- Parenting & Family Parenting Family Pregnancy
- Courses Marriage Save My Marriage Pre Marriage
- Quizzes Relationship Quizzes Love Quizzes Couples Quiz
- Find a Therapist

What Is Marriage? Definition, Purpose, Types, and Importance
Angela Welch is a Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist and Licensed Chemical Dependency Counselor Intern from Valparaiso,IN. She earned her Master of Arts in Marriage and... Read More

Talented writer Calantha Quinlan explores the human experience with raw honesty and emotional depth. Covers love, relationships, personal growth, and spirituality.

In This Article
Marriage, a timeless institution, is the beautiful journey of two lives woven together, each thread representing shared dreams, laughter, and the promise of tomorrow.
It’s a commitment beyond words, a journey filled with moments that define a lifetime. Marriage is not just a contract; it’s a shared adventure where love is the compass, understanding is the map, and trust is the guiding star.
if you wonder, what is marriage, it’s an embrace of both calm seas and stormy weather, a sanctuary for vulnerability and strength. Join us in exploring the essence of marriage – a celebration of partnership, companionship, and a love story that never truly ends.
What is marriage?
What does marriage mean? Marriage is the mix of love and a heartfelt commitment between two people who promise to stand by each other through life’s journey. It’s the union of hearts, a bond that goes beyond friendship, making two souls partners for life.
Definition of marriage
Those looking for marriage definition or marriage meaning may not be aware of how deep this concept is.
Marriage is a legally recognized and often ceremonious union between two individuals, typically based on love and mutual commitment. It involves sharing responsibilities and emotions and building a life together as a married couple.
What is another word for marriage?
Marriage can also be referred to as matrimony, wedlock, or the act of tying the knot. These words all describe the same beautiful union where two people become one in a loving partnership.
A brief history of marriage
Marriage has a long and diverse history . It has evolved from arranged alliances for economic and social reasons to today’s focus on love and companionship. Through time, it has adapted to different cultures and beliefs, remaining a cornerstone of human society, symbolizing unity and togetherness.
Talking about the origin of marriage, it is again an ancient concept.
Marriage, with its roots deep in human history, finds its earliest known instance dating back thousands of years. In ancient Mesopotamia, the Sumerians, around 2350 BCE, inscribed the laws of Ur-Nammu on clay tablets.
Among these ancient legal codes was the recognition and regulation of marriage, a testament to the enduring institution’s significance in human society.
This early example showcased the institution’s role in governing relationships, inheritance, and social structure, marking the beginning of a tradition that continues to evolve, shape, and reflect the values of countless civilizations across the ages.
Why is marriage important?
Marriage is like the heart of a society, pumping love, stability, and partnership. It’s a cornerstone that strengthens families, creates a sense of belonging, and offers a warm embrace for individuals to share their lives.
The importance of marriage is seen in its ability to foster love, companionship, and emotional support, shaping not only individual lives but society as a whole.
The societal impact of marriage
Marriage carries a significant societal impact.
Studies indicate that married couples often enjoy better physical and mental health, higher levels of happiness, and financial stability.
Children raised in married households tend to fare well academically and emotionally. Marriage can promote a sense of responsibility and community, strengthening the social fabric. The benefits of marriage are well-documented and contribute to the overall well-being of society.
The role of marriage in different cultures
Marriage isn’t a one-size-fits-all concept; it’s beautifully diverse across cultures. From traditional arranged marriages in India to love marriages in Western societies, the purpose and customs vary widely.
For example, in Japan, marriage is often seen as a way to continue family lines and traditions, while in Scandinavia, it’s a symbol of gender equality. Across the globe, the role of marriage serves as a reflection of cultural values, beliefs, and traditions that enrich the tapestry of human existence.
Talking about modern trends, a research finding also indicates that between 1960 and 2011, the stage at which men and women enter a married relationship increased by three to five years.
What is the purpose of marriage?
What is the point of marriage? Let’s try to understand what is marriage’s purpose in our lives.
The purpose of marriage in people’s lives and social setup is complex and multifaceted.
Marriage provides emotional companionship, social support, procreation and family formation, and legal and financial benefits that contribute to the stability and security of individuals and families. It creates a sense of belonging and community, providing a stable environment for raising children.
Furthermore, marriage acts as a social institution that helps to create a sense of belonging and social support. It provides individuals with a network of family and friends, creating a community of support and connection.
As per Umberson et al., 2010 , having a strong social support system is linked to better mental health and increased longevity.
Children growing up in stable and loving marital households also tend to have better emotional well-being and outcomes in life. Thus, it can be concluded that marriage plays a vital role in the well-being and happiness of individuals, families, and society as a whole.
Characteristics and types of marriages
Marriage and marriage rules come in a variety of forms, each with its own unique characteristics and dynamics. The type of marriage individuals choose is influenced by cultural, religious, and personal factors. Let’s explore some of the main types of marriages .
- Monogamous marriage: This is the most common form of marriage, where a person is married to only one partner at a time. It is based on the principle of exclusive commitment and fidelity between two individuals. Monogamous marriages form the foundation of many societies worldwide.
- Polygamous marriage: Polygamy is the practice of having multiple spouses simultaneously. It can be further divided into two types: polygyny, where a man has multiple wives, and polyandry, where a woman has multiple husbands. Polygamous marriages are found in various cultures and have specific customs and rules governing them.
