- Paraphrase Online

Paraphrasing and Summarizing Exercises with Answers

Paraphrasing and Summarizing are two skills that are highly useful for writers. With these two techniques, writers can get help creating their content and providing it to their readers in an easy-to-peruse way.
However, if you happen to be new to the field of writing, you could be a little unaware and untrained in both these skills. But don’t worry. Everyone starts out as a beginner.
In this post, we’re going to be looking at some paraphrasing and summarizing exercises along with their answers and explanations. By following along, you’ll get a good idea about how you can use these techniques in your own capacity.
Let’s begin!
What is Paraphrasing and Summarizing?
Before we get to the exercises, let’s digress a little and understand what paraphrasing and summarization actually are.
Let’s start with paraphrasing.
Paraphrasing is the process in which a particular piece of content is reworded and rephrased in such a way that it looks different from its original version but it has the same meaning and context.
A simple example of paraphrasing would be to change “John likes his cat” to “John adores his feline pet”. Paraphrasing can be as slight as merely changing some words in the text, or it can be as drastic as fully changing the tone, structure, order, and words of the content.
On the other hand, Summarizing is the process in which a piece of content is shrunk and shortened to about one-tenth of its original size. In this shortened version, the main idea and concept of the content is provided.
Summarization is usually used by authors and writers when they want to give a brief outline of a book or article to their readers.
Now that we’ve looked at the definitions of both, let’s move ahead to look at some exercises.
Paraphrasing Exercises (with Answers)
The main purpose of providing these exercises along with their answers is to help you understand what these techniques look like when they are implemented. Since we have explained their core definition above, you can try and work along the exercises to improve your skills a little as well.
Related: Difference Between Paraphrasing And Rephrasing
Paraphrasing Exercise # 1:
Here is a sample paragraph that we will be paraphrasing as an exercise. We’ll write the paragraph alone first, and then provide the answer after a brief explanation.
Sample Paragraph:
"John could not find the butter in his fridge. He went to buy some from the store. On coming back, he saw his cat sitting on the floor, smacking its lips. There was some yellow stuff smeared all around its face. Thus, John solved the mystery of the missing butter."
So, as we mentioned earlier, paraphrasing can be done simply and sparingly, or it can be done drastically.
One of the primary and basic ways of paraphrasing is to simply change some words in the provided content with their synonyms. This is, we reiterate, a very basic level of paraphrasing, and it is often very easy to see through it.
So, for this first exercise, we are going to be doing only that level of paraphrasing as a way to illustrate how it looks like.
Here is what the above paragraph looks like when paraphrased:
Paraphrased Paragraph:
"John could not locate the butter in the refrigerator. He went to purchase some from the shop. On coming back, he observed his cat sitting on the ground, licking its lips. There was some yellow material smeared all around its face. Hence, John solved the mystery of the missing butter."
While we are on this discussion, it will also be salubrious to understand that when changing words with their synonyms for the purpose of paraphrasing, you have to be careful that you pick those that don’t mess up the context and intent of the lines.
Paraphrasing Exercise # 2:
Moving on, let’s look at another paraphrasing exercise. Here is the paragraph that we will be using for this one:
"John’s cat got lost in the forest. He went looking for it in the night time. He heard some movement in one of the bushes. He put his hand in and felt the fur. He pulled the thing out, thinking it to be his cat. After coming home, he realized it was an angry raccoon."
We mentioned in the last exercise that the basic level of paraphrasing is to change some of the words in the given text with their synonyms. And we also mentioned how that sort of paraphrasing can be easily detected.
So, for writers who want to paraphrase something in such a way that it does not resemble its original form a lot, there’s a step further that they can go, and that is to change the sentence structures + phrases.
Essentially, by changing the phrases used in the content as well as the arrangement of the sentences, the overall look of the paraphrased piece looks very different. If someone wants to go even ahead of that, they can shuffle the sentence order as well.
Considering this type of ‘extensive’ paraphrasing, here is the answer to the paragraph given above:
"John’s cat went missing in the forest. He went to search for it when it was dark. He discerned some movement in the hedge. After putting his hand inside it, he felt some fur. Thinking that it was his cat, he pulled the animal out. It was only after coming home that he realized that it was a frustrated raccoon."
Read more: How And Why to Paraphrase Your Content?
Summarizing Exercises (with Answers)
Now that we have looked at the paraphrasing exercises, let’s move on to look at some for summarizing.
Just as we’ve looked at two types of paraphrasing above, we’ll also look at two different types of summarizing.
Actually, it’ll be better if we explain those two types before getting to the exercises.
Basically, there are two types of summaries . One of them is called extractive and the other is called abstractive .
In extractive summarization, the summary of a piece of content is generated merely by taking out some sentences from it and joining them together. This is usually the type of summaries that you get from automated tools.
When extractive summaries are created, there is no effort to understand the actual meaning and context of the text. Rather, the purpose is only to take some lines from it and join them together in such a way that they make sense.
On the other hand, abstractive summaries are those that are written using a completely new and different set of words, phrases and sentences than the content (that is being summarized). As opposed to extractive summarization, abstractive summarization involves understanding the meaning and context of the text, and then creating a completely new summary that features all those concepts and ideas.
Summarizing Exercise # 1 (Extractive)
In order to demonstrate and explain extractive summarization, we’re going to first write a paragraph here and then provide its summary afterwards:
Sample paragraph:
"John’s car broke down. He stopped by the road side and screamed at people to stop and help him. But no one stopped for him. He continued howling and howling for hours. People kept driving by. After getting tired, he picked up a sheet and wrapped it around himself. Then, he started spinning on his spot. He grew dizzy. He kept spinning and spinning until he fell asleep."
Now, since we have to use the “extractive” summarization technique here, we’ll create the summary using the lines and sentences used in the content itself.
"John’s car broke down. But no one stopped for him. Then, he started spinning on the spot. He kept spinning and spinning until he fell asleep."
Summarizing Exercise # 2 (Abstractive)
For this exercise, we will use the same para that we did above. However, the technique used for the summarization will be different.
Since we will be using the abstractive technique here, the summary will be created using different words and phrases as the original.
"John’s vehicle went phut. But, no one stopped their car to help him. After he was tired, he made himself dizzy by spinning and then went to sleep."
So, that’s about it.
If you were a little confused about paraphrasing and summarization techniques, hopefully you’re a little more confident about them now.
These skills can come in handy for writers in a lot of different situations. If you don’t have the hang of them already, you should try and get it as quick as you can.
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Inferences Worksheets
- Context Clues Worksheets
- Theme Worksheets
- Main Idea Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Summary Worksheets
- Online Tests
- Figurative Language Worksheets
- Short Stories with Questions
- Nonfiction Passages
- Genre Worksheets
BECOME A MEMBER!
Summarizing worksheets & activities.
Summarizing is one of those skills that may seem very easy to a teacher but can be difficult for students who have not been properly taught how to summarize. For many years I did not even teach my seventh and eighth grade students how to summarize. I would just ask them to summarize texts and then get mad at them when they failed to produce quality summaries. I was wrong in doing this. Now I always teach my students how to write summaries.
Additionally, as per the Common Core State Standards, summaries should not contain opinions, background knowledge, or personal information; rather, a summary should be entirely text based. After years of learning to make connections between the text and themselves, students must be retrained to keep themselves out of their writing in regards to summaries. Teaching this skill surely warrants some of your class time.
Here are some resources that I used in my classroom to teach my students how to summarize. I hope that you find this page useful:

