federal income taxes.
Not any more!
Thanks to the law I wrote and signed big companies now have to pay a minimum of 15%.
But that’s still less than working people pay in federal taxes.
It’s time to raise the corporate minimum tax to at least 21% so every big corporation finally begins to pay their fair share.
I also want to end the tax breaks for Big Pharma, Big Oil, private jets, and massive executive pay!
End it now!
There are 1,000 billionaires in America.
You know what the average federal tax rate for these billionaires is? 8.2 percent!
That’s far less than the vast majority of Americans pay.
No billionaire should pay a lower tax rate than a teacher, a sanitation worker, a nurse!
That’s why I’ve proposed a minimum tax of 25% for billionaires. Just 25%.
That would raise $500 Billion over the next 10 years.
Imagine what that could do for America. Imagine a future with affordable child care so millions of families can get the care they need and still go to work and help grow the economy.
Imagine a future with paid leave because no one should have to choose between working and taking care of yourself or a sick family member.
Imagine a future with home care and elder care so seniors and people living with disabilities can stay in their homes and family caregivers get paid what they deserve!
Tonight, let’s all agree once again to stand up for seniors!
Many of my Republican friends want to put Social Security on the chopping block.
If anyone here tries to cut Social Security or Medicare or raise the retirement age I will stop them!
Working people who built this country pay more into Social Security than millionaires and billionaires do. It’s not fair.
We have two ways to go on Social Security.
Republicans will cut Social Security and give more tax cuts to the wealthy.
I will protect and strengthen Social Security and make the wealthy pay their fair share!
Too many corporations raise their prices to pad their profits charging you more and more for less and less.
That’s why we’re cracking down on corporations that engage in price gouging or deceptive pricing from food to health care to housing.
In fact, snack companies think you won’t notice when they charge you just as much for the same size bag
but with fewer chips in it.
Pass Senator Bob Casey’s bill to put a stop to shrinkflation!
I’m also getting rid of junk fees those hidden fees added at the end of your bills without your knowledge. My administration just announced we’re cutting credit card late fees from $32 to just $8.
The banks and credit card companies don’t like it.
I’m saving American families $20 billion a year with all of the junk fees I’m eliminating.
And I’m not stopping there.
My Administration has proposed rules to make cable travel utilities and online ticket sellers tell you the total price upfront so there are no surprises.
It matters.
And so does this.
In November, my team began serious negotiations with a bipartisan group of Senators.
The result was a bipartisan bill with the toughest set of border security reforms we’ve ever seen
in this country.
That bipartisan deal would hire 1,500 more border security agents and officers.
100 more immigration judges to help tackle a backload of 2 million cases.
4,300 more asylum officers and new policies so they can resolve cases in 6 months instead of 6 years.
100 more high-tech drug detection machines to significantly increase the ability to screen and stop vehicles from smuggling fentanyl into America.
This bill would save lives and bring order to the border.
It would also give me as President new emergency authority to temporarily shut down the border when the number of migrants at the border is overwhelming.
The Border Patrol Union endorsed the bill.
The Chamber of Commerce endorsed the bill.
I believe that given the opportunity a majority of the House and Senate would endorse it as well.
But unfortunately, politics have derailed it so far.
I’m told my predecessor called Republicans in Congress and demanded they block the bill. He feels it would be a political win for me and a political loser for him.
It’s not about him or me.
It’d be a winner for America!
My Republican friends you owe it to the American people to get this bill done.
We need to act.
And if my predecessor is watching instead of playing politics and pressuring members of Congress to block this bill, join me in telling Congress to pass it!
We can do it together. But here’s what I will not do.
I will not demonize immigrants saying they “poison the blood of our country” as he said in his own words.
I will not separate families.
I will not ban people from America because of their faith.
Unlike my predecessor, on my first day in office I introduced a comprehensive plan to fix our immigration system, secure the border, and provide a pathway to citizenship for Dreamers and so much more.
Because unlike my predecessor, I know who we are
as Americans.