- Same-sex marriage: In recent years, there has been a growing acknowledgment and acceptance of same-sex marriages . These are marriages between individuals of the same gender. This type of marriage has gained legal recognition in many countries, reflecting a shift in societal attitudes and values.
- Arranged marriage: Arranged marriages are based on the premise that families or intermediaries play a significant role in choosing a spouse for an individual. In many cultures, parents or other family members take the lead in finding a suitable match based on factors such as compatibility, social status, and family background.
- Love marriage: Love marriages are based on the mutual attraction and emotional connection between two individuals . In this type of marriage, individuals choose their partners based on their personal feelings and desires. Love marriages are prevalent in many Western cultures and are gaining popularity globally.
It’s important to note that these are general categories, and marriages can have overlapping characteristics or may fall into multiple types depending on the specific context and cultural practices.
In addition to the various types of marriages, each marriage has its own set of characteristics that contribute to its dynamics and longevity.
Characteristics of marriages include commitment, communication, trust, shared values, flexibility and adaptability, emotional support, and intimacy . These are important factors that contribute to the dynamics and longevity of a marriage.
Marriage vs. Common Law Marriage: What’s the difference?
Marriage and common law marriage are two different types of relationships. Let’s dig into the differences
Marriage is a legally recognized union between two individuals that comes with legal rights, responsibilities, and obligations. It is usually formalized through a wedding ceremony or a legal process.
In a marriage, couples typically obtain a marriage license and have their union solemnized by a marriage officiant. Marriage provides various legal protections, such as inheritance rights, tax benefits, and the ability to make medical decisions for your spouse.
Common Law Marriage
What is common law marriage?
A common law marriage, also known as a de facto marriage or informal marriage, is a type of relationship where a couple lives together as married partners without a formal wedding ceremony or marriage license.
In some jurisdictions, couples who meet certain criteria for cohabitation and present themselves as married may be recognized as having a common-law marriage. The specific requirements for common-law marriage vary by jurisdiction.
As per the American Bar Association , the main difference between marriage and common law marriage is the legal recognition and formalization. While marriage has legal standing and provides explicit rights and responsibilities, common law marriage is recognized based on the couple’s behavior and cohabitation without a formalized process.
It’s important to note that the recognition of common-law marriages varies depending on the jurisdiction. Some countries or states recognize and validate common law marriages, while others do not. It’s advisable to consult the laws of your specific jurisdiction to determine the legal status of common law relationships.
What is a marriage license, and how to apply for it?
A marriage license is a legal document that authorizes a couple to marry. It is a prerequisite in most jurisdictions before a marriage ceremony can be performed. Here’s some simple yet informative information on marriage licenses
- Check the requirements: Find out what documents and information you’ll need to provide, such as identification and proof of eligibility to marry.
- Complete the application: Fill out the marriage license application form with your personal details.
- Submit required documents: Gather any necessary documents, like identification and divorce decrees if applicable.
- Pay the fee: There is usually a fee associated with the marriage license application.
- Wait and pick up the license: Some jurisdictions have a waiting period before the license is issued. Once approved, you can collect the marriage license, which is typically valid for a specific period.
Remember to check the specific requirements and procedures of your local government office for accurate and up-to-date information.
What are the benefits of marriage?
Marriage is a big step in a relationship and brings about several benefits . Let’s take a look at some of them
Legal benefits
Marriage is a legally binding agreement that provides each spouse with certain legal rights and protections. For example, a married couple has the right to make medical decisions for each other and can inherit each other’s assets if one were to pass away without a will.
Social benefits
Marriage provides a sense of social support and companionship, giving you a partner to share life’s ups and downs. Studies have shown that married couples tend to have more fulfilling partnerships than those who are not married.
Health benefits
Married individuals tend to have better health outcomes than those who are not married. They are less likely to develop chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or depression; moreover, they tend to have a longer lifespan.
Tax benefits
Married couples can benefit from tax breaks from the government. They can file joint tax returns that may help them qualify for certain credits, deductions, and exemptions.
Some couples get a “bonus” on their federal income taxes by virtue of being married. Other couples suffer a “penalty”. The amount can be significant. What are the deciding factors? WSJ’s Jason Bellin explains in this video:
Marriage laws: Legal rights & requirements
Marriage laws govern the legal rights and requirements for couples who want to get married . Here’s a simple and informative overview of marriage laws
Legal rights:
Marriage laws grant several legal rights to married couples. These rights can vary depending on the jurisdiction, but they often include:
- Inheritance rights: Spouses have the right to inherit property and assets from each other.
- Decision-making rights: Married couples can make important medical, financial, and legal decisions on behalf of their spouse if necessary.
- Family benefits: Marriage can provide access to benefits like health insurance, social security, and pension plans.
- Parental rights: Married couples have automatic legal recognition as parents and may have certain rights and responsibilities regarding children.
Requirements:
