Breastfeeding Essays
The benefits and challenges of breastfeeding, the significance of breastfeeding in nursing: advantages, challenges, and interventions, breastfeeding vs. formula feeding, breastmilk is best for newborns, the advantages and the potential disadvantages or concerns associated with breastfeeding, breastfeeding in public, benefits of co-sleeping, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Breastfeeding — The Importance Of Breastfeeding And The Issue Of Breastfeeding In Public

The Importance of Breastfeeding and The Issue of Breastfeeding in Public
- Categories: Breastfeeding Breastfeeding in Public Motherhood
About this sample

Words: 2352 |
12 min read
Published: May 14, 2021
Words: 2352 | Pages: 5 | 12 min read
Bibliography
- Ballard, Olivia, and Ardythe L Morrow. “Human Milk Composition: Nutrients and Bioactive Factors.” Pediatric Clinics of North America, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Feb. 2013.
- “Benefits of Breastfeeding.” AAP.org.
- “Breastfeeding and Breast Milk.” Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- “Breastfeeding: Breast When United.” SUWANNEE RIVER AREA HEALTH EDUCATION CENTER, 13 Aug. 2018.
- Johnson, Tahra, et al. Breastfeeding State Laws.Lewis, Katherine. “Why Employers Should Provide a Lactation Room for Nursing Employees.” The Balance Careers, The Balance Careers, 29 Apr. 2019.
- Lucia, Carole Anderson, and Carole Anderson Lucia. “The Benefits of Breastfeeding.” Parents.“Making the Decision to Breastfeed.” Womenshealth.gov, 14 Mar. 2019.
- “Mother's Milk: NYC Braces for New Workplace Lactation Room Requirements.” Labor & Employment Law Blog, 18 Dec. 2018.Simon, Javier. “The Cost of Baby Formula.” SmartAsset, SmartAsset, 7 May 2019.
- “The Physiological Basis of Breastfeeding.” Infant and Young Child Feeding: Model Chapter for Textbooks for Medical Students and Allied Health Professionals., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 1 Jan. 1970.
- “Why Baby May Suddenly Refuse the Breast.” Why Baby May Suddenly Refuse the Breast | WIC Breastfeeding.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health Social Issues Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
5 pages / 2332 words
2 pages / 799 words
4 pages / 1991 words
4 pages / 2018 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Breastfeeding
In conclusion, breastfeeding is a natural and beneficial method of feeding infants. It provides numerous health benefits for both mother and child, including improved immune function, cognitive development, and reduced risk of [...]
Breastfeeding is a topic that often sparks strong opinions and debates among parents, healthcare professionals, and society as a whole. From the benefits of breast milk for infants to the social stigma surrounding nursing in [...]
In the research article, a qualitative data analysis method has been used in order to verify the main research question. The four reasons can be provided in support of the claim that it was a qualitative research method. Seven [...]
Breastfeeding in connection with intelligence has long been a study of scientists in psychological professions in the years succeeding a 1929 study on the subject. Argumentation has gone back and forth, with some arguing that [...]
He lowers his hand to reach down, and curves a strong grip around her small wrist, abruptly stopping her in her tracks. “What is it, what's troubling you?” he asked in an anxious voice once again. “It's...I'm pregnant!” Finally [...]
Louse-borne typhus is one of the oldest pernicious diseases, that has been haunting mankind since ages. Known by the many names such as “camp fever”, “war fever”, “jail fever” and “tabarillo” and confused with many other fevers [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Benefits of Breastfeeding Versus Formula-Feeding Essay
Introduction, history of breastfeeding, advantages of breastfeeding over bottle-feeding, advantages of bottle-feeding over breastfeeding, importance of research.
Nowadays, one of the most challenging tasks many young mothers have to face is the necessity of choosing between breastfeeding and formula/bottle-feeding. It is easy to surf the web and find several correlational, cohort, or experimental studies where different authors defend their positions on the chosen topic. On the one hand, breastfeeding is deemed preferable due to its perfect balance of nutrients, protection against allergies and diseases, and easy digestion for babies.
On the other hand, formula-feeding is characterized by certain merits, such as the possibility for another person to feed a baby anytime, a mother’s freedom to be involved in different activities or even start working, and no dependence on the mother-child diet. Although some mothers might still choose to bottle-feed their infants with formula due to practical concerns, research shows that breastfeeding is preferable due to its impact on maternal and child health.
The history of breastfeeding is as long as the existence of life on the planet. In ancient cultures and in modern times women continued to breastfeed children to nourish them. However, some cultures did not focus on breastfeeding as an intimate link between the mother and the child. For example, while most ancient civilizations had mothers feed their children, more structurally segregated Western European countries created the role of a wet nurse – a woman whose job was to breastfeed children of royal and noblewomen.
Various cultures assigned different meanings to the process of breastfeeding and followed their sets of rules to determine how, when, and where to feed children. In ancient times, Egyptian and Greek civilizations did not treat breastfeeding as a job fit only for common folk and allowed women of all social statuses to feed their children. Nevertheless, wet nurses still had a place in the culture and were respected for their work. In Japan, breastfeeding was common but declined in popularity in the 20th century due to the interest of mothers in modern medicine and artificial feeding options. However, with a well-thought-out campaign, the government was able to elevate breastfeeding to be the primary choice of mothers in the country.
Western countries faced similar challenges earlier, during the middle ages, and then again at the beginning of the 19th century. Here, the history of breastfeeding was firmly connected to the cultural aspects of these civilizations. Countries with a rigid societal structure viewed breastfeeding as a job for lower classes and the process became plagued with many preconceptions. The combination of men’s opinions on breastfeeding and their lack of medical knowledge pressured women into declining breastfeeding. Later efforts in raising the popularity of breastfeeding emphasized health benefits for mothers and children and an establishment of an emotional connection between the parent and the child.
The breastfeeding vs. formula-feeding dilemma appears as soon as women find out that they are pregnant. They have to evaluate all the pros and cons of their pregnancy outcomes, understand if they want to take sick leave, and recognize the relationship between baby feeding and health. All circumstances have to be taken into consideration to make the best decision. Both methods, breastfeeding and bottle-feeding, have their advantages and disadvantages.
Sometimes, it is hard to make a choice, and extensive research is required. This dilemma may be considered through the prism of health, social factors, emotional stability, and personal convenience. In this paper, special attention to the works by Belfort et al. (2013), Boué et al. (2018), Fallon, Komninou, Bennett, Halford, and Harrold (2017), Horta and Victoria (2013) will be made to clarify if the benefits of breastfeeding prevail over the benefits of bottle-feeding in terms of health.
The first months after a baby is born may be defined as the period when it is necessary to choose to breastfeed over bottle-feeding and establish a strong mother-child contact. There are many short- and long-term health benefits for both participants of a process that may be enhanced through its exclusivity and duration (Fallon et al., 2017). The representatives of the World Health Organization admit that exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months can decrease morbidity from allergies and gastrointestinal diseases due to the presence of nutritional benefits in human milk (Horta & Victoria, 2013).
For example, the nutrient n-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) found in breast milk aims at improving the functions of the brain (Belfort et al., 2013). Therefore, when the advantages of breastfeeding have to be identified, this point plays an important role.
In addition to nutrients, breastfeeding is a method in terms of which infants can control their condition and take as much amount of milk as they may need. They do not take more or less, just the portion they need at that moment. Mothers should take responsibility for the quality of milk they offer to their children and follow simple hygiene rules and schedules.
Another important aspect that underlines the necessity of breastfeeding is the protection of children against diseases and other health threats. Probiotics and prebiotics, also known as important live microorganisms, protect the body and establish a gut microbiota that promotes positive health outcomes through the creation of barriers to pathogens, improvement of metabolic function, and energy salvation (Boué et al., 2018). Stomach viruses and other conditions that may cause discomfort are also significantly reduced with breastfeeding.
Allergies pose another serious threat to infants. It is hard for a mother to comprehend what product is safe for a child and what ingredients should be avoided. Breast milk is characterized by appropriate natural filters and the possibility to avoid ingesting real food until the body is properly developed. It helps babies digest food and uses the enzymes in a mother’s milk to speed up digestion and avoid complications.
Finally, breastfeeding is preferable because of the promotion of the bond between a mother and a child, and its price. This process of feeding is a unique chance for mothers to be relieved from anxiety and develop an emotional attachment to their children. Sometimes, it is not enough for mothers to talk to their children, observe their smile, and touch them. Breastfeeding is an exclusive type of contact that is not available to other people, including even the closest family members. This relationship is priceless. Indeed, when talking about the price, it is also necessary to admit that compared to bottle-feeding, which requires buying special ingredients, bottles, and hygienic goods, breastfeeding is a cheap process with no additional products except a mother and a child being present in it.
However, despite all the benefits of breastfeeding, it is wrong to believe that formula-feeding is solely negative or does not have important characteristics that breast-feeding cannot offer. Many significant aspects should be considered by mothers who still have some doubts about their choice. For example, some mothers may be challenged by poor health or inappropriate health status for breastfeeding.
Mothers may suffer from the inability to breastfeed as they are unable to produce milk or the milk is of poor quality. In these cases, mothers still want to find new ways to be close to their children and support them and formula-feeding is one option that they can rely on on under any condition. No connection between the health problems of a mother and a child is observed. Bottle-feeding creates several good opportunities for mothers to stabilize their personal and professional lives. Fallon et al. (2017) admit that the choice of the formula is usually explained by breastfeeding management, not biological issues. Therefore, the advantages of bottle-feeding over breastfeeding in terms of health care are based on the emotional aspects and mental health of mothers.
An understanding of the differences between breastfeeding and formula-feeding should be based on thorough research. For example, a study developed by Horta and Victoria (2013) asserts that formula-fed children may have serious hormonal and insulin responses to feeding and an increased number of adipocytes compared to breast-fed children. Bottles have to be cleaned and properly stored to avoid the growth of bacteria that may harm a child (Boué et al., 2018). Finally, the study by Fallon et al. (2017) shows that mothers may feel guilt and stigma in case they choose formula as the main method of feeding. All these studies prove that research is a crucial step to comprehend the benefits of breastfeeding nowadays.