We are the only nation in the world with a heart and soul that draws from old and new.
Home to Native Americans whose ancestors have been here for thousands of years. Home to people from every place on Earth.
Some came freely.
Some chained by force.
Some when famine struck, like my ancestral family in Ireland.
Some to flee persecution.
Some to chase dreams that are impossible anywhere but here in America.
That’s America, where we all come from somewhere, but we are all Americans.
We can fight about the border, or we can fix it. I’m ready to fix it.
Send me the border bill now!
A transformational moment in our history happened 59 years ago today in Selma, Alabama.
Hundreds of foot soldiers for justice marched across the Edmund Pettus Bridge, named after a Grand Dragon of the KKK, to claim their fundamental right to vote.
They were beaten bloodied and left for dead.
Our late friend and former colleague John Lewis was at the march.
We miss him.
Joining us tonight are other marchers who were there including Betty May Fikes, known as the “Voice of Selma”.
A daughter of gospel singers and preachers, she sang songs of prayer and protest on that Bloody Sunday,
to help shake the nation’s conscience. Five months later, the Voting Rights Act was signed into law. But 59 years later, there are forces taking us back in time.
Voter suppression. Election subversion. Unlimited dark money. Extreme gerrymandering.
John Lewis was a great friend to many of us here. But if you truly want to honor him and all the heroes who marched with him, then it’s time for more than just talk.
Pass and send me the Freedom to Vote Act and the John Lewis Voting Rights Act!
And stop denying another core value of America our diversity across American life.
Banning books.
It’s wrong!
Instead of erasing history, let’s make history!
I want to protect other fundamental rights!
Pass the Equality Act, and my message to transgender Americans: I have your back!
Pass the PRO Act for workers rights! And raise the federal minimum wage because every worker has the right to earn a decent living!
We are also making history by confronting the climate crisis, not denying it.
I’m taking the most significant action on climate ever in the history of the world.
I am cutting our carbon emissions in half by 2030.
Creating tens of thousands of clean-energy jobs, like the IBEW workers building and installing 500,000 electric vehicle charging stations.
Conserving 30% of America’s lands and waters by 2030.
Taking historic action on environmental justice for fence-line communities smothered by the legacy of pollution.
And patterned after the Peace Corps and Ameri Corps, I’ve launched a Climate Corps to put 20,000 young people to work at the forefront of our clean energy future.
I’ll triple that number this decade.
All Americans deserve the freedom to be safe, and America is safer today than when I took office.
The year before I took office, murders went up 30% nationwide the biggest increase in history.
That was then.
Now, through my American Rescue Plan, which every Republican voted against, I’ve made the largest investment in public safety ever.
Last year, the murder rate saw the sharpest decrease in history, and violent crime fell to one of the lowest levels in more than 50 years.
But we have more to do.
Help cities and towns invest in more community police officers, more mental health workers, and more community violence intervention.
Give communities the tools to crack down on gun crime, retail crime, and carjacking.
Keep building public trust, as I’ve been doing by taking executive action on police reform, and calling for it to be the law of the land, directing my Cabinet to review the federal classification of marijuana, and expunging thousands of convictions for mere possession, because no one should be jailed for using or possessing marijuana!
To take on crimes of domestic violence, I am ramping up federal enforcement of the Violence Against Women Act, that I proudly wrote, so we can finally end the scourge of violence against women in America!
And there’s another kind of violence I want to stop.
With us tonight is Jasmine, whose 9-year-old sister Jackie was murdered with 21 classmates and teachers at her elementary school in Uvalde, Texas.
Soon after it happened, Jill and I went to Uvalde and spent hours with the families.
We heard their message, and so should everyone in this chamber do something.
I did do something by establishing the first-ever Office of Gun Violence Prevention in the White House that Vice President Harris is leading.
Meanwhile, my predecessor told the NRA he’s proud he did nothing on guns when he was President.
After another school shooting in Iowa he said we should just “get over it.”
I say we must stop it.
I’m proud we beat the NRA when I signed the most significant gun safety law in nearly 30 years!