In order to get married, couples must meet certain requirements set by the law. While these requirements can differ from one jurisdiction to another, some common ones include:
- Age requirement: Couples must meet the minimum age requirement to get married , which may vary by jurisdiction.
- Consent: Both individuals must freely and willingly consent to the marriage.
- Marriage license: Couples typically need to obtain a marriage license from the local government office before getting married.
- Waiting period: Some jurisdictions have a waiting period between obtaining the marriage license and the actual wedding ceremony.
- Ceremony formalities: Depending on the jurisdiction, couples may need to have a formal wedding ceremony, which could involve witnesses or a marriage officiant.
What are the red flags in a marriage?
Marriage is a wonderful thing, albeit a challenging one as well. However, there are certain signs that may indicate that your marriage is in trouble. Here are some red flags to look out for:
- Communication breakdown
One of the most concerning red flags in a marriage is when communication between spouses breaks down. When couples start having trouble communicating, they tend to become distant from each other, which can eventually lead to bigger problems like misunderstandings, distrust, and resentment.
- Lack of intimacy
Physical intimacy is an important aspect of a healthy marriage. If you or your spouse have lost interest in spending intimate moments together, staying physically close, or something that used to come naturally, that may indicate a deeper underlying issue.
In any relationship, cheating or infidelity is the ultimate betrayal. When one partner cheats, it can lead to a loss of trust and can cause irreparable damage to the relationship. Rebuilding trust and healing from such a betrayal is a challenging journey.
A lack of honesty is another sign that a marriage is in trouble. When one partner is dishonest, it can cause a breakdown of trust and make it difficult to move forward in the relationship.
- Constant fighting
Frequent conflicts with your spouse may stem from unmet needs, past issues, or communication breakdowns . To address these deeper concerns, couples should consider therapy or counseling to build understanding and healing.
Marriage is a complex and beautiful journey filled with questions and challenges. Let’s explore some common questions about marriage, its ups and downs, and the role of communication and understanding in this lifelong partnership.
What does the Bible say about marriage?
Understanding what is marriage in the Bible is worth understanding and considering. The definition of marriage in the Bible is simple yet beautiful to go through.
It is cherished as a sacred covenant between two people, emphasizing love, commitment, and faithfulness. Verses like “ What God has joined together, let no one separate ” (Matthew 19:6) underscore the sanctity of marriage.
The Bible teaches spouses to love, respect, and support one another, forming the foundation of a strong and lasting union.
What are the most challenging years of marriage?
The early years and midlife often present the most challenging phases in a marriage . The initial adjustment period can be tough as couples adapt to living together.
Later, midlife crises and the demands of raising children and managing careers can strain the relationship. Open communication and support are crucial during these times.
Why is a marriage license so important?
A marriage license is more than a legal document; it signifies the state’s recognition of your union. It grants essential rights and benefits, like tax advantages and inheritance rights. It also provides a framework for the legal dissolution of a marriage if needed, protecting both spouses.
What are some common challenges in marriage?
Common challenges include communication breakdowns, financial stress, raising children, and navigating differences in values and goals. Addressing these challenges requires patience, understanding, and compromise from both partners.
Why is communication important in a marriage?
Communication is the lifeblood of a marriage. It fosters understanding, trust, and emotional connection. Open and honest conversations help resolve conflicts, build intimacy, and ensure both partners’ needs and feelings are heard and respected.
How do married couples handle sexual intimacy conflicts?
Sexual intimacy conflicts are common but manageable. The key is open dialogue without judgment. Discuss desires, boundaries, and concerns openly, ensuring both partners feel safe and respected. Seeking guidance from a therapist or counselor can also be beneficial in addressing these issues.
Marriage and its various hues
Marriage has many facets – social, legal, financial, and emotional – that can have a profound impact on our lives.
Legalizing a commitment to a partner and gaining a companion for life are only a couple of reasons why marriage has been a widely practiced cultural tradition.
It’s essential to be aware of the pros and cons of marriage before committing, as well as be mindful of common challenges that married couples might face, such as communication breakdowns, loss of intimacy, infidelity, dishonesty, and constant fighting .
However, with a strong foundation of love, trust, and communication, married couples can navigate these ups and downs and create a harmonious and fulfilling partnership .
Marriage is not always easy, and it won’t always be smooth sailing, but with patience, understanding, and willingness to work together, couples can enjoy the many benefits that a committed partnership can bring.
Share this article on
Calantha Quinlan is a talented writer with a passion for exploring the depths of the human experience. Her writing is characterized by its raw honesty, emotional depth, and sensitivity to the complexities of life. Calantha’s work Read more covers a wide range of topics, from love and relationships to personal growth and spirituality. Her writing is known for its ability to inspire readers to live more meaningful and fulfilling lives and to approach challenges with courage and grace. When she’s not writing, Calantha can be found indulging in her love for photography, capturing the beauty of the world through her lens. She also enjoys practicing yoga and meditation, which help her to stay centered and grounded in a busy world. Read less
Want to have a happier, healthier marriage?
If you feel disconnected or frustrated about the state of your marriage but want to avoid separation and/or divorce, the marriage.com course meant for married couples is an excellent resource to help you overcome the most challenging aspects of being married.
Take Course
Learn More On This Topic