Summarizing Common Core State Standards
120 comments, kowsar seyfudin mahmax.
Thank you very much
I want to express my gratitude for the work you have put into this site.
I have used your site for students for almost a decade now and they have not disappointed once.
Thank you for coming back!
I really appreciate these worksheets and all the worksheets you have published. I work as a volunteer for a literacy group, and we don’t have many resources at this level. I was an SLP so I have had no professional experience as a language arts teacher. These resources allow me to teach better and not have to create items from scratch.
thank you it was informative.
Alphonsa Anis
Thanks it was extremely helpful.
Absolutely fabulous. I’m using them for two employees who are struggling to summarise information. Very, very helpful – thank you.
Hello, can these great worksheets be linked to Google Classroom? Also, how can I have my students access the online assessments? Thank you.
There is a Google Classroom button on the title slide of each online assignment. Press this button to assign it. Google Classroom integration is pretty thin right now, but I’m hoping that they open up their platform more sometime soon!
Thank you, Mr. Morton, for sharing your tips and worksheets for summary teaching and writing practices. Very useful!
Some great activities, really helpful. One thing I want to point out is that shinobi-no-mono is NOT Chinese – this is Japanese. And in the text the characters given are Japanese, NOT Chinese. This is quite a big oversight. As language teachers we need to be aware of different languages.
Thank you. I appreciate the insight.
I want summary and practice sheets for grade 6
Please send me an answer key for the summarizing test.
Acutually 忍の者 isnt chinese the word の is japanses, while in chinese and japanese they call ninja , 忍者. Other than that this is some really good stuff to study my summary from
great material. I´ve been looking for this type of easy to read/ understand material for a long time.
Would it be possible to have the solutions to the test?
Thanks in advance.
Diane Thomas
These are wonderful!Thank you so much!
Thanks a lot .
JANINE RAINES
DO YOU HAVE THE ANSWER KEY TO THE SUMMARIZING TEST?
Mrs. Robinson
Hello, I’m looking for the answer guide for the Summarizing test, please advise if it is available?
Loan Nguyen
Thanks for your sharing. Invaluable resources for teachers. It would be highly appreciated if you can send me the key for the summary test.
Is there an answer sheet for the summarizing test?
EXCELLENT worksheets!
Like many of the above comments, I was hoping that there was an answer key for the summarizing test.
I’m pleased that today is the day that I can finally say, “ Here you go .”
Thank you so much!!
Thank you very much. Bless you!
Thank you, Mr. Morton, for sharing these materials. Indeed this is of great help in my class.
The materials are awesome!! I’d like to separate them to two levels of my students. I’m teaching international students, the comparasion of the good and bad summary really works a lot. I really appriciate for your sharing. However, could you share the summarising answer keys as well? That would help me a lot. Thank you!
Would you consider making something for the 4th & 5th grade level? The examples were all very helpful, but many of my students read below grade level. Thank you again! Jill C.
Thanks from Toronto! Great help for ESL classes here.
Thanks so much from Istanbul! Kids loved it and saved me so much precious precious time
saida merad
Thank you for your valuable help!
Thank you for putting all the material together.
I couldn’t find the answers for the Summarizing Test. They will surely save me some time. Please send them to me, or let me know where I can find them. Thank you so much,
Did you get the answer sheet?
Thank you for all the great materials to use, they will prove to be a great resource!
I was wondering if you would mind pointing out the source from which you pulled the information about ninjas for your worksheet on them. I just wanted to make sure I had the right information because from the bit of research that I pulled up, I see that both in history (concept / existence) and etymology, ninjas are Japanese. The Japanese use kanji, which are essentially Chinese characters, and is only one of the three different “alphabet” sets they use for written communication. So words like “shinobi” and “shinobi no mono” are all Japanese in origin, but written using Chinese characters and not really associated with Chinese culture. This is especially true because “no mono” is a Japanese phrase. Please let me know if there is a source that does say otherwise, so that I can have all the information. Thank you again!
Hello. I pulled that content from a Wikipedia page a long time ago. I’m no expert on the subject. I was just writing a worksheet that I hope would interest students.
These worksheets are helpful but the commenter above is correct, none of these words are or have ever been Chinese. “Shinobi” was in Japanese poems in the 8th century, not Chinese. Shinobi was the Chinese reading of the characters, but it was always a Japanese word. It might be helpful to fix this worksheet to avoid presenting incorrect information to students.
What is the answer key for summary test please?
Thanks a million for this Mr. Morton. This lesson will help me and my students understand summarizing better. God bless your sir!
Thank you so much for helpful material
Brian Samson
What a phenomenal effort you’ve done in putting together all these. Appreciate your ideas. Fabulous!
How amazing to come across your Summarising resouces with explicit instructions. Your comments about teaching the students how to effectively summarise was the most important fact. This in turn forced me to reflect on my own teaching. Thank you for the step by step instructions, they were very valuable. Have you posted any other reading strategy hints?
Sure, I’ve posted them all around this site. Feel free to explore a bit.
What’s the reading level for summary worksheet 3?
Can I get answers for summarizing test about Gutenberg
It is an awesome sight.I got to now today from where the school gives us topics in worksheets.Very useful,but one problems that we don’t get the answers of the questions so that we can check and correct our answers
Mary Jane Dela Cerna
Good day Mr. Morton 😀 what is the answer keys for the summary test? I am not sure in my answer 😀
Wow, just wanted to thank you for your hard work and generosity to publish them for everybody. Thank you so much.
I was studying for an exam and couldn’t find enough information on summarizing. I was very excited when I found your site. It was very helpful.Thanks a million!
A terrific resource. Thank you so much for sharing. I came across your site as I was looking for help with teaching summarising – no need to look any further! Powerpoint and practice sheets, examples …. awesome.
Gracie Alexander
Is there an answer key for the Test?
Kristen Moore
What an incredible site! Thank you for sharing your resources and ideas. Especially the Summary power point. I’ve been struggling to get my students to differentiate between a summary and a list of details. This will help so much!
Amy Gartland
I just discovered this site today. I teach high school ELL and was looking for good nonfiction texts that were accessible for my students. I will definitely be looking around some more and plan on using material in my lessons this week!
This was VERY helpful. Even for a university student who needed a refresher!
An answer key for the Summary would be helpful if provided. And also a whole passage summary, not just the summary for each paragraph.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Author's Purpose Worksheets
- Characterization Worksheets
- Conflict Worksheets
- Fact and Opinion Worksheets
- Figurative Language Activities
- Figurative Language Poems with Questions
- Genre Activities
- Irony Worksheets
- Making Predictions
- Mood Worksheets
- Nonfiction Passages and Functional Texts
- Parts of Speech Worksheets
- Poetic Devices
- Point of View Worksheets
- School Project Ideas
- Setting Worksheets
- Simile and Metaphor Worksheets
- Story Structure Worksheets
- Text Structure Worksheets
- Tone Worksheets
- ALL PAGES AND WORKSHEETS
Best 5 Paraphrasing Exercises
Read on to see our helpful paraphrasing exercises and tips in this article to get you started.
One of the most important skills you can hone as a student or writer is to paraphrase the words of other academics and experts effectively. Since new knowledge is built upon that which is already known, it makes sense that you’d want to reference the ideas of others in your work. However, this is often easier said than done. Paraphrasing, especially if you want to do it well, can be challenging.
Fortunately, as is the case with most other skills in life, you can improve your ability to paraphrase through practice. For instance, you can improve this skill by regularly doing paraphrasing exercises. As I was an academic for a long time in my life, I thought it might be helpful to those who have little or no experience in paraphrasing if I provided a list of paraphrasing exercises. If you’re such a person, I hope that this article will get you started on your journey toward mastering the art of paraphrasing. Your academic or writing career will undoubtedly be better off for it when you do.
The Art of Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing exercises and activities to help you master the skill, 1. broaden your vocabulary, 2. create a word map, 3. paraphrase in small chunks, 4. ways to paraphrase shorter and easier sentences, 5. imagine you’re explaining the source material to someone, helpful tips, 1. avoid plagiarism, 2. summarizing is not paraphrasing, 3. changing word order is not paraphrasing.
Although paraphrasing is an essential skill when writing papers, essays, or articles, it’s one that many find challenging to master. To paraphrase the words of others, you need first to comprehend their meaning, and then you need to express this meaning in your own words. To do this effectively requires a broad and sophisticated range of vocabulary and advanced grammar skills.
As stated in the introduction, you can improve your paraphrasing skills through paraphrasing exercises. Doing this will help you construct meaningful and original paraphrased sentences and increase the speed at which you work. Especially when you’re a student, reading, and paraphrasing the words of other scholars and experts can form a big chunk of your work. Learning how to paraphrase well and at a quick pace will enhance your academic experience and will open up your schedule for other activities, such as sports or parties.
Our paraphrasing vs. summarizing guide might be helpful.
Now that you know the importance of paraphrasing, let’s dive right in and look at some exercises and activities that can help you improve. Remember, as is the case when learning any other new skill, you need to engage with these exercises regularly.