Now we must beat the NRA again!
I’m demanding a ban on assault weapons and high-capacity magazines!
Pass universal background checks!
None of this violates the Second Amendment or vilifies responsible gun owners.
As we manage challenges at home, we’re also managing crises abroad including in the Middle East.
I know the last five months have been gut-wrenching for so many people, for the Israeli people, the Palestinian people, and so many here in America.
This crisis began on October 7th with a massacre by the terrorist group Hamas.
1,200 innocent people women and girls men and boys slaughtered, many enduring sexual violence.
The deadliest day for the Jewish people since the Holocaust.
250 hostages taken.
Here in the chamber tonight are American families whose loved ones are still being held by Hamas.
I pledge to all the families that we will not rest until we bring their loved ones home.
We will also work around the clock to bring home Evan and Paul, Americans being unjustly detained all around the world.
Israel has a right to go after Hamas.
Hamas could end this conflict today by releasing the hostages, laying down arms, and surrendering those responsible for October 7th.
Israel has an added burden because Hamas hides and operates among the civilian population. But Israel also has a fundamental responsibility to protect innocent civilians in Gaza.
This war has taken a greater toll on innocent civilians than all previous wars in Gaza combined.
More than 30,000 Palestinians have been killed.
Most of whom are not Hamas.
Thousands and thousands are innocent women and children.
Girls and boys also orphaned.
Nearly 2 million more Palestinians under bombardment or displaced.
Homes destroyed, neighborhoods in rubble, cities in ruin.
Families without food, water, medicine.
It’s heartbreaking.
We’ve been working non-stop to establish an immediate ceasefire that would last for at least six weeks.
It would get the hostages home, ease the intolerable humanitarian crisis, and build toward something more enduring.
The United States has been leading international efforts to get more humanitarian assistance into Gaza.
Tonight, I’m directing the U.S. military to lead an emergency mission to establish a temporary pier in the Mediterranean on the Gaza coast that can receive large ships carrying food, water, medicine and temporary shelters.
No U.S. boots will be on the ground.
This temporary pier would enable a massive increase in the amount of humanitarian assistance getting into Gaza every day.
But Israel must also do its part.
Israel must allow more aid into Gaza and ensure that humanitarian workers aren’t caught in the cross fire.
To the leadership of Israel I say this.
Humanitarian assistance cannot be a secondary consideration or a bargaining chip.
Protecting and saving innocent lives has to be a priority.
As we look to the future, the only real solution is a two-state solution.
I say this as a lifelong supporter of Israel and the only American president to visit Israel in wartime.
There is no other path that guarantees Israel’s security and democracy.
There is no other path that guarantees Palestinians can live with peace and dignity.
There is no other path that guarantees peace between Israel and all of its Arab neighbors, including Saudi Arabia.
Creating stability in the Middle East also means containing the threat posed by Iran.
That’s why I built a coalition of more than a dozen countries to defend international shipping and freedom of navigation in the Red Sea.
I’ve ordered strikes to degrade Houthi capabilities and defend U.S. Forces in the region.
As Commander in Chief, I will not hesitate to direct further measures to protect our people and military personnel.
For years, all I’ve heard from my Republican friends and so many others is China’s on the rise and America is falling behind.
They’ve got it backward.
America is rising.
We have the best economy in the world.
Since I’ve come to office, our GDP is up.
And our trade deficit with China is down to the lowest point in over a decade.
We’re standing up against China’s unfair economic practices.
And standing up for peace and stability across the Taiwan Strait.
I’ve revitalized our partnerships and alliances in the Pacific.
I’ve made sure that the most advanced American technologies can’t be used in China’s weapons.
Frankly for all his tough talk on China, it never occurred to my predecessor to do that.
We want competition with China, but not conflict.
And we’re in a stronger position to win the competition for the 21st Century against China or anyone else for that matter.
Here at home I’ve signed over 400 bipartisan bills.
But there’s more to do to pass my Unity Agenda.