Relationship
By noah williams.

Mental Health
By sylvia smith.

By Marriage.com Editorial Team, Relationship & Marriage Advice

By Rosemary K

By David Essel, Counselor

By Calantha Quinlan

By Jenni Jacobsen, Licensed Clinical Social Worker
You may also like.

Emotional Intimacy
Approved by angela welch, marriage & family therapist.

Approved By Dionne Eleanor, Coach

Zodiac Signs

By Kelli H, Licensed Clinical Social Worker

Approved By Christiana Njoku, Licensed Professional Counselor

By Draven Porter
Recent articles.

By Callen Winslow

By Dylan Banks
Popular topics on married life.

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Marriage and Domestic Partnership
Marriage, a prominent institution regulating sex, reproduction, and family life, is a route into classical philosophical issues such as the good and the scope of individual choice, as well as itself raising distinctive philosophical questions. Political philosophers have taken the organization of sex and reproduction to be essential to the health of the state, and moral philosophers have debated whether marriage has a special moral status and relation to the human good. Philosophers have also disputed the underlying moral and legal rationales for the structure of marriage, with implications for questions such as the content of its moral obligations and the legal recognition of same-sex marriage. Feminist philosophers have seen marriage as playing a crucial role in women’s oppression and thus a central topic of justice. In this area philosophy courts public debate: in 1940, Bertrand Russell’s appointment to an academic post was withdrawn on the grounds that the liberal views expressed in Marriage and Morals made him morally unfit for such a post. Likewise, debate over same-sex marriage has been highly charged. Unlike some contemporary issues sparking such wide interest, there is a long tradition of philosophical thought on marriage.
Philosophical debate concerning marriage extends to what marriage, fundamentally, is; therefore, Section 1 examines its definition. Section 2 sets out the historical development of the philosophy of marriage, which shapes today’s debates. Many of the ethical positions on marriage can be understood as divided on the question of whether marriage should be defined contractually by the spouses or by its institutional purpose, and they further divide on whether that purpose necessarily includes procreation or may be limited to the marital love relationship. Section 3 taxonomizes ethical views of marriage accordingly. Section 4 will examine rival political understandings of marriage law and its rationale. Discussion of marriage has played a central role in feminist philosophy; Section 5 will outline the foremost critiques of the institution.
1. Defining Marriage
2. understanding marriage: historical orientation, 3.1 contractual views, 3.2 institutional views, 4.1 marriage and legal contract, 4.2 the rationale of marriage law, 4.3 same-sex marriage, 4.4 arguments for marriage reform, 5.1 feminist approaches, 5.2 the queer critique, contemporary works, historical works, other internet resources, related entries.
‘Marriage’ can refer to a legal contract and civil status, a religious rite, and a social practice, all of which vary by legal jurisdiction, religious doctrine, and culture. History shows considerable variation in marital practices: polygyny has been widely practiced, some societies have approved of extra-marital sex and, arguably, recognized same-sex marriages, and religious or civil officiation has not always been the norm (Boswell 1994; Mohr 2005, 62; Coontz 2006). More fundamentally, while the contemporary Western ideal of marriage involves a relationship of love, friendship, or companionship, marriage historically functioned primarily as an economic and political unit used to create kinship bonds, control inheritance, and share resources and labor. Indeed, some ancients and medievals discouraged ‘excessive’ love in marriage. The Western ‘love revolution’ in marriage dates popularly to the 18 th century (Coontz 2006, Part 3). The understanding of marriage as grounded in individual choice and romantic love reflects historically and culturally situated beliefs and practices. Most notably, the aspect of consent or voluntary entry - often taken to be crucial to marriage (Cott 2000) - is challenged where practices of forced or child marriage are prevalent (Narayan 1997; Bhandary 2018). Arranged marriage, which is compatible with the consent of the spouses, prioritizes caregiving and economic aspects of the institution over romantic love (Bhandary 2018).
The global variety of marriage practices and law is difficult to encapsulate: notable variations in law include recognition of same-sex marriage, polygamy, and ‘common-law’ marriage, restrictions on marriages between members of the same family or of different social castes, the existence of civil marriage, practices of arranged, forced, or child marriage, and women’s rights within marriage (see Moses 2018 for an entry into the literature on these differences), as well as cultural and religious practices of temporary marriage (Shrage 2013, Nolan 2016) or polyamorous marriage (Brake 2018). Religious, cultural, and philosophical traditions also shape ideals of marriage. For instance, Xiaorong Li writes that “Confucian ideals of family, society, and women’s role” influence expectations of marriage in China (Li 1995, 413). However, scholarship on such differences must be careful to avoid misrepresentation (see for example discussion of misleading Western accounts of ‘sati’ and dowry-murder in India in Narayan 1997).