In general, it is hard to neglect the existing dilemma of breastfeeding vs. bottle-feeding. Mothers have to weigh all the pros and cons of both processes and understand what method is more appropriate to them. Regarding the chosen cohort and experimental studies and past research, it is concluded that despite several positive socio-cultural and emotional outcomes of formula-feeding, breastfeeding remains the preferred method due to its effects on health, the establishment of mother-child relations, and the promotion of the cognitive development of children.
Belfort, M. B., Rifas-Shiman, S. L., Kleinman, K. P., Guthrie, L. B., Bellinger, D. C., Taveras, E. M.,… Oken, E. (2013). Infant feeding and childhood cognition at ages 3 and 7 years: Effects of breastfeeding duration and exclusivity. JAMA Pediatrics, 167 (9), 836-844.
Boué, G., Cummins, E., Guillou, S., Antignac, J. P., Le Bizec, B., & Membré, J. M. (2018). Public health risks and benefits associated with breast milk and infant formula consumption. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 58 (1), 126-145.
Fallon, V., Komninou, S., Bennett, K. M., Halford, J. C., & Harrold, J. A. (2017). The emotional and practical experiences of formula‐feeding mothers. Maternal & Child Nutrition, 13 (4), 1-14.
Horta, B. L., & Victoria, C. G. (2013). Long-term effects of breastfeeding: A systematic review . Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, October 23). Benefits of Breastfeeding Versus Formula-Feeding. https://ivypanda.com/essays/benefits-of-breastfeeding-versus-formula-feeding/
"Benefits of Breastfeeding Versus Formula-Feeding." IvyPanda , 23 Oct. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/benefits-of-breastfeeding-versus-formula-feeding/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Benefits of Breastfeeding Versus Formula-Feeding'. 23 October.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Benefits of Breastfeeding Versus Formula-Feeding." October 23, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/benefits-of-breastfeeding-versus-formula-feeding/.
1. IvyPanda . "Benefits of Breastfeeding Versus Formula-Feeding." October 23, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/benefits-of-breastfeeding-versus-formula-feeding/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Benefits of Breastfeeding Versus Formula-Feeding." October 23, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/benefits-of-breastfeeding-versus-formula-feeding/.
- Infant Feeding Options in the First Six Months
- Natural Law in Mother-Child Medical Cases
- Self-Perception in Mother-Child Conversations
- Mother-Child Relationship - Psychology
- Some Facts About Breastfeeding
- Discussion: Barriers to Breastfeeding
- Short and Long Term Health Benefits of Breast-Feeding
- Breastfeeding and Bottle Feeding: Pros and Cons
- Breastfeeding Health Teaching Project
- Transportation and Public Health Issues
- Breastfeeding and Children Immunity
- Angelman Syndrome, Communication and Behavior
- At-Risk Children's Healthcare Programs
- Premature Infants and Their Challenges
- Pediatric Health Care and Insurance in the USA
Essays on Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is an important part of a baby’s life, providing essential nutrition and forming the bond between mother and child. It has numerous benefits for both mother and baby, including physical, emotional and psychological advantages. Breast milk contains all the nutrients a baby needs to grow strong and healthy. It also helps to boost immunity by passing on antibodies from the mother. Furthermore, breastfeeding can help reduce risks of certain illnesses such as asthma, obesity and diabetes in later life. For mothers it can lower their risk of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and osteoporosis.On an emotional level, breastfeeding encourages affectionate contact between mother and baby which promotes secure attachment that will benefit them throughout their lives. Psychologically speaking breastfeeding provides comfort when babies cry or are feeling stressed due to colic or teething pain; they feel safe when being held close while nursing which releases oxytocin (the bonding hormone) into both mom’s bloodstream as well as her baby’s making them feel relaxed in each other’s presence. In addition to these many benefits there are practical considerations too: breastfed babies tend to feed more often than formula-fed babies so parents do not have to worry about preparing bottles every time the little one gets hungry ” plus breastmilk is always at just the right temperature. Finally it is worth mentioning that breastfeeding reduces healthcare costs for families with no need for purchasing costly formulas or specialist bottles/accessories – saving money over time. All in all it is clear that breastfeeding should be encouraged whenever possible due its multiple positive impacts on both mother & child alike; however this does not mean parents who choose formula feeding cannot provide loving care for their children either.
Introduction The issue of whether women should adhere more to breastfeed their babies or resort to modern feeding methods such as bottle feeding remains a controversial and contentious topic that has sparked heated debate from both divides. While other people claim that breastfeeding is the only natural mechanisms that a mother can create the special […]
Breastfeeding is very important to a mother and child, yet rates are not as high as recommendations of AAP and WHO. Investigation of why more women do not breastfeed focus on breastfeeding challenges including issues related to breastfeeding in public. There is a need to implement strategies which support public breastfeeding and change stigma surrounding […]
Breastfeeding, also referred to as nursing, is the act of feeding infants using milk from the mother’s breasts. It is widely recognized as the optimal method for nourishing babies and is often preferred by mothers. Although breastfeeding is a natural occurrence, it can be challenging in the early stages of motherhood, emphasizing the importance of […]
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Search for samples, answers to your questions and flashcards.
- Enter your topic/question
- Receive an explanation
- Ask one question at a time
- Enter a specific assignment topic
- Aim at least 500 characters
- a topic sentence that states the main or controlling idea
- supporting sentences to explain and develop the point you’re making
- evidence from your reading or an example from the subject area that supports your point
- analysis of the implication/significance/impact of the evidence finished off with a critical conclusion you have drawn from the evidence.
- Open access
- Published: 26 November 2021
Women’s Perceptions and Experiences of Breastfeeding: a scoping review of the literature
- Bridget Beggs 1 ,
- Liza Koshy 1 &
- Elena Neiterman 1
BMC Public Health volume 21 , Article number: 2169 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
11k Accesses
22 Citations
4 Altmetric
Metrics details
Despite public health efforts to promote breastfeeding, global rates of breastfeeding continue to trail behind the goals identified by the World Health Organization. While the literature exploring breastfeeding beliefs and practices is growing, it offers various and sometimes conflicting explanations regarding women’s attitudes towards and experiences of breastfeeding. This research explores existing empirical literature regarding women’s perceptions about and experiences with breastfeeding. The overall goal of this research is to identify what barriers mothers face when attempting to breastfeed and what supports they need to guide their breastfeeding choices.
This paper uses a scoping review methodology developed by Arksey and O’Malley. PubMed, CINAHL, Sociological Abstracts, and PsychInfo databases were searched utilizing a predetermined string of keywords. After removing duplicates, papers published in 2010–2020 in English were screened for eligibility. A literature extraction tool and thematic analysis were used to code and analyze the data.
In total, 59 papers were included in the review. Thematic analysis showed that mothers tend to assume that breastfeeding will be easy and find it difficult to cope with breastfeeding challenges. A lack of partner support and social networks, as well as advice from health care professionals, play critical roles in women’s decision to breastfeed.
While breastfeeding mothers are generally aware of the benefits of breastfeeding, they experience barriers at individual, interpersonal, and organizational levels. It is important to acknowledge that breastfeeding is associated with challenges and provide adequate supports for mothers so that their experiences can be improved, and breastfeeding rates can reach those identified by the World Health Organization.
Peer Review reports
Public health efforts to educate parents about the importance of breastfeeding can be dated back to the early twentieth century [ 1 ]. The World Health Organization is aiming to have at least half of all the mothers worldwide exclusively breastfeeding their infants in the first 6 months of life by the year 2025 [ 2 ], but it is unlikely that this goal will be achieved. Only 38% of the global infant population is exclusively breastfed between 0 and 6 months of life [ 2 ], even though breastfeeding initiation rates have shown steady growth globally [ 3 ]. The literature suggests that while many mothers intend to breastfeed and even make an attempt at initiation, they do not always maintain exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life [ 4 , 5 ]. The literature identifies various barriers, including return to paid employment [ 6 , 7 ], lack of support from health care providers and significant others [ 8 , 9 ], and physical challenges [ 9 ] as potential factors that can explain premature cessation of breastfeeding.
From a public health perspective, the health benefits of breastfeeding are paramount for both mother and infant [ 10 , 11 ]. Globally, new mothers following breastfeeding recommendations could prevent 974,956 cases of childhood obesity, 27,069 cases of mortality from breast cancer, and 13,644 deaths from ovarian cancer per year [ 11 ]. Global economic loss due to cognitive deficiencies resulting from cessation of breastfeeding has been calculated to be approximately USD $285.39 billion dollars annually [ 11 ]. Evidently, increasing exclusive breastfeeding rates is an important task for improving population health outcomes. While public health campaigns targeting pregnant women and new mothers have been successful in promoting breastfeeding, they also have been perceived as too aggressive [ 12 ] and failing to consider various structural and personal barriers that may impact women’s ability to breastfeed [ 1 ]. In some cases, public health messaging itself has been identified as a barrier due to its rigid nature and its lack of flexibility in guidelines [ 13 ]. Hence, while the literature on women’s perceptions regarding breastfeeding and their experiences with breastfeeding has been growing [ 14 , 15 , 16 ], it offers various, and sometimes contradictory, explanations on how and why women initiate and maintain breastfeeding and what role public health messaging plays in women’s decision to breastfeed.
The complex array of the barriers shaping women’s experiences of breastfeeding can be broadly categorized utilizing the socioecological model, which suggests that individuals’ health is a result of the interplay between micro (individual), meso (institutional), and macro (social) factors [ 17 ]. Although previous studies have explored barriers and supports to breastfeeding, the majority of articles focus on specific geographic areas (e.g. United States or United Kingdom), workplaces, or communities. In addition, very few articles focus on the analysis of the interplay between various micro, meso, and macro-level factors in shaping women’s experiences of breastfeeding. Synthesizing the growing literature on the experiences of breastfeeding and the factors shaping these experiences, offers researchers and public health professionals an opportunity to examine how various personal and institutional factors shape mothers’ breastfeeding decision-making. This knowledge is needed to identify what can be done to improve breastfeeding rates and make breastfeeding a more positive and meaningful experience for new mothers.