Since you cannot paraphrase appropriately without a decent range of vocabulary, it makes sense to aim to add more words to your vocabulary bank constantly. Of course, if you’re an academic, you’ll want to focus on improving your academic vocabulary in your specific field. However, since academic language has a formal tone, you can add general terms to your vocabulary bank to help you express yourself more sophisticatedly. Examples of such words, for instance, are verbs such as “theorize,” “opine,” “constitute,” and “approximate.”
There are various ways in which you can enrich your academic vocabulary. These include:
- Keeping a word journal: A great way to learn new words is to carry a little book along with you, in which you can write down words that you don’t know. You can write down the word and then look up the meaning when you have time. It can also be helpful to construct your sentence with the word once you’ve jotted down its definition.
- Highlight words in texts: Whether you’re working with a physical copy of a text or a digital version, it’s good to highlight or underline words that you don’t know. You can then either write a definition of the words in the margin or, if you’re working with a digital copy, you can add a comment. Another good tip is to write by hand – people learn better when writing something by hand than if they typed the same information.
- Read as much as you can: Although this may be obvious, the best way to improve your vocabulary is to read as many books and articles as you can fit into your schedule. Even if you don’t have the time to look up the meaning of each word that you don’t understand, just seeing the word pop up in different contexts will help you work out the meaning for yourself over time. Apart from reading, you can also listen to podcasts or watch documentaries and news channels.
If you’re battling to paraphrase an original paragraph or sentence into your own words, it can be helpful to create a word map. You can, for instance, write a few complex words or phrases down on a piece of paper. Next, draw a box around each word or phrase, and leave enough space around each so that you can draw and link other boxes. As a next step, you can draw boxes in which you write the synonym of each word. You can also write down the definition of each word if you’re unsure of its meaning.
Next, you need to clarify the relationship between these words or terms. Draw arrows between them indicating patterns, correlation, or cause and effect. You can also add boxes between the original words or phrases in which you add other words, such as verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, or adjectives. Doing so can help you further explain the terms or link them meaningfully. Once you’ve added all the information you can think of, try to create a paraphrased sentence or paragraph from your word map.
A valuable way to learn how to paraphrase when you’re a beginner is to break sentences into smaller parts. For example, instead of paraphrasing a long and complex sentence, which can become overwhelming if you’re not used to this process, you can focus on shorter phrases. Let’s take a look at an example. Here, for instance, is a long and complex sentence:
“ Many impacts are unavoidable and will hit the world’s most vulnerable populations hardest, it warns — but collective action from governments to both curb greenhouse-gas emissions and prepare communities to live with global warming could yet avert the worst outcomes. “
You may find it challenging to paraphrase this sentence as a whole. However, breaking it into smaller chunks makes the task more doable. You can break this sentence up in the following way:
- Many impacts are unavoidable
- And will hit the world’s most vulnerable populations hardest, it warns
- But collective actions from governments
- To both curb greenhouse-gas emissions
- And prepare communities to live with global warming
- Could yet avert the worst outcomes
Remember, the sentence structure of your paraphrased version can and often will look different from the source. This means that you can form two or multiple sentences if this helps you create a meaningful paraphrased version, even if the original is one sentence.
If you want to practice your paraphrasing skills, you can do so by paraphrasing a sentence in two or three different ways. You can practice finding different synonyms, grammar, and sentence structures while retaining the meaning across all versions.
If you have time, you can do this exercise with longer sentences. However, it may be good to start by paraphrasing shorter sentences. Doing so will allow you to focus on finding multiple synonyms and different ways to write the same sentence.
Here’s an example:
“ Scientists know that bees are dying from a variety of factors. “
Paraphrased version 1:
“Experts maintain that the future of bees is in danger due to multiple causes.”
Paraphrased version 2:
“There are many different reasons why bees are going extinct, according to scientists.”
A helpful way of practicing paraphrasing while reading through articles or research papers is to recite your paraphrased version of some more complex sentences. Since the first step of paraphrasing is to ensure that you’ve correctly understood the source, repeating what you’ve just read in your own words can help you grasp the meaning of the source material.
You don’t need to use formal academic language and complex terms when doing this paraphrasing exercise. Instead, the aim is to repeat what you’ve read in plain and simple terms. Also, since you don’t need to write anything down for this paraphrasing exercise, it’s something you can regularly do while you’re reading through the source material.
It’s vital that you understand what you’re reading and that all the information is not just going over your head. Doing this exercise, primarily when you find yourself drifting off or having problems grasping a sentence, will ensure that you’ve understood the section you’ve read. At the same time, you get to practice your paraphrasing skills.
Here are some helpful tips to keep in mind while paraphrasing.
Even though you’re not using direct quotes when paraphrasing but rather stating another author’s ideas in your own words, you still need to reference their work. Failing to do so amounts to plagiarism, a serious offense, whether you’re producing academic work or an article for a web page.
The format you have to use when citing the work of others varies. For instance, in academic writing, you need to provide in-text citations and a list of references at the end of your essay, article, or thesis. The precise way you’ll write your in-text citations and list of references will be determined by the formatting style, whether this is APA , Harvard , Chicago , or MLA .
Although both tools or techniques involve using your own words to describe somebody else’s text, they are different. You need to retain the original work’s meaning with both techniques while using your own words. When you’re summarizing a work , you’re selecting only the most essential points of the text and rewriting these in your own words. This means that you provide a short overview of what a text is about.
It would be best to remain far more loyal to the source material with paraphrasing. You refer to specific ideas an author has provided to incorporate these into your work. To ensure that you’re not changing the original version too much or skewing the meaning the author intended to bring across, you have to rewrite actual sentences and paragraphs. You can’t just write a summary of large chunks of text.
Although this is a “technique” employed by lazy students, you should be aware that merely swapping around the word order of an original text does not constitute paraphrasing. It’s also not good enough to merely change a sentence from passive voice to active voice or vice versa.
Using either of these as your only paraphrasing method when rewriting somebody else’s words can amount to plagiarism since you’ve not used your own words or demonstrated your understanding of the source material. In such instances, you’d be better off simply rewriting the author’s exact words and placing these in quotation marks.
To learn more, check out our guide on paraphrasing vs. plagiarism .