Ethical and political questions regarding marriage are sometimes answered by appeal to the definition of marriage. But the historical and cultural variation in marital practices has prompted some philosophers to argue that marriage is a ‘family resemblance’ concept, with no essential purpose or structure (Wasserstrom 1974; see also the interesting discussion of whether the many different practices identified by anthropologists as marriage should be counted as marriages in Nolan, forthcoming). If marriage has no essential features, then one cannot appeal to definition to justify particular legal or moral obligations. For instance, if monogamy is not an essential feature of marriage, then one cannot appeal to the definition of marriage to justify a requirement that legal marriage be monogamous. To a certain extent, the point that actual legal or social definitions cannot settle the question of what features marriage should have is just. First, past applications of a term need not yield necessary and sufficient criteria for applying it: ‘marriage’ (like ‘citizen’) may be extended to new cases without thereby changing its meaning (Mercier 2001). Second, appeal to definition may be uninformative: for example, legal definitions are sometimes circular, defining marriage in terms of spouses and spouses in terms of marriage (Mohr 2005, 57). Third, appeal to an existing definition in the context of debate over what the law of marriage, or its moral obligations, should be risks begging the question: in debate over same-sex marriage, for example, appeal to the current legal definition begs the normative question of what the law should be. However, this point also tells against the argument for the family resemblance view of marriage, as the variation of marital forms in practice does not preclude the existence of a normatively ideal form. Thus, philosophers who defend an essentialist definition of marriage offer normative definitions, which appeal to fundamental ethical or political principles. Defining marriage must depend on, rather than precede, ethical and political inquiry.
Setting the agenda for contemporary debate, ancient and medieval philosophers raised recurring themes in the philosophy of marriage: the relation between marriage and the state, the role of sex and procreation in marriage, and the gendered nature of spousal roles. Their works reflect evolving, and overlapping, ideas of marriage as an economic or procreative unit, a religious sacrament, a contractual association, and a relationship of mutual support.
In his depiction of the ideal state, Plato (427–347 BCE) described a form of marriage contrasting greatly with actual marriage practices of his time. He argued that, just as male and female watchdogs perform the same duties, men and women should work together, and, among Guardians, ‘wives and children [should be held] in common’ ( The Republic , ca. 375–370 BCE, 423e–424a). To orchestrate eugenic breeding, temporary marriages would be made at festivals, where matches, apparently chosen by lot, would be secretly arranged by the Rulers. Resulting offspring would be taken from biological parents and reared anonymously in nurseries. Plato’s reason for this radical restructuring of marriage was to extend family sympathies from the nuclear family to the state itself: the abolition of the private family was intended to discourage private interests at odds with the common good and the strength of the state ( ibid ., 449a-466d; in Plato’s Laws , ca. 355–47 BCE, private marriage is retained but still designed for public benefit).
Aristotle (384–322 BCE) sharply criticized this proposal as unworkable. On his view, Plato errs in assuming that the natural love for one’s own family can be transferred to all fellow-citizens. The state arises from component parts, beginning with the natural procreative union of male and female. It is thus a state of families rather than a family state, and its dependence on the functioning of individual households makes marriage essential to political theory ( Politics , 1264b). The Aristotelian idea that the stability of society depends on the marital family influenced Hegel, Rawls, and Sandel, among others. Aristotle also disagreed with Plato on gender roles in marriage, and these views too would prove influential. Marriage, he argued, is properly structured by gender: the husband, “fitter for command,” rules. The sexes express their excellences differently: “the courage of a man is shown in commanding, of a woman in obeying,” a complementarity which promotes the marital good ( Politics , ca. 330 BCE, 1253b, 1259b, 1260a; Nicomachean Ethics , ca. 325 BCE, 1160–62).
In contrast to the ancients, whose philosophical discussion of sex and sexual love was not confined to marriage, Christian philosophers introduced a new focus on marriage as the sole permissible context for sex, marking a shift from viewing marriage as primarily a political and economic unit. St. Augustine (354–430), following St. Paul, condemns sex outside marriage and lust within it. “[A]bstinence from all sexual union is better even than marital intercourse performed for the sake of procreating,” and the unmarried state is best of all ( The Excellence of Marriage , ca. 401, §6, 13/15). But marriage is justified by its goods: “children, fidelity [between spouses], and sacrament.” Although procreation is the purpose of marriage, marriage does not morally rehabilitate lust. Instead, the reason for the individual marital sexual act determines its permissibility. Sex for the sake of procreation is not sinful, and sex within marriage solely to satisfy lust is a pardonable (venial) sin. As marital sex is preferable to “fornication” (extra-marital sex), spouses owe the “marriage debt” (sex) to protect against temptation, thereby sustaining mutual fidelity ( Marriage and Desire , Book I, ca. 418–19, §7, 8, 17/19, 14/16).
St. Thomas Aquinas (ca. 1225–1274) grounded concurring judgments about sexual morality in natural law, explicating marriage in terms of basic human goods, including procreation and fidelity between spouses (Finnis 1997). Monogamous marriage, as the arrangement fit for the rearing of children, “belong[s] to the natural law.” Monogamous marriage secures paternal guidance, which a child needs; fornication is thus a mortal sin because it “tends to injure the life of the offspring.” (Aquinas rejects polygamy on similar grounds while, like Augustine, arguing that it was once permitted to populate the earth.) Marital sex employs the body for its purpose of preserving the species, and pleasure may be a divinely ordained part of this. Even within marriage, sex is morally troubling because it involves “a loss of reason,” but this is compensated by the goods of marriage ( Summa Theologiae , unfinished at Aquinas’ death, II-II, 153, 2; 154, 2). Among these goods, Aquinas emphasizes the mutual fidelity of the spouses, including payment of the “marriage debt” and “partnership of a common life”—a step towards ideas of companionate marriage ( Summa Theologiae, Supp. 49, 1).