The aim of this scoping review is to synthesize evidence gathered from empirical literature on women’s perceptions about and experiences of breastfeeding. Specifically, the following questions are examined:
What does empirical literature report on women’s perceptions on breastfeeding?
What barriers do women face when they attempt to initiate or maintain breastfeeding?
What supports do women need in order to initiate and/or maintain breastfeeding?
Focusing on women’s experiences, this paper aims to contribute to our understanding of women’s decision-making and behaviours pertaining to breastfeeding. The overarching aim of this review is to translate these findings into actionable strategies that can streamline public health messaging and improve breastfeeding education and supports offered by health care providers working with new mothers.
This research utilized Arksey & O’Malley’s [ 18 ] framework to guide the scoping review process. The scoping review methodology was chosen to explore a breadth of literature on women’s perceptions about and experiences of breastfeeding. A broad research question, “What does empirical literature tell us about women’s experiences of breastfeeding?” was set to guide the literature search process.
Search methods
The review was undertaken in five steps: (1) identifying the research question, (2) identifying relevant literature, (3) iterative selection of data, (4) charting data, and (5) collating, summarizing, and reporting results. The inclusion criteria were set to empirical articles published between 2010 and 2020 in peer-reviewed journals with a specific focus on women’s self-reported experiences of breastfeeding, as well as how others see women’s experiences of breastfeeding. The focus on women’s perceptions of breastfeeding was used to capture the papers that specifically addressed their experiences and the barriers that they may encounter while breastfeeding. Only articles written in English were included in the review. The keywords utilized in the search strategy were developed in collaboration with a librarian (Table 1 ). PubMed, CINAHL, Sociological Abstracts, and PsychInfo databases were searched for the empirical literature, yielding a total of 2885 results.
Search outcome
The articles deemed to fit the inclusion criteria ( n = 213) were imported into RefWorks, an online reference manager tool and further screened for eligibility (Fig. 1 ). After the removal of 61 duplicates and title/abstract screening, 152 articles were kept for full-text review. Two independent reviewers assessed the papers to evaluate if they met the inclusion criteria of having an explicit analytic focus on women’s experiences of breastfeeding.
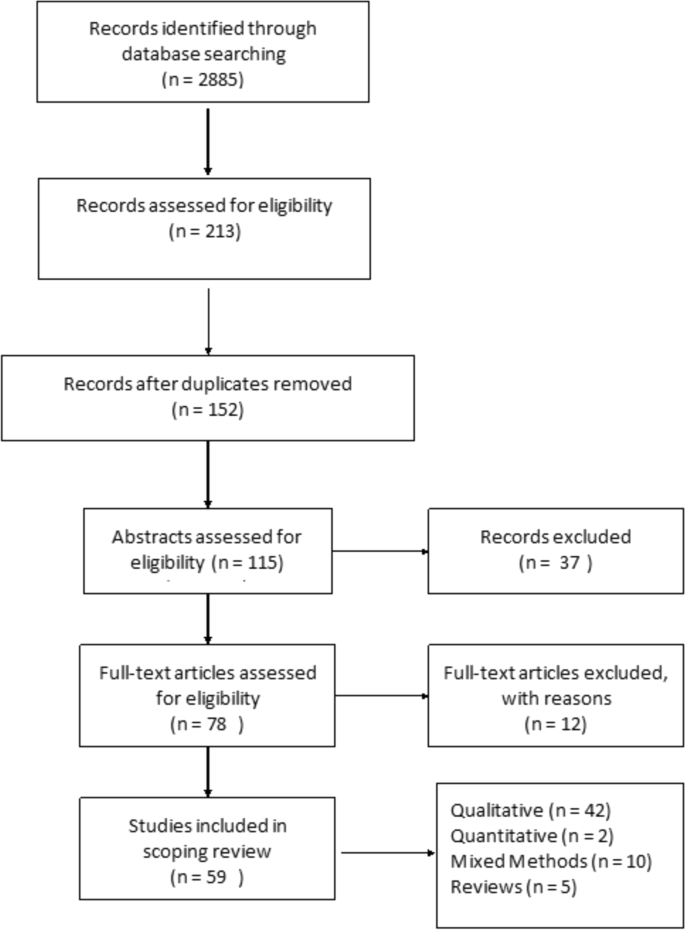
Prisma Flow Diagram
Quality appraisal
Consistent with scoping review methodology [ 18 ], the quality of the papers included in the review was not assessed.
Data abstraction
A literature extraction tool was created in MS Excel 2016. The data extracted from each paper included: (a) authors names, (b) title of the paper, (c) year of publication, (d) study objectives, (e) method used, (f) participant demographics, (g) country where the study was conducted, and (h) key findings from the paper.
Thematic analysis was utilized to identify key topics covered by the literature. Two reviewers independently read five papers to inductively generate key themes. This process was repeated until the two reviewers reached a consensus on the coding scheme, which was subsequently applied to the remainder of the articles. Key themes were added to the literature extraction tool and each paper was assigned a key theme and sub-themes, if relevant. The themes derived from the analysis were reviewed once again by all three authors when all the papers were coded. In the results section below, the synthesized literature is summarized alongside the key themes identified during the analysis.
In total, 59 peer-reviewed articles were included in the review. Since the review focused on women’s experiences of breastfeeding, as would be expected based on the search criteria, the majority of articles ( n = 42) included in the sample were qualitative studies, with ten utilizing a mixed method approach (Fig. 2 ). Figure 3 summarizes the distribution of articles by year of publication and Fig. 4 summarizes the geographic location of the study.
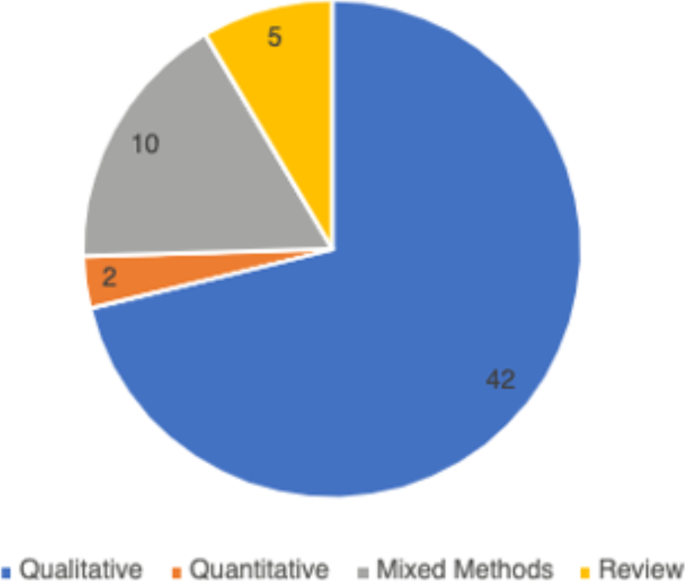
Types of Articles
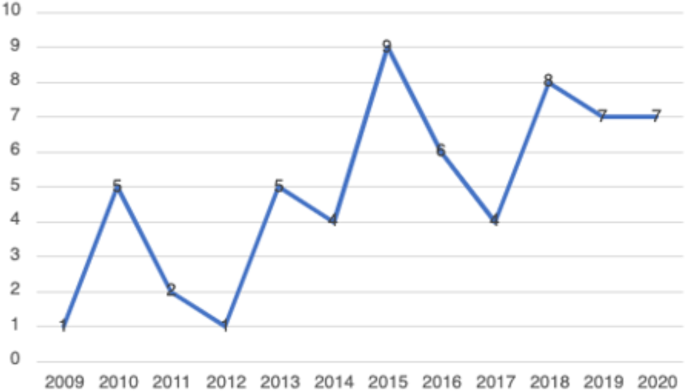
Years of Publication
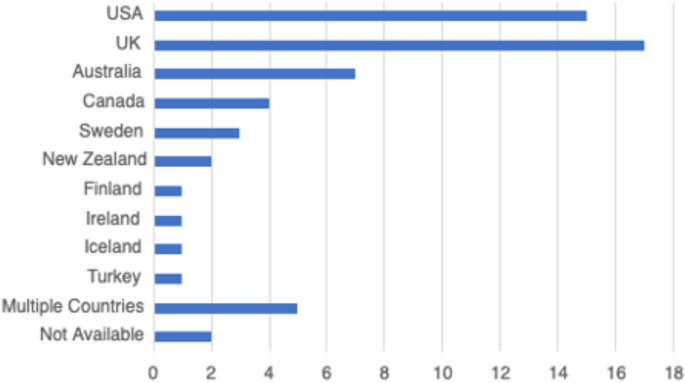
Countries of Focus Examined in Literature Review
Perceptions about breastfeeding
Women’s perceptions about breastfeeding were covered in 83% ( n = 49) of the papers. Most articles ( n = 31) suggested that women perceived breastfeeding as a positive experience and believed that breastfeeding had many benefits [ 19 , 20 ]. The phrases “breast is best” and “breastmilk is best” were repeatedly used by the participants of studies included in the reviewed literature [ 21 ]. Breastfeeding was seen as improving the emotional bond between the mother and the child [ 20 , 22 , 23 ], strengthening the child’s immune system [ 24 , 25 ], and providing a booster to the mother’s sense of self [ 1 , 26 ]. Convenience of breastfeeding (e.g., its availability and low cost) [ 19 , 27 ] and the role of breastfeeding in weight loss during the postpartum period were mentioned in the literature as other factors that positively shape mothers’ perceptions about breastfeeding [ 28 , 29 ].