Bryan Collins is the owner of Become a Writer Today. He's an author from Ireland who helps writers build authority and earn a living from their creative work. He's also a former Forbes columnist and his work has appeared in publications like Lifehacker and Fast Company.
View all posts

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 12 min read
How to Paraphrase and Summarize Work
Summing up key ideas in your own words.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Imagine you're preparing a presentation for your CEO. You asked everyone in your team to contribute, and they all had plenty to say!
But now you have a dozen reports, all in different styles, and your CEO says that she can spare only 10 minutes to read the final version. What do you do?
The solution is to paraphrase and summarize the reports, so your boss gets only the key information that she needs, in a form that she can process quickly.
In this article, we explain how to paraphrase and how to summarize, and how to apply these techniques to text and the spoken word. We also explore the differences between the two skills, and point out the pitfalls to avoid.
What Is Paraphrasing?
When you paraphrase, you use your own words to express something that was written or said by another person.
Putting it into your own words can clarify the message, make it more relevant to your audience , or give it greater impact.
You might use paraphrased material to support your own argument or viewpoint. Or, if you're putting together a report , presentation or speech , you can use paraphrasing to maintain a consistent style, and to avoid lengthy quotations from the original text or conversation.
Paraphrased material should keep its original meaning and (approximate) length, but you can use it to pick out a single point from a longer discussion.
What Is Summarizing?
In contrast, a summary is a brief overview of an entire discussion or argument. You might summarize a whole research paper or conversation in a single paragraph, for example, or with a series of bullet points, using your own words and style.
People often summarize when the original material is long, or to emphasize key facts or points. Summaries leave out detail or examples that may distract the reader from the most important information, and they simplify complex arguments, grammar and vocabulary.
Used correctly, summarizing and paraphrasing can save time, increase understanding, and give authority and credibility to your work. Both tools are useful when the precise wording of the original communication is less important than its overall meaning.
How to Paraphrase Text
To paraphrase text, follow these four steps:
1. Read and Make Notes
Carefully read the text that you want to paraphrase. Highlight, underline or note down important terms and phrases that you need to remember.
2. Find Different Terms
Find equivalent words or phrases (synonyms) to use in place of the ones that you've picked out. A dictionary, thesaurus or online search can be useful here, but take care to preserve the meaning of the original text, particularly if you're dealing with technical or scientific terms.
3. Put the Text into Your Own Words
Rewrite the original text, line by line. Simplify the grammar and vocabulary, adjust the order of the words and sentences, and replace "passive" expressions with "active" ones (for example, you could change "The new supplier was contacted by Nusrat" to "Nusrat contacted the new supplier").
Remove complex clauses, and break longer sentences into shorter ones. All of this will make your new version easier to understand .
4. Check Your Work
Check your work by comparing it to the original. Your paraphrase should be clear and simple, and written in your own words. It may be shorter, but it should include all of the necessary detail.
Paraphrasing: an Example
Despite the undoubted fact that everyone's vision of what constitutes success is different, one should spend one's time establishing and finalizing one's personal vision of it. Otherwise, how can you possibly understand what your final destination might be, or whether or not your decisions are assisting you in moving in the direction of the goals which you've set yourself?
The two kinds of statement – mission and vision – can be invaluable to your approach, aiding you, as they do, in focusing on your primary goal, and quickly identifying possibilities that you might wish to exploit and explore.
We all have different ideas about success. What's important is that you spend time defining your version of success. That way, you'll understand what you should be working toward. You'll also know if your decisions are helping you to move toward your goals.
Used as part of your personal approach to goal-setting, mission and vision statements are useful for bringing sharp focus to your most important goal, and for helping you to quickly identify which opportunities you should pursue.
How to Paraphrase Speech
In a conversation – a meeting or coaching session, for example – paraphrasing is a good way to make sure that you have correctly understood what the other person has said.
This requires two additional skills: active listening and asking the right questions .
Useful questions include:
- If I hear you correctly, you're saying that…?
- So you mean that…? Is that right?
- Did I understand you when you said that…?
You can use questions like these to repeat the speaker's words back to them. For instance, if the person says, "We just don't have the funds available for these projects," you could reply: "If I understand you correctly, you're saying that our organization can't afford to pay for my team's projects?"
This may seem repetitive, but it gives the speaker the opportunity to highlight any misunderstandings, or to clarify their position.
When you're paraphrasing conversations in this way, take care not to introduce new ideas or information, and not to make judgments on what the other person has said, or to "spin" their words toward what you want to hear. Instead, simply restate their position as you understand it.
Sometimes, you may need to paraphrase a speech or a presentation. Perhaps you want to report back to your team, or write about it in a company blog, for example.
In these cases it's a good idea to make summary notes as you listen, and to work them up into a paraphrase later. (See How to Summarize Text or Speech, below.)
How to Summarize Text or Speech
Follow steps 1-5 below to summarize text. To summarize spoken material – a speech, a meeting, or a presentation, for example – start at step three.
1. Get a General Idea of the Original
First, speed read the text that you're summarizing to get a general impression of its content. Pay particular attention to the title, introduction, conclusion, and the headings and subheadings.
2. Check Your Understanding
Build your comprehension of the text by reading it again more carefully. Check that your initial interpretation of the content was correct.
3. Make Notes
Take notes on what you're reading or listening to. Use bullet points, and introduce each bullet with a key word or idea. Write down only one point or idea for each bullet.
If you're summarizing spoken material, you may not have much time on each point before the speaker moves on. If you can, obtain a meeting agenda, a copy of the presentation, or a transcript of the speech in advance, so you know what's coming.
Make sure your notes are concise, well-ordered, and include only the points that really matter.
The Cornell Note-Taking System is an effective way to organize your notes as you write them, so that you can easily identify key points and actions later. Our article, Writing Meeting Notes , also contains plenty of useful advice.
4. Write Your Summary
Bullet points or numbered lists are often an acceptable format for summaries – for example, on presentation slides, in the minutes of a meeting, or in Key Points sections like the one at the end of this article.
However, don't just use the bulleted notes that you took in step 3. They'll likely need editing or "polishing" if you want other people to understand them.
Some summaries, such as research paper abstracts, press releases, and marketing copy, require continuous prose. If this is the case, write your summary as a paragraph, turning each bullet point into a full sentence.
Aim to use only your own notes, and refer to original documents or recordings only if you really need to. This helps to ensure that you use your own words.
If you're summarizing speech, do so as soon as possible after the event, while it's still fresh in your mind.
5. Check Your Work
Your summary should be a brief but informative outline of the original. Check that you've expressed all of the most important points in your own words, and that you've left out any unnecessary detail.
Summarizing: an Example
So how do you go about identifying your strengths and weaknesses, and analyzing the opportunities and threats that flow from them? SWOT Analysis is a useful technique that helps you to do this.
What makes SWOT especially powerful is that, with a little thought, it can help you to uncover opportunities that you would not otherwise have spotted. And by understanding your weaknesses, you can manage and eliminate threats that might otherwise hurt your ability to move forward in your role.
If you look at yourself using the SWOT framework, you can start to separate yourself from your peers, and further develop the specialized talents and abilities that you need in order to advance your career and to help you achieve your personal goals.
SWOT Analysis is a technique that helps you identify strengths, weakness, opportunities, and threats. Understanding and managing these factors helps you to develop the abilities you need to achieve your goals and progress in your career.
Permission and Citations
If you intend to publish or circulate your document, it's important to seek permission from the copyright holder of the material that you've paraphrased or summarized. Failure to do so can leave you open to allegations of plagiarism, or even legal action.
It's good practice to cite your sources with a footnote, or with a reference in the text to a list of sources at the end of your document. There are several standard citation styles – choose one and apply it consistently, or follow your organization's house style guidelines.
As well as acknowledging the original author, citations tell you, the reader, that you're reading paraphrased or summarized material. This enables you to check the original source if you think that someone else's words may have been misused or misinterpreted.
Some writers might use others' ideas to prop up their own, but include only what suits them, for instance. Others may have misunderstood the original arguments, or "twisted" them by adding their own material.
If you're wary, or you find problems with the work, you may prefer to seek more reliable sources of information. (See our article, How to Spot Real and Fake News , for more on this.)
Paraphrasing means rephrasing text or speech in your own words, without changing its meaning. Summarizing means cutting it down to its bare essentials. You can use both techniques to clarify and simplify complex information or ideas.
To paraphrase text:
- Read and make notes.
- Find different terms.
- Put the text into your own words.
- Check your work.
You can also use paraphrasing in a meeting or conversation, by listening carefully to what's being said and repeating it back to the speaker to check that you have understood it correctly.
To summarize text or speech:
- Get a general idea of the original.
- Check your understanding.
- Make notes.
- Write your summary.
Seek permission for any copyrighted material that you use, and cite it appropriately.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Blanchard's abcd model of trust.
Strengthening the Four Elements of Trust
Critical Thinking
Developing the Right Mindset and Skills
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!


