
Home » Writing » Autobiography vs. Biography vs. Memoir


Autobiography vs. Biography vs. Memoir
The three primary formats of a memory book , used to tell a life story, are a biography, an autobiography, and a memoir. Distinguishing between the three can feel a bit confusing since they all share several similarities. But there are some distinct differences.
Simply put, a biography is the life history of an individual, written by someone else. An autobiography is the story of a person’s life, written by that person. And a memoir is a collection of memories written by the person themselves.

What is a Biography?
A biography, also called a bio, is a non-fiction piece of work giving an objective account of a person’s life. The main difference between a biography vs. an autobiography is that the author of a biography is not the subject. A biography could be someone still living today, or it could be the subject of a person who lived years ago.
Biographies include details of key events that shaped the subject’s life, and information about their birthplace, education, work, and relationships. Biographers use a number of research sources, including interviews, letters, diaries, photographs, essays, reference books, and newspapers. While a biography is usually in the written form, it can be produced in other formats such as music composition or film.
If the target person of the biography is not alive, then the storytelling requires an immense amount of research. Interviews might be required to collect information from historical experts, people who knew the person (e.g., friends and family), or reading other older accounts from other people who wrote about the person in previous years. In biographies where the person is still alive, the writer can conduct several interviews with the target person to gain insight on their life.
The goal of a biography is to take the reader through the life story of the person, including their childhood into adolescence and teenage years, and then their early adult life into the rest of their years. The biography tells a story of how the person learned life’s lessons and the ways the person navigated the world. It should give the reader a clear picture of the person’s personality, traits, and their interaction in the world.
Biographies can also be focused on groups of people and not just one person. For example, a biography can be a historical account of a group of people from hundreds of years ago. This group could have the main person who was a part of the group, and the author writes about the group to tell a story of how they shaped the world.
Fictional biographies mix some true historical accounts with events to help improve the story. Think of fictional biographies as movies that display a warning that the story is made of real characters, but some events are fictional to add to the storyline and entertainment value. A lot of research still goes into a fictional biography, but the author has more room to create a storyline instead of sticking to factual events.
Examples of famous biographies include:
- His Excellency: George Washington by Joseph J. Ellis
- Einstein: The Life and Times by Ronald William Clark
- Princess Diana – A Biography of The Princess of Wales by Drew L. Crichton

What is an Autobiography?
An autobiography is the story of a person’s life written by that person. Because the author is also the main character of the story, autobiographies are written in the first person. Usually, an autobiography is written by the person who is the subject of the book, but sometimes the autobiography is written by another person. Because an autobiography is usually a life story for the author, the theme can be anything from religious to a personal account to pass on to children.
The purpose of an autobiography is to portray the life experiences and achievements of the author. Therefore, most autobiographies are typically written later in the subject’s life. It’s written from the point of view of the author, so it typically uses first person accounts to describe the story.
An autobiography often begins during early childhood and chronologically details key events throughout the author’s life. Autobiographies usually include information about where a person was born and brought up, their education, career, life experiences, the challenges they faced, and their key achievements.
On rare occasions, an autobiography is created from a person’s diary or memoirs. When diaries are used, the author must organize them to create a chronological and cohesive story. The story might have flashbacks or flashforwards to describe a specific event, but the main storyline should follow chronological order from the author’s early life to their current events.
One of the main differences between an autobiography vs. a biography is that autobiographies tend to be more subjective. That’s because they are written by the subject, and present the facts based on their own memories of a specific situation, which can be biased. The story covers the author’s opinions on specific subjects and provides an account of their feelings as they navigate certain situations. These stories are also very personal because it’s a personal account of the author’s life rather than a biography where a third party writes about a specific person.
Examples of famous autobiographies include:
- The Story of My Life by Helen Keller
- The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank
- Losing My Virginity by Richard Branson

What is a Memoir?
Memoir comes from the French word mémoire , meaning memory or reminiscence. Similar to an autobiography, a memoir is the story of a person’s life written by that person. These life stories are often from diary entries either from a first-person account or from a close family member or friend with access to personal diaries.
The difference between a memoir vs. an autobiography is that a memoir focuses on reflection and establishing an emotional connection, rather than simply presenting the facts about their life. The author uses their personal knowledge to tell an intimate and emotional story about the private or public happenings in their life. The author could be the person in the story, or it can be written by a close family member or friend who knew the subject person intimately. The topic is intentionally focused and does not include biographical or chronological aspects of the author’s life unless they are meaningful and relevant to the story.
Memoirs come in several types, all of which are written as an emotional account of the target person. They usually tell a story of a person who went through great struggles or faced challenges in a unique way. They can also cover confessionals where the memoir tells the story of the author’s account that contradicts another’s account.
This genre of writing is often stories covering famous people’s lives, such as celebrities. In many memoir projects, the celebrity or person of interest needs help with organization, writing the story, and fleshing out ideas from the person’s diaries. It might take several interviews before the story can be fully outlined and written, so it’s not uncommon for a memoir project to last several months.
Memoirs do not usually require as much research as biographies and autobiographies, because you have the personal accounts in diary entries and documents with the person’s thoughts. It might require several interviews, however, before the diary entries can be organized to give an accurate account on the person’s thoughts and emotions. The story does not necessarily need to be in chronological order compared to an autobiography, but it might be to tell a better story.
Examples of famous memoirs include:
- Angela’s Ashes by Frank McCourt
- I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings by Maya Angelou
- Personal Memoirs of Ulysses S. Grant by Ulysses S. Grant
Autobiography vs. Biography vs. Memoir Comparison Chart
Check out some of our blogs to learn more about memoirs:
- What is a memoir?
- 5 tips for writing a memoir
- Your memoir is your legacy
Ready to get started on your own memoir, autobiography, or biography? Download our free desktop book-making software, BookWright .
Autobiographies , Biographies , memoirs
This post doesn't have any comment. Be the first one!
This is a unique website which will require a more modern browser to work! Please upgrade today!
This is a modern website which will require Javascript to work.
Please turn it on!

How to write a book about yourself

1. What is a book that you write about yourself called?
2. How to start writing a book about your life
3. What to put in an autobiography or memoir
4. How to write an introduction for an autobiography or memoir
5. Tips for writing an autobiography or memoir
6. I want someone to write a book about my life
7. How to write a biography about someone else
8. Examples of published life stories, autobiographies and memoirs
9. How to publish an autobiography
➡️ An autobiography is a book about your entire life up until you write your book, while a memoir focuses on a specific event or time period in your life.
➡️ Autobiographies and memoirs are almost always written in the 1st person. They should include emotive descriptions of key events in your life, as well as background information about your past and hopes for your future.
➡️ Self-publishing is a powerful approach for memoirists and autobiography writers. It allows you to share your story with greater freedom than traditional publishing.
Everyone has a story to tell. Whether you’ve travelled the world, danced with movie stars, or brought up an incredible family, many people have fantastic life experiences they want to share with the world. Writing a book about yourself is a powerful, rewarding way to revisit and record some of the most important moments in your life.
But writing a book about yourself can be daunting. You need to be able to craft your experience into a story. That means writing a book that’s full of suspense, intrigue - and real-life experience.
This guide is designed to help you learn how to write a book about yourself - and get it published.
What is a book that you write about yourself called?
Let’s start with the basics. Books about the author’s life typically fall into one of two categories: memoirs and autobiographies. While there are some similarities between these two formats - the major one being that they’re both subjective, first-person accounts of real-life events - there are also some key differences.
What is a memoir?
A memoir is usually focused on a specific event, or a particular time period of a person’s life. For example, your memoir could focus on your formative adolescent years, or a traumatic event that affected you. Memoirs are often written by non-famous people about larger-than-life events.
What is an autobiography?
An autobiography usually recounts the writer’s entire life up until the point the book is written. Autobiographies are usually reserved for celebrities and other famous figures.
What is a biography?
A biography is an account of a person’s life written by someone else. Biographies can be authorised or unauthorised. Authorised biographies have the cooperation and approval of the person the biography is about. Unauthorised biographies, meanwhile, rely on external sources for their information.
How to start writing a book about your life
Writing a book takes a lot of time. It’s extremely rewarding, but can be frustrating - particularly if you’re not sure where to begin. These 4 steps will help you take the plunge into writing a book about yourself.
- Make sure you’re ready - Delving into your memory can be exhilarating, joyful, and painful - so make sure you’re emotionally prepared for the experience. Take some time for self-reflection before you begin planning your autobiography or memoir.
- Make a list of the events in your life you want to include - If possible, take a few minutes to journal about these events as you list them. This can help jog your memory and stir up emotions that will help you write vividly and honestly.
- Tell your loved ones you’re writing a book about yourself - This is especially important if they’re going to feature as identifiable characters in the story. They may have some reservations about their inclusion in the book, so make sure you’re on the same page before you start writing.
- Plan your story - If you haven’t written a book before, mapping your memoir out in advance may be beneficial. An outline can help you stay on track, and give structure and pace to your story. The importance of these elements can’t be underestimated, so planning your book puts you in a strong position to start writing.
What to put in an autobiography or memoir
If you’re writing a book about yourself, you probably already know which key moments you want to include. But it’s important that you take the time to build up context and intrigue in the reader, so you’ll also need to give them some background information about you.
Here are 5 key components every autobiography and memoir should include:
- Your childhood and adolescence - Your formative years will help your readers understand the actions you take and feelings you have in later life. Make sure to explore the events that shaped you in your early years.
- Key life events - These events are the reason you want to write your autobiography or memoir - so be sure to give them the colour and depth they deserve. Write honestly. Give readers details that help them understand and envisage the situation.
- Information about the other characters in your story - The real people in your life who feature in your book also need some backstory. That said, it’s important to discuss the details you’re including in your book with your friends and family before you publish it.
- Episodes of despondency - Without some degree of grief or loss, most stories would be pretty boring. So even if you’re happy, successful and rich now, it’s important to include moments of failure or sadness you’ve experienced in life. This gives the reader a more rounded view of you, and helps them to sympathise with your story.
- Your hopes for the future - Even when the book is finished, your story continues. Ending your autobiography or memoir with a hopeful message is a satisfying way to tie things up.
How to write an introduction for an autobiography or memoir
As in any book, the introduction to your autobiography should be intriguing and make the reader want to learn more. That means you don’t necessarily need to start at the beginning of your life. In fact, unless you had a particularly interesting birth, it’s probably best to skip ahead to a more pivotal moment.
This is particularly true if you’re writing a memoir. In a memoir, you’re writing about a particular time period or event you experienced - so your introduction should relate to that event.
Remember that your introduction sets the scene for the rest of your book, so it should be punchy, relevant, and captivating.
Tips for writing an autobiography or memoir
No matter what theme or tone your book will take, here are some useful tips for how to write a professional autobiography or memoir.
- Write in 1st person - Use the pronouns ‘I’ and ‘we’ throughout your book. Not only is this the accepted perspective for this kind of writing, it also lends your work subjective authority. This is your story, so make sure the reader knows that by using the 1st person voice.
- Read other autobiographies and memoirs - Reading published work that’s similar to the book you want to write will help you understand the conventions of autobiographical writing.
- Do your research - Even though you’re writing about your own life, it’s possible that you won’t recall the correct details of every incident you’re recounting. Double check all kinds of factual information - such as dates, ages, and names - before you publish your story.
- Write with the benefit of hindsight - You know things now that you didn’t know when the events took place. Writing honestly means being truthful about mistakes you may have made in the past, and acknowledging them with the information you now have.
- Be emotive - You want your readers to understand what you felt at each life stage you’re writing about. Express your emotions in writing to give your readers a sense of empathy.
I want someone to write a book about my life
If you think your life story would make an intriguing read, but you want someone else to write the book on your behalf, you can hire a ghostwriter to write the book for you.
Unlike biographers, ghostwriters write your autobiography as if they are you. Often, you can decide whether or not to credit the ghostwriter. If you credit them, their name will appear on the cover alongside yours - for example: My Story by Joe Bloggs, as told to Jane Doe. If you choose not to credit them, their name won’t appear on the cover. Most ghostwriters charge more for non-credited work.
How to write a biography about someone else
Biographies are similar to autobiographies in structure, but the form is usually very different. Because biographies are written about someone other than the author, they are almost always written in the 3rd person, rather than 1st person. Biographies also tend to depend less on emotion and more on factual information, because the author isn’t writing about their personal experiences.
While research is key for autobiographical writing, it’s doubly important for biographies. If you’re writing a book about someone else’s life, you’ll need to ensure you have all your facts right. That means reading and researching multiple accounts of the same event to ensure you’ve corroborated your information. Biographical inaccuracies can discredit you at best; at worst, they can result in libel lawsuits. So if you’re planning to write a book about someone else, make sure to do as much research as possible.
Examples of published life stories, autobiographies and memoirs
Many famous and non-famous people have published successful autobiographies and memoirs over the years. Here are some bestselling autobiographies and memoirs from well-known public figures:
- I Know Why The Caged Bird Sings - Maya Angelou
- On Writing - Stephen King
- Becoming - Michelle Obama
Many self-published memoirs and autobiographies have also achieved mainstream success. Some examples of these include:
- Grit: The Banter and Brutality of the Late-Night Cab - Karl Wiggins
- When I Was Lost: A Mother's Struggle with Bipolar Disorder - Glenna Gill
- Beautiful Affliction - Lene Fogelberg
Reading work by other writers is a great way to find out what works in an autobiography or memoir. It’s sure to help you avoid many of the common pitfalls of writing and self-publishing a book .
Penguin has a great list of the best memoirs of all time , as voted by their readers.
How to publish an autobiography
Autobiographies and memoirs from previously unpublished authors are notoriously difficult to market to risk-averse traditional publishers. But that doesn’t mean you should quit before you’ve begun.
Self-publishing is a great publishing option for memoirists who haven’t previously been published. With a self-published book, you’ll receive a higher percentage of royalties than if you’re traditionally published. Plus, there are lots of self-publishing companies out there who can help you get your book in front of a wider audience.
If you choose to self-publish your autobiography or memoir, you’ll be responsible for marketing, printing, and selling your book. This gives you much greater freedom around the content of your book, as well as your marketing and pricing strategy .
Find out more about the world of self-publishing in our writing advice .
Advice from a published writer
Drop us a message, we'll be happy to help.

"I'd like to express my heartfelt gratitude to the team for the exceptional book cover design!"

Should I start writing a book?
We're an independent website which is partly supported by ads and affiliate links. We may receive compensation from third-party advertisers, but that doesn’t affect our author opinions. Our marketing partners don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Related articles.