The literature suggested that women’s perceptions of breastfeeding and feeding choices were also shaped by the advice of healthcare providers [ 30 , 31 ]. Paradoxically, messages about the importance and relative simplicity of breastfeeding may also contribute to misalignment between women’s expectations and the actual experiences of breastfeeding [ 32 ]. For instance, studies published in Canada and Sweden reported that women expected breastfeeding to occur “naturally”, to be easy and enjoyable [ 23 ]. Consequently, some women felt unprepared for the challenges associated with initiation or maintenance of breastfeeding [ 31 , 33 ]. The literature pointed out that mothers may feel overwhelmed by the frequency of infant feedings [ 26 ] and the amount as well as intensity of physical difficulties associated with breastfeeding initiation [ 33 ]. Researchers suggested that since many women see breastfeeding as a sign of being a “good” mother, their inability to breastfeed may trigger feelings of personal failure [ 22 , 34 ].
Women’s personal experiences with and perceptions about breastfeeding were also influenced by the cultural pressure to breastfeed. Welsh mothers interviewed in the UK, for instance, revealed that they were faced with judgement and disapproval when people around them discovered they opted out of breastfeeding [ 35 ]. Women recalled the experiences of being questioned by others, including strangers, when they were bottle feeding their infants [ 9 , 35 , 36 ].
Barriers to breastfeeding
The vast majority ( n = 50) of the reviewed literature identified various barriers for successful breastfeeding. A sizeable proportion of literature (41%, n = 24) explored women’s experiences with the physical aspects of breastfeeding [ 23 , 33 ]. In particular, problems with latching and the pain associated with breastfeeding were commonly cited as barriers for women to initiate breastfeeding [ 23 , 28 , 37 ]. Inadequate milk supply, both actual and perceived, was mentioned as another barrier for initiation and maintenance of breastfeeding [ 33 , 37 ]. Breastfeeding mothers were sometimes unable to determine how much milk their infants consumed (as opposed to seeing how much milk the infant had when bottle feeding), which caused them to feel anxious and uncertain about scheduling infant feedings [ 28 , 37 ]. Women’s inability to overcome these barriers was linked by some researchers to low self-efficacy among mothers, as well as feeling overwhelmed or suffering from postpartum depression [ 38 , 39 ].
In addition to personal and physical challenges experienced by mothers who were planning to breastfeed, the literature also highlighted the importance of social environment as a potential barrier to breastfeeding. Mothers’ personal networks were identified as a key factor in shaping their breastfeeding behaviours in 43 (73%) articles included in this review. In a study published in the UK, lack of role models – mothers, other female relatives, and friends who breastfeed – was cited as one of the potential barriers for breastfeeding [ 36 ]. Some family members and friends also actively discouraged breastfeeding, while openly questioning the benefits of this practice over bottle feeding [ 1 , 17 , 40 ]. Breastfeeding during family gatherings or in the presence of others was also reported as a challenge for some women from ethnic minority groups in the United Kingdom and for Black women in the United States [ 41 , 42 ].
The literature reported occasional instances where breastfeeding-related decisions created conflict in women’s relationships with significant others [ 26 ]. Some women noted they were pressured by their loved one to cease breastfeeding [ 22 ], especially when women continued to breastfeed 6 months postpartum [ 43 ]. Overall, the literature suggested that partners play a central role in women’s breastfeeding practices [ 8 ], although there was no consistency in the reviewed papers regarding the partners’ expressed level of support for breastfeeding.
Knowledge, especially practical knowledge about breastfeeding, was mentioned as a barrier in 17% ( n = 10) of the papers included in this review. While health care providers were perceived as a primary source of information on breastfeeding, some studies reported that mothers felt the information provided was not useful and occasionally contained conflicting advice [ 1 , 17 ]. This finding was reported across various jurisdictions, including the United States, Sweden, the United Kingdom and Netherlands, where mothers reported they had no support at all from their health care providers which made it challenging to address breastfeeding problems [ 26 , 38 , 44 ].
Breastfeeding in public emerged as a key barrier from the reviewed literature and was cited in 56% ( n = 33) of the papers. Examining the experiences of breastfeeding mothers in the United States, Spencer, Wambach, & Domain [ 45 ] suggested that some participants reported feeling “erased” from conversations while breastfeeding in public, rendering their bodies symbolically invisible. Lack of designated public spaces for breastfeeding forced many women to alter their feeding in public and to retreat to a private or a more secluded space, such as one’s personal car [ 25 ]. The oversexualization of women’s breasts was repeatedly noted as a core reason for the United States women’s negative experiences and feelings of self-consciousness about breastfeeding in front of others [ 45 ]. Studies reported women’s accounts of feeling the disapproval or disgust of others when breastfeeding in public [ 46 , 47 ], and some reported that women opted out of breastfeeding in public because they did not want to make those around them feel uncomfortable [ 25 , 40 , 48 ].
Finally, return to paid employment was noted in the literature as a significant challenge for continuation of breastfeeding [ 48 ]. Lack of supportive workplace environments [ 39 ] or inability to express milk were cited by women as barriers for continuing breastfeeding in the United States and New Zealand [ 39 , 49 ].
Supports needed to maintain breastfeeding
Due to the central role family members played in women’s experiences of breastfeeding, support from partners as well as female relatives was cited in the literature as key factors shaping women’s breastfeeding decisions [ 1 , 9 , 48 ]. In the articles published in Canada, Australia, and the United Kingdom, supportive family members allowed women to share the responsibility of feeding and other childcare activities, which reduced the pressures associated with being a new mother [ 19 , 20 ]. Similarly, encouragement, breastfeeding advice, and validation from healthcare professionals were identified as positively impacting women’s experiences with breastfeeding [ 1 , 22 , 28 ].
Community resources, such as peer support groups, helplines, and in-home breastfeeding support provided mothers with the opportunity to access help when they need it, and hence were reported to be facilitators for breastfeeding [ 19 , 22 , 33 , 44 ]. An increase in the usage of social media platforms, such as Facebook, among breastfeeding mothers for peer support were reported in some studies [ 47 ]. Public health breastfeeding clinics, lactation specialists, antenatal and prenatal classes, as well as education groups for mothers were identified as central support structures for the initiation and maintenance of breastfeeding [ 23 , 24 , 28 , 33 , 39 , 50 ]. Based on the analysis of the reviewed literature, however, access to these services varied greatly geographically and by socio-economic status [ 33 , 51 ]. It is also important to note that local and cultural context played a significant role in shaping women’s perceptions of breastfeeding. For example, a study that explored women’s breastfeeding experiences in Iceland highlighted the importance of breastfeeding in Icelandic society [ 52 ]. Women are expected to breastfeed and the decision to forgo breastfeeding is met with disproval [ 52 ]. Cultural beliefs regarding breastfeeding were also deemed important in the study of Szafrankska and Gallagher (2016), who noted that Polish women living in Ireland had a much higher rate of initiating breastfeeding compared to Irish women [ 53 ]. They attributed these differences to familial and societal expectations regarding breastfeeding in Poland [ 53 ].
Overall, the reviewed literature suggested that women faced socio-cultural pressure to breastfeed their infants [ 36 , 40 , 54 ]. Women reported initiating breastfeeding due to recognition of the many benefits it brings to the health of the child, even when they were reluctant to do it for personal reasons [ 8 ]. This hints at the success of public health education campaigns on the benefits of breastfeeding, which situates breastfeeding as a new cultural norm [ 24 ].
This scoping review examined the existing empirical literature on women’s perceptions about and experiences of breastfeeding to identify how public health messaging can be tailored to improve breastfeeding rates. The literature suggests that, overall, mothers are aware of the positive impacts of breastfeeding and have strong motivation to breastfeed [ 37 ]. However, women who chose to breastfeed also experience many barriers related to their social interactions with significant others and their unique socio-cultural contexts [ 25 ]. These different factors, summarized in Fig. 5 , should be considered in developing public health activities that promote breastfeeding. Breastfeeding experiences for women were very similar across the United Kingdom, United States, Canada, and Australia based on the studies included in this review. Likewise, barriers and supports to breastfeeding identified by women across the countries situated in the global north were quite similar. However, local policy context also impacted women’s experiences of breastfeeding. For example, maintaining breastfeeding while returning to paid employment has been identified as a challenge for mothers in the United States [ 39 , 45 ], a country with relatively short paid parental leave. Still, challenges with balancing breastfeeding while returning to paid employment were also noticed among women in New Zealand, despite a more generous maternity leave [ 49 ]. This suggests that while local and institutional policies might shape women’s experiences of breastfeeding, interpersonal and personal factors can also play a central role in how long they breastfeed their infants. Evidently, the importance of significant others, such as family members or friends, in providing support to breastfeeding mothers was cited as a key facilitator for breastfeeding across multiple geographic locations [ 29 , 34 , 48 ]. In addition, cultural beliefs and practices were also cited as an important component in either promoting breastfeeding or deterring women’s desire to initiate or maintain breastfeeding [ 15 , 29 , 37 ]. Societal support for breastfeeding and cultural practices can therefore partly explain the variation in breastfeeding rates across different countries [ 15 , 21 ]. Figure 5 summarizes the key barriers identified in the literature that inhibit women’s ability to breastfeed.