Introducing Mind Tools for Business
Mind Tools for Business is a comprehensive library of award-winning performance and management support resources.
Whether you want to increase engagement, upskill teams, or complement your existing workplace programs – this is content designed to achieve impactful results.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Most Popular
Newest Releases

What Are Henri Fayol's Five Functions of Management?

Henri Fayol's Principles of Management
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Connecting remote and hybrid workers to organizational mission.
Bringing people together through a shared purpose
Is Our Partnership at Risk?
Identify Those Areas of Partnership Work Which May Have Been Left Open to Risk
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
You, inc: the art of selling yourself.
Harry Beckwith and Christine Clifford Beckwith
Book Insights
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on April 8, 2022 by Courtney Gahan and Jack Caulfield. Revised on June 1, 2023.
Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas into your own words. Paraphrasing a source involves changing the wording while preserving the original meaning.
Paraphrasing is an alternative to quoting (copying someone’s exact words and putting them in quotation marks ). In academic writing, it’s usually better to integrate sources by paraphrasing instead of quoting. It shows that you have understood the source, reads more smoothly, and keeps your own voice front and center.
Every time you paraphrase, it’s important to cite the source . Also take care not to use wording that is too similar to the original. Otherwise, you could be at risk of committing plagiarism .
What is your plagiarism score?
Compare your paper with 99.3 billion webpages and 8 million publications.
- Best plagiarism checker of 2021
- Plagiarism report & percentage
- Largest plagiarism database
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
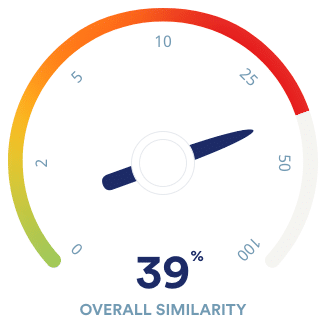
Table of contents
How to paraphrase in five easy steps, how to paraphrase correctly, examples of paraphrasing, how to cite a paraphrase, paraphrasing vs. quoting, paraphrasing vs. summarizing, avoiding plagiarism when you paraphrase, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about paraphrasing.
If you’re struggling to get to grips with the process of paraphrasing, check out our easy step-by-step guide in the video below.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Putting an idea into your own words can be easier said than done. Let’s say you want to paraphrase the text below, about population decline in a particular species of sea snails.
Incorrect paraphrasing
You might make a first attempt to paraphrase it by swapping out a few words for synonyms .
Like other sea creatures inhabiting the vicinity of highly populated coasts, horse conchs have lost substantial territory to advancement and contamination , including preferred breeding grounds along mud flats and seagrass beds. Their Gulf home is also heating up due to global warming , which scientists think further puts pressure on the creatures , predicated upon the harmful effects extra warmth has on other large mollusks (Barnett, 2022).
This attempt at paraphrasing doesn’t change the sentence structure or order of information, only some of the word choices. And the synonyms chosen are poor:
- “Advancement and contamination” doesn’t really convey the same meaning as “development and pollution.”
- Sometimes the changes make the tone less academic: “home” for “habitat” and “sea creatures” for “marine animals.”
- Adding phrases like “inhabiting the vicinity of” and “puts pressure on” makes the text needlessly long-winded.
- Global warming is related to climate change, but they don’t mean exactly the same thing.
Because of this, the text reads awkwardly, is longer than it needs to be, and remains too close to the original phrasing. This means you risk being accused of plagiarism .
Correct paraphrasing
Let’s look at a more effective way of paraphrasing the same text.
Here, we’ve:
- Only included the information that’s relevant to our argument (note that the paraphrase is shorter than the original)
- Introduced the information with the signal phrase “Scientists believe that …”
- Retained key terms like “development and pollution,” since changing them could alter the meaning
- Structured sentences in our own way instead of copying the structure of the original
- Started from a different point, presenting information in a different order
Because of this, we’re able to clearly convey the relevant information from the source without sticking too close to the original phrasing.
Explore the tabs below to see examples of paraphrasing in action.
- Journal article
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
Once you have your perfectly paraphrased text, you need to ensure you credit the original author. You’ll always paraphrase sources in the same way, but you’ll have to use a different type of in-text citation depending on what citation style you follow.
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Prevent plagiarism. run a free check..
It’s a good idea to paraphrase instead of quoting in most cases because:
- Paraphrasing shows that you fully understand the meaning of a text
- Your own voice remains dominant throughout your paper
- Quotes reduce the readability of your text
But that doesn’t mean you should never quote. Quotes are appropriate when:
- Giving a precise definition
- Saying something about the author’s language or style (e.g., in a literary analysis paper)
- Providing evidence in support of an argument
- Critiquing or analyzing a specific claim
A paraphrase puts a specific passage into your own words. It’s typically a similar length to the original text, or slightly shorter.
When you boil a longer piece of writing down to the key points, so that the result is a lot shorter than the original, this is called summarizing .
Paraphrasing and quoting are important tools for presenting specific information from sources. But if the information you want to include is more general (e.g., the overarching argument of a whole article), summarizing is more appropriate.
When paraphrasing, you have to be careful to avoid accidental plagiarism .
This can happen if the paraphrase is too similar to the original quote, with phrases or whole sentences that are identical (and should therefore be in quotation marks). It can also happen if you fail to properly cite the source.
Paraphrasing tools are widely used by students, and can be especially useful for non-native speakers who may find academic writing particularly challenging. While these can be helpful for a bit of extra inspiration, use these tools sparingly, keeping academic integrity in mind.
To make sure you’ve properly paraphrased and cited all your sources, you could elect to run a plagiarism check before submitting your paper. And of course, always be sure to read your source material yourself and take the first stab at paraphrasing on your own.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Critical thinking
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
To paraphrase effectively, don’t just take the original sentence and swap out some of the words for synonyms. Instead, try:
- Reformulating the sentence (e.g., change active to passive , or start from a different point)
- Combining information from multiple sentences into one
- Leaving out information from the original that isn’t relevant to your point
- Using synonyms where they don’t distort the meaning
The main point is to ensure you don’t just copy the structure of the original text, but instead reformulate the idea in your own words.
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism , because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly cite the source . This means including an in-text citation and a full reference, formatted according to your required citation style .
As well as citing, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas in your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely in your own words and properly cite the source .
Try our services
To present information from other sources in academic writing , it’s best to paraphrase in most cases. This shows that you’ve understood the ideas you’re discussing and incorporates them into your text smoothly.
It’s appropriate to quote when:
- Changing the phrasing would distort the meaning of the original text
- You want to discuss the author’s language choices (e.g., in literary analysis )
- You’re presenting a precise definition
- You’re looking in depth at a specific claim
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. & Caulfield, J. (2023, June 01). How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/how-to-paraphrase/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, how to write a summary | guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in apa, mla & chicago, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources.