How to write a great book synopsis

How to write an author bio as a new writer

How much do authors make?
Order your book cover.
If you have any questions or if you're ready to go ahead, please fill out our short design enquiry form.
Professional book services for self-publishing and indie writers. Say hi: [email protected]
The Differences between Memoir, Autobiography, and Biography - article
Creative nonfiction: memoir vs. autobiography vs. biography.
Writing any type of nonfiction story can be a daunting task. As the author, you have the responsibility to tell a true story and share the facts as accurately as you can—while also making the experience enjoyable for the reader.
There are three primary formats to tell a creative nonfiction story: memoir, autobiography, and biography. Each has its own distinct characteristics, so it’s important to understand the differences between them to ensure you’re writing within the correct scope.
A memoir is a collection of personal memories related to specific moments or experiences in the author’s life. Told from the perspective of the author, memoirs are written in first person point of view.
The defining characteristic that sets memoirs apart from autobiographies and biographies is its scope. While the other genres focus on the entire timeline of a person’s life, memoirs structure themselves on one aspect, such as addiction, parenting, adolescence, disease, faith, etc.
They may tell stories from various moments in the author’s life, but they should read like a cohesive story—not just a re-telling of facts.
“You don’t want a voice that simply relates facts to the reader. You want a voice that shows the reader what’s going on and puts him or her in the room with the people you’re writing about.” – Kevan Lyon in Writing a Memoir
Unlike autobiographies and biographies, memoirs focus more on the author’s relationship to and feelings about his or her own memories. Memoirs tend to read more like a fiction novel than a factual account, and should include things like dialogue , setting, character descriptions, and more.
Authors looking to write a memoir can glean insight from both fiction and nonfiction genres. Although memoirs tell a true story, they focus on telling an engaging narrative, just like a novel. This gives memoir authors a little more flexibility to improve upon the story slightly for narrative effect.
However, you should represent dialogue and scenarios as accurately as you can, especially if you’re worried about libel and defamation lawsuits .
Examples of popular memoirs include Eat, Pray, Love by Elizabeth Gilbert and The Glass Castle by Jeannette Walls.
Key traits of a memoir:
- Written in 1 st person POV from the perspective of the author - Less formal compared to autobiographies and biographies - Narrow in scope or timeline - Focused more on feelings and memories than facts - More flexibility to change the story for effect
Autobiography
Like a memoir, an autobiography is the author’s retelling of his or her life and told in first person point of view, making the author the main character of the story.
Autobiographies are also narrative nonfiction, so the stories are true but also include storytelling elements such as a protagonist (the author), a central conflict, and a cast of intriguing characters.
Unlike memoirs, autobiographies focus more on facts than emotions. Because of this, a collaborator often joins the project to help the author tell the most factual, objective story possible.
While a memoir is limited in scope, an autobiography details the author’s entire life up to the present. An autobiography often begins when the author is young and includes detailed chronology, events, places, reactions, movements and other relevant happenings throughout the author’s life.
“In many people’s memoir, they do start when they’re younger, but it isn’t an, ‘I got a dog, then we got a fish, and then I learned to tie my shoes’…it isn’t that kind of detail.” – Linda Joy Meyers in Memoir vs. Autobiography
The chronology of an autobiography is organized but not necessarily in date order. For instance, the author may start from current time and employ flashbacks or he/she may organize events thematically.
Autobiographers use many sources of information to develop the story such as letters, photographs, and other personal memorabilia. However, like a memoir, the author’s personal memory is the primary resource. Any other sources simply enrich the story and relay accurate and engaging experiences.
A good autobiography includes specific details that only the author knows and provides context by connecting those details to larger issues, themes, or events. This allows the reader to relate more personally to the author’s experience.
Examples of popular autobiographies include The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank and I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings by Maya Angelou.
Key traits of an autobiography:
- Written in 1 st person POV from the perspective of the author, occasionally with the help of a collaborator - More formal and objective than memoirs, but more subjective than biographies - Broad in scope or timeline, often covering the author’s entire life up to the present - Focused more on facts than emotions - Requires more extensive fact-checking and research than memoirs, but less than biographies
A biography is the story of events and circumstances of a person’s life, written by someone other than that person. Usually, people write biographies about a historical or public figure . They can be written with or without the subject’s authorization.
Since the author is telling the account of someone else, biographies are always in third person point of view and carry a more formal and objective tone than both memoirs and autobiographies.
Like an autobiography, biographies cover the entire scope of the subject’s life, so it should include details about his or her birthplace, educational background, work history, relationships, death and more.
Good biographers will research and study a person’s life to collect facts and present the most historically accurate, multi-faceted picture of an individual’s experiences as possible. A biography should include intricate details—so in-depth research is necessary to ensure accuracy.
“If you’re dealing principally with historical figures who are long dead, there are very few legal problems…if you’re dealing with a more sensitive issue…then the lawyers will be crawling all over the story.” – David Margolick in Legal Issues with Biographies
However, biographies are still considered creative nonfiction, so the author has the ability to analyze and interpret events in the subject’s life, looking for meaning in their actions, uncovering mistakes, solving mysteries, connecting details, and highlighting the significance of the person's accomplishments or life activities.
Authors often organize events in chronological order, but can sometimes organize by themes or specific accomplishments or topics, depending on their book’s key idea.
Examples of popular biographies include Steve Jobs by Walter Isaacson and The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks by Rebecca Skloot.
Key traits of a biography:
- Written about another person, often a celebrity or public figure, and told in 3 rd person point of view - More formal and objective than both memoirs and autobiographies - Broad in scope or timeline, often covering the subject’s entire life up to the present - Focused solely on facts - Requires meticulous research and fact-checking to ensure accuracy
- Biographies and Memoirs
- Zeinab el Ghatit</a> and <span class="who-likes">7 others</span> like this" data-format="<span class="count"><span class="icon"></span>{count}</span>" data-configuration="Format=%3Cspan%20class%3D%22count%22%3E%3Cspan%20class%3D%22icon%22%3E%3C%2Fspan%3E%7Bcount%7D%3C%2Fspan%3E&IncludeTip=true&LikeTypeId=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000" >

Met you this morning briefly and just bought your book on Amazon. Congratulations.
Very helpful. I think I am heading down the path of a memoir.
Thank you explaining the differences between the three writing styles!
Very useful article. Well done. Please can we have more. Doctor's Orders !!!
My first book, "Tales of a Meandering Medic" is definitely a Memoir.
© Copyright 2018 Author Learning Center. All Rights Reserved

How To Write an Autobiography 2024 (Tips, Templates, & Guide)
Your life story has value, merit, and significance. You want to share it with the world, but maybe you don’t know how .
Here’s how to write an autobiography:
Write an autobiography by creating a list of the most important moments, people, and places in your life. Gather photos, videos, letters, and notes about these experiences. Then, use an outline, templates, sentence starters, and questions to help you write your autobiography .
In this article, you are going to learn the fastest method for writing your autobiography.
We are going to cover everything you need to know with examples and a free, downloadable, done-for-you template.
What Is an Autobiography?

Table of Contents
Before you can write an autobiography, you must first know the definition.
An autobiography is the story of your life, written by you. It covers the full span of your life (at least, up until now), hitting on the most significant moments, people and events.
When you write your autobiography, you write an intimate account of your life.
What Should I Include In an Autobiography?
If you are scratching your head, baffled about what to include in your autobiography, you are not alone.
After all, a big part of how to write an autobiography is knowing what to put in and what to leave out of your life story. Do you focus on every detail?
Every person? Won’t your autobiography be too long?
A good way to think about how to write an autobiography is to use the Movie Trailer Method.
What do movie trailers include?
- High emotional moments
- The big events
- The most important characters
When you plan, organize, and write your autobiography, keep the Movie Trailer Method in mind. You can even watch a bunch of free movie trailers on YouTube for examples of how to write an autobiography using the Movie Trailer Method.
When wondering what to include in your autobiography, focus on what would make the cut for a movie trailer of your life:
- Most important people (like family, friends, mentors, coaches, etc.)
- Significant events (like your origin story, vacations, graduations, life turning points, life lessons)
- Emotional moments (When you were homeless, when you battled a life-threatening condition, or when you fell in love)
- Drama or suspense (Did you make it into Harvard? Did your first surgery go well? Did your baby survive?)
Autobiography Structure Secrets
Like any compelling story, a well-structured autobiography often follows a pattern that creates a logical flow and captures readers’ attention.
Traditionally, autobiographies begin with early memories, detailing the writer’s childhood, family background, and the events or people that shaped their formative years.
From here, the narrative typically progresses chronologically, covering major life events like schooling, friendships, challenges, achievements, career milestones, and personal relationships.
It’s essential to weave these events with introspective insights.
This allows readers to understand not just the what, but also the why behind the author’s choices and experiences.
Towards the end, an effective autobiography often includes reflections on lessons learned, changes in perspective over time, and the wisdom acquired along life’s journey.
Example of the Structure:
- Introduction: A gripping event or anecdote that gives readers a hint of what to expect. It could be a pivotal moment or challenge that defines the essence of the story.
- Childhood and Early Memories: Recounting family dynamics, birthplace, cultural background, and memorable incidents from early years.
- Adolescence and Discovering Identity: Experiences during teenage years, challenges faced, friendships formed, and personal evolutions.
- Pursuits and Passions: Describing education, early career choices, or any particular hobby or skill that played a significant role in the author’s life.
- Major Life Events and Challenges: Chronicles of marriage, parenthood, career shifts, or any significant setbacks and how they were overcome.
- Achievements and Milestones: Celebrating major accomplishments and recounting the journey to achieving them.
- Reflections and Wisdom: Sharing life lessons, changes in beliefs or values over time, and offering insights gained from lived experiences.
- Conclusion: Summarizing the journey, contemplating on the present state, and sharing hopes or aspirations for the future.
How To Write an Autobiography Quickly: Strategies & Templates
Want the quickest way to organize and write your autobiography in record time? You can literally write your autobiography in 7 days or less with this method.
The secret is to use done-for-you templates.
I have personally designed and collected a series of templates to take you from a blank page to a fully complete Autobiography. I call this the How to Write an Autobiography Blueprint.
And it’s completely free to download right from this article. 🙂
In the How to Write an Autobiography Blueprint, you get:
- The Autobiography Questions Template
- The Autobiography Brainstorm Templates
- The Autobiography Outline Template
Here is an image of it so that you know exactly what you get when you download it:

How To Write an Autobiography: Step-by-Step
When you sit down to write an autobiography, it’s helpful to have a step-by-step blueprint to follow.
You already have the done-for-you templates that you can use to organize and write an autobiography faster than ever before. Now here’s a complete step-by-step guide on how to maximize your template.
- Brainstorm Ideas
- Order your sections (from medium to high interest)
- Order the ideas in each section (from medium to high interest)
- Write three questions to answer in each section
- Choose a starter sentence
- Complete a title template
- Write each section of your by completing the starter sentence and answering all three questions
Brainstorm Your Autobiography
The first step in writing your autobiography is to brainstorm.
Give yourself time and space to write down the most significant people, events, lessons, and experiences in your life. The templates in the How to Write an Autobiography Blueprint provide sections for you to write down your brainstormed ideas.

This will help you organize your ideas into what will become the major sections of your book.
These will be:
- Y our most significant events and experiences.
- The people who impacted you the most.
- The challenges you have overcome.
- Your achievements and successes.
- The lessons you have learned.
The “other” sections on the second page of the Brainstorm template is for creating your own sections or to give you more space for the sections I provided in case you run out of space.
As I brainstorm, I find asking myself specific questions really activates my imagination.
So I have compiled a list of compelling questions to help you get ideas down on paper or on your screen.

Order Your Sections (From Medium to High Interest)
The next step is to order your main sections.
The main sections are the five (or more) sections from your Brainstorm templates (Significant events, significant people, life lessons, challenges, successes, other, etc). This order will become the outline and chapters for your book.
How do you decide what comes first, second or third?
I recommend placing the sections in order of interest. Ask yourself, “What’s the most fascinating part of my life?”
If it’s a person, then write the name of that section (Significant People) on the last line in the How to Write an Autobiography Outline Template. If it’s an experience, place the name of that section (Significant Events) on the last line.
For example, if you met the Pope, you might want to end with that nugget from your life. If you spent three weeks lost at sea and survived on a desert island by spearfishing, that is your ending point.
Then complete the Outline by placing the remaining sections in order of interest. You can work your way backward from high interest to medium interest.
If you are wondering why I say “medium to high interest” instead of “low to high interest” it is because there should be no “low interest” parts of your autobiography.
But wait, what if you met the Pope AND spent three weeks lost at sea? How do you choose which one comes first or last?
First of all, I want to read this book! Second, when in doubt, default to chronological order. Whatever event happened first, start there.
Here is an example of how it might look:

Order The Ideas in Each Section (From Medium To High Interest)
Now, organize the ideas inside of each section. Again, order the ideas from medium to high interest).
Within your “Significant People” section, decide who you want to talk about first, second, third, etc. You can organize by chronological order (who you met first) but I recommend building to the most interesting or most significant person.
This creates a more compelling read.
Keep in mind that the most significant person might not be the most well-known, most famous, or most popular. The most significant person might be your family member, friend, partner, or child.
It comes down to who shaped your life the most.
So, if your “significant people list” includes your dad, a famous social media influencer, and Mike Tyson, your dad might come last because he had the biggest significance in your life.
Write Three Questions to Answer in Each Section
Ok, you’ve done the heavy lifting already. You have the major sections organized and outlined.
Next on your autobiography to-do list is to choose and write down three questions you are going to answer in each section. You can write your questions down in the provided “boxes” for each section on the template outline (or on another piece of paper.
This is easier than it might seem.
Simply choose one of the sample autobiography questions below or create your own:
- Why did I choose this person/event?
- What does this person/event mean to me?
- How did I meet this person?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- Why did it happen?
- How did it happen?
- What is the most interesting part?
- How did I feel about this person or event?
- How do I feel now?
- Why does this person or event matters to me?
- How did this person or event change my life?
- What is the most challenging part?
- How did I fail?
- How did I succeed?
- What did I learn?
Questions are the perfect way to write quickly and clearly. I LOVE writing to questions. It’s how I write these blog posts and articles.
Choose a Starter Sentence
Sometimes the hardest part of any project is knowing how to start.
Even though we know we can always go back and edit our beginnings, so many of us become paralyzed with indecision at the starting gate.
That’s why I provided sample starter sentences in your How to Write an Autobiography Blueprint.
Here are the story starters:
- I began writing this book when…
- Of all the experiences in my life, this one was the most…
- I’ve been a…
- My name is…
- Growing up in…
- It wasn’t even a…
- It all started when…
- I first…
- I was born…
Keep in mind that you do not need to begin your book with one of these story starters. I provide them simply to get you going.
The key is to not get bogged down in this, or any, part of writing your autobiography. Get organized and then get writing.
Complete a Title Template
At the top of the How to Write an Autobiography Outline is a place for you to write your book title.
Some authors struggle forever with a title. And that’s ok. What’s not ok is getting stuck. What’s not ok is if coming up with your title prevents you from finishing your book.
So, I provided a few title templates to help juice your creativity.
Just like the story starters, you do not need to use these title templates, but you certainly can. All you need to do is fill in the title templates below and then write your favorite one (for now) at the top of your outline. Presto! You have your working title.
You can always go back and change it later.
How to Write an Autobiography Title templates:
- [Your Name]: [Phrase or Tag Line]
- The [Your Last Name] Files
- Born [Activity]: A [Career]’s Life
- The Perfect [Noun]: The Remarkable Life of [Your Name]
Examples using the Templates:
- Christopher Kokoski: Blog Until You Drop
- The Kokoski Files
- Born Writing: A Blogger’s Life
- The Perfect Freelancer: The Remarkable Life of Christopher Kokoski
Write Your Autobiography
You have your outline. You have your title, templates, and sentence starters. All that is left to do is write your autobiography.
However, you can use tools like Jasper AI and a few other cool tricks to craft the most riveting book possible.
This is the easy way to remarkable writing.
Check out this short video that goes over the basics of how to write an autobiography:
How To Write an Autobiography (All the Best Tips)
Now that you are poised and ready to dash out your first draft, keep the following pro tips in mind:
- Be vulnerable. The best autobiographies share flaws, faults, foibles, and faux pas. Let readers in on the real you.
- Skip the boring parts. There is no need to detail every meal, car ride, or a gripping trip to the grocery store. Unless you ran into the Russian Mafia near the vegetables or the grocery store is perched on the side of a mountain above the jungles of Brazil.
- Keep your autobiography character-driven . This is the story of YOU!
- Be kind to others (or don’t). When writing about others in your story, keep in mind that there may be fallout or backlash from your book.
- Consider a theme: Many autobiographies are organized by theme. A perfect example is Becoming . Each section of the book includes “becoming” in the title. Themes connect and elevate each part of the autobiography.
- Write your story in vignettes (or scenes). Each vignette is a mini-story with a beginning, middle, and end. Each vignette builds. Each vignette should be described in rich sensory language that shows the reader the experience instead of telling the reader about the experience. Each vignette is immersive, immediate, and intimate.
- Include snippets of dialogue. Use quotation marks just like in fiction. Show the dialogue in brief back-and-forth tennis matches of conversation. Remember to leave the boring parts out!
- Choose a consistent tone. Some autobiographies are funny like Bossy Pants by Tina Fey. Others are serious such as Open by Andre Agassi. Your story (like most stories) will likely include a mix of emotions but choose an overall tone and stick with it.
- Don’t chronicle, captivate . Always think about how to make each section, each chapter, each page, each paragraph, and each sentence more compelling. You want to tell the truth, but HOW you tell the truth is up to you. Create suspense, conflict, and mystery. Let drama linger until it becomes uncomfortable. Don’t solve problems quickly or take away tension right away.
How Do I Format an Autobiography?
Most autobiographies are written in the first person (using the pronouns I, me, we, and us).
Your autobiography is written about you so write as yourself instead of pretending to be writing about someone else.
Most autobiographies are also written in chronological order, from birth right up to your current age, with all the boring parts left out. That doesn’t mean you can’t play around with the timeline.
Sometimes it’s more interesting to start at a high moment, backtrack to the beginning and show how you got to that high moment.
Whatever format you choose, be intentional, and make the choice based on making the most compelling experience possible for your readers.
How Long Should an Autobiography Be?
There are no rules to how long an autobiography should be but a rough guideline is to aim for between 200 and 400 pages.
This will keep your book in line with what most readers expect for books in general, and will help get your book traditionally published or help with marketing your self-published book.
How To Write a Short Autobiography
You write a short autobiography the same way that you write a long autobiography.
You simply leave more out of the story.
You cut everything down to the bones. Or you choose a slice of your life as you do in a memoir. This often means limiting the people in your book, reducing the events and experiences, and shrinking your story to a few pivotal moments in your life.
How To Start an Autobiography
The truth is that you can start your autobiography in any number of ways.
Here are four common ways to begin an autobiography.
- Start at the beginning (of your life, career or relationship, etc.)
- Start at a high moment of drama or interest.
- Start at the end of the story and work backward
- Start with why you wrote the book.
Good Autobiography Titles
If you are still stuck on titling your autobiography, consider going to Amazon to browse published works. You can even just Google “autobiographies.”
When you read the titles of 10, 20, or 50 other autobiographies, you will start to see patterns or get ideas for your own titles. (HINT: the title templates in the Autobiography Blueprint were reverse-engineered from popular published books.
Also, check out the titles of the full autobiography examples below that I have included right here in this article.
Types of Autobiographies
There are several different kinds of autobiographies.
Each one requires a similar but slightly nuanced approach to write effectively. The lessons in this article will serve as a great starting point.
Autobiography Types:
- Autobiography for School
- Autobiography Novel
- Autobiography for a Job
- Short Autobiography
- Autobiography for Kids
Therefore, there is actually not just one way to write an autobiography.
Memoir vs. Autobiography: Are They The Same?
It’s common to feel confused about a memoir and an autobiography. I used to think they were the same thing.
But, nope, they’re not.
They are pretty similar, which is the reason for all the confusion. A memoir is the story of one part of your life. An autobiography is the story of your full life (up until now).
What Is the Difference Between an Autobiography and a Biography?
An autobiography is when you write about your own life. A biography, on the other hand, is when you write the story of someone else’s life.
So, if I write a book about the life of the President, that’s a biography.
If the President writes a story about his or her own life, that’s an autobiography.
What Not To Include In an Autobiography
Autobiographies are meant to be a snapshot of our lives that we can share with others, but there are some things that are best left out.
Here are three things you should avoid including in your autobiography:
1) Anything That Readers Will Skip
Your life may not be filled with non-stop excitement, but that doesn’t mean you need to include every mundane detail in your autobiography.
Stick to the highlights and leave out the low points.
2) Character Attacks on Others
It’s okay to discuss conflicts you’ve had with others, but don’t use your autobiography as a platform to attack someone’s character.
Keep it civil and focus on your own experiences and how they’ve affected you.
3) Skipping Highlights
Just because something embarrassing or painful happened to you doesn’t mean you should gloss over it in your autobiography.
These are the moments that shape us and make us who we are today, so don’t skip past them just because they’re uncomfortable.
By following these simple tips, you can ensure that your autobiography is interesting, honest, and engaging.
How To Write an Autobiography: Autobiography Examples
I have always found examples to be extremely instructive. Especially complete examples of finished products. In this case, books.
Below you will find examples of published autobiographies for adults and for kids. These examples will guide you, motivate you and inspire you to complete your own life story.
They are listed here as examples, not as endorsements, although I think they are all very good.
The point is that you don’t have to agree with anything written in the books to learn from them.
Autobiography Examples for Adults
- A Promised Land (Autobiography of Barack Obama)
- If You Ask Me: (And of Course You Won’t) (Betty White)
- It’s a Long Story: My Life (Willie Nelson)
- Stories I Only Tell My Friends: An Autobiography (Rob Lowe)
- Becoming (Michelle Obama)
Autobiography Examples for Kids
- This Kid Can Fly: It’s About Ability (NOT Disability) (Aaron Philips)
- Bee Fearless: Dream Like a Kid (Mikaila Ulmer)
Final Thoughts: How To Write An Autobiography
Thank you for reading my article on How to Write an Autobiography.
Now that you know all of the secrets to write your book, you may want to get it published, market it, and continue to upskill yourself as an author.
In that case, read these posts next:
- Can Anyone Write A Book And Get It Published?
- The Best Writing Books For Beginners 2022 (My 10 Favorites)
- Why Do Writers Hate Adverbs? (The Final Answer)
- How To Write a Manifesto: 20 Ultimate Game-Changing Tips
2 thoughts on “How To Write an Autobiography 2024 (Tips, Templates, & Guide)”
Pingback: How To Write Like Danielle Steel - CHRISTOPHER KOKOSKI
Pingback: How Many Characters Should A Book Have? - CHRISTOPHER KOKOSKI
Comments are closed.
What Is Biography? Definition, Usage, and Literary Examples
Biography definition.
A biography (BYE-og-ruh-fee) is a written account of one person’s life authored by another person. A biography includes all pertinent details from the subject’s life, typically arranged in a chronological order. The word biography stems from the Latin biographia , which succinctly explains the word’s definition: bios = “life” + graphia = “write.”
Since the advent of the written word, historical writings have offered information about real people, but it wasn’t until the 18th century that biographies evolved into a separate literary genre. Autobiographies and memoirs fall under the broader biography genre, but they are distinct literary forms due to one key factor: the subjects themselves write these works. Biographies are popular source materials for documentaries, television shows, and motion pictures.
The History of Biographies
The biography form has its roots in Ancient Rome and Greece. In 44 BCE, Roman writer Cornelius Nepos published Excellentium Imperatorum Vitae ( Lives of the Generals ), one of the earliest recorded biographies. In 80 CE, Greek writer Plutarch released Parallel Lives , a sweeping work consisting of 48 biographies of famous men. In 121 CE, Roman historian Suetonius wrote De vita Caesarum ( On the Lives of the Caesars ), a series of 12 biographies detailing the lives of Julius Caesar and the first 11 emperors of the Roman Empire. These were among the most widely read biographies of their time, and at least portions of them have survived intact over the millennia.
During the Middle Ages, the Roman Catholic Church had a notable influence on biographies. Historical, political, and cultural biographies fell out of favor. Biographies of religious figures—including saints, popes, and church founders—replaced them. One notable exception was Italian painter/architect Giorgio Vasari’s 1550 biography, The Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects , which was immensely popular. In fact, it is one of the first examples of a bestselling book.
Still, it wasn’t until the 18th century that authors began to abandon multiple subjects in a single work and instead focus their research and writing on one subject. Scholars consider James Boswell’s 1791 The Life of Samuel Johnson to be the first modern biography. From here, biographies were established as a distinct literary genre, separate from more general historical writing.
As understanding of psychology and sociology grew in the 19th and early 20th centuries, biographies further evolved, offering up even more comprehensive pictures of their subjects. Authors who played major roles in this contemporary approach to biographing include Lytton Strachey, Gamaliel Bradford, and Robert Graves.
Types of Biographies
While all biographical works chronicle the lives of real people, writers can present the information in several different ways.
- Popular biographies are life histories written for a general readership. The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks by Rebecca Skloot and Into the Wild by Jon Krakauer are two popular examples.
- Critical biographies discuss the relationship between the subject’s life and the work they produced or were involved in; for example, The Billionaire Who Wasn’t: How Chuck Feeney Secretly Made and Gave Away a Fortune by Conor O’Clery and Unpresidented: A Biography of Donald Trump by Martha Brockenbrough.
- Historical biographies put greater understanding on how the subject’s life and contributions affected or were affected by the times in which they lived; see John Adams by David McCullough and Catherine the Great by Peter K. Massie.
- Literary biographies concentrate almost exclusively on writers and artists, blending a conventional narrative of the historical facts of the subject’s life with an exploration of how these facts impacted their creative output. Some examples include Savage Beauty: The Life of Edna St. Vincent Millay by Nancy Milford and Jackson Pollock: An American Saga by Gregory White Smith and Steven Naifeh.
- Reference biographies are more scholarly writings, usually written by multiple authors and covering multiple lives around a single topic. They verify facts, provide background details, and contribute supplemental information resources, like bibliographies, glossaries, and historical documents; for example, Black Americans in Congress, 1870-2007 and the Dictionary of Canadian Biography .
- Fictional biographies, or biographical novels, like The Other Boleyn Girl by Philippa Gregory, incorporate creative license into the retelling of a real person’s story by taking on the structure and freedoms of a novel. The term can also describe novels in which authors give an abundance of background information on their characters, to the extent that the novel reads more like a biography than fiction. An example of this is George R.R. Martin’s Fire and Blood , a novel detailing the history of a royal family from his popular A Song of Ice and Fire
Biographies and Filmed Entertainment
Movie makers and television creators frequently produce biographical stories, either as dramatized productions based on real people or as nonfiction accounts.
Documentary
This genre is a nonfictional movie or television show that uses historical records to tell the story of a subject. The subject might be a one person or a group of people, or it might be a certain topic or theme. To present a biography in a visually compelling way, documentaries utilize archival footage, recreations, and interviews with subjects, scholars, experts, and others associated with the subject.
Famous film documentaries include Grey Gardens, a biography of two of Jacqueline Kennedy’s once-wealthy cousins, who, at the time of filming, lived in squalor in a condemned mansion in the Hamptons; and I Am Not Your Negro , a biography of the life and legacy of pioneering American author James Baldwin.
Television documentary series tell one story over the course of several episodes, like The Jinx : The Life and Deaths of Robert Durst , a biography of the real estate heir and alleged serial killer that focused on his suspected crimes. There are many nonfiction television shows that use a documentary format, but subjects typically change from one episode to the next, such as A&E’s Biography and PBS’s POV .
These films are biographical motion pictures, written by screenwriters and performed by actors. They often employ a certain amount of creative liberty in their interpretation of a real life. This is largely done to maintain a feasible runtime; capturing all of the pivotal moments of a subject’s life in a 90- or 120-minute movie is all but impossible. So, filmmakers might choose to add, eliminate, or combine key events and characters, or they may focus primarily on one or only a few aspects of the subject’s life. Some popular examples: Coal Miner’s Daughter , a biography of country music legend Loretta Lynn; Malcom X , a biopic centered on the civil rights leader of the same name; and The King’s Speech , a dramatization of Prince Albert’s efforts to overcome a stutter and ascend the English throne.
Semi-fictionalized account
This approach takes a real-life event and interprets or expands it in ways that stray beyond what actually happened. This is done for entertainment and to build the story so it fits the filmmaker’s vision or evolves into a longer form, such as a multi-season television show. These accounts sometimes come with the disclaimer that they are “inspired by true events.” Examples of semi-fictionalized accounts are the TV series Orange Is the New Black , Masters of Sex , and Mozart of the Jungle —each of which stem from at least one biographical element, but showrunners expounded upon to provide many seasons of entertainment.
The Functions of Biography
Biographies inform readers about the life of a notable person. They are a way to introduce readers to the work’s subject—the historical details, the subject’s motivations and psychological underpinnings, and their environment and the impact they had, both in the short and long term.
Because the author is somewhat removed from their subject, they can offer a more omniscient, third-person narrative account. This vantage point allows the author to put certain events into a larger context; compare and contrast events, people, and behaviors predominant in the subject’s life; and delve into psychological and sociological themes of which the subject may not have been aware.
Also, a writer structures a biography to make the life of the subject interesting and readable. Most biographers want to entertain as well as inform, so they typically use a traditional plot structure—an introduction, conflict , rising of tension, a climax, a resolution, and an ending—to give the life story a narrative shape. While the ebb and flow of life is a normal day-to-day rhythm, it doesn’t necessarily make for entertaining reading. The job of the writer, then, becomes one of shaping the life to fit the elements of a good plot.
Writers Known for Biographies
Many modern writers have dedicated much of their careers to biographies, such as:
- Kitty Kelley, author of Jackie Oh! An Intimate Biography; His Way: The Unauthorized Biography of Frank Sinatra ; and The Family: The Real Story of the Bush Dynasty
- Antonia Fraser, author of Mary Queen of Scots ; Cromwell; Our Chief of Men ; and The Gunpowder Plot: Terror and Faith in 1605
- David McCullough, author of The Path Between the Seas; Truman ; and John Adams
- Andrew Morton, author of Diana: Her True Story in Her Own Words; Madonna ; and Tom Cruise: An Unauthorized Biography
- Alison Weir, author of The Six Wives of Henry VIII; Eleanor of Aquitaine: By the Wrath of God; Queen of England ; and Katherine Swynford: The Story of John of Gaunt and His Scandalous Duchess
Examples of Biographies
1. James Boswell, The Life of Samuel Johnson
The biography that ushered in the modern era of true-life writing, The Life of Samuel Johnson covered the entirety of its subject’s life, from his birth to his status as England’s preeminent writer to his death. Boswell was a personal acquaintance of Johnson, so he was able to draw on voluminous amounts of personal conversations the two shared.
What also sets this biography apart is, because Boswell was a contemporary of Johnson, readers see Johnson in the context of his own time. He wasn’t some fabled figure that a biographer was writing about centuries later; he was someone to whom the author had access, and Boswell could see the real-world influence his subject had on life in the here and now.
2. Sylvia Nasar, A Beautiful Mind
Nasar’s 1998 Pulitzer Prize-nominated biography of mathematician John Nash introduced legions of readers to Nash’s remarkable life and genius. The book opens with Nash’s childhood and follows him through his education, career, personal life, and struggles with schizophrenia. It ends with his acceptance of the 1994 Nobel Prize for Economics. In addition to a Pulitzer nomination, A Beautiful Mind won the National Book Critics Circle Award for Biography, was a New York Times bestseller, and provided the basis for the Academy Award-winning 2001 film of the same name.
3. Catherine Clinton, Harriet Tubman: The Road to Freedom
Clinton’s biography of the abolitionist icon is a large-scale epic that chronicles Tubman’s singular life. It starts at her birth in the 1820s as the slave Araminta Ross, continuing through her journey to freedom; her pivotal role in the Underground Railroad; her Moses-like persona; and her death in 1913.
Because Tubman could not read or write, she left behind no letters, diaries, or other personal papers in her own hand and voice. Clinton reconstructed Tubman’s history entirely through other source material, and historians often cite this work as the quintessential biography of Tubman’s life.
4. Megan Mayhew Bergman, Almost Famous Women
Almost Famous Women is not a biography in the strictest sense of the word; it is a fictional interpretation of real-life women. Each short story revolves around a woman from history with close ties to fame, such as movie star Marlene Dietrich, Standard Oil heiress Marion “Joe” Carstairs, aviatrix Beryl Markham, Oscar Wilde’s niece Dolly, and Lord Byron’s daughter Allegra. Mayhew Bergman imagines these colorful women in equally colorful episodes that put them in a new light—a light that perhaps offers them the honor and homage that history denied them.
Further Resources on Biography
Newsweek compiled their picks for the 75 Best Biographies of All Time .
The Open Education Database has a list of 75 Biographies to Read Before You Die .
Goodreads put together a list of readers’ best biography selections .
If you’re looking to write biographies, Infoplease has instructions for writing shorter pieces, while The Writer has practical advice for writing manuscript-length bios.
Ranker collected a comprehensive list of famous biographers .
Related Terms
- Autobiography
- Short Story
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
The Best Short Professional Bios (Examples + Templates)
- Resume Tips
- Best Resume Writing Services
- Things To Avoid On A Resume
- Resume Paper To Use
- What To Include In A Resume
- How To Write A Bio
- How To Write A Personal Statement
- Lied on Your Resume?
- Avoid Age Discrimination
- Words and Phrases You Shouldn't Include in Your Resume
- How Many Skills Should You List On A Resume
- Send A Resume As A Pdf
- Resume Critique
- Make A Resume Stand Out
- Resume Spelling
- Resume Past Or Present Tense
- How To List Projects On A resume
- Best Resume Action Words
- How To Quantify Your Resume
- Resume Bullet Points
- Are Resume Writers Worth It
- How Many Jobs To List On Resume
Summary. To write a short bio you should first make an initial introduction introducing yourself in the first or first person. Your short bio should include your brand, your accomplishments, and your values and goals. Your short bio should be one to three short paragraphs or four to eight sentences long.
Knowing how to write a concise, informative, and interesting biography about yourself can help throughout various parts of the professional process. You can use your bio to capture the attention of potential employers or clients and convince them to choose to employ or work with you.
In this article, you’ll learn more about what goes into a short bio and how to write one, and you’ll also get to see some short bio templates and examples to help you get an idea of what yours should look like.
Key Takeaways
A short bio serves to introduce you, your achievements, and what you offer professionally to potential employers or clients.
It’s important to keep your bio brief so that readers stay engaged and will remember your main points.
You may need to adjust your bio for different audiences, as your clients may want to know different information than a recruiter would.
Talk about your skills and accomplishments in your bio, but don’t exaggerate them.
What Is a Short Bio?
How to write a short bio, what to include in a short professional bio, short bio examples, short bio templates, tips for writing a short bio, writing a short bio faq.
- Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs
A short bio serves as your introduction to the professional world. In terms of finding or expanding on your job, a bio will cover your:
Work history
Achievements
Any other relevant professional information
Think of it as a professional memoir that a hiring manager or consumer can read and understand quickly. It’s usually about one to three paragraphs depending on experience.
There’s an emphasis on being succinct when it comes to writing a professional bio. This is because a bio is supposed to be a preface to attract recruiter attention and incline them to reach out for more information. Many readers will get lost or bored with a lengthy bio.
Using a short bio can be helpful across very different industries, from marketing to accounting, from psychiatry to sales.
You’re probably familiar with providing short bios on social media websites and applications. While the information and skills you include in a professional bio may differ, the general formatting is similar.
There’s a lot of considerations to take into account when writing a short bio, and it can quickly become intimidating. Deciding what information is relevant and how to keep it near 140 characters is no small task.
If you’re having difficulty writing a short bio, follow the outline below to craft an introduction that engages your reader.
Make an initial introduction. You can’t jump right into everything you’ve done and what you want to do in the future before introducing yourself.
Your bio’s first sentence should begin with your full name in the third person or introduce yourself in the first person and continue to briefly outline your most notable skills and accomplishments. It’s a good place to state your current job and employer.
Go deeper with what motivates you. Once you’ve catchily illustrated who you are in your short bio, you can use the second sentence to describe your motivations for your work.
Stating what drives you to do the work you do is essential to employers and customers alike. Whether you work as a physician or fitness consultant , there’s a reason why this is your profession, and you should explain that in your short professional bio.
Describe your accomplishments. Your short bio is for detailing why you’re the ideal candidate to be trusted with handling an employer or consumer’s business. By describing your prior accomplishments, you let them know what you could offer as an employee and how you’ve succeeded in the past.
While you should avoid sounding braggy, the reader is looking for information about what your qualifications are , and your accomplishments generally measure these qualities.
Even though you could probably go on for ages about the details of your accomplishments, save that for an interview . In a short bio, only include the most impressive of your achievements to outline.
Accomplishments relevant to a short bio could include:
Impressive results on a project
Former promotions
Awards received in your field
Certifications received
Include contact information. The purpose of a short bio as either a business or a job seeker is to inspire the reader to reach out. Without contact information, this pursuit becomes futile. Make sure your short bio has some way to contact you at the end.
Relevant contact information may include:
Phone number
Professional networking profile
A short professional bio includes:
Your full name. You can choose to write your bio in the first person (I, me, my) or third person (he, she, they), but either way, you need to include your full name at some point. Branding doesn’t work so well without a brand name (i.e., you!)
Your brand. Of course, if you have an actual brand that you’re trying to market, you should include the brand name as well.
What you do. Summarize what you want the reader to know about what you do in one sentence — tricky, we know.
Your accomplishments. For a short bio, you can stick with just one major accomplishment from your professional life. Or, if you have a string of impressive achievements, try condensing all of them down to one sentence.
Your goals and values. Let the reader know what makes you tick — why do you do what you do and what do you hope to achieve with your work? People are compelled by a story more than anything else, so it’s important to get this part right.
Something personal (optional). If you have a quirky tidbit about yourself you’d like to include, go for it. Just make sure it doesn’t throw off te the tone of the rest of your bio.
Contact info (optional). If your bio is serving as a call-to-action to drum up business or get leads on job opportunities, it makes sense to include your contact information at the end of your bio. It’s not necessary if that information is available elsewhere on the page , though.
Entry-Level Job-Seeker Bio Example
Mitchell Morrison is an upcoming video producer and editor who believes in the art of visual organization. He is a recent graduate from the University of Washington and focused on post-production during his time studying there. He was introduced to the magical world of visual art production by watching his father work on editing commercials growing up and has been working towards his dream of becoming a video editor ever since. During his last year of college, Mitchell participated in a competitive internship with Digital Space Films. He was chosen out of 2,000 applicants based on his academic portfolio and personal statement essay. This internship was an incredible learning experience and resulted in three professional accreditations for music video editing. Mitchell currently lives in Seattle, Washington pursuing freelance opportunities and spending time with his Dog, Pikachu. To get into contact with Mitchell: MitchellMorrisonVideo.com/contact
Working Professional Website Bio Example
Lisa Kennedy is an experienced real estate professional. She knows how important a home is for long-term happiness and has invested her career in putting people in the house they’ve always dreamed of. Lisa was driven to pursue real estate from her passion for helping people during life-altering times, and a keen interest in high-end, luxury homes. She’s been working in the real estate industry for ten years and in that time has assisted over 3,500 people in finding homes. She was educated at the University of Los Angeles with a bachelor’s in business management. She’s worked for some of the most respectable Real Estate companies in Los Angeles and individually under her agency “Kennedy Homes.” Lisa has also been published in Real Estate Quarterly Magazine as the 2017 winner of the “Top Luxury Home Seller” award. Lisa loves the culture of Los Angeles and has been living there with her family of five since she graduated from college. She enjoys spending her free time exploring towns along the West Coast and swimming. If you’d like to get in touch with Lisa: Email: [email protected]
Professional Networking Profile Bio Example
Bianca Jones Marketing Manager Miami, FL The first step towards customer satisfaction is being reached by stellar product marketing, and that’s what I aim to provide. My professional experience as a product marketing manager has allowed me to assist many organizations in improving their sales margins and audience response to emerging products. I’ve brought dedication and positive results to the companies I’ve worked for because I am passionate about product perception, marketing, and business statistics. What drives a product to success interests and inspires me. I specialize in long-term growth strategies and audience outreach. In addition to eight years of experience in professional product marketing, I have also published two books on creating a career as a marketer called “What to Do After Your Bachelor’s” and “A Marketer’s How-To.” If you’re interested in learning more about how to market your business better, or just discuss more, feel free to contact me by email at [email protected].
Your first choice is whether you want your bio to be written in the third person or first person. These short bio templates show both options, and also include different ideas for what to include, and how. Feel free to pick and choose your favorite parts of each of the two.
[Full Name] is a [job title] who [believes/knows] in the power of [what you do]. [He/She/They] began their journey in [field] by [how you got started in the field], and now dreams of [what you hope to accomplish]. [His/Her/Their] biggest accomplishment to date has been [your biggest accomplishment]. [Full Name] lives in [where you live] and participates in [a hobby/interest]. To get in touch with [Full Name], call/email/message me on [how you’d like to be contacted].
I am a [job title] who helps [who you help] [what you help them do]. It’s my belief that [your unique perspective on the field]. In the past [# of years] years, I’ve [major accomplishment #1] through [how you accomplished it]. I have a passion for [your professional passion], but on the side, I also enjoy [personal passion]. Get in touch with me today at [contact info] — I look forward to talking with you about [what you want to talk to your readers about].
You have a firm grasp of the structure of a short bio and what to include. Now, you may need some tips for how to polish your short professional bio and make it stand out from the competition.
Be mindful of length. While you’re probably getting sick of hearing that your bio should be short, it’s good to keep in mind throughout the writing process. It’s easy to go off on a tangent while trying to include everything relevant or rationalize, making your bio too long.
Avoid this impulse. The point of a bio is that it’s limited. You want to intrigue the reader enough to inspire them to seek more information about you or your services.
Tailor your bio to your intended audience. Whether you’re using a short bio to attract a particular customer base or potential employer, tailoring it to fit their wants and needs is crucial. Consider your intended audience base and what they’re looking for in a candidate or service.
Be genuine. Your short bio should be an authentic representation of your traits, experience, and personality. People are repelled by what they interpret as stretching the truth. If you’re being received as disingenuous by the reader, they’ll probably move on.
Proofread. The only way to steer clear of errors in your short bio is by proofreading it. Imagine a hiring manager being completely interested in your bio.
They love what you have to say about yourself and find your prior experience enticing. That is, until they come across a mistake that clearly shows you didn’t do proofread or edit.
Include links to your portfolio, website, or networking profile. One way to circumvent the confining factor of keeping your bio short is by including links to more detailed sources.
This can be in the form of linking your portfolio or website to allow the reader to go deeper into your discussed skills if they please, without taking up more space in your bio.
Implement these links seamlessly into your bio by attaching them to anchor words that describe what clicking will lead them to.
Add some personality. You aren’t the only person who has an impressive list of accomplishments to put on a bio, so you’re going to need to find some additional ways to make an impression.
What should a short bio include?
A short bio should include your name, what you do, and your achievements. You should also include your company or product’s brand, if you have one, and your goals and motivations for doing what you do. This humanizes you and helps you stand out from the rest of the pack.
How long is a short bio?
A short bio is typically one to three paragraphs long. These should be short paragraphs though, as other experts say that between four and eight sentences is the ideal length for a short bio.
What makes a good bio?
A good bio is succinct and memorable. Readers don’t want to spend long reading about your professional and personal life, so go back and cut it down to the important parts multiple times after you draft it. You might be surprised at how little you actually need to include.
What should you avoid putting in a short bio?
You should avoid including anything negative or arrogate. It’s never a good idea to write anything negative about previous jobs or employers. Only include positive things in your professional short bio.
It’s important to include your achievements in a short bio, but there is a fine line between mentioning your achievements and bragging about them. Stick to the facts when talking about your accomplishments.
Fremont University – Building Your Professional Bio
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Sky Ariella is a professional freelance writer, originally from New York. She has been featured on websites and online magazines covering topics in career, travel, and lifestyle. She received her BA in psychology from Hunter College.
Don Pippin is an executive and HR leader for Fortune 50 and 500 companies and startups. In 2008, Don launched area|Talent with a focus on helping clients identify their brand. As a Certified Professional Resume Writer, Certified Digital Career Strategist, and Certified Personal Branding Strategist, Don guides clients through career transitions.
Recent Job Searches
- Registered Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Truck Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Call Center Representative Jobs Resume Location
- Customer Service Representative Jobs Resume
- Delivery Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Warehouse Worker Jobs Resume Location
- Account Executive Jobs Resume Location
- Sales Associate Jobs Resume Location
- Licensed Practical Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Company Driver Jobs Resume
Related posts