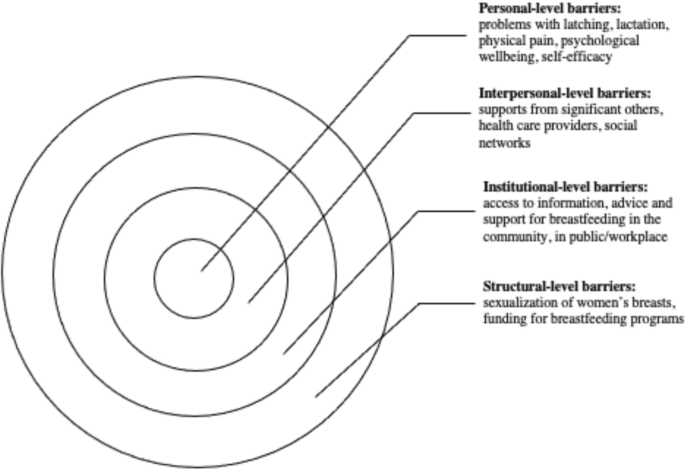
Barriers to Breastfeeding
At the individual level, women might experience challenges with breastfeeding stemming from various physiological and psychological problems, such as issues with latching, perceived or actual lack of breastmilk, and physical pain associated with breastfeeding. The onset of postpartum depression or other psychological problems may also impact women’s ability to breastfeed [ 54 ]. Given that many women assume that breastfeeding will happen “naturally” [ 15 , 40 ] these challenges can deter women from initiating or continuing breastfeeding. In light of these personal challenges, it is important to consider the potential challenges associated with breastfeeding that are conveyed to new mothers through the simplified message “breast is best” [ 21 ]. While breastfeeding may come easy to some women, most papers included in this review pointed to various challenges associated with initiating or maintaining breastfeeding [ 19 , 33 ]. By modifying public health messaging regarding breastfeeding to acknowledge that breastfeeding may pose a challenge and offering supports to new mothers, it might be possible to alleviate some of the guilt mothers experience when they are unable to breastfeed.
Barriers that can be experienced at the interpersonal level concern women’s communication with others regarding their breastfeeding choices and practices. The reviewed literature shows a strong impact of women’s social networks on their decision to breastfeed [ 24 , 33 ]. In particular, significant others – partners, mothers, siblings and close friends – seem to have a considerable influence over mothers’ decision to breastfeed [ 42 , 53 , 55 ]. Hence, public health messaging should target not only mothers, but also their significant others in developing breastfeeding campaigns. Social media may also be a potential medium for sharing supports and information regarding breastfeeding with new mothers and their significant others.
There is also a strong need for breastfeeding supports at the institutional and community levels. Access to lactation consultants, sound and practical advice from health care providers, and availability of physical spaces in the community and (for women who return to paid employment) in the workplace can provide more opportunities for mothers who want to breastfeed [ 18 , 33 , 44 ]. The findings from this review show, however, that access to these supports and resources vary greatly, and often the women who need them the most lack access to them [ 56 ].
While women make decisions about breastfeeding in light of their own personal circumstances, it is important to note that these circumstances are shaped by larger structural, social, and cultural factors. For instance, mothers may feel reluctant to breastfeed in public, which may stem from their familiarity with dominant cultural perspectives that label breasts as objects for sexualized pleasure [ 48 ]. The reviewed literature also showed that, despite the initial support, mothers who continue to breastfeed past the first year may be judged and scrutinized by others [ 47 ]. Tailoring public health care messaging to local communities with their own unique breastfeeding-related beliefs might help to create a larger social change in sociocultural norms regarding breastfeeding practices.
The literature included in this scoping review identified the importance of support from community services and health care providers in facilitating women’s breastfeeding behaviours [ 22 , 24 ]. Unfortunately, some mothers felt that the support and information they received was inadequate, impractical, or infused with conflicting messaging [ 28 , 44 ]. To make breastfeeding support more accessible to women across different social positions and geographic locations, it is important to acknowledge the need for the development of formal infrastructure that promotes breastfeeding. This includes training health care providers to help women struggling with breastfeeding and allocating sufficient funding for such initiatives.
Overall, this scoping review revealed the need for healthcare professionals to provide practical breastfeeding advice and realistic solutions to women encountering difficulties with breastfeeding. Public health messaging surrounding breastfeeding must re-invent breastfeeding as a “family practice” that requires collaboration between the breastfeeding mother, their partner, as well as extended family to ensure that women are supported as they breastfeed [ 8 ]. The literature also highlighted the issue of healthcare professionals easily giving up on women who encounter problems with breastfeeding and automatically recommending the initiation of formula use without further consideration towards solutions for breastfeeding difficulties [ 19 ]. While some challenges associated with breastfeeding are informed by local culture or health care policies, most of the barriers experienced by breastfeeding women are remarkably universal. Women often struggle with initiation of breastfeeding, lack of support from their significant others, and lack of appropriate places and spaces to breastfeed [ 25 , 26 , 33 , 39 ]. A change in public health messaging to a more flexible messaging that recognizes the challenges of breastfeeding is needed to help women overcome negative feelings associated with failure to breastfeed. Offering more personalized advice and support to breastfeeding mothers can improve women’s experiences and increase the rates of breastfeeding while also boosting mothers’ sense of self-efficacy.
Limitations
This scoping review has several limitations. First, the focus on “women’s experiences” rendered broad search criteria but may have resulted in the over or underrepresentation of specific findings in this review. Also, the exclusion of empirical work published in languages other than English rendered this review reliant on the papers published predominantly in English-speaking countries. Finally, consistent with Arksey and O’Malley’s [ 18 ] scoping review methodology, we did not appraise the quality of the reviewed literature. Notwithstanding these limitations, this review provides important insights into women’s experiences of breastfeeding and offers practical strategies for improving dominant public health messaging on the importance of breastfeeding.
Women who breastfeed encounter many difficulties when they initiate breastfeeding, and most women are unsuccessful in adhering to current public health breastfeeding guidelines. This scoping review highlighted the need for reconfiguring public health messaging to acknowledge the challenges many women experience with breastfeeding and include women’s social networks as a target audience for such messaging. This review also shows that breastfeeding supports and counselling are needed by all women, but there is also a need to tailor public health messaging to local social norms and culture. The role social institutions and cultural discourses have on women’s experiences of breastfeeding must also be acknowledged and leveraged by health care professionals promoting breastfeeding.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Wolf JH. Low breastfeeding rates and public health in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2003;93(12):2000–2010. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/ https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.93.12.2000
World Health Organization, UNICEF. Global nutrition targets 2015: Breastfeeding policy brief 2014.
United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF). Breastfeeding in the UK. 2019 [cited 2021 Apr 21]. Available from: https://www.unicef.org.uk/babyfriendly/about/breastfeeding-in-the-uk/
Semenic S, Loiselle C, Gottlieb L. Predictors of the duration of exclusive breastfeeding among first-time mothers. Res Nurs Health. 2008;31(5):428–441. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/ https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.20275
Hauck YL, Bradfield Z, Kuliukas L. Women’s experiences with breastfeeding in public: an integrative review. Women Birth. 2020;34:e217–27.
Hendaus MA, Alhammadi AH, Khan S, Osman S, Hamad A. Breastfeeding rates and barriers: a report from the state of Qatar. Int. J Women's Health. 2018;10:467–75 [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC6110662/.
Google Scholar
Ogbo FA, Ezeh OK, Khanlari S, Naz S, Senanayake P, Ahmed KY, et al. Determinants of exclusive breastfeeding cessation in the early postnatal period among culturally and linguistically diverse (CALD) Australian mothers. Nutrients. 2019;11(7):1611 [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/7/1611 .
Article Google Scholar
Ayton JE, Tesch L, Hansen E. Women’s experiences of ceasing to breastfeed: Australian qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(5):26234 [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://bmjopen.bmj.com/ .
Brown CRL, Dodds L, Legge A, Bryanton J, Semenic S. Factors influencing the reasons why mothers stop breastfeeding. Can J Public Heal. 2014;105(3):e179–e185. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/ https://doi.org/10.17269/cjph.105.4244
Sharma AJ, Dee DL, Harden SM. Adherence to breastfeeding guidelines and maternal weight 6 years after delivery. Pediatrics. 2014;134(Supplement 1):S42–S49. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: www.pediatrics.org/cgi/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-0646H
Walters DD, Phan LTH, Mathisen R. The cost of not breastfeeding: Global results from a new tool. Health Policy Plan. 2019;34(6):407–17 [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: https://academic.oup.com/heapol/article/34/6/407/5522499 .
Friedman M. For whom is breast best? Thoughts on breastfeeding, feminism and ambivalence. J Mother Initiat Res Community Involv. 2009;11(1):26–35 [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://jarm.journals.yorku.ca/index.php/jarm/article/viewFile/22506/20986 .
Blixt I, Johansson M, Hildingsson I, Papoutsi Z, Rubertsson C. Women’s advice to healthcare professionals regarding breastfeeding: “offer sensitive individualized breastfeeding support” - an interview study. Int Breastfeed J 2019;14(1):51. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://internationalbreastfeedingjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13006-019-0247-4
Obeng C, Dickinson S, Golzarri-Arroyo L. Women’s perceptions about breastfeeding: a preliminary study. Children. 2020;7(6):61 [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9067/7/6/61 .
Choudhry K, Wallace LM. ‘Breast is not always best’: South Asian women’s experiences of infant feeding in the UK within an acculturation framework. Matern Child Nutr. 2012;8(1):72–87. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/ https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1740-8709.2010.00253.x
Da Silva TD, Bick D, Chang YS. Breastfeeding experiences and perspectives among women with postnatal depression: a qualitative evidence synthesis. Women Birth. 2020;33(3):231–9.
Kilanowski JF. Breadth of the socio-ecological model. J Agromedicine. 2017;22(4):295–7 [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?journalCode=wagr20 .
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol Theory Pract. 2005;8(1):19–32 [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?journalCode=tsrm20 .
Brown A, Lee M. An exploration of the attitudes and experiences of mothers in the United Kingdom who chose to breastfeed exclusively for 6 months postpartum. Breastfeed Med. 2011;6(4):197–204. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://www.liebertpub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2010.0097
Morns MA, Steel AE, Burns E, McIntyre E. Women who experience feelings of aversion while breastfeeding: a meta-ethnographic review. Women Birth. 2021;34:128–35.
Jackson KT, Mantler T, O’Keefe-McCarthy S. Women’s experiences of breastfeeding-related pain. MCN Am J Matern Nurs. 2019;44(2):66–72 [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://journals.lww.com/00005721-201903000-00002 .