University Centre for Academic English
Paraphrasing and summarising
You are advised to work through the activities in the order in which they are presented.
Paraphrasing
You will consider some basic guidelines for paraphrasing another writer's ideas and learn to recognise good paraphrasing style.
- View paraphrasing activity
Paraphrasing main points
You will practise selecting the main points from some short text extracts and paraphrase them in an appropriate way.
- View paraphrasing main points activity
Paraphrasing paragraphs
Practice in paraphrasing more demanding text.
- View paraphrasing paragraphs activity
Paraphrasing a long text
You will practise extending your paraphrasing skills with a longer text.
- View paraphrasing a long text activity
Module 2: Reading Strategies
Summarizing and paraphrasing, learning objectives.
- Summarize a passage of reading
- Paraphrase a passage of reading
Have you ever heard, “the best way to learn something is to teach it to someone else”?
Writing a summary of a source is a very similar process to teaching someone the content—but in this case, the student you’re teaching is yourself.
Summarizing , or condensing someone else’s ideas and putting it into your own shortened form, allows you to be sure that you’ve accurately captured the main idea of the text you’re reading. When reading, summarizing is helpful for checking your understanding of a longer text and remembering the author’s main ideas. When writing, summarizing is critical when reviewing, writing an abstract, preparing notes for a study guide, creating an annotated bibliography, answering essay questions, recording results of an experiment, describing the plot of a fictional work or film, or writing a research paper.
How to Write Summary Statements
Use these processes to help you write summary statements:
- Underline important information and write keywords in the margin.
- Record ideas using a two-column note-taking system. Record questions you have about the text concepts in the left column and answers you find in the reading in the right column.
- Identify how concepts relate to what you already know.
- Add examples and details
For retaining key ideas as you read, write a summary statement at the end of each paragraph or section. For capturing the major ideas of the entire work, write a summary paragraph (or more) that describes the entire text.
Tips for Summary
For longer, overall summary projects that capture an entire reading, consider these guidelines for writing a summary:
- A summary should contain the main thesis or standpoint of the text, restated in your own words. (To do this, first find the thesis statement in the original text.)
- A summary is written in your own words. It contains few or no quotes.
- A summary is always shorter than the original text, often about 1/3 as long as the original. It is the ultimate fat-free writing. An article or paper may be summarized in a few sentences or a couple of paragraphs. A book may be summarized in an article or a short paper. A very large book may be summarized in a smaller book.
- A summary should contain all the major points of the original text , and should ignore most of the fine details, examples, illustrations or explanations.
- The backbone of any summary is formed by crucial details (key names, dates, events, words and numbers). A summary must never rely on vague generalities.
- If you quote anything from the original text, even an unusual word or a catchy phrase, you need to put whatever you quote in quotation marks (” “).
- A summary must contain only the ideas of the original text. Do not insert any of your own opinions, interpretations, deductions or comments into a summary.
You can view the transcript for “Summarizing” here (opens in new window) .
Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing is the act of putting an author’s ideas into your own words. When reading, paraphrasing is helpful for checking your understanding of what you read as well as remembering what you read. When writing, paraphrasing is an important skill to have when constructing a research paper and incorporating the ideas of others alongside your own.
Click to view the transcript for “Paraphrasing” here (opens in new window) .
paraphrasing : rewriting a passage of text in your own words
summarizing : condensing someone else’s ideas and putting it into your own shortened form
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- PQRST Script. Provided by : Lethbridge College. Located at : http://www.lethbridgecollege.net/elearningcafe/index.php/pqrst-script . Project : eLearning Cafe. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Summarizing. Provided by : Excelsior College. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/orc/what-to-do-after-reading/summarizing/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Why Use Quotes?. Authored by : The News Manual. Provided by : Media Helping Media. Located at : http://www.mediahelpingmedia.org/training-resources/journalism-basics/659-how-to-use-quotes-in-news-stories-and-features . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- How to Write an A-plus Summary of a Text. Authored by : Owen M. Williamson. Provided by : The University of Texas at El Paso. Located at : http://utminers.utep.edu/omwilliamson/engl0310/summaryhints.htm . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright

- Memberships
- Institutional Members
- Teacher Members

Improve your paraphrasing skills
by AEUK | Jan 29, 2022 | Lessons , Referencing , Writing