Strengthen penalties on fentanyl trafficking.
Pass bipartisan privacy legislation to protect our children online.
Harness the promise of A.I. and protect us from its peril.
Ban A.I. voice impersonation and more!
And keep our one truly sacred obligation, to train and equip those we send into harm’s way and care for them and their families when they come home, and when they don’t.
That’s why I signed the PACT Act, one of the most significant laws ever, helping millions of veterans who were exposed to toxins and who now are battling more than 100 cancers.
Many of them didn’t come home.
We owe them and their families.
And we owe it to ourselves to keep supporting our new health research agency called ARPA-H and remind us that we can do big things like end cancer as we know it!
Let me close with this.
I know I may not look like it, but I’ve been around a while.
And when you get to my age certain things become clearer than ever before.
I know the American story.
Again and again I’ve seen the contest between competing forces in the battle for the soul of our nation.
Between those who want to pull America back to the past and those who want to move America into the future.
My lifetime has taught me to embrace freedom and democracy.
A future based on the core values that have defined America.
Honesty. Decency. Dignity. Equality.
To respect everyone. To give everyone a fair shot. To give hate no safe harbor.
Now some other people my age see a different story.
An American story of resentment, revenge, and retribution.
That’s not me.
I was born amid World War II when America stood for freedom in the world.
I grew up in Scranton, Pennsylvania and Claymont, Delaware among working people who built this country.
I watched in horror as two of my heroes, Dr. King and Bobby Kennedy, were assassinated and their legacies inspired me to pursue a career in service.
A public defender, county councilman, elected United States Senator at 29, then Vice President, to our first Black President, now President, with our first woman Vice President.
In my career I’ve been told I’m too young and I’m too old.
Whether young or old, I’ve always known what endures.
Our North Star.
The very idea of America, that we are all created equal and deserve to be treated equally throughout our lives.
We’ve never fully lived up to that idea, but we’ve never walked away from it either.
And I won’t walk away from it now.
My fellow Americans the issue facing our nation isn’t how old we are it’s how old our ideas are?
Hate, anger, revenge, retribution are among the oldest of ideas.
But you can’t lead America with ancient ideas that only take us back.
To lead America, the land of possibilities, you need a vision for the future of what America can and should be.
Tonight you’ve heard mine.
I see a future where we defend democracy not diminish it.
I see a future where we restore the right to choose and protect other freedoms not take them away.
I see a future where the middle class finally has a fair shot and the wealthy finally have to pay their fair share in taxes.
I see a future where we save the planet from the climate crisis and our country from gun violence.
Above all, I see a future for all Americans!
I see a country for all Americans!
And I will always be a president for all Americans!
Because I believe in America!
I believe in you the American people.
You’re the reason I’ve never been more optimistic about our future!
So let’s build that future together!
Let’s remember who we are!
We are the United States of America.
There is nothing beyond our capacity when we act together!
May God bless you all.
May God protect our troops.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate. This step-by-step guide takes you through the entire writing process, ... You do not need to start by writing the introduction. Begin where it feels most natural for you ...
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
7. Write your first draft of the body. The body of your paper argues, explains or describes your topic. Start with the first topic from your outline. Ideally, you have organized your notes in a way that you can work through your research paper outline and have all the notes ready. 8.
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
Research beforehand. Before you even type the first word, dig deep into your topic. Consult sources, both primary and secondary, to have a well-rounded understanding of the issue. Check the following aspects before moving to the next step: Identify Keywords: Find relevant keywords that are related to your topic.
Unlike essays, research papers usually divide the body into sections with separate headers to facilitate browsing and scanning. Use the divisions in your outline as a guide. Follow along your outline and go paragraph by paragraph. Because this is just the first draft, don't worry about getting each word perfect.
By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers. 5. Write a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction.
A research paper introduction uses primary sources and data to support its thesis statement. A research paper's thesis statement has a lot in common with a thesis for an essay, or other non-research assignment. The difference lies in the fact that in a research thesis, you gather evidence from valid sources to prove your perspective on a topic.