How To Make Your Resume Stand Out (With Examples)
How To Put Projects On A Resume (With Examples)

How To Make A Resume PDF (And When To Use It)
When And How To Use A Two-Page Resume
- Career Advice >
Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on Jun 30, 2023
How to Write a Biography: A 7-Step Guide [+Template]
From time to time, nonfiction authors become so captivated by a particular figure from either the present or the past, that they feel compelled to write an entire book about their life. Whether casting them as heroes or villains, there is an interesting quality in their humanity that compels these authors to revisit their life paths and write their story.
However, portraying someone’s life on paper in a comprehensive and engaging way requires solid preparation. If you’re looking to write a biography yourself, in this post we’ll share a step-by-step blueprint that you can follow.
How to write a biography:
1. Seek permission when possible
2. research your subject thoroughly, 3. do interviews and visit locations, 4. organize your findings, 5. identify a central thesis, 6. write it using narrative elements, 7. get feedback and polish the text.

FREE RESOURCE
Biography Outline Template
Craft a satisfying story arc for your biography with our free template.
While you technically don’t need permission to write about public figures (or deceased ones), that doesn't guarantee their legal team won't pursue legal action against you. Author Kitty Kelley was sued by Frank Sinatra before she even started to write His Way , a biography that paints Ol Blue Eyes in a controversial light. (Kelley ended up winning the lawsuit, however).

Whenever feasible, advise the subject’s representatives of your intentions. If all goes according to plan, you’ll get a green light to proceed, or potentially an offer to collaborate. It's a matter of common sense; if someone were to write a book about you, you would likely want to know about it well prior to publication. So, make a sincere effort to reach out to their PR staff to negotiate an agreement or at least a mutual understanding of the scope of your project.
At the same time, make sure that you still retain editorial control over the project, and not end up writing a puff piece that treats its protagonist like a saint or hero. No biography can ever be entirely objective, but you should always strive for a portrayal that closely aligns with facts and reality.
If you can’t get an answer from your subject, or you’re asked not to proceed forward, you can still accept the potential repercussions and write an unauthorized biography . The “rebellious act” of publishing without consent indeed makes for great marketing, though it’ll likely bring more headaches with it too.
✋ Please note that, like other nonfiction books, if you intend to release your biography with a publishing house , you can put together a book proposal to send to them before you even write the book. If they like it enough, they might pay you an advance to write it.