Burns E, Schmied V, Sheehan A, Fenwick J. A meta-ethnographic synthesis of women’s experience of breastfeeding. Matern Child Nutr. 2009;6(3):201–219. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/ https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1740-8709.2009.00209.x
Claesson IM, Larsson L, Steen L, Alehagen S. “You just need to leave the room when you breastfeed” Breastfeeding experiences among obese women in Sweden - A qualitative study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018;18(1):1–10. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://link.springer.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-017-1656-2
Asiodu IV, Waters CM, Dailey DE, Lyndon • Audrey. Infant feeding decision-making and the influences of social support persons among first-time African American mothers. Matern Child Health J. 2017;21:863–72.
Forster DA, McLachlan HL. Women’s views and experiences of breast feeding: positive, negative or just good for the baby? Midwifery. 2010;26(1):116–25.
Demirci J, Caplan E, Murray N, Cohen S. “I just want to do everything right:” Primiparous Women’s accounts of early breastfeeding via an app-based diary. J Pediatr Heal Care. 2018;32(2):163–72.
Furman LM, Banks EC, North AB. Breastfeeding among high-risk Inner-City African-American mothers: a risky choice? Breastfeed Med. 2013;8(1):58–67. [cited 2021 Apr 20]Available from: http://www.liebertpub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2012.0012
Cottrell BH, Detman LA. Breastfeeding concerns and experiences of african american mothers. MCN Am J Matern Nurs. 2013;38(5):297–304 [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://journals.lww.com/00005721-201309000-00009 .
Wambach K, Domian EW, Page-Goertz S, Wurtz H, Hoffman K. Exclusive breastfeeding experiences among mexican american women. J Hum Lact. 2016;32(1):103–111. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/0890334415599400
Regan P, Ball E. Breastfeeding mothers’ experiences: The ghost in the machine. Qual Health Res. 2013;23(5):679–688. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732313481641
Hinsliff-Smith K, Spencer R, Walsh D. Realities, difficulties, and outcomes for mothers choosing to breastfeed: Primigravid mothers experiences in the early postpartum period (6-8 weeks). Midwifery. 2014;30(1):e14–9.
Palmér L. Previous breastfeeding difficulties: an existential breastfeeding trauma with two intertwined pathways for future breastfeeding—fear and longing. Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2019;14(1) [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?journalCode=zqhw20 .
Francis J, Mildon A, Stewart S, Underhill B, Tarasuk V, Di Ruggiero E, et al. Vulnerable mothers’ experiences breastfeeding with an enhanced community lactation support program. Matern Child Nutr 2020;16(3):16. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12957
Palmér L, Carlsson G, Mollberg M, Nyström M. Breastfeeding: An existential challenge - Women’s lived experiences of initiating breastfeeding within the context of early home discharge in Sweden. Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being 2010;5(3). [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?journalCode=zqhw20https://doi.org/ https://doi.org/10.3402/qhw.v5i3.5397
Grant A, Mannay D, Marzella R. ‘People try and police your behaviour’: the impact of surveillance on mothers and grandmothers’ perceptions and experiences of infant feeding. Fam Relationships Soc. 2018;7(3):431–47.
Thomson G, Ebisch-Burton K, Flacking R. Shame if you do - shame if you don’t: women’s experiences of infant feeding. Matern Child Nutr. 2015;11(1):33–46. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/ https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12148
Dietrich Leurer M, Misskey E. The psychosocial and emotional experience of breastfeeding: reflections of mothers. Glob Qual. Nurs Res. 2015;2:2333393615611654 [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28462320 .
Fahlquist JN. Experience of non-breastfeeding mothers: Norms and ethically responsible risk communication. Nurs Ethics. 2016;23(2):231–241. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733014561913
Gross TT, Davis M, Anderson AK, Hall J, Hilyard K. Long-term breastfeeding in African American mothers: a positive deviance inquiry of WIC participants. J Hum Lact. 2017;33(1):128–139. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/0890334416680180
Spencer RL, Greatrex-White S, Fraser DM. ‘I thought it would keep them all quiet’. Women’s experiences of breastfeeding as illusions of compliance: an interpretive phenomenological study. J Adv Nurs. 2015;71(5):1076–1086. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/ https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.12592
Twamley K, Puthussery S, Harding S, Baron M, Macfarlane A. UK-born ethnic minority women and their experiences of feeding their newborn infant. Midwifery. 2011;27(5):595–602.
PubMed Google Scholar
Lutenbacher M, Karp SM, Moore ER. Reflections of Black women who choose to breastfeed: influences, challenges, and supports. Matern Child Health J. 2016;20(2):231–9.
Dowling S, Brown A. An exploration of the experiences of mothers who breastfeed long-term: what are the issues and why does it matter? Breastfeed Med. 2013;8(1):45–52. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://www.liebertpub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1089/bfm.2012.0057
Fox R, McMullen S, Newburn M. UK women’s experiences of breastfeeding and additional breastfeeding support: a qualitative study of baby Café services. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2015;15(1):147. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://bmcpregnancychildbirth.biomedcentral.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0581-5
Spencer B, Wambach K, Domain EW. African American women’s breastfeeding experiences: cultural, personal, and political voices. Qual Health Res. 2015;25(7):974–987. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732314554097
McBride-Henry K. The influence of the They: An interpretation of breastfeeding culture in New Zealand. Qual Health Res. 2010;20(6):768–777. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732310364220
Newman KL, Williamson IR. Why aren’t you stopping now?!’ Exploring accounts of white women breastfeeding beyond six months in the east of England. Appetite. 2018 Oct;1(129):228–35.
Dowling S, Pontin D. Using liminality to understand mothers’ experiences of long-term breastfeeding: ‘Betwixt and between’, and ‘matter out of place.’ Heal (United Kingdom). 2017;21(1):57–75. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/1363459315595846
Payne D, Nicholls DA. Managing breastfeeding and work: a Foucauldian secondary analysis. J Adv Nurs. 2010;66(8):1810–1818. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/ https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2009.05156.x
Keely A, Lawton J, Swanson V, Denison FC. Barriers to breast-feeding in obese women: a qualitative exploration. Midwifery. 2015;31(5):532–9.
Afoakwah G, Smyth R, Lavender DT. Women’s experiences of breastfeeding: A narrative review of qualitative studies. Afr J Midwifery Womens Health. 2013 ;7(2):71–77. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: https://www.magonlinelibrary.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.12968/ajmw.2013.7.2.71
Símonardóttir S. Getting the green light: experiences of Icelandic mothers struggling with breastfeeding. Sociol Res Online. 2016;21(4):1.
Szafranska M, Gallagher DL. Polish women’s experiences of breastfeeding in Ireland. Pract Midwife. 2016;19(1):30–2 [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: https://europepmc.org/article/med/26975131 .
Pratt BA, Longo J, Gordon SC, Jones NA. Perceptions of breastfeeding for women with perinatal depression: a descriptive phenomenological study. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2020;41(7):637–644. [cited 2021 Apr 21] Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1080/01612840.2019.1691690
Durmazoğlu G, Yenal K, Okumuş H. Maternal emotions and experiences of mothers who had breastfeeding problems: a qualitative study. Res Theory Nurs Pract. 2020;34(1):3–20. [cited 2021 Apr 20] Available from: http://connect.springerpub.com/lookup/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1891/1541-6577.34.1.3
Burns E, Triandafilidis Z. Taking the path of least resistance: a qualitative analysis of return to work or study while breastfeeding. Int Breastfeed J. 2019;14(1):1–13.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the assistance of Jackie Stapleton, the University of Waterloo librarian, for her assistance with developing the search strategy used in this review.
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Public Health Sciences, University of Waterloo, 200 University Ave West, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1, Canada
Bridget Beggs, Liza Koshy & Elena Neiterman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
BB was responsible for the formal analysis and organization of the review. LK was responsible for data curation, visualization and writing the original draft. EN was responsible for initial conceptualization and writing the original draft. BB and LK were responsible for reviewing and editing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
BB is completing her Bachelor of Science (BSc) degree at the School of Public Health Sciences at the University of Waterloo.
LK is completing her Bachelor of Public Health (BPH) degree at the School of Public Health Sciences at the University of Waterloo.
EN (PhD), is a continuing lecturer at the School of Public Health Sciences at the University of Waterloo. Her areas of expertise are in women’s reproductive health and sociology of health, illness, and healthcare.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bridget Beggs .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Beggs, B., Koshy, L. & Neiterman, E. Women’s Perceptions and Experiences of Breastfeeding: a scoping review of the literature. BMC Public Health 21 , 2169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-12216-3
Download citation
Received : 23 June 2021
Accepted : 10 November 2021
Published : 26 November 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-12216-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Breastfeeding
- Experiences
- Public health
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Nursing Essay Examples

Nursing Essay Examples That Will Help You Write a Stellar Paper
Published on: May 6, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

Share this article
Many nursing students struggle with writing effective nursing essays, which are an essential part of their education and professional development.
Poor essay writing skills can lead to low grades and an inability to effectively communicate important information.
This blog provides a comprehensive guide to writing nursing essays with examples and tips for effective writing. Whether you are a nursing student or a professional looking to improve your writing skills, this blog has something for you.
By following the tips and examples provided, you can write compelling nursing essays that showcase your dedication to the field.
Let’s get started.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Nursing Essay?
A nursing essay is a type of academic writing that aims to explore a particular topic related to nursing. It also presents a clear and concise argument or viewpoint supported by evidence.
Nursing essays can take many forms, including:
- Descriptive essays
- Reflective essays
- Analytical essays
- Persuasive essays
What is the Importance of the Nursing Essay?
Nursing essays are important for several reasons. First, they help nursing students develop critical thinking skills by requiring them to analyze and evaluate information.
Second, they help students develop research skills by requiring them to locate and use credible sources to support their arguments.
Third, nursing essays help students develop communication skills by requiring them to present their ideas clearly and concisely in writing. Finally, nursing essays are important for nursing education because they prepare students for the types of writing.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
To help students better understand how to write nursing essays, it can be helpful to review examples.