Paraphrasing is using your own words to express someone else’s message or ideas. In a paraphrase, the ideas and meaning of the original source must be maintained; the main ideas need to be expressed, but the wording has to be your own.
Paraphrasing video.
A 10-minute video on how to paraphrase effectively using the 4-key stages of paraphrasing. This video is based on our Paraphrasing Lesson 1.
The key skills to paraphrasing are:
- Change in word forms
- Change in sentence structure
- Reference to the author
PDF Lesson Download
Paraphrasing lesson 1 – how to paraphrase effectively [updated 2021].
It starts by discussing the differences between quotation, paraphrase and summary. It takes students through the basics of identifying keywords, finding synonyms and then changing the grammatical structure. There is plenty of practice, all with efficient teacher’s notes. Level ** ** * [B1/B2/C1] Example / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
£5.00 – Add to cart Checkout Added to cart
Paraphrasing Lesson 2 – improve your paraphrasing skills [new for 2021]
This lesson helps students to improve their paraphrasing skills. The guided learning approach includes a text analysis activity where students identify the paraphrasing strategies, five sentence-level tasks to practise the strategies and two paragraph-level exercises to build on the previous tasks.. Level ** ** * [B1/B2/C1] Example / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Advertisement

Paraphrasing Exercises
Taken from paraphrasing lesson 2 – improve your paraphrasing skills.
Task: Underline the key words you do not have to change in the following sentences.
- Reports predict that zero waste shops are on the increase.
- Many actors feel that funding for performance arts is currently too low.
For a detailed worksheet and more exercises – buy the download Paraphrasing Lesson 2 below.
Task: Replace the underlined words with synonyms in the following sentences.
- Every day 8 million pieces of plastic are discarded in the oceans.
- The introduction of bike lanes in many cities has been successful in reducing traffic accidents.
- Every day 8 million pieces of plastic are disposed of in the oceans.
- The introduction of bike lanes in many cities has been effective in reducing traffic accidents.
Task: Rewrite the sentences using a different word form. Use the word in brackets.
1.The sales of electric cars will increase dramatically this year . (dramatic)
___________________________________________________________________
2. The UK’s Test and Trace system failed mainly due to a lack of planning. (failure)
- There will be a dramatic increase in the sales of electric cars this year.
- The failure of the UK’s Test and Trace system was mainly due to a lack of planning.
Task 4: Change the sentence structure in the following sentences. Use the prompt given.
- Although fast food can cause a number of health issues, many people still continue to consume this type of food.
Despite________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Despite fast food causing a number of health issues, many people still continue to consume this type of food.
Task 4: Practice all four strategies (synonyms, word form, word order & sentence structure) and add a reporting verb. Use the author in brackets.
The principles of designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use and regenerating natural systems is defined as the circular economy (Macarthur, 2020).
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Possible answer:
Macarthur (2020) defines the circular economy as the method of eliminating waste and pollution, the continual use of resources and the restoration of physical and biological materials.
NEW! Academic Paraphrasing Lesson 2 Download
Academic paraphrasing lesson 1 download, referencing lessons.
- Harvard Referencing Guide
- APA 7th Edition Referencing Guide
Referencing Guide: Harvard
This is a basic reference guide to citing and creating a reference list or a bibliography. It shows the correct way to create in-text citations and reference lists for books, journals, online newspapers and websites. Web page link . TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Free Download
Referencing Guide: APA 7th Edition
Referencing: harvard referencing worksheet 1 [updated 2021].
Two part worksheet that is a paragraph and reference list. Students have to put in the correct in-text reference. The second part is a reference list exercise where students have to put the sections in the correct order. A nice lesson to introduce students to referencing and becoming aware of key referencing principles. Level ** ** * [B1/B2/C1] Example / Webpage link / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
£4.00 – Add to cart Checkout Added to cart
Referencing: Harvard Referencing Worksheet 2 [new for 2021]
This lesson supports students in their understanding and use of Harvard referencing. It contains six worksheets: a discussion on referencing, a noticing activity, a reordering task, an error identification exercise, a sentence completion task, a gap-fill activity and a reference list task. Level ** ** * [B1/B2/C1] Example / Webpage link / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP

Two part worksheet that is a paragraph and reference list. Students have to put in the correct in-text reference. The second part is a reference list exercise where students have to put the sections in the correct order. A nice lesson to introduce students to referencing and becoming aware of key referencing principles. Level ** ** * [B1/B2/C1] Example / Webpage link / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
This lesson supports students in their understanding and use of APA referencing. It contains six worksheets: a discussion on referencing, a noticing activity, a reordering task, an error identification exercise, a sentence completion task, a gap-fill activity and a reference list task. Level ** ** * [B1/B2/C1] Example / Webpage link / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Reporting Verbs
Use the verbs in the box to put into the sentences in the worksheet. Each sentence has a description of the type of verb needed. Check the grammar of the verb too! Web page link . TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Writing a paragraph – using quotes about smoking
Students are given a worksheet with nine quotes taken from The New Scientist, BBC News, The Economist, etc… After selecting only three, they use these three quotes to write a paragraph trying to paraphrase the quotes and produce a cohesion piece of writing. Level ** ** * [B1/B2/C1] Example / Webpage link / TEACHER MEMBERSHIP / INSTITUTIONAL MEMBERSHIP
Memberships (Teacher / Institutional)
Full access to everything - £80 / £200 / £550
Join today * x
More writing resources
Academic phrases, academic style [1], academic style [2], academic style [3], academic word list , writing websites, error correction, hedging [1], hedging [2], noun phrases [1], noun phrases [2], referencing, in-text referencing, harvard referencing, apa referencing, reference generators, reference lists, reporting verbs, credible sources, evaluating sources, academic integrity, ‘me’ in writing, writing skills, paraphrasing [1], paraphrasing [2], paraphrase (quotes), summarising , summary language, critical thinking, argument essays, spse essays, parallelism, sentence structure [1], sentence structure [2], punctuation, structure , essay structure, introductions, thesis statements, paragraphing, topic sentences, definitions, conclusions, linking words, marking criteria, more blog posts….

Advertisement:

Start with a clear topic sentence that addresses the given topic. Give three supporting subtopics and illustrate these subtopics with details, explanations, and examples drawn from the source samples.
The Terry Fox Foundation had nearly $19 million to give to cancer research during 200/2005. (Research, 13-14)
Selection A: Terry Fox Funded Research [refer to as "Research"]
http://www.terryfoxrun.org/english/research/default.asp?s=1
Selection B: TERRY FOX [ refer to as "CBC"]
http://www.cbc.ca/greatest/top_ten/nominee/fox-terry.html
Selection C - Terry Fox (1958-1981) [Refer to as "Collections"]
http://www.collectionscanada.ca/2/6/h6-214-e.html
- Olympic College
- Research Guides
- Summarize, Paraphrase, and Quote
- ENGL 91 Library Guide
- Read for Comprehension
- Writing Basics
- Plan Your Writing
- Write a Thesis Sentence
- Revising & Proofreading
- Find Library Resources
- Find Web Resources
Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing
- Quoting, Summarizing, Paraphrasing, from OWL of Purdue Three ways of incorporating the words and ideas of other people into your own writing as explained by Purdue University Online Writing Lab.
Examples and Exercises for Understand Paraphrasing and Summarizing
Practice identifying appropriately paraphrased passages with the University of Arizona's Global Campus Writing Center Paraphrasing Activity .
Practice summarizing and paraphrasing with this introductory exercise from the Owl of Purdue, answers provided.
Write your own paraphrases and evaluate then with the OWL of Purdue paraphrasing exercise and answers .
Examples of plagiarism and Tutorials to learn more
- Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Quoting from the OWL of Purdue
- Academic Integrity Tutorial with examples from NIU
- Examples of Plagiarism from Bowdoin College
- Plagiarism Tutorial from IU
- Plagiarism Tutorial playllist on YouTube from Texas A&M
See also...
- MLA Guide to Avoiding Plagiarism
- MLA 9th Edition Guide from OC Libraries
- MLA Guide from OWL of Purdue
- Zotero Bib Free, high-quality citation generator with no ads
- << Previous: Write a Thesis Sentence
- Next: Revising & Proofreading >>
- Last Updated: Oct 6, 2023 12:10 PM
- URL: https://libguides.olympic.edu/ENGL91