Book Proposal Template
Craft a professional pitch for your nonfiction book with our handy template.
Once you’ve settled (or not) the permission part, it’s time to dive deep into your character’s story.
Deep and thorough research skills are the cornerstone of every biographer worth their salt. To paint a vivid and accurate portrait of someone's life, you’ll have to gather qualitative information from a wide range of reliable sources.
Start with the information already available, from books on your subject to archival documents, then collect new ones firsthand by interviewing people or traveling to locations.
Browse the web and library archives

Put your researcher hat on and start consuming any piece on your subject you can find, from their Wikipedia page to news articles, interviews, TV and radio appearances, YouTube videos, podcasts, books, magazines, and any other media outlets they may have been featured in.
Establish a system to orderly collect the information you find 一 even seemingly insignificant details can prove valuable during the writing process, so be sure to save them.
Depending on their era, you may find most of the information readily available online, or you may need to search through university libraries for older references.
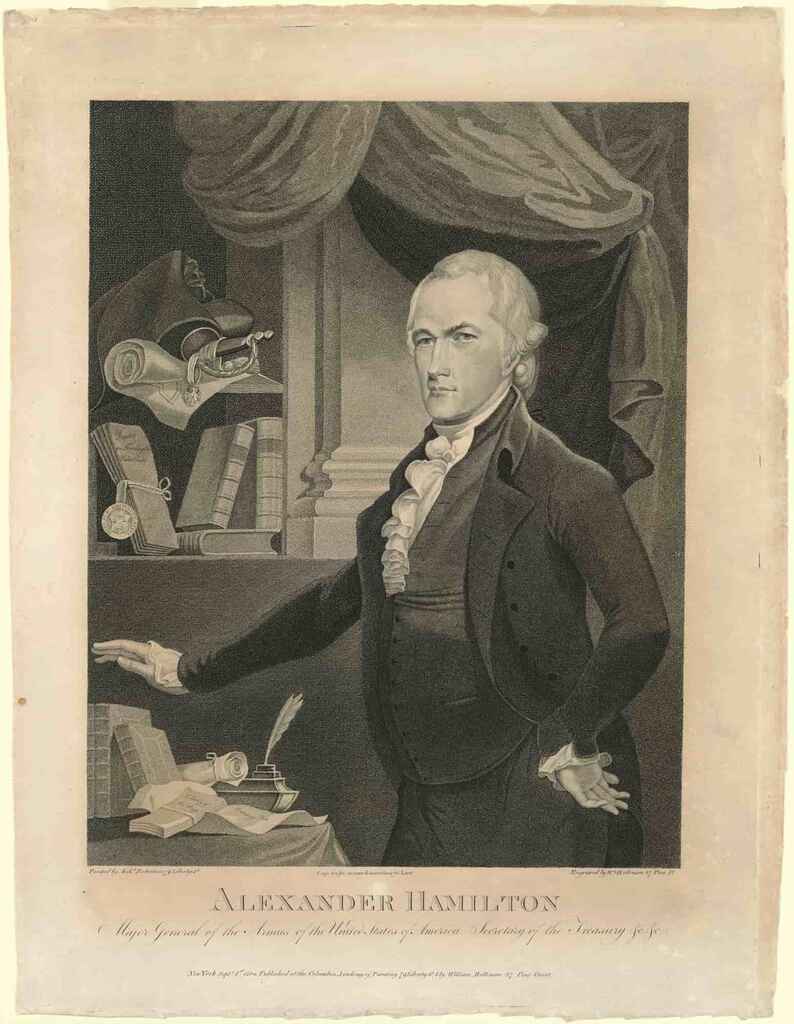

For his landmark biography of Alexander Hamilton, Ron Chernow spent untold hours at Columbia University’s library , reading through the Hamilton family papers, visiting the New York Historical Society, as well as interviewing the archivist of the New York Stock Exchange, and so on. The research process took years, but it certainly paid off. Chernow discovered that Hamilton created the first five securities originally traded on Wall Street. This finding, among others, revealed his significant contributions to shaping the current American financial and political systems, a legacy previously often overshadowed by other founding fathers. Today Alexander Hamilton is one of the best-selling biographies of all time, and it has become a cultural phenomenon with its own dedicated musical.
Besides reading documents about your subject, research can help you understand the world that your subject lived in.
Try to understand their time and social environment
Many biographies show how their protagonists have had a profound impact on society through their philosophical, artistic, or scientific contributions. But at the same time, it’s worth it as a biographer to make an effort to understand how their societal and historical context influenced their life’s path and work.
An interesting example is Stephen Greenblatt’s Will in the World . Finding himself limited by a lack of verified detail surrounding William Shakespeare's personal life, Greenblatt, instead, employs literary interpretation and imaginative reenactments to transport readers back to the Elizabethan era. The result is a vivid (though speculative) depiction of the playwright's life, enriching our understanding of his world.

Many readers enjoy biographies that transport them to a time and place, so exploring a historical period through the lens of a character can be entertaining in its own right. The Diary of Samuel Pepys became a classic not because people were enthralled by his life as an administrator, but rather from his meticulous and vivid documentation of everyday existence during the Restoration period.
Once you’ve gotten your hands on as many secondary sources as you can find, you’ll want to go hunting for stories first-hand from people who are (or were) close to your subject.
With all the material you’ve been through, by now you should already have a pretty good picture of your protagonist. But you’ll surely have some curiosities and missing dots in their character arc to figure out, which you can only get by interviewing primary sources.
Interview friends and associates
This part is more relevant if your subject is contemporary, and you can actually meet up or call with relatives, friends, colleagues, business partners, neighbors, or any other person related to them.
In writing the popular biography of Steve Jobs, Walter Isaacson interviewed more than one hundred people, including Jobs’s family, colleagues, former college mates, business rivals, and the man himself.
🔍 Read other biographies to get a sense of what makes a great one. Check out our list of the 30 best biographies of all time , or take our 30-second quiz below for tips on which one you should read next.
Which biography should you read next?
Discover the perfect biography for you. Takes 30 seconds!
When you conduct your interviews, make sure to record them with high quality audio you can revisit later. Then use tools like Otter.ai or Descript to transcribe them 一 it’ll save you countless hours.
You can approach the interview with a specific set of questions, or follow your curiosity blindly, trying to uncover revealing stories and anecdotes about your subject. Whatever your method, author and biography editor Tom Bromley suggests that every interviewer arrives prepared, "Show that you’ve done your work. This will help to put the interviewee at ease, and get their best answers.”
Bromley also places emphasis on the order in which you conduct interviews. “You may want to interview different members of the family or friends first, to get their perspective on something, and then go directly to the main interviewee. You'll be able to use that knowledge to ask sharper, more specific questions.”
Finally, consider how much time you have with each interviewee. If you only have a 30-minute phone call with an important person, make it count by asking directly the most pressing questions you have. And, if you find a reliable source who is also particularly willing to help, conduct several interviews and ask them, if appropriate, to write a foreword as part of the book’s front matter .
Sometimes an important part of the process is packing your bags, getting on a plane, and personally visiting significant places in your character’s journey.
Visit significant places in their life
A place, whether that’s a city, a rural house, or a bodhi tree, can carry a particular energy that you can only truly experience by being there. In putting the pieces together about someone’s life, it may be useful to go visit where they grew up, or where other significant events of their lives happened. It will be easier to imagine what they experienced, and better tell their story.
In researching The Lost City of Z , author David Grann embarked on a trek through the Amazon, retracing the steps of British explorer Percy Fawcett. This led Grann to develop new theories about the circumstances surrounding the explorer's disappearance.

Hopefully, you won’t have to deal with jaguars and anacondas to better understand your subject’s environment, but try to walk into their shoes as much as possible.
Once you’ve researched your character enough, it’s time to put together all the puzzle pieces you collected so far.
Take the bulk of notes, media, and other documents you’ve collected, and start to give them some order and structure. A simple way to do this is by creating a timeline.
Create a chronological timeline
It helps to organize your notes chronologically 一 from childhood to the senior years, line up the most significant events of your subject’s life, including dates, places, names and other relevant bits.
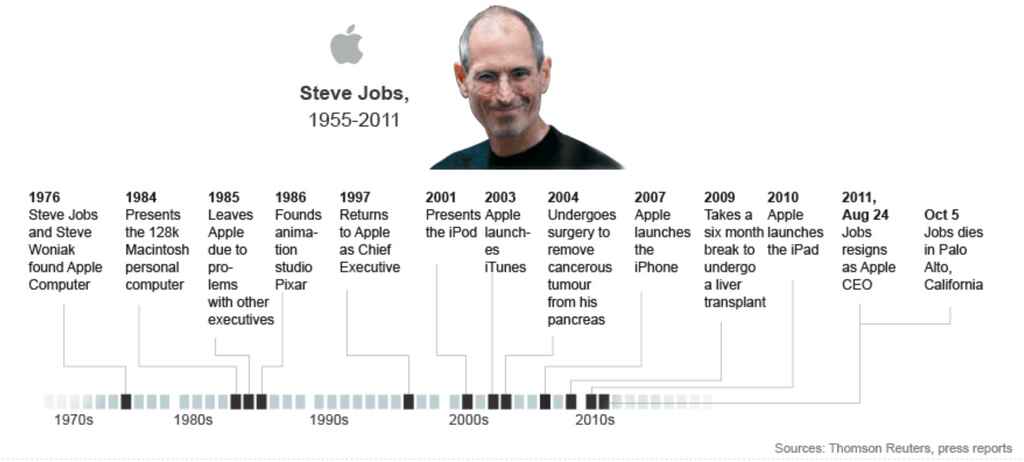
You should be able to divide their life into distinct periods, each with their unique events and significance. Based on that, you can start drafting an outline of the narrative you want to create.
Draft a story outline
Since a biography entails writing about a person’s entire life, it will have a beginning, a middle, and an end. You can pick where you want to end the story, depending on how consequential the last years of your subject were. But the nature of the work will give you a starting character arc to work with.
To outline the story then, you could turn to the popular Three-Act Structure , which divides the narrative in three main parts. In a nutshell, you’ll want to make sure to have the following:
- Act 1. Setup : Introduce the protagonist's background and the turning points that set them on a path to achieve a goal.
- Act 2. Confrontation : Describe the challenges they encounter, both internal and external, and how they rise to them. Then..
- Act 3. Resolution : Reach a climactic point in their story in which they succeed (or fail), showing how they (and the world around them) have changed as a result.
Only one question remains before you begin writing: what will be the main focus of your biography?
Think about why you’re so drawn to your subject to dedicate years of your life to recounting their own. What aspect of their life do you want to highlight? Is it their evil nature, artistic genius, or visionary mindset? And what evidence have you got to back that up? Find a central thesis or focus to weave as the main thread throughout your narrative.

Or find a unique angle
If you don’t have a particular theme to explore, finding a distinct angle on your subject’s story can also help you distinguish your work from other biographies or existing works on the same subject.
Plenty of biographies have been published about The Beatles 一 many of which have different focuses and approaches:
- Philip Norman's Shout is sometimes regarded as leaning more towards a pro-Lennon and anti-McCartney stance, offering insights into the band's inner dynamics.
- Ian McDonald's Revolution in the Head closely examines their music track by track, shifting the focus back to McCartney as a primary creative force.
- Craig Brown's One Two Three Four aims to capture their story through anecdotes, fan letters, diary entries, and interviews.
- Mark Lewisohn's monumental three-volume biography, Tune In , stands as a testament to over a decade of meticulous research, chronicling every intricate detail of the Beatles' journey.

Finally, consider that biographies are often more than recounting the life of a person. Similar to how Dickens’ Great Expectations is not solely about a boy named Pip (but an examination and critique of Britain’s fickle, unforgiving class system), a biography should strive to illuminate a broader truth — be it social, political, or human — beyond the immediate subject of the book.
Once you’ve identified your main focus or angle, it’s time to write a great story.

While biographies are often highly informative, they do not have to be dry and purely expository in nature . You can play with storytelling elements to make it an engaging read.
You could do that by thoroughly detailing the setting of the story , depicting the people involved in the story as fully-fledged characters , or using rising action and building to a climax when describing a particularly significant milestone of the subject’s life.
One common way to make a biography interesting to read is starting on a strong foot…
Hook the reader from the start
Just because you're honoring your character's whole life doesn't mean you have to begin when they said their first word. Starting from the middle or end of their life can be more captivating as it introduces conflicts and stakes that shaped their journey.
When he wrote about Christopher McCandless in Into the Wild , author Jon Krakauer didn’t open his subject’s childhood and abusive family environment. Instead, the book begins with McCandless hitchhiking his way into the wilderness, and subsequently being discovered dead in an abandoned bus. By starting in medias res , Krakauer hooks the reader’s interest, before tracing back the causes and motivations that led McCandless to die alone in that bus in the first place.

You can bend the timeline to improve the reader’s reading experience throughout the rest of the story too…
Play with flashback
While biographies tend to follow a chronological narrative, you can use flashbacks to tell brief stories or anecdotes when appropriate. For example, if you were telling the story of footballer Lionel Messi, before the climax of winning the World Cup with Argentina, you could recall when he was just 13 years old, giving an interview to a local newspaper, expressing his lifelong dream of playing for the national team.
Used sparsely and intentionally, flashbacks can add more context to the story and keep the narrative interesting. Just like including dialogue does…
Reimagine conversations
Recreating conversations that your subject had with people around them is another effective way to color the story. Dialogue helps the reader imagine the story like a movie, providing a deeper sensory experience.

One thing is trying to articulate the root of Steve Jobs’ obsession with product design, another would be to quote his father , teaching him how to build a fence when he was young: “You've got to make the back of the fence just as good looking as the front of the fence. Even though nobody will see it, you will know. And that will show that you're dedicated to making something perfect.”
Unlike memoirs and autobiographies, in which the author tells the story from their personal viewpoint and enjoys greater freedom to recall conversations, biographies require a commitment to facts. So, when recreating dialogue, try to quote directly from reliable sources like personal diaries, emails, and text messages. You could also use your interview scripts as an alternative to dialogue. As Tom Bromley suggests, “If you talk with a good amount of people, you can try to tell the story from their perspective, interweaving different segments and quoting the interviewees directly.”

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you’ve finished your manuscript, it’s a good idea to ask for feedback.
If you’re going to self-publish your biography, you’ll have to polish it to professional standards. After leaving your work to rest for a while, look at it with fresh eyes and self-edit your manuscript eliminating passive voice, filler words, and redundant adverbs.

Then, have a professional editor give you a general assessment. They’ll look at the structure and shape of your manuscript and tell you which parts need to be expanded on or cut. As someone who edited and commissioned several biographies, Tom Bromley points out that a professional “will look at the sources used and assess whether they back up the points made, or if more are needed. They would also look for context, and whether or not more background information is needed for the reader to understand the story fully. And they might check your facts, too.”
In addition to structural editing, you may want to have someone copy-edit and proofread your work.

MEET EDITORS
Polish your book with expert help
Sign up, meet 1500+ experienced editors, and find your perfect match.
Importantly, make sure to include a bibliography with a list of all the interviews, documents, and sources used in the writing process. You’ll have to compile it according to a manual of style, but you can easily create one by using tools like EasyBib . Once the text is nicely polished and typeset in your writing software , you can prepare for the publication process.
In conclusion, by mixing storytelling elements with diligent research, you’ll be able to breathe life into a powerful biography that immerses readers in another individual’s life experience. Whether that’ll spark inspiration or controversy, remember you could have an important role in shaping their legacy 一 and that’s something not to take lightly.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph?
From fiction to nonfiction works, the length of a paragraph varies depending on its purpose. Here's everything you need to know.
Narrative Structure: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
What's the difference between story structure and narrative structure? And how do you choose the right narrative structure for you novel?

What is the Proust Questionnaire? 22 Questions to Write Better Characters
Inspired by Marcel Proust, check out the questionnaire that will help your characters remember things past.

What is Pathos? Definition and Examples in Literature
Pathos is a literary device that uses language to evoke an emotional response, typically to connect readers with the characters in a story.

How to Start a Children’s Book: Coming Up with Your Big Idea
If you've ever dreamed of writing a children's book but aren't sure where to start, check out this post to learn more about how you can create the perfect story for kids.

How to Become a Travel Writer in 5 Steps: A Guide for Travel Bugs
If you want to get paid to share your adventures, learn how to become a travel writer with these five tips.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
We have an app for that
Build a writing routine with our free writing app.


1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

How to Write a Biography
Biographies are big business. Whether in book form or Hollywood biopics, the lives of the famous and sometimes not-so-famous fascinate us.
While it’s true that most biographies are about people who are in the public eye, sometimes the subject is less well-known. Mostly though, famous or not, the person who is written about has led a life that is in some way incredible.
While your students will most likely have a basic understanding of a biography, it’s worth taking a little time before they put pen to paper to tease out a crystal clear definition of a biography.

What Is a Biography?