Indeed, we see indications of discontent with the economic model of marriage a century earlier in the letters of Héloïse (ca. 1100–1163) to Abelard (1079–1142). Héloïse attacks marriage, understood as an economic transaction, arguing that a woman marrying for money or position deserves “wages, not gratitude” and would “prostitute herself to a richer man, if she could.” In place of this economic relation she praises love, understood on a Ciceronian model of friendship: the “name of wife may seem more sacred or more binding, but sweeter for me will always be the word friend ( amica ), or, if you will permit me, that of concubine or whore” (Abelard and Héloïse, Letters , ca. 1133–1138, 51–2). The relation between love and marriage will continue to preoccupy later philosophers. Do marital obligations and economic incentives threaten love, as Héloïse suggested? (Cave 2003, Card 1996) As Søren Kierkegaard (1813–1855) dramatically suggests in The Seducer’s Diary , are the obligations of marriage incompatible with romantic and erotic love? Or, instead, does marital commitment uniquely enable spousal love, as Aquinas suggested? (Finnis 1997; cf. Kierkegaard’s Judge William’s defense of marriage [ Either/Or , 1843, vol. 2].)
Questions of the relation between love and marriage emerge from changing understandings of the role of marriage; in the early modern era, further fault lines appear as new understandings of human society conflict with the traditional structure of marriage. For Aristotle, Augustine, and Aquinas, marriage was unproblematically structured by sexual difference, and its distinctive features explained by nature or sacrament. But in the early modern era, as doctrines of equal rights and contract appeared, a new ideal of relationships between adults as free choices between equals appeared. In this light, the unequal and unchosen content of the marriage relationship raised philosophical problems. Thomas Hobbes (1588–1679) acknowledged that his arguments for rough equality among humans apply to women: “whereas some have attributed the dominion [over children] to the man only, as being of the more excellent sex; they misreckon in it. For there is not always that difference of strength, or prudence between the man and the woman, as that the right can be determined without war.” Nonetheless, Hobbes admits that men dominate in marriage, which he explains (inadequately) thus: “for the most part commonwealths have been erected by the fathers, not by the mothers of families” ( Leviathan , 1651, Ch. 20; Okin 1979, 198–199, Pateman 1988, 44–50).
Likewise, defending marital hierarchy posed a problem for John Locke (1632–1704). Locke ties his rejection of political patriarchy to a rejection of the patriarchal family, arguing that marriage, like the state, rests on consent, not natural hierarchy; marriage is a “voluntary compact.” But Locke fails to follow this reasoning consistently, for Lockean marriage remains hierarchical: in cases of conflict, “the rule … naturally falls to the man’s as the abler and stronger.” Ceding decision-making power to one party on the basis of a presumed natural hierarchy creates an internal tension in Locke’s views ( The Second Treatise of Government , 1690, §77, 81, 82; Okin 1979, 199–200). This inconsistency prompted Mary Astell’s (1666–1731) response: “If all Men are born free , how is it that all women are born slaves? as they must be if the being subjected to the inconstant, uncertain, unknown, arbitrary Will of Men, be the perfect Condition of Slavery ?” (“Reflections upon Marriage,” 1700, 18) Similar tensions arise for Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712–1778), whose treatise on education, Émile , describes the unequal status of Émile’s wife, Sophie. Her education, a template for all women’s, prepares her only to please and serve her husband and rear children. Mary Wollstonecraft (1759–1798) attacked Rousseau’s views on women’s nature, education, and marital inequality in A Vindication of the Rights of Woman (see also Okin 1979, Chapter 6).
The contractual understanding of marriage prompts the question as to why marital obligations should be fixed other than by spousal agreement. Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) combined a contractual account of marriage with an Augustinian preoccupation with sexual morality to argue that the distinctive content of the marriage contract was required to make sex permissible. In Kant’s view, sex involves morally problematic objectification, or treatment of oneself and other as a mere means. The marriage right, a “right to a person akin to a right to a thing,” gives spouses “lifelong possession of each other’s sexual attributes,” a transaction supposed to render sex compatible with respect for humanity: “while one person is acquired by the other as if it were a thing , the one who is acquired acquires the other in turn; for in this way each reclaims itself and restores its personality.” But while these rights, according to Kant, make sex compatible with justice, married sex is not clearly virtuous unless procreation is a possibility ( Metaphysics of Morals , 1797–98, Ak 6:277–79, 6:424–427). Kant’s account of sexual objectification has had wide influence—from feminists to new natural lawyers. More surprisingly, given his views on gender inequality and the wrongness of same-sex sexual activity, Kant’s account of marriage has been sympathetically reconstructed by feminists and defenders of same-sex marriage drawn by Kant’s focus on equality, reciprocity, and the moral rehabilitation of sex within marriage (Herman 1993, Altman 2010, Papadaki 2010). Kant interestingly suggests that morally problematic relationships can be reconstructed through equal juridical rights, but how such reconstruction occurs is puzzling (Herman 1993, Brake 2005). Among other things, it is difficult to see how Kant’s insistence on equal marriage rights can be reconciled with his views on gender inequality (Sticker 2020).