Below are some examples of nursing essays.
Nursing School Essay Examples
College Nursing Essay Examples
Graduate Nursing Essay Examples
Nursing Scholarship Essay Examples
Nursing Essay Conclusion Examples
Nursing Essay Examples of Different Fields
Nursing is a diverse field with many different specialties and areas of focus. As a result, nursing essays can take many different forms and cover a wide range of topics.
Given below are some examples of different types of nursing essays:
Personal Philosophy Of Nursing - Essay Examples
Cal State Fullerton Nursing Essay Examples
Evidence Based Practice Nursing In Medical Field - Essay Examples
Leadership In Nursing And Healthcare Professionals - Essay Examples
Principles Of Professional Practice Of Nursing Professionals And Pharmacists
If you're seeking additional examples of nursing essays, you're in luck!
Below are some more examples that can help you gain a better understanding of nursing essays:
Health Care And Reflective Models For Nursing - Essay Examples
History Of Nursing Essay Examples
Ethical Dilemma In Nurses Work - Essay Examples
Mental Health Nursing Essay Examples
Why I Want To Be A Nurse Essay
Working In A Team And Collaboration In Nursing
How to Write a Nursing Essay
Writing a nursing essay can seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be a rewarding experience.
Here are the key steps involved in writing a nursing essay:
Understanding the Topic and Question
The first step in writing a nursing essay is to carefully read and understand the topic and question.
This will help you determine what information you need to research and include in your essay. Make sure you understand any key terms or concepts related to the topic. Consider different perspectives or viewpoints that may be relevant.
Researching the Topic
Once you have a clear understanding of the topic and question, it's time to research.
Start by gathering information from credible sources such as academic journals, textbooks, and government websites.
Consider both primary and secondary sources, and make sure to take detailed notes as you read.
Organizing and Outlining the Essay
Once you have completed your research, it's time to organize your ideas and create an outline for your essay.
Start by identifying the main points or arguments you want to make, and then organize them into a logical order that flows well.
Your outline should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Writing the Essay
With your outline in place, it's time to start writing your essay. Make sure to follow your outline closely, and use clear and concise language that effectively communicates your ideas.
Use evidence from your research to support your arguments, and cite your sources appropriately.
Editing and Revising the Essay
Once you have completed a first draft of your essay, take some time to edit and revise it. Look for any errors in grammar, spelling, or punctuation, and make sure your essay is well-organized and flows well.
Consider asking a peer or instructor to review your essay and provide feedback.
What To Include In Your Nursing Essay
When writing a nursing essay, there are several key elements that you should include. Here are some important things to keep in mind:
- Introduction
Your introduction should provide a brief overview of the topic and purpose of your essay. It should also include a clear thesis statement that presents your main argument or point of view.
- Background Information
Provide some background information on the topic to help the reader better understand the context of your essay. This can include relevant statistics, historical information, or other contextual details.
- Evidence and Examples
Use evidence and examples from your research to support your arguments and demonstrate your knowledge of the topic. Make sure to cite your sources appropriately and use a variety of sources to strengthen your argument.
- Analysis and Evaluation
Provide analysis and evaluation of the evidence and examples you've presented. This can include discussing strengths and weaknesses, comparing and contrasting different viewpoints, or offering your own perspective on the topic.
Your conclusion should summarize the main points of your essay and restate your thesis statement. It should also offer some final thoughts or suggestions for further research or action.
Nursing Essay Topic Ideas
Choosing a topic for your nursing essay can be challenging, but there are many areas in the field that you can explore. Here are some nursing essay topic ideas to consider:
- The role of technology in nursing practice
- The impact of cultural diversity on healthcare delivery
- Nursing leadership and management in healthcare organizations
- Ethical issues in nursing practice
- The importance of patient-centered care in nursing practice
- The impact of evidence-based practice on nursing care
- The role of nursing in promoting public health
- Nursing education and the importance of lifelong learning
- The impact of nursing shortages on healthcare delivery
- The importance of communication in nursing practice
These are just a few ideas to get you started. You can also explore other topics related to nursing that interest you or align with your academic or professional goals.
Remember to choose a topic that is relevant, interesting, and feasible to research and write about.
Tips for Writing an Effective Nursing Essay
Writing a successful nursing essay requires careful planning, research, and attention to detail. Here are some tips to help you write an effective nursing essay:
- Writing Concisely and Clearly
Nursing essays should be written in clear and concise language, avoiding unnecessary jargon or technical terms. Use simple language and short sentences to help ensure that your ideas are communicated clearly and effectively.
- Stating a Clear Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly state your main argument and provide a roadmap for the rest of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and located at the end of your introduction.
- Using Proper Citation and Referencing
Citing and referencing your sources is crucial in any academic writing, including nursing essays. Make sure to use proper citation and referencing styles, such as APA or MLA. Include a reference list or bibliography at the end of your essay.
- Seeking Feedback and Revising
Before submitting your nursing essay, seek feedback from peers, professors, or writing tutors. Use their feedback to revise and improve your essay. Make sure that it is well-structured, coherent, and effectively communicates your point of view.
By following these tips, you can write a nursing essay that demonstrates your knowledge and skills in the field.
In conclusion, writing a successful nursing essay requires careful planning, research, and attention to detail.
To showcase your knowledge in the field of nursing, it is important to have a clear understanding of the topic at hand. When writing your nursing essay, be sure to include relevant examples, incorporate current research, and use proper citation and referencing.
And remember , seeking feedback and revising your essay is key to ensuring that it effectively communicates your ideas and arguments.
If you need help with your nursing essay or any other type of academic writing, consider using our AI essay writer .
Our nursing essay writing service can provide personalized support to help you succeed in your academic goals.
So, why wait? Contact us to get college essay writing help today!
Cathy A. (Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Law
Free Breastfeeding Essay Example
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Law , Criminal Justice , Parents , Breastfeeding , Family , Children , Health , Women
Words: 1200
Published: 03/21/2020
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
The breastfeeding of a baby by the mother is an important act of nurture that deserves to be encouraged for the interests of both the child and maternal health. Mothers are supposed to breastfeed their babies sparingly to assure them of normal health and proper growth and development. Many organizations such as the WHO, the CDC as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics encourage extended baby breastfeeding as a way of ensuring the health of both the child and the mother and as a way of mitigating public health problems (Ketan & Ketan 2005). Doctors and medical experts usually state that for the first six months of a baby’s life, he or she should be exclusively fed the mother’s milk. This is because the mother’s milk contains all the nutrients that are required for the baby’s growth and development during this crucial stage of life (Lawrence & Lawrence, 2010). In addition, breastfeeding enables the mother and the baby to establish an unbreakable bond and connection that is actually exhibited throughout the child’s life (Ketan & Ketan 2005). There are no designated times for breastfeeding. For instance, a mother cannot plan to be breastfeeding her baby at particular times of the day and not breastfeeding at other times. Breastfeeding is, in fact, an activity that often occurs or takes place randomly whenever the baby gets hungry. Unfortunately, mothers have increasingly found themselves unable to conduct this basic act of nurture due to several legal restrictions and hurdles. Mothers sometimes find themselves unable to breastfeed their babies especially when they are in an environment that discourages or completely disallows breastfeeding of babies (Li et al., 2004). This can be equated to denying a baby of its basic right of food. Breastfeeding a baby is a harmless activity that does not encompass any element of indecency as many of the individuals and organizations who oppose breastfeeding, for instance in public places claim. Many mothers in the state of Indiana occasionally find themselves in trouble when they are caught breastfeeding in what are deemed to be “inappropriate places’. Many may even find themselves being publicly embarrassed and being publicly told to leave certain premises when they are caught breastfeeding and are deemed to be engaging in immoral or lewd conduct (Li et al., 2004). This has not only been happening in Indiana but also in other states throughout the country. There has been increased advocacy for new laws that remove some of these restrictive measures of breastfeeding and mothers to be given freedom to breastfeed their babies without any restrictions It is proposed that a new law be passed in the state of Indian giving all mothers the freedom to breastfeed their babies at any location or place where they are legally allowed or authorized to be. This means that if a mother and a baby are currently in a location that they have the legal authorization to be in, the mother has the right and freedom to breastfeed her baby at any time and the organization or individual who is in charge of the location has no right whatsoever to prohibit the mother from breastfeeding the baby. It is proposed that the new law also makes it clear that the breastfeeding by a mother or the exposure of the mother’s breast should not be considered as unlawful, indecent, lewd or immoral. It should henceforth be considered as a basic act of nurture that facilitates the attainment of good health to the child, mother and the public in general since this child will be a key member of the public in the future and for him to be useful member of this society, he or she must have good health. This law shall prohibit any entity or individual from harassing, restricting and penalizing a mother who has breastfed her child. In addition, the law will restrict individuals or entities from requesting mothers to move to different locations to breastfeed the baby if the mother and the baby are authorized to be in that particular location at that particular time. Requesting a mother to move will comprise of law violation. It is also proposed that a mother who is currently breastfeeding should be excused for state and federal duties that she is obligated to until she has stopped breastfeeding. This includes jury duty. The mother will not be obliged to the mandatory jury duty until it has been established that she is no longer breastfeeding. At the workplace, it is proposed that mothers be given sufficient break time to express milk for their babies. The employer shall take the initiative of providing an efficient space or setting where the mother can conduct this activity in privacy. No mother shall be denied a break after a sufficient working time to express milk for the baby. Any employer who violates this law can be subjected to a significant legal penalty. Any individual who goes against the stipulations of this law should be subjected to civil court action, and an applicable fine should be enforced. A mother who makes an official complaint to the district attorney or prosecutor or the state attorney should be listened to, and if viable, court action should be taken against the individual accused of contravening the law. The departments of children and human services in the state should be at the forefront of developing as well as distributing various material that give information on the rights of a woman to breastfeed her child whether it is in a private or public space. Organizations that particularly feature public accommodation elements should be properly educated on why breastfeeding is an important activity that should never be discouraged. This proposal is the first step towards improving maternal and should health in the state of Indiana. Many individuals do not realize the benefits that can be accrued from proper breastfeeding. It is not just the baby who benefits but the mother benefits also. This leads to an overall achievement of maternal and child health. The enactment of such a law in one state will without a doubt stimulate or encourage another state to move towards the same direction. It is unimaginable the number of states where mothers and their children have been silently suffering due to restrictions against breastfeeding when the activity is indeed a basic act of nurture that every individual in the society goes through. For this proposal to grow and become a bill that can be brought before the house, it will require the support of not only mothers who are the main stakeholders but nurses and other health experts throughout the state. Public health organizations as well as women and child welfare organizations should take an active part in supporting this proposal so that it can eventually become law.