Simply put, a biography is an account of someone’s life written by someone else . While there is a genre known as a fictional biography, for the most part, biographies are, by definition, nonfiction.
Generally speaking, biographies provide an account of the subject’s life from the earliest days of their childhood right up to the present day or their death if the subject is deceased.
The job of a biography is more than just to outline the bare facts of a person’s life.
Rather than just listing the basic details of their upbringing, hobbies, education, work, relationships, and death, a well-written biography should also paint a picture of the subject’s personality, and as well as their experience of life.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING BIOGRAPHIES

Teach your students to write AMAZING BIOGRAPHIES & AUTOBIOGRAPHIES using proven RESEARCH SKILLS and WRITING STRATEGIES .
- Understand the purpose of both forms of biography.
- Explore the language and perspective of both.
- Prompts and Challenges to engage students in writing a biography.
- Dedicated lessons for both forms of biography.
- Biographical Projects can expand students’ understanding of reading and writing a biography.
- A COMPLETE 82-PAGE UNIT – NO PREPARATION REQUIRED.
What Are the Main Features of a Biography?
Before students begin writing a biography, they’ll need to have a firm grasp of the main features of the genre. A good way to determine how well they understand these essential elements of the genre is by asking them to compile a checklist.
At a minimum, their checklists should contain the items below. Be sure to help them fill in any gaps before moving on to the writing process.
The purpose of a biography is to provide an account of someone’s life.
Biography structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Open your biography with a strong hook to grab the reader’s attention
SEQUENCING: In most cases, biographies are written in chronological order unless you are a very competent writer consciously trying to break from this trend.
COVER: childhood, upbringing, education, influences, accomplishments, relationships, etc. – everything that helps the reader to understand the person.
CONCLUSION: Wrap your biography up with some details about what the subject is doing now if they are still alive. If they have passed away, make mention of what impact they have made and what their legacy is or will be.
BIOGRAPHY FEATURES
LANGUAGE Use descriptive and figurative language that will paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read. Use time connectives to link events.
PERSPECTIVE Biographies are written from the third person’s perspective.
DETAILS: Give specific details about people, places, events, times, dates, etc. Reflect on how events shaped the subject. You might want to include some relevant photographs with captions. A timeline may also be of use depending upon your subject and what you are trying to convey to your audience.
TENSE Written in the past tense (though ending may shift to the present/future tense)
THE PROCESS OF WRITING A BIOGRAPHY
Like any form of writing, you will find it simple if you have a plan and follow it through. These steps will ensure you cover the essential bases of writing a biography essay.
Firstly, select a subject that inspires you. Someone whose life story resonates with you and whose contribution to society intrigues you. The next step is to conduct thorough research. Engage in extensive reading, explore various sources, watch documentaries, and glean all available information to provide a comprehensive account of the person’s life.
Creating an outline is essential to organize your thoughts and information. The outline should include the person’s early life, education, career, achievements, and any other significant events or contributions. It serves as a map for the writing process, ensuring that all vital information is included.
Your biography should have an engaging introduction that captivates the reader’s attention and provides background information on the person you’re writing about. It should include a thesis statement that summarizes the main points of the biography.
Writing a biography in chronological order is crucial . You should begin with the person’s early life and move through their career and achievements. This approach provides clarity on how the person’s life unfolded and how they accomplished their goals.
A biography should be written in a narrative style , capturing the essence of the person’s life through vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and quotes. Avoid dry, factual writing and focus on creating a compelling narrative that engages the reader.
Adding personal insights and opinions can enhance the biography’s overall impact, providing a unique perspective on the person’s achievements, legacy, and impact on society.
Editing and proofreading are vital elements of the writing process. Thoroughly reviewing your biography ensures that the writing is clear, concise, and error-free. You can even request feedback from someone else to ensure that it is engaging and well-written.
Finally, including a bibliography at the end of your biography is essential. It gives credit to the sources that were used during research, such as books, articles, interviews, and websites.
Tips for Writing a Brilliant Biography
Biography writing tip #1: choose your subject wisely.
There are several points for students to reflect on when deciding on a subject for their biography. Let’s take a look at the most essential points to consider when deciding on the subject for a biography:
Interest: To produce a biography will require sustained writing from the student. That’s why students must choose their subject well. After all, a biography is an account of someone’s entire life to date. Students must ensure they choose a subject that will sustain their interest throughout the research, writing, and editing processes.
Merit: Closely related to the previous point, students must consider whether the subject merits the reader’s interest. Aside from pure labors of love, writing should be undertaken with the reader in mind. While producing a biography demands sustained writing from the author, it also demands sustained reading from the reader.
Therefore, students should ask themselves if their chosen subject has had a life worthy of the reader’s interest and the time they’d need to invest in reading their biography.
Information: Is there enough information available on the subject to fuel the writing of an entire biography? While it might be a tempting idea to write about a great-great-grandfather’s experience in the war. There would be enough interest there to sustain the author’s and the reader’s interest, but do you have enough access to information about their early childhood to do the subject justice in the form of a biography?
Biography Writing Tip #2: R esearch ! Research! Research!
While the chances are good that the student already knows quite a bit about the subject they’ve chosen. Chances are 100% that they’ll still need to undertake considerable research to write their biography.
As with many types of writing , research is an essential part of the planning process that shouldn’t be overlooked. If a student wishes to give as complete an account of their subject’s life as possible, they’ll need to put in the time at the research stage.
An effective way to approach the research process is to:
1. Compile a chronological timeline of the central facts, dates, and events of the subject’s life
2. Compile detailed descriptions of the following personal traits:
- Physical looks
- Character traits
- Values and beliefs
3. Compile some research questions based on different topics to provide a focus for the research:
- Childhood : Where and when were they born? Who were their parents? Who were the other family members? What education did they receive?
- Obstacles: What challenges did they have to overcome? How did these challenges shape them as individuals?
- Legacy: What impact did this person have on the world and/or the people around them?
- Dialogue & Quotes: Dialogue and quotations by and about the subject are a great way to bring color and life to a biography. Students should keep an eagle eye out for the gems that hide amid their sources.
As the student gets deeper into their research, new questions will arise that can further fuel the research process and help to shape the direction the biography will ultimately go in.
Likewise, during the research, themes will often begin to suggest themselves. Exploring these themes is essential to bring depth to biography, but we’ll discuss this later in this article.
Research Skills:
Researching for biography writing is an excellent way for students to hone their research skills in general. Developing good research skills is essential for future academic success. Students will have opportunities to learn how to:
- Gather relevant information
- Evaluate different information sources
- Select suitable information
- Organize information into a text.
Students will have access to print and online information sources, and, in some cases, they may also have access to people who knew or know the subject (e.g. biography of a family member).
These days, much of the research will likely take place online. It’s crucial, therefore, to provide your students with guidance on how to use the internet safely and evaluate online sources for reliability. This is the era of ‘ fake news ’ and misinformation after all!
COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON INTERNET RESEARCH SKILLS USING GOOGLE SEARCH

Teach your students ESSENTIAL SKILLS OF THE INFORMATION ERA to become expert DIGITAL RESEARCHERS.
⭐How to correctly ask questions to search engines on all devices.
⭐ How to filter and refine your results to find exactly what you want every time.
⭐ Essential Research and critical thinking skills for students.
⭐ Plagiarism, Citing and acknowledging other people’s work.
⭐ How to query, synthesize and record your findings logically.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip #3: Find Your Themes In Biography Writing
Though predominantly a nonfiction genre, the story still plays a significant role in good biography writing. The skills of characterization and plot structuring are transferable here. And, just like in fiction, exploring themes in a biographical work helps connect the personal to the universal. Of course, these shouldn’t be forced; this will make the work seem contrived, and the reader may lose faith in the truthfulness of the account. A biographer needs to gain and maintain the trust of the reader.
Fortunately, themes shouldn’t need to be forced. A life well-lived is full of meaning, and the themes the student writer is looking for will emerge effortlessly from the actions and events of the subject’s life. It’s just a case of learning how to spot them.
One way to identify the themes in a life is to look for recurring events or situations in a person’s life. These should be apparent from the research completed previously. The students should seek to identify these patterns that emerge in the subject’s life. For example, perhaps they’ve had to overcome various obstacles throughout different periods of their life. In that case, the theme of overcoming adversity is present and has been identified.
Usually, a biography has several themes running throughout, so be sure your students work to identify more than one theme in their subject’s life.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip: #4 Put Something of Yourself into the Writing
While the defining feature of a biography is that it gives an account of a person’s life, students must understand that this is not all a biography does. Relating the facts and details of a subject’s life is not enough. The student biographer should not be afraid to share their thoughts and feelings with the reader throughout their account of their subject’s life.
The student can weave some of their personality into the fabric of the text by providing commentary and opinion as they relate the events of the person’s life and the wider social context at the time. Unlike the detached and objective approach we’d expect to find in a history textbook, in a biography, student-writers should communicate their enthusiasm for their subject in their writing.
This makes for a more intimate experience for the reader, as they get a sense of getting to know the author and the subject they are writing about.
Student Examples of Biography Writing
- Year 5 Example
- Year 7 Example
- Year 9 Example
“The Rock ‘n’ Roll King: Elvis Presley”
Elvis Aaron Presley, born on January 8, 1935, was an amazing singer and actor known as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Even though he’s been dead for nearly 50 years, I can’t help but be fascinated by his incredible life!
Elvis grew up in Tupelo, Mississippi, in a tiny house with his parents and twin brother. His family didn’t have much money, but they shared a love for music. Little did they know Elvis would become a music legend!
When he was only 11 years old, Elvis got his first guitar. He taught himself to play and loved singing gospel songs. As he got older, he started combining different music styles like country, blues, and gospel to create a whole new sound – that’s Rock ‘n’ Roll!
In 1954, at the age of 19, Elvis recorded his first song, “That’s All Right.” People couldn’t believe how unique and exciting his music was. His famous hip-swinging dance moves also made him a sensation!
Elvis didn’t just rock the music scene; he also starred in movies like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.” But fame came with challenges. Despite facing ups and downs, Elvis kept spreading happiness through his music.

Tragically, Elvis passed away in 1977, but his music and charisma live on. Even today, people worldwide still enjoy his songs like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love.” Elvis Presley’s legacy as the King of Rock ‘n’ Roll will live forever.
Long Live the King: I wish I’d seen him.
Elvis Presley, the Rock ‘n’ Roll legend born on January 8, 1935, is a captivating figure that even a modern-day teen like me can’t help but admire. As I delve into his life, I wish I could have experienced the magic of his live performances.
Growing up in Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis faced challenges but found solace in music. At 11, he got his first guitar, a symbol of his journey into the world of sound. His fusion of gospel, country, and blues into Rock ‘n’ Roll became a cultural phenomenon.
The thought of being in the audience during his early performances, especially when he recorded “That’s All Right” at 19, sends shivers down my spine. Imagining the crowd’s uproar and feeling the revolutionary energy of that moment is a dream I wish I could have lived.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical prodigy; he was a dynamic performer. His dance moves, the embodiment of rebellion, and his roles in films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock” made him a true icon.
After watching him on YouTube, I can’t help but feel a little sad that I’ll never witness the King’s live performances. The idea of swaying to “Hound Dog” or being enchanted by “Can’t Help Falling in Love” in person is a missed opportunity. Elvis may have left us in 1977, but he was the king of rock n’ roll. Long live the King!
Elvis Presley: A Teen’s Take on the Rock ‘n’ Roll Icon”
Elvis Presley, born January 8, 1935, was a revolutionary force in the music world, earning his title as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Exploring his life, even as a 16-year-old today, I’m captivated by the impact he made.
Hailing from Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis grew up in humble beginnings, surrounded by the love of his parents and twin brother. It’s inspiring to think that, despite financial challenges, this young man would redefine the music scene.
At 11, Elvis got his first guitar, sparking a self-taught journey into music. His early gospel influences evolved into a unique fusion of country, blues, and gospel, creating the electrifying genre of Rock ‘n’ Roll. In 1954, at only 19, he recorded “That’s All Right,” marking the birth of a musical legend.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical innovator; he was a cultural phenomenon. His rebellious dance moves and magnetic stage presence challenged the norms. He transitioned seamlessly into acting, starring in iconic films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.”

However, fame came at a cost, and Elvis faced personal struggles. Despite the challenges, his music continued to resonate. Even now, classics like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love” transcend generations.
Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is undeniable. He was known for his unique voice, charismatic persona, and electrifying performances. He sold over one billion records worldwide, making him one of the best-selling solo artists in history. He received numerous awards throughout his career, including three Grammy Awards and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Elvis’s influence can still be seen in today’s music. Many contemporary artists, such as Bruno Mars, Lady Gaga, and Justin Timberlake, have cited Elvis as an inspiration. His music continues to be featured in movies, TV shows, and commercials.
Elvis left us in 1977, but his legacy lives on. I appreciate his breaking barriers and fearlessly embracing his artistic vision. Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is timeless, a testament to the enduring power of his artistry. His music has inspired generations and will continue to do so for many years to come.

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING TEACHING IDEAS AND LESSONS
We have compiled a sequence of biography-related lessons or teaching ideas that you can follow as you please. They are straightforward enough for most students to follow without further instruction.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 1:
This session aims to give students a broader understanding of what makes a good biography.
Once your students have compiled a comprehensive checklist of the main features of a biography, allow them to use it to assess some biographies from your school library or on the internet using the feature checklist.
When students have assessed a selection of biographies, take some time as a class to discuss them. You can base the discussion around the following prompts:
- Which biographies covered all the criteria from their checklist?
- Which biographies didn’t?
- Which biography was the most readable in terms of structure?
- Which biography do you think was the least well-structured? How would you improve this?
Looking at how other writers have interpreted the form will help students internalize the necessary criteria before attempting to produce a biography. Once students have a clear understanding of the main features of the biography, they’re ready to begin work on writing a biography.
When the time does come to put pen to paper, be sure they’re armed with the following top tips to help ensure they’re as well prepared as possible.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 2:
This session aims to guide students through the process of selecting the perfect biography subject.
Instruct students to draw up a shortlist of three potential subjects for the biography they’ll write.
Using the three criteria mentioned in the writing guide (Interest, Merit, and Information), students award each potential subject a mark out of 5 for each of the criteria. In this manner, students can select the most suitable subject for their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 3:
This session aims to get students into the researching phase and then prioritise events and organise them chronologically.
Students begin by making a timeline of their subject’s life, starting with their birth and ending with their death or the present day. If the student has yet to make a final decision on the subject of their biography, a family member will often serve well for this exercise as a practice exercise.
Students should research and gather the key events of the person’s life, covering each period of their life from when they were a baby, through childhood and adolescence, right up to adulthood and old age. They should then organize these onto a timeline. Students can include photographs with captions if they have them.
They can present these to the class when they have finished their timelines.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 4:
Instruct students to look over their timeline, notes, and other research. Challenge them to identify three patterns that repeat throughout the subject’s life and sort all the related events and incidents into specific categories.
Students should then label each category with a single word. This is the thematic concept or the broad general underlying idea. After that, students should write a sentence or two expressing what the subject’s life ‘says’ about that concept.
This is known as the thematic statement . With the thematic concepts and thematic statements identified, the student now has some substantial ideas to explore that will help bring more profound meaning and wider resonance to their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 5:
Instruct students to write a short objective account of an event in their own life. They can write about anyone from their past. It needn’t be more than a couple of paragraphs, but the writing should be strictly factual, focusing only on the objective details of what happened.
Once they have completed this, it’s time to rewrite the paragraph, but they should include some opinion and personal commentary this time.
The student here aims to inject some color and personality into their writing, to transform a detached, factual account into a warm, engaging story.
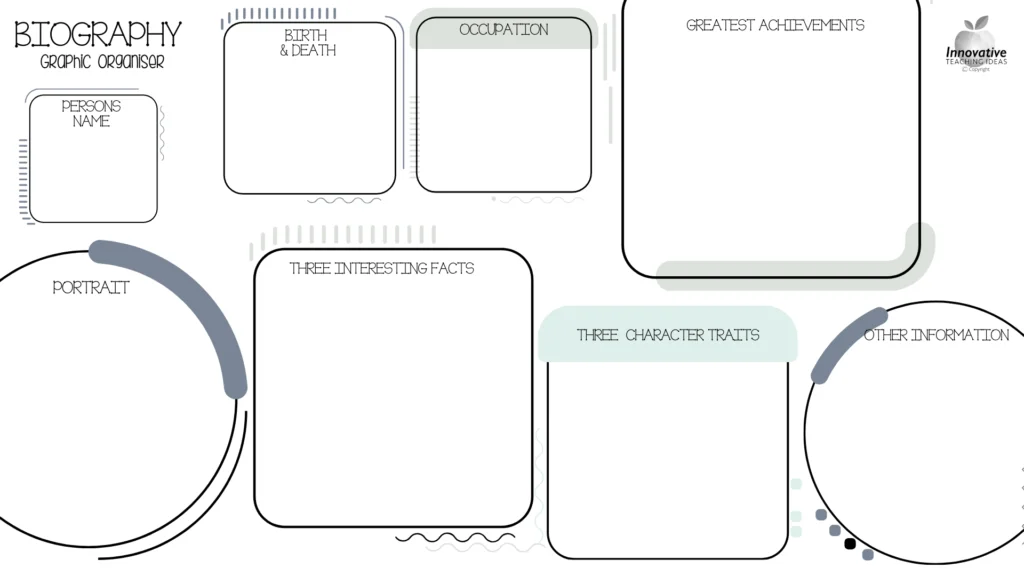
Get our FREE Biography Writing Graphic Organizer
Use this valuable tool in the research and writing phases to keep your students on track and engaged.
WRITING CHECKLIST & RUBRIC BUNDLE