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Summarizing

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource provides guidelines for paraphrasing and summarizing the sources you have researched.
In many situations, you will not have to provide the level of detail that the original writer did. At such times, you should summarize, or remove minor details. Here’s an example:
Example: Overall, the first two quarters of 2008 have been profitable to the company. Nineteen of twenty departments report cutting costs at least twenty percent, and sales from fifteen departments have risen five percent, or about $5 million. Despite these positive developments, most department heads believe that they will not be able to maintain these levels for the remainder of the year.
Revision: The company has driven profits from January to June of 2008, but the rest of the year is not expected to be as good.
Unlike paraphrasing, the basic order of the original text is maintained. However, some words have been changed to close synonyms. When summarizing, avoid cutting too much important information.
For more information on paraphrasing, visit the OWL’s resource, Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Paraphrase. Paraphrase the following sentences. The student requested that the professor excuses her absence, but the professor refused. There will be a music concert next to Vienna coffee shop.
Paraphrasing and Summarizing Exercises with Answers. Read Time: 10 min. Paraphrasing and Summarizing are two skills that are highly useful for writers. With these two techniques, writers can get help creating their content and providing it to their readers in an easy-to-peruse way. However, if you happen to be new to the field of writing, you ...
The exercises in this section provide opportunities for second language writers (ESL) of various proficiency levels to practice with paraphrase and summary writing. Exercises in this section were developed by Kamal Belmihoub. Last Update May 29, 2014. Please use the navigation bar on the left or the links below to access the individual exercises.
Summarizing Test. Here is a test to help you evaluate your students' ability to summarize. Students read a long passage about Johannes Gutenberg and highlight important information in the text. Then they summarize each paragraph, answer multiple-choice questions, and create extended responses. Summarizing Test Links.
Paraphrase Exercise. Please read the following passages carefully and paraphrase it. "In the United States, about six out of ten students in graduate schools are women. The same is true of today's young adults who already have a degree beyond college. As a result, the Census Bureau expects that more women than men will hold professions such ...
Writing Exercise Steps. 1. Create a "source" article. 2. "Publish" the article and write a bibliographical citation. 3. Use each other's source articles to write a summary, a paraphrase, and a quotation. 4. Use this summary, paraphrase, and quotation to write a short essay and "Works Cited" page.
2. Create a Word Map. If you're battling to paraphrase an original paragraph or sentence into your own words, it can be helpful to create a word map. You can, for instance, write a few complex words or phrases down on a piece of paper.
Follow steps 1-5 below to summarize text. To summarize spoken material - a speech, a meeting, or a presentation, for example - start at step three. 1. Get a General Idea of the Original. First, speed read the text that you're summarizing to get a general impression of its content.
Paraphrasing vs. summarizing. A paraphrase puts a specific passage into your own words. It's typically a similar length to the original text, or slightly shorter. When you boil a longer piece of writing down to the key points, so that the result is a lot shorter than the original, this is called summarizing.
Paraphrasing and Summarizing: Express ideas in a quicker, more straightforward way. Avoid unnecessary details. Condense large ideas into compact, easily understood chunks that can add to your writing. Quotations: Restate someone else's ideas in a respectable, cited manner. Clarify that a passage or phrase is not your own.
Paraphrasing. You will consider some basic guidelines for paraphrasing another writer's ideas and learn to recognise good paraphrasing style. View paraphrasing activity; Paraphrasing main points. You will practise selecting the main points from some short text extracts and paraphrase them in an appropriate way. View paraphrasing main points ...
A summary is written in your own words. It contains few or no quotes. A summary is always shorter than the original text, often about 1/3 as long as the original. It is the ultimate fat-free writing. An article or paper may be summarized in a few sentences or a couple of paragraphs. A book may be summarized in an article or a short paper.
The exercise below provides students with a text and asks them to paraphrase, summarize, and cite it. The instructor must then evaluate their work. To give students more control over the assignment, instructors can ask them to work with an Internet text of their own choosing. Students must understand the difference between paraphrasing and ...
Directions: On a separate piece of paper, write a paraphrase of each of the following passages. Try not to look back at the original passage. 1. "The Antarctic is the vast source of cold on our planet, just as the sun is the source of our heat, and it exerts tremendous control on our climate," [Jacques] Cousteau told the camera.
Paraphrasing Lesson 1 - how to paraphrase effectively [updated 2021] It starts by discussing the differences between quotation, paraphrase and summary. It takes students through the basics of identifying keywords, finding synonyms and then changing the grammatical structure. There is plenty of practice, all with efficient teacher's notes.
Paraphrasing Created by: Heran Zhang 3 Paraphrasing Exercise (The answers are on the next page.) Directions: Write a paraphrase of each of the following sentences or passages. 1. The student requested that the professor excuses her absence, but the professor refused. 2. International Center is hosting English Conversation classes.
In order to write your paragraph, use a combination of paraphrasing, summarizing, or quoting, as required. Refer to each text according to the reference given in brackets, and the corresponding line number. For example, you might say: The Terry Fox Foundation had nearly $19 million to give to cancer research during 200/2005. (Research, 13-14)
A paraphrase covers every point in the passage; a summary condenses and includes only main ideas. A paraphrase records ideas in the same order as the original passage; a summary changes the order of ideas when necessary to make the summary more coherent. A paraphrase does not interpret; a summary might explain or interpret.
Examples and Exercises for Understand Paraphrasing and Summarizing. Practice identifying appropriately paraphrased passages with the University of Arizona's Global Campus Writing Center Paraphrasing Activity. Practice summarizing and paraphrasing with this introductory exercise from the Owl of Purdue, answers provided.
Paraphrase. 1. The student requested that the professor excuses her absence, but the professor refused. Possible Solution: The professor denied the student's request for an excused absence. 2. There will be a music concert next to Vienna coffee shop.
Paraphrasing will also provide a lower Turnitin score than quoting since it incorporates your own academic voice. Summarizing is reserved for when you need to provide your reader with broad background information or a general overview of a topic, theory, practice, or a literary work or film. A short summary might be included in an introductory ...
The important skill of paraphrasing is initially interrogated in this lesson and eventually plans relating to summarizing and quoting will be added. There is an interactive equivalent to this plan, "Paraphrasing In a Pinch", which can be used in a classroom that has an electronic device for each student and a strong WiFi signal. The interactive plan can also be used to flip a classroom.
Summarizing. In many situations, you will not have to provide the level of detail that the original writer did. At such times, you should summarize, or remove minor details. Here's an example: Example: Overall, the first two quarters of 2008 have been profitable to the company. Nineteen of twenty departments report cutting costs at least ...