Ketan, G., & Ketan, S. (2005). American Academy of Pediatrics: Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Pediatrics, 115(2), 496-506. Lawrence, R. A., & Lawrence, R. M. (2010). Breastfeeding: a guide for the medical professional. Elsevier Health Sciences. Li, R., Hsia, J., Fridinger, F., Hussain, A., Benton-Davis, S., & Grummer-Strawn, L. (2004). Public beliefs about breastfeeding policies in various settings. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 104(7), 1162-1168.

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 2054
This paper is created by writer with
ID 285423988
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Free culture essay sample, potential solutions to water supply problems in africa report sample, contract law case study case study, disease in the renaissance essay samples, free essay on use of self concept by marketers in implementing effective marketing strategies, the discreet bully critical thinking template for faster writing, a level essay on combating terrorism for free use, question answer on korean philosopher chinul, free research paper on the psychological effects of abortion, the loves of the gods a sample essay for inspiration mimicking, miss julie essays, strindberg essays, marcus garvey essays, tanya essays, merit pay essays, kopp essays, bully essays, supremacy essays, gurgle essays, rugby union essays, coliseum essays, delineation essays, hord essays, blasius essays, diffusional essays, strickler essays, leipsic essays, storks essays, beamed essays, gyneco essays, libreville essays, god of abraham essays, cerebral hemisphere essays, berz essays, warga essays, human overpopulation essays, trover essays, gibbert essays, wiencke essays, franchisor research papers, eightfold research papers, life after death research papers, trade unions research papers.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
The Study Blog
Term Paper Writing Help

If you aren't sure whether you are good at expressing yourself through writing, then if you find it difficult to do so (e.g., when trying to write an english essay), we can help you overcome those obstacles by assisting you in improving your communication through writing. We help students compose essays or other types of papers for their courses. Now is the time to come visit us!
How to Overcome the Complexity of a Nursing Essay
There aren't many alternatives for professional translations. Before writing a good summary of something, you need to know your subject well enough to be able to write an accurate one. A research paper requires mastery of research language, a deep understanding of their subjects to be able to write about them clearly, and a careful consideration of possible problems before proposing solutions. Students often have trouble understanding medical terminology when they first encounter it, because they have never heard of these words before. When writing a cohesive psychology essay, students must be familiar with some psychological concepts. We have a wealth of experience under our belt, so we know where they need help. Although you may be able to find better deals elsewhere, there is no way to tell if these sites offer superior customer service and top-quality results. Read customer reviews before making any online purchases. If you don't think there's a market for them, it's perhaps best to skip them.
Professional Help from Copywriters
If you would like us to write anything from an essay in history to a term paper for you, we’d be happy to oblige. When writing something, there's a precise formula for choosing the best word. You can rest assured that you'll receive an expertly written paper from those who know exactly what they're doing. No need to write anything down today; there are no reasons why you shouldn't let others edit your document for you. Don't waste your time trying to convince them to do it for you, instead, invest it in something more productive! Order term papers online and go there! Founded in a simple belief that we are capable of delivering top-quality content to you, we offer a range of guarantees. Test it out yourself! The results must be presented after all the research has been completed.
Cheap Business Essay Writing Services
Before being accepted into our company, we underwent extensive background checks. Check their credentials to confirm that they have been writing professionally for some time. If they are members of professional associations, check, for instance.

Fun Tips to Spend Orthodox Easter Away from Home
In "Student Life"
Welcome to the New Bloggers
In "Degree Essentials"
Mastering Warwick as a Postgraduate
In "Looking After You"
Comments are closed.
Copyright, 2023

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In conclusion, breastfeeding is a natural and beneficial method of feeding infants. It provides numerous health benefits for both mother and child, including improved immune function, cognitive development, and reduced risk of diseases. Despite the clear advantages, there are still misconceptions and societal barriers that prevent many women ...
Breastfeeding Anthropology. Breastfeeding is an action that is bio cultural and biosocial in nature. Breastfeeding is a biological process that involves a woman providing milk for an infant. Culturally speaking, breastfeeding is not always an action by the biological mother. In some cases, the mother needs to return to work not long after birth.
Cognitive benefits. In addition to the nutritional and immunological benefits of breast milk, breastfeeding may help preemies get ahead intellectually. Breast milk is associated with increases in child cognitive ability and educational achievements. Cognitive development of social and psychomotor skills gains increases with the consumption and ...
One of the main benefits of breastfeeding is the provision of essential nutrients. This is due to the fact that the mother's milk contains all the necessary components that ensure the complete and correct development of the baby (1, 6). In addition, they help to reduce the possibility of problems with the digestive system, such as colic (3).
The stigma surrounding breastfeeding is further aggravated by the fact that as the society continues to view or regard the practice as out of place, they have become internalised into the cultural taboos especially for young mothers (Chong, 2015). Studies exploring some stigma surrounding breastfeeding and its effect on child health have revealed that through stigma, women are more embarrassed ...
Persuasive Speech on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding is a topic that often sparks strong opinions and debates among parents, healthcare professionals, and society as a whole. From the benefits of breast milk for infants to the social stigma surrounding nursing in public, there are numerous aspects to consider when discussing this important issue.
The Importance And Role Of Breastfeeding. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. I am taking this opportunity to address why breastfeeding is the most favorable method to feed an infant.
Breastfeeding the Latch Scoring System. PAGES 2 WORDS 810. For the newborn, birth weight, gestational age, and 1-minute and 5-minute Apgar scores were recorded. Post-discharge phone calls were made on day four and at week six. Each participant was asked if she was still breastfeeding at the time of the phone call.
Breastfeeding is when a mother nurses her infant by directly providing breast milk or pumping it out from the breast and bottle feeding them. This process of breastfeeding keeps the baby healthier. Along with complimentary food and formula feeding introduction, maternal breastfeeding is most preferred for the child's well-being.
Many changes take place in the early stages of pregnancy that prepare the breasts for lactation. Hormones like estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, and other hormones help promote blood flow to the breasts.
Cognitive benefits. In addition to the nutritional and immunological benefits of breast milk, breastfeeding may help preemies get ahead intellectually. Breast milk is associated with increases in child cognitive ability and educational achievements. Cognitive development of social and psychomotor skills gains increases with the consumption and ...
Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. "Breastfeeding is beneficial to the health of both women and infants" (WHO, 2013). In this essay I will be exploring the current ongoing public health issue that is breastfeeding and the stigma that ensues and surrounds this topic. During my exploration and analysis of ...
The representatives of the World Health Organization admit that exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months can decrease morbidity from allergies and gastrointestinal diseases due to the presence of nutritional benefits in human milk (Horta & Victoria, 2013). For example, the nutrient n-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) found in ...
UK Evidence Based Approach to Breast Feeding Essay Example. 1067 words 4 pages. Breastfeeding, also referred to as nursing, is the act of feeding infants using milk from the mother's breasts. It is widely recognized as the optimal method for nourishing babies and is often preferred by mothers. Although breastfeeding is a natural occurrence ...
Perceptions about breastfeeding. Women's perceptions about breastfeeding were covered in 83% (n = 49) of the papers.Most articles (n = 31) suggested that women perceived breastfeeding as a positive experience and believed that breastfeeding had many benefits [19, 20].The phrases "breast is best" and "breastmilk is best" were repeatedly used by the participants of studies included in ...
EXAMPLE ANALYTICAL ESSAY This example of an analytical essay is presented in association with Price, B and Harrington, A (2010) Critical Thinking and Writing for Nursing Students, Exeter, Learning Matters. Readers are introduced to the process of critical and reflective thinking and the translation of these into coursework that will help them ...
Breastfeeding. "Breastfeeding is beneficial to the health of both women and infants" (WHO, 2013). In this essay I will be exploring the current ongoing public health issue that is breastfeeding and the stigma that ensues and surrounds this topic. During my exploration and analysis of this public health issue I will be using epidemiology.
Free Breastfeeding Essay Example. The breastfeeding of a baby by the mother is an important act of nurture that deserves to be encouraged for the interests of both the child and maternal health. Mothers are supposed to breastfeed their babies sparingly to assure them of normal health and proper growth and development.
As a result, nursing essays can take many different forms and cover a wide range of topics. Given below are some examples of different types of nursing essays: Personal Philosophy Of Nursing - Essay Examples. Cal State Fullerton Nursing Essay Examples. Evidence Based Practice Nursing In Medical Field - Essay Examples.
The breastfeeding of a baby by the mother is an important act of nurture that deserves to be encouraged for the interests of both the child and maternal health.
Breastfeeding Debate. On March 23, 2016, Emily Locke of Pennsylvania was told that she was in violation of an Ohioan museum's policies because she was breastfeeding her 9 month old baby in public. Locke's protest about the situation at the museum and on social media had brought this huge controversy back into the public's eye (Fox News 1).
Breastfeeding Knowledge For A Nurse. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. After giving birth to a newborn, there are many adjustments you may need to get accustomed to. Aside, from recovering from the delivery a newborn.
Cheap Business Essay Writing Services. Before being accepted into our company, we underwent extensive background checks. Check their credentials to confirm that they have been writing professionally for some time. If they are members of professional associations, check, for instance. Some students may have difficulty completing their research ...