To Conclude
By this stage, your students should have an excellent technical overview of a biography’s essential elements.
They should be able to choose their subject in light of how interesting and worthy they are, as well as give consideration to the availability of information out there. They should be able to research effectively and identify emerging themes in their research notes. And finally, they should be able to bring some of their personality and uniqueness into their retelling of the life of another.
Remember that writing a biography is not only a great way to develop a student’s writing skills; it can be used in almost all curriculum areas. For example, to find out more about a historical figure in History, to investigate scientific contributions to Science, or to celebrate a hero from everyday life.
Biography is an excellent genre for students to develop their writing skills and to find inspiration in the lives of others in the world around them.
HOW TO WRITE A BIOGRAPHY TUTORIAL VIDEO

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO BIOGRAPHY WRITING

How to write an Autobiography

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

15 Awesome Recount & Personal Narrative Topics

Personal Narrative Writing Guide
+1 888 598 4094

- Memoir Writing
- Children Book Writing
- Book Writing
- eBook Writing
- Business Book Writing
- Medical Writing
- Wikipedia Page Creation Services
- Book Editing
- Book Formatting
- Book Proofreading
- Book Cover Designers
- Amazon Book Publishing Services
- Book Marketing
- Hip Hop Ghostwriting
- Speech Writing
- Children’s Book Editing
+1 888 512 0705
A Guide on How to Write a Biography Book About Yourself
- December 22, 2023
Writing a biography book about yourself is a deeply personal and introspective journey. It’s not just about narrating events from your life; it’s about delving into the depths of your experiences, challenges, triumphs, and growth. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore every aspect of crafting your own biography, ensuring it is not only engaging and impactful but also optimized for search engines. Let’s embark on this literary adventure, starting with the fundamental step of defining your purpose.
Defining Your Purpose
Before you put pen to paper, it’s crucial to understand why you want to write your biography. Are you aiming to inspire others, share life lessons, or simply preserve your memories for future generations? Defining your purpose will shape the tone, style, and content of your book, making it resonate deeply with your readers. This clarity of purpose will guide you throughout your writing journey, ensuring your narrative remains focused and impactful.
Navigating the Journey of Self-Biography
Navigating the intricate paths of self-biography requires introspection and honesty. It’s not just a recollection of events; it’s a profound exploration of your identity, values, and beliefs. As you embark on this journey, you will encounter challenges and triumphs, moments of self-discovery, and reflections that will shape your narrative. Embrace this journey with an open heart and mind, and your biography will undoubtedly reflect the authenticity of your experiences.
1. Getting Started
Once your purpose is defined, the next step is to identify your target audience. Who are you writing for? Understanding your audience helps you tailor your story to meet their expectations and resonate with their emotions. Whether it’s young adults seeking inspiration or history enthusiasts intrigued by personal narratives, knowing your audience guides your writing style, language, and the themes you choose to explore.
Setting Clear Objectives
Set clear objectives for your biography. Are you aiming for a chronological retelling of your life, or do you intend to focus on specific themes and experiences? Establishing these objectives provides a roadmap for your writing, helping you stay organized and ensuring your narrative remains coherent and engaging.
Gathering Essential Materials
Collecting essential materials is akin to gathering the raw ingredients for a culinary masterpiece. These materials include photographs, letters, diaries, and other memorabilia that provide a tangible connection to your past. These artifacts not only enrich your narrative but also serve as visual aids, immersing readers in the world you are describing. Use these materials strategically, weaving them into your story to enhance the reader’s experience.
2. Choosing Your Narrative Approach
Your narrative approach is the lens through which readers will perceive your story. You have several options: first-person perspective, where you narrate your experiences directly; third-person perspective, where an external narrator tells your story; or a blend of both, allowing for a multifaceted exploration of your life. Each approach offers unique advantages, shaping the reader’s connection with your narrative. Choose the one that aligns with your purpose and resonates with your audience.
First-Person Perspective
Writing in the first person provides an intimate and immersive experience for the reader. It allows them to step into your shoes, experiencing the events and emotions firsthand. This approach creates a strong sense of empathy, making it ideal for personal and emotional narratives. When adopting the first-person perspective, focus on authenticity, capturing your voice, emotions, and thought processes with vivid detail.
Third-Person Perspective
In contrast, the third-person perspective provides a degree of detachment, allowing for a more objective portrayal of your life. This approach is often used for biographies that aim to analyze your life from an outsider’s perspective. It offers a broader view, enabling you to explore societal, cultural, or historical contexts that influenced your experiences. When employing the third-person perspective, maintain a balance between objectivity and empathy, ensuring your story remains engaging and relatable.
Blending Perspectives for Impact
For a nuanced and impactful narrative, consider blending perspectives. Combining the first-person account with an external narrator’s viewpoint offers the best of both worlds. You can share your innermost thoughts and emotions while providing an objective analysis of your life. This approach adds depth and complexity to your story, captivating readers and inviting them into the intricate layers of your experiences.
3. Crafting Your Personal Story
With your narrative approach in place, it’s time to delve into the heart of your biography: your personal story. This section focuses on shaping your early life, highlighting milestones and transformative events, and discussing the challenges and triumphs that defined your journey.
Writing Your Early Life
Begin your biography by painting a vivid picture of your early life. Describe the environment, family dynamics, and cultural influences that shaped your upbringing. Share anecdotes, memories, and experiences that had a profound impact on your character and values. Engage the reader’s senses, allowing them to smell, taste, hear, and feel the world you inhabited during your formative years.
Highlighting Milestones and Transformative Events
Milestones and transformative events are the cornerstones of your narrative. These moments define your character, marking significant turning points in your life. Whether it’s a personal achievement, a relationship, an epiphany, or a tragedy, these events shape your identity and provide a compelling arc to your story. Dive deep into the emotions you experienced during these moments, allowing readers to empathize with your joys, sorrows, and personal growth.
Discussing Challenges and Triumphs
Life is a journey of challenges and triumphs, and your biography should reflect this reality. Be candid about the obstacles you faced, whether they were internal struggles, societal pressures, or external adversities. Describe how these challenges tested your resilience, leading to personal growth and transformation. Balance these narratives with stories of triumph, showcasing your determination, perseverance, and the lessons you learned along the way.
4. Character Development
In a self-biography, you are not only the protagonist but also the storyteller. As the author, your task is to portray yourself and the people in your life with depth and authenticity. This section explores the art of character development, emphasizing relatability and the role of dialogue in bringing your characters to life.
Portraying Yourself and Others
When portraying yourself, be honest and vulnerable. Acknowledge your flaws, fears, and insecurities, as these elements make you relatable and genuine. Balance self-reflection with self-compassion, allowing readers to see your growth and resilience in the face of challenges. When depicting others, whether family, friends, or mentors, capture their unique personalities, quirks, and contributions to your journey. Humanize them, showcasing the impact they had on your life and the dynamics of your relationships.
Building Relatable Characters
Relatability is the key to connecting with your readers. Regardless of the differences in life experiences, emotions are universal. Readers should empathize with your characters, seeing aspects of themselves reflected in your narrative. To achieve this, focus on the shared human experiences—love, loss, joy, and pain. Describe emotions in vivid detail, allowing readers to feel the depth of your experiences. By creating relatable characters, you forge an emotional bond with your audience, drawing them into your story on a profound level.
The Role of Dialogue
Dialogue is a powerful tool for character development. It adds authenticity to your narrative, allowing characters to express their thoughts, emotions, and unique voices. When incorporating dialogue, pay attention to natural speech patterns and nuances of language. Use dialogue to reveal your characters’ personalities, relationships, and conflicts. Engage readers in conversations that are meaningful and revealing, shedding light on the dynamics between you and others. Well-crafted dialogue enhances the realism of your story, immersing readers in the world you’ve created.
5. Structuring Your Biography
The structure of your biography determines how your story unfolds. Whether you choose a chronological order or a thematic structure, your decision impacts the pacing, flow, and emotional impact of your narrative. This section explores the pros and cons of different structures and offers guidance on creating engaging chapters that balance plot and personal growth.
Chronological Order vs. Thematic Structure
Chronological order presents events in the order they occurred, offering a clear timeline of your life. This structure provides a logical and easy-to-follow narrative, allowing readers to witness your growth and development over time. It’s particularly effective for autobiographies, as it mirrors the natural progression of life events. However, be mindful of monotony; ensure your narrative doesn’t become a mere recitation of facts. Infuse each event with emotion, reflection, and context, making it relevant to the overarching themes of your biography.
Thematic structure, on the other hand, organizes your narrative around specific themes or topics. This approach allows you to delve deeply into key aspects of your life, exploring related events and experiences in a cohesive manner. Thematic biographies offer flexibility, enabling you to focus on the themes that are most significant to your story. However, maintaining a coherent flow can be challenging. To overcome this, establish clear connections between themes, weaving them together with transitions and reflections. Each thematic chapter should contribute to the overall narrative arc, revealing different facets of your personality, challenges, and growth.
Creating Engaging Chapters
Regardless of the chosen structure, each chapter of your biography should be engaging and purposeful. Begin each chapter with a compelling hook, drawing readers into the story. This could be a moment of suspense, a thought-provoking question, or a poignant reflection. The opening sets the tone for the chapter, capturing the reader’s attention and curiosity. As the chapter unfolds, maintain a balance between storytelling and introspection. Blend descriptive narrative with reflective insights, allowing readers to experience the events while understanding their significance to your personal growth.
Balancing Plot and Personal Growth
Your biography is not just a sequence of events; it’s a narrative of personal growth and transformation. Balancing plot-driven elements with introspective insights is crucial. While events provide the external framework, your internal journey—emotions, thoughts, and reflections—forms the heart of your story. Strive for a harmonious blend of external events and internal revelations. For every plot point, delve into its emotional impact, exploring how it shaped your beliefs, values, and perspectives. By balancing plot and personal growth, you create a dynamic and enriching narrative that resonates deeply with readers.
6. Research and Fact-Checking
Accurate and reliable information forms the foundation of your biography. Thorough research and meticulous fact-checking are essential to ensure the credibility of your narrative. This section provides guidelines on sourcing information, fact-checking techniques, and ethical considerations to uphold the integrity of your work.
Sourcing Reliable Information
When researching your life events, rely on credible sources. This could include personal documents, official records, interviews with key figures, and historical archives. Verify the authenticity of each source, cross-referencing information to ensure accuracy. For events involving other people, such as family members or friends, consider their perspectives and experiences. Multiple viewpoints add depth to your narrative, presenting a holistic picture of the events in question. Respect the privacy and consent of individuals involved, seeking permission before including their stories in your biography.
Fact-Checking Techniques
Fact-checking is a meticulous process that involves verifying the accuracy of details, dates, names, and events mentioned in your biography. Create a comprehensive list of all factual claims made in your narrative and cross-check each detail with reliable sources. Fact-checking tools and databases can aid in confirming historical events and figures. Additionally, consult experts or historians for specialized knowledge, ensuring the authenticity of specific topics. Be thorough in your fact-checking, leaving no room for inaccuracies that could compromise the credibility of your work.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount when writing a biography, especially when it involves sensitive or controversial topics. Respect the privacy and dignity of individuals mentioned in your narrative, refraining from divulging private information without consent. If your biography involves living persons, obtain their permission before including their stories or experiences. Be mindful of cultural sensitivities, avoiding stereotypes or biases that could perpetuate harmful narratives. Ethical writing fosters trust with your readers, demonstrating your commitment to integrity and respect for the individuals portrayed in your biography.
7. Writing Style and Tone
The writing style and tone of your biography influence how readers perceive your story. Choosing the right tone, incorporating descriptive language, and honing your writing style are essential aspects of creating a captivating and immersive reading experience.
Choosing the Right Tone
The tone of your biography sets the mood and emotional atmosphere of your narrative. Consider the themes and messages you want to convey. Will your tone be reflective and introspective, inviting readers into your inner thoughts? Or will it be inspirational and motivational, encouraging readers to overcome challenges and embrace personal growth? Tailor your tone to align with your purpose and audience. Consistency in tone creates a cohesive reading experience, allowing readers to engage with your narrative on a deeper level.
Incorporating Descriptive Language
Descriptive language is the palette with which you paint vivid images in the minds of your readers. Engage the senses, describing sights, sounds, smells, tastes, and textures with rich detail. Create immersive settings that transport readers to specific moments in your life. Use metaphors, similes, and sensory imagery to evoke emotions and enhance the reader’s connection with your experiences. Balance descriptive passages with introspective insights, allowing readers to both visualize the scenes and understand their significance to your personal growth.
Honing Your Writing Style
Your writing style is your unique voice as an author. It reflects your personality, perspective, and creativity. Experiment with different styles, exploring various narrative techniques, sentence structures, and literary devices. Whether you prefer a lyrical prose, a straightforward narrative, or a blend of poetic and pragmatic language, find a style that resonates with your voice. Consistency in your writing style fosters a sense of familiarity for readers, immersing them in your story while appreciating your distinct authorial voice.
8. Editing and Proofreading
Writing the initial draft of your biography is just the beginning. The editing and proofreading process is where your narrative truly comes to life. This section explores self-editing strategies, seeking feedback, and the importance of professional editing in refining your manuscript.
Self-Editing Strategies
Self-editing is the first step in refining your manuscript. Begin by reviewing your work with a critical eye, focusing on clarity, coherence, and consistency. Check for grammatical errors, punctuation issues, and awkward phrasing. Assess the flow of your narrative, ensuring smooth transitions between paragraphs and chapters. Trim unnecessary details and repetitions, keeping the narrative concise and focused. Pay attention to the pacing, balancing slower, reflective moments with faster-paced, engaging scenes. Self-editing allows you to polish your manuscript before seeking external feedback.
Seeking Feedback
External feedback is invaluable in gaining perspective on your work. Share your manuscript with beta readers, writing groups, or trusted friends and family members. Encourage them to provide honest feedback on the overall structure, pacing, character development, and emotional impact of your narrative. Constructive criticism helps you identify strengths and weaknesses, guiding your revisions. Be open to feedback, considering different viewpoints and suggestions. As the author, you are deeply immersed in your story, making external feedback essential in identifying areas that may require further refinement.
The Importance of Professional Editing
Professional editing is a crucial investment in the quality of your biography. A professional editor provides expert insights, addressing issues related to grammar, syntax, consistency, and narrative flow. They offer constructive feedback on character development, plot coherence, and emotional resonance. Additionally, an editor ensures your biography adheres to publishing standards and guidelines. Whether you choose a developmental editor, copy editor, or proofreader, their expertise elevates the overall quality of your manuscript. A polished, professionally edited biography enhances your credibility as an author, making your work more appealing to readers and publishers alike.
9. Adding Depth with Reflection
Reflection is the soul of your biography. It adds depth, introspection, and meaning to your narrative. This section explores the importance of analyzing personal growth, the self-discovery inherent in writing, and offering insightful reflections that resonate with readers.
Analyzing Personal Growth
Your biography is not just a chronicle of events; it’s a profound exploration of personal growth and self-discovery. Reflect on your experiences, analyzing how each event shaped your beliefs, values, and perspectives. Delve into moments of transformation, examining the lessons learned and the insights gained. Be introspective, exploring your emotional responses, challenges faced, and the resilience that carried you through. Analyzing personal growth adds authenticity to your narrative, allowing readers to witness your evolution as an individual.
Self-Discovery in Writing
Writing your biography is a transformative journey in itself. As you delve into your past, you uncover hidden facets of yourself, gaining new insights and perspectives. Embrace this process of self-discovery, allowing it to enrich your narrative. Be open to confronting vulnerabilities and embracing your authentic self. Writing becomes a cathartic experience, enabling you to heal old wounds, reconcile past conflicts, and find closure. This self-discovery permeates your narrative, infusing it with genuine emotions and a profound sense of authenticity.
Offering Insight to Readers
While your biography is a personal story, it also offers universal insights to readers. Share the wisdom gained from your experiences, offering valuable life lessons and perspectives that resonate beyond the pages of your book. Your insights can inspire, motivate, and guide readers facing similar challenges. Be generous with your wisdom, offering practical advice, philosophical reflections, and emotional support. By offering insight, you create a meaningful connection with readers, transforming your biography into a source of inspiration and empowerment.
10. Balancing Honesty and Privacy
Balancing honesty and privacy is a delicate task in writing a biography, especially when it involves personal or sensitive details. This section explores the nuances of sharing personal information, protecting sensitive data, and striking the right balance between transparency and privacy.
Sharing Personal Details
Honesty is the cornerstone of any autobiography. Readers expect authenticity, a genuine portrayal of your experiences, emotions, and perspectives. Share personal details that are relevant to your story and contribute to your personal growth. Be open about your challenges, fears, and vulnerabilities, as these elements humanize you and make your narrative relatable. When sharing intimate details, focus on their significance to your personal development, allowing readers to empathize with your experiences.
Protecting Sensitive Information
While honesty is crucial, it’s equally important to protect sensitive information, respecting the privacy of yourself and others. Evaluate the impact of sharing specific details on yourself, your family, and individuals involved in your narrative. Exercise discretion, omitting details that could harm relationships or invade personal boundaries. When mentioning others, obtain their consent before divulging private information. Create a safe space for yourself and your loved ones, ensuring your biography is both candid and respectful.
Striking the Right Balance
Striking the right balance between honesty and privacy requires discernment and empathy. Consider the potential consequences of sharing sensitive information, weighing the benefits against the potential harm. Reflect on your intentions, ensuring your narrative aims to inspire and enlighten rather than sensationalize or harm. Consult with individuals mentioned in your biography, discussing the extent to which their stories will be shared. By approaching the balance with sensitivity and respect, you maintain the integrity of your narrative while honoring the privacy of yourself and others.
11. Showcasing Your Personality
Your personality is a vital element that infuses life into your biography. Injecting humor and wit, revealing vulnerability, and captivating the reader with your unique voice are techniques that showcase your personality and create a memorable reading experience.
Injecting Humor and Wit
Humor and wit add lightness to your narrative, making it engaging and enjoyable for readers. Infuse your biography with anecdotes, amusing incidents, or witty observations from your life. Humor can serve as a coping mechanism during challenging times, highlighting your resilience and perspective. Use humor judiciously, ensuring it enhances the narrative without diminishing the significance of serious events. A well-timed joke or a clever turn of phrase can captivate readers, drawing them closer to your personality.
Revealing Vulnerability
Vulnerability is a powerful tool in connecting with readers on a deep emotional level. Sharing your vulnerabilities—your fears, insecurities, and moments of self-doubt—makes you relatable and endearing. It humanizes you, allowing readers to empathize with your struggles and triumphs. Be candid about your fears and failures, demonstrating the courage it took to overcome them. Vulnerability fosters intimacy, inviting readers to share in your emotional journey and creating a profound bond between author and audience.
Captivating the Reader
Captivating the reader requires more than a compelling plot; it demands a captivating personality. Your unique voice, perspective, and quirks are what make your biography distinctive. Use descriptive language to paint a vivid picture of your experiences. Engage the reader’s emotions, eliciting laughter, empathy, and introspection. Be genuine, allowing your true self to shine through your words. Captivate readers with your authenticity, inviting them to embark on a personal and meaningful journey through the pages of your biography.
12. The Art of Storytelling
Storytelling is the essence of your biography. Craft compelling beginnings that grab the reader’s attention, build suspense and interest throughout the narrative, and create memorable endings that leave a lasting impression. Mastering the art of storytelling ensures your biography resonates with readers long after they have turned the final page.
Crafting Compelling Beginnings
The beginning of your biography is your opportunity to captivate readers from the first sentence. Craft a compelling opening that intrigues, surprises, or challenges the reader’s expectations. Start with a moment of significance, an intriguing question, or a vivid description that immerses readers in your world. A strong beginning sets the tone for the entire narrative, enticing readers to explore further. Consider starting with a pivotal moment from your life, a reflective insight, or a powerful quote that encapsulates the essence of your story. Whatever approach you choose, ensure it piques the reader’s curiosity and compels them to read on.
Building Suspense and Interest
Maintaining suspense and interest throughout your biography keeps readers engaged and invested in your story. Introduce conflicts, challenges, and obstacles that create tension and anticipation. Allow the narrative to unfold organically, revealing information gradually and strategically. Use foreshadowing to hint at future events, sparking curiosity and encouraging readers to uncover the mysteries within your story. Intersperse moments of reflection and introspection with dynamic, action-driven scenes, maintaining a balance between emotional depth and narrative momentum. By building suspense and interest, you ensure readers remain captivated, eagerly turning pages to discover the next twist in your story.
Crafting Memorable Endings
The ending of your biography is as crucial as the beginning. Craft a memorable conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Reflect on the overarching themes of your narrative, offering insights and resolutions that resonate on a profound level. Tie up loose ends, providing closure to the story arcs and character journeys. End with a powerful message, a poignant reflection, or a thought-provoking question that lingers in the reader’s mind. A well-crafted ending creates a sense of fulfillment, leaving readers with a sense of satisfaction and contemplation. Consider the emotional impact you want to leave on your readers, crafting an ending that resonates with the themes and messages of your biography.
13. Designing Your Book
The design of your book plays a crucial role in enhancing the reader’s experience. From cover design to formatting and illustrations, thoughtful design elements contribute to the visual appeal and readability of your biography.
Cover Design
Your book cover is the first impression readers have of your biography. Design a visually striking and thematically relevant cover that captures the essence of your story. Consider the use of colors, typography, and imagery that evoke the mood and themes of your narrative. A well-designed cover attracts attention, conveying the genre and tone of your biography. Collaborate with a professional graphic designer to create a visually appealing cover that entices readers and reflects the spirit of your story.
Formatting and Layout
Interior formatting and layout impact the readability of your biography. Choose legible fonts and font sizes for the body text, headings, and subheadings. Pay attention to spacing, margins, and alignment to create a clean and professional layout. Consistent formatting enhances the reader’s experience, allowing them to focus on the content without distractions. Incorporate chapter breaks, page numbers, and headers for a structured and organized presentation. Ensure the formatting is consistent across digital and print versions of your book, providing a seamless reading experience for readers.
Illustrations and Photographs
Illustrations and photographs add visual interest to your biography, providing readers with a visual connection to your story. Include relevant photographs, illustrations, or artwork that complement the themes and events described in your narrative. Images of significant locations, people, or objects enhance the reader’s understanding of your experiences. Ensure the quality and resolution of images are suitable for print or digital formats. Caption each image with descriptive text, providing context and relevance to the narrative. Thoughtfully chosen illustrations and photographs enhance the overall aesthetics of your biography, enriching the reader’s visual experience.
14. Publishing and Distribution
Publishing and distributing your biography are essential steps in sharing your story with the world. This section explores the options of traditional vs. self-publishing, strategies for marketing your biography, and reaching your target audience effectively.
Traditional vs. Self-Publishing
Consider the publishing route that aligns with your goals, budget, and creative control. Traditional publishing involves submitting your manuscript to literary agents or publishing houses, who handle the editing, design, printing, and distribution processes. While traditional publishing offers wider distribution and marketing support, it often involves a competitive selection process and longer timelines.
Self-publishing provides authors with greater control over the publishing process. You can choose independent publishing platforms, such as Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing or other self-publishing services, to publish your biography. Self-publishing allows for creative freedom in cover design, formatting, and pricing. Authors retain the rights to their work and receive higher royalties per sale. However, self-publishing requires active marketing efforts and a strategic approach to reach your target audience effectively.
Marketing Your Biography
Effective marketing is essential to reach a wider audience and generate interest in your biography. Develop a marketing plan that includes online and offline strategies. Utilize social media platforms, author websites, and blogging to create an online presence. Engage with readers through author interviews, guest posts, and book reviews. Leverage email newsletters to connect with your audience and provide updates about your biography. Consider organizing book launch events, author signings, and virtual readings to promote your work locally and globally.
Reaching Your Target Audience
Identifying and reaching your target audience is key to the success of your biography. Research your readership demographics, interests, and preferences. Tailor your marketing efforts to appeal to your specific audience. If your biography addresses themes such as personal growth, overcoming adversity, or inspirational stories, target readers interested in self-help, memoirs , or motivational literature. Utilize keywords, tags, and categories relevant to your genre when publishing online to enhance discoverability. Engage with book clubs, reading groups, and online communities related to your niche. Building a strong author-reader connection ensures your biography resonates with the right audience, fostering positive reviews, word-of-mouth recommendations, and long-term readership.
15. Conclusion
Writing a biography book about yourself is a transformative and rewarding endeavor. It’s not just about documenting events; it’s about sharing your journey, your wisdom, and your essence with the world. As you celebrate the accomplishment of completing your biography, you are not only leaving a lasting legacy for future generations but also inspiring others to embrace their stories and embark on their writing journeys.
Embrace the lessons learned, the challenges overcome, and the personal growth achieved during this process. Your biography is a testament to your resilience, courage, and authenticity. It is a gift to the world, inviting readers into the depths of your experiences and the wisdom gained along the way.
As you reflect on your writing journey, consider the impact your biography may have on others. Your story has the power to inspire, motivate, and transform lives. Celebrate the connections made with readers who resonate with your narrative. Acknowledge the voices you have touched and the hearts you have moved with your words.
In this conclusion, take a moment to acknowledge your growth as a writer and an individual. Recognize the strength it took to share your vulnerabilities, the courage to confront your challenges, and the wisdom to offer insights to others. Your biography is not just a book; it is a legacy—an indelible mark left on the literary landscape.
As you close this chapter of your writing journey, consider the next steps in your creative endeavors. Whether it’s exploring new genres, writing sequels, or embarking on entirely different projects, your experience in writing a biography has equipped you with valuable skills, resilience, and passion. Embrace the endless possibilities that await in your writing journey, knowing that your unique voice will continue to inspire and enrich the lives of readers around the world.
CONTACT US TODAY TO AVAIL UPTO 80% OFF
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Register Now to Avail an 80% Discount
Schedule a consultation and converse with our team of book authoring specialists