Step 4: Create a Research Paper Outline. Outlining is a key part of crafting an effective essay. Your research paper outline should include a rough introduction to the topic, a thesis statement, supporting details for each main idea, and a brief conclusion. You can outline in whatever way feels most comfortable for you.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research. To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery.
7. Edit and proofread. You may have thought the real writing for a research paper was done in step 5, but the truth is you're just getting to it. However, you're also at the last step for writing a research paper—so close to the finish line. To edit effectively, you must consider both the big picture and the details.
Start strong. In your research, have you come across an odd factoid or interesting quote? Try starting your paper with that. How about starting with an anecdotal story or humor? Middle Sentences : The middle sentences cover the different points in your paper. If you've already planned which order to write the points in the paper, you already ...
After you get enough feedback and decide on the journal you will submit to, the process of real writing begins. Copy your outline into a separate file and expand on each of the points, adding data and elaborating on the details. When you create the first draft, do not succumb to the temptation of editing.
Research Paper Introduction. Research paper introduction is the first section of a research paper that provides an overview of the study, its purpose, and the research question(s) or hypothesis(es) being investigated. It typically includes background information about the topic, a review of previous research in the field, and a statement of the research objectives.
Step 3: Defining the Research Question. Refining your chosen topic involves writing a clear and specific research question leading to a well-crafted abstract. This question serves as the guiding force throughout your research, ensuring a focused and purposeful exploration of the chosen subject.
Most likely, you'll bounce around from topic to topic until one sticks. You'll need time to rebound and to change topics. College professors recommend that you get started on your research paper the day it is assigned. The more time and effort you put into it, the better your grade will be. So get started now.
Step 2: Identifying Grade Criteria. A Grade: A research paper that merits an A demonstrates a generally high degree of competence and control of language. Typically, such a paper meets all of the following criteria: Responds to the assignment thoroughly, thoughtfully, and with insight or originality.
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
You may read this TIP Sheet from start to finish before you begin your paper, or skip to the steps that are causing you the most grief. 1. Choosing a topic: Interest, information, and focus. Your job will be more pleasant, and you will be more apt to retain information if you choose a topic that holds your interest.
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don't need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary. Or it may come in the form of a sentence that
Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the ...
Write to your audience. A concept paper is a piece of academic writing, so use a professional tone. Avoid colloquialisms, slang, and other conversational language. Your concept paper should use the same tone and style as your accompanying research paper. Write according to your reader's familiarity with the subject of your concept paper.
Experimental Research Paper: Experimental research papers provide a detailed report on a particular research experiment undertaken by a researcher and its outcomes or findings. Based on the research experiment, the researcher explains the experimental design and procedure, shows sufficient data, presents analysis, and draws a conclusion. Such ...
Here's a guide with steps and examples: Step 1. Understand the Assignment. Before diving into writing a thesis statement, thoroughly understand the assignment's requirements, including the topic, length, and specific guidelines provided by your instructor or the prompt. Step 2.
U. of Pittsburgh Legal Studies Research Paper No. 2024-07. 44 Pages Posted: 14 Mar 2024. See all articles by David A. Harris David A. Harris. ... Do you have negative results from your research you'd like to share? Submit Negative Results. Paper statistics. Downloads. 2. Abstract Views. 34. 13 References.
It's time for a generative AI (gen AI) reset. The initial enthusiasm and flurry of activity in 2023 is giving way to second thoughts and recalibrations as companies realize that capturing gen AI's enormous potential value is harder than expected.. With 2024 shaping up to be the year for gen AI to prove its value, companies should keep in mind the hard lessons learned with digital and AI ...
It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature; Evaluate sources; Identify themes, debates, and gaps
Among them: some newly unemployed workers seized the moment of disruption to start their own enterprises; Americans had extra money from stimulus bills signed by Trump and Biden; interest rates ...
Thanks to my Chips and Science Act the United States is investing more in research and development than ever before. ... I want to give every child a good start by providing access to pre-school ...