Characteristically, G. W. F. Hegel’s (1770–1831) account of marriage synthesizes the preceding themes. Hegel returns to Aristotle’s understanding of (nuclear) marriage as the foundation of a healthy state, while explicating its contribution in terms of spousal love. Hegel criticized Kant’s reduction of marriage to contract as “disgraceful” because spouses begin “from the point of view of contract—i.e. that of individual personality as a self-sufficient unit— in order to supersede it .” They “consent to constitute a single person and to give up their natural and individual personalities within this union.” The essence of marriage is ethical love, “the consciousness of this union as a substantial end, and hence in love, trust, and the sharing of the whole of individual existence.” Ethical love is not, like sexual love, contingent: “Marriage should not be disrupted by passion, for the latter is subordinate to it” ( Elements of the Philosophy of Right , 1821, §162–63, 163A).
Like his predecessors, Hegel must justify the distinctive features of marriage, and in particular, why, if it is the ethical love relationship which is ethically significant, formal marriage is necessary. Hegel’s contemporary Friedrich von Schlegel had argued that love can exist outside marriage—a point which Hegel denounced as the argument of a seducer! For Hegel, ethical love depends on publicly assuming spousal roles which define individuals as members in a larger unit. Such unselfish membership links marriage and the state. Marriage plays an important role in Hegel’s system of right, which culminates in ethical life, the customs and institutions of society: family, civil society, and the state. The role of marriage is to prepare men to relate to other citizens as sharers in a common enterprise. In taking family relationships as conditions for good citizenship, Hegel follows Aristotle and influences Rawls and Sandel; it is also notable that he takes marriage as a microcosm of the state.
Kant and Hegel attempted to show that the distinctive features of marriage could be explained and justified by foundational normative principles. In contrast, early feminists argued that marital hierarchy was simply an unjust remnant of a pre-modern era. John Stuart Mill (1806–1873) argued that women’s subordination within marriage originated in physical force—an anomalous holdover of the ‘law of the strongest’. Like Wollstonecraft in her 1792 A Vindication of the Rights of Woman , Mill compared marriage and slavery: under coverture wives had no legal rights, little remedy for abuse, and, worse, were required to live in intimacy with their ‘masters’. This example of an inequality based on force had persisted so long, Mill argued, because all men had an interest in retaining it. Mill challenged the contractual view that entry into marriage was fully voluntary for women, pointing out that their options were so limited that marriage was “only Hobson’s choice, ‘that or none’” ( The Subjection of Women , 1869, 29). He also challenged the view that women’s nature justified marital inequality: in light of different socialization of girls and boys, there was no way to tell what woman’s nature really was. Like Wollstonecraft, Mill described the ideal marital relationship as one of equal friendship (Abbey and Den Uyl, 2001). Such marriages would be “schools of justice” for children, teaching them to treat others as equals. But marital inequality was a school of injustice, teaching boys unearned privilege and corrupting future citizens. The comparison of marriage with slavery has been taken up by more recent feminists (Cronan 1973), as has the argument that marital injustice creates unjust citizens (Okin 1994).
Marxists also saw marriage as originating in ancient exercises of force and as continuing to contribute to the exploitation of women. Friedrich Engels (1820–1895) argued that monogamous marriage issued from a “ world historical defeat of the female sex ” (Engels 1884, 120). Exclusive monogamy “was not in any way the fruit of individual sex love, with which it had nothing whatever to do … [but was based on] economic conditions—on the victory of private property over primitive, natural communal property” ( ibid ., 128). Monogamy allowed men to control women and reproduction, thereby facilitating the intergenerational transfer of private property by producing undisputed heirs. Karl Marx (1818–83) argued that abolishing the private family would liberate women from male ownership, ending their status “as mere instruments of production” ( The Communist Manifesto , Marx 1848, 173). The Marxist linking of patriarchy and capitalism, in particular its understanding of marriage as an ownership relation ideologically underpinning the capitalist order, has been especially influential in feminist thought (Pateman 1988, cf. McMurtry 1972).
3. Marriage and Morals
The idea that marriage has a special moral status and entails fixed moral obligations is widespread—and philosophically controversial. Marriage is a legal contract, although an anomalous one (see 4.1); as the idea of it as a contract has taken hold, questions have arisen as to how far its obligations should be subject to individual choice. The contractual view of marriage implies that spouses can choose marital obligations to suit their interests. However, to some, the value of marriage consists precisely in the limitations it sets on individual choice in the service of a greater good: thus, Hegel commented that arranged marriage is the most ethical form of marriage because it subordinates personal choice to the institution. The institutional view holds that the purpose of the institution defines its obligations, taking precedence over spouses’ desires, either in the service of a procreative union or to protect spousal love, in the two most prominent forms of this view. These theories have implications for the moral status of extra-marital sex and divorce, as well as the purpose of marriage.