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A biography, also called a bio, is a non-fiction piece of work giving an objective account of a person's life. The main difference between a biography vs. an autobiography is that the author of a biography is not the subject. A biography could be someone still living today, or it could be the subject of a person who lived years ago.
9. Tell jokes. Create some jokes when you will figure out how to write a biography about yourself. Another way to communicate with your audience is to make them laugh. While you need to maintain a professional tone throughout the rest of your biography, it's a good idea to add a humorous note at the beginning or end.
2. Introduce yourself… like a real person. This is one of the most important pieces of understanding how to write a personal biography. Always start with your name. When many people start learning how to write a bio, they skip this important part. People need to know who you are before they learn what you do.
️ An autobiography is a book about your entire life up until you write your book, while a memoir focuses on a specific event or time period in your life. ️ Autobiographies and memoirs are almost always written in the 1st person.They should include emotive descriptions of key events in your life, as well as background information about your past and hopes for your future.
A biography is simply a written account of someone's life. It is written by someone other than whom the book is about. For example, an author named Walter Isaacson has written biographies on Steve Jobs, Leonardo da Vinci, and Einstein . Biographies usually focus on the significant events that occurred in a person's life, along with their ...
Key traits of a biography: - Written about another person, often a celebrity or public figure, and told in 3 rd person point of view - More formal and objective than both memoirs and autobiographies - Broad in scope or timeline, often covering the subject's entire life up to the present - Focused solely on facts
The strict definition of autobiography is a first-person account of its author's entire life. A memoir does not document the memoirist's full life story but rather a selected era or a specific multi-era journey within that author's life. Memoirs tend to be much more focused than autobiographies. The main difference between memoir and ...
Include your first and last name at the beginning of your bio. State your brand name, if applicable. Claim your current role. Describe at least one professional achievement. Explain your values. Summarize your personal life. Think about incorporating humor. Related: Guide to Writing a Bio (With Examples) 1.
Order your sections (from medium to high interest) Order the ideas in each section (from medium to high interest) Write three questions to answer in each section. Choose a starter sentence. Complete a title template. Write each section of your by completing the starter sentence and answering all three questions.
Usually written in the first person, but could also be a biography. Biography. A biography is also a comprehensive account of one's life, highly concerned with accuracy, but written in the third person (using pronouns "he, she, and it") by someone other than the subject. Many published biographies are written about noteworthy or famous persons ...
One of the best-known autobiographies, The Diary of a Young Girl, is an excellent example of a journal-style layout. Featuring the story of a young girl who is hiding during the Holocaust, aspiring writers will find inspiration in Frank's raw emotions and candor. 2. Autobiography of a Yogi by Paramahansa Yogananda.
A biography (BYE-og-ruh-fee) is a written account of one person's life authored by another person. A biography includes all pertinent details from the subject's life, typically arranged in a chronological order. The word biography stems from the Latin biographia, which succinctly explains the word's definition: bios = "life" + graphia = "write."
Your short bio should include your brand, your accomplishments, and your values and goals. Your short bio should be one to three short paragraphs or four to eight sentences long. Knowing how to write a concise, informative, and interesting biography about yourself can help throughout various parts of the professional process.
Facebook. These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you've finished your manuscript, it's a good idea to ask for feedback. 7. Get feedback and polish the text. If you're going to self-publish your biography, you'll have to polish it to professional standards.
Simply put, a biography is an account of someone's life written by someone else.While there is a genre known as a fictional biography, for the most part, biographies are, by definition, nonfiction. Generally speaking, biographies provide an account of the subject's life from the earliest days of their childhood right up to the present day or their death if the subject is deceased.
Introduce yourself. The text should immediately leave a good impression on you. Therefore, after your full name, you can directly give the reader a spoiler: tell about your education, about your most significant achievement, and so on. It can grab the recruiter's attention and motivate them to read on.
6. Keep your bio short and sweet. Your personal bio should concisely recap all your professional experience with a little flair and personality, but perhaps as important as what to include is what not to include. Boil down your life story into as short a word count as you can. Exclude any extraneous details.
7. Writing Style and Tone. The writing style and tone of your biography influence how readers perceive your story. Choosing the right tone, incorporating descriptive language, and honing your writing style are essential aspects of creating a captivating and immersive reading experience.
How to write about yourself example Use this example of a brief professional biography to inspire your own writing: Dana Holcomb, author of "Reading Waves: Using Sonar to Enhance Marine Biology Tracking," is an independent researcher who uses sonar and traditional tracking methods to study whale migration patterns along waterways. She has experience tracking marine animals like dolphins, orcas ...
1. Introduce yourself. Start your bio with a brief introduction that describes who you are. The first sentence can include your name followed by a few details you want to highlight, such as your education, certifications or achievements. Include other relevant details, such as your job title, industry experience and professional duties.
1. Select nonfiction for the book's genre in the drop-down menu. 2. Fill in the details. For the next question, if you have a book description, type "yes" and add your description in the text box. If you don't have a description yet, answer "no" and fill out the questions.
It's called a memoir. Memoir is a subset of autobiography, which is a subset of biography. A biography is the story of someone's life. Autobiography is when you write your own biography. Memoir is writing about your own life but without the scope of a biography. Your book may span many decades, but it's short and focused on certain events.
Here are some steps you can follow to help you write a successful short bio: 1. Choose a voice. The first step in writing a short bio is deciding on a voice. For our purposes, choosing a voice involves deciding whether you are writing in the first or third person. Writing in the first person means using the words "I" and "me", and writing in ...