On the contractual view, the moral terms and obligations of marriage are understood as promises between spouses. Their content is supplied by surrounding social and legal practices, but their promissory nature implies that parties to the promise can negotiate the terms and release each other from marital obligations.
One rationale for treating marital obligations as such promises might be thought to be the voluntaristic account of obligation. On this view, all special obligations (as opposed to general duties) are the result of voluntary undertakings; promises are then the paradigm of special obligations (see entry on Special Obligations). Thus, whatever special obligations spouses have to one another must originate in voluntary agreement, best understood as promise. We will return to this below. A second rationale is the assumption that existing marriage practices are morally arbitrary, in the sense that there is no special moral reason for their structure. Further, there are diverse social understandings of marriage. If the choice between them is morally arbitrary, there is no moral reason for spouses to adopt one specific set of marital obligations; it is up to spouses to choose their terms. Thus, the contractual account depends upon the assumption that there is no decisive moral reason for a particular marital structure.
On the contractual account, not just any contracts count as marriages. The default content of marital promises is supplied by social and legal practice: sexual exclusivity, staying married, and so on. But it entails that spouses may release one another from these moral obligations. For example, extra-marital sex has often been construed as morally wrong by virtue of promise-breaking: if spouses promise sexual exclusivity, extra-marital sex breaks a promise and is thereby prima facie wrong. However, if marital obligations are simply promises between the spouses, then the parties can release one another, making consensual extra-marital sex permissible (Wasserstrom 1974). Marriage is also sometimes taken to involve a promise to stay married. This seems to make unilateral divorce morally problematic, as promisors cannot release themselves from promissory obligations (Morse 2006). But standard conditions for overriding promissory obligations, such as conflict with more stringent moral duties, inability to perform, or default by the other party to a reciprocal promise would permit at least some unilateral divorces (Houlgate 2005, Chapter 12). Some theorists of marriage have suggested that marital promises are conditional on enduring love or fulfilling sex (Marquis 2005, Moller 2003). But this assumption is at odds with the normal assumption that promissory conditions are to be stated explicitly.
Release from the marriage promise is not the only condition for permissible divorce on the contractual view. Spouses may not be obligated to one another to stay married—but they may have parental duties to do so: if divorce causes avoidable harm to children, it is prima facie wrong (Houlgate 2005, Chapter 12, Russell 1929, Chapter 16). However, in some cases divorce will benefit the child—as when it is the means to escape abuse. A vast empirical literature disputes the likely effects of divorce on children (Galston 1991, 283–288, Young 1995). What is notable here, philosophically, is that this moral reason against divorce is not conceived as a spousal, but a parental, duty.
Marriage is widely taken to have an amatory core, suggesting that a further marital promise is a promise to love, as expressed in wedding vows ‘to love and cherish’. But the possibility of such promises has met with skepticism. If one cannot control whether one loves, the maxim that ‘ought implies can’ entails that one cannot promise to love. One line of response has been to suggest that marriage involves a promise not to feel but to behave a certain way—to act in ways likely to sustain the relationship. But such reinterpretations of the marital promise face a problem: promises depend on what promisors intend to promise—and presumably most spouses do not intend to promise mere behavior (Martin 1993, Landau 2004, Wilson 1989, Mendus 1984, Brake 2012, Chapter 1; see also Kronqvist 2011). However, developing neuroenhancement technology promises to bring love under control through “love drugs” which would produce bonding hormones such as oxytocin. While the use of neuroenhancement to keep one’s vows raises questions about authenticity and the nature of love (as well as concerns regarding its use in abusive relationships), it is difficult to see how such technology morally differs from other love-sustaining devices such as romantic dinners—except that it is more likely to be effective (Savulescu and Sandberg 2008).
One objection to the contractual account is that, without appeal to the purpose of the institution, there is no reason why not just any set of promises count as marriage (Finnis 2008). The objection continues that the contractual account cannot explain the point of marriage. Some marriage contractualists accept this implication. According to the “bachelor’s argument,” marriage is irrational: chances of a strongly dis-preferred outcome (a loveless marriage) are too high (Moller 2003). Defenders of the rationality of marriage have replied that marital obligations are rational because they help agents to secure their long-term interests in the face of passing desires (Landau 2004). From the institutional perspective, evaluating the rationality of marriage thus, in terms of fulfilling subjective preferences, clashes with the tradition of viewing it as uniquely enabling certain objective human goods; however, a positive case must be made for the latter view.
Another objection to the contractual view concerns voluntarism. Critics of the voluntarist approach to the family deny that family morality is exhausted by voluntary obligations (Sommers 1989). Voluntarist conceptions of the family conflict with common-sense intuitions that there are unchosen special duties between family members, such as filial duties. However, even if voluntarism is false, this does not suffice to establish special spousal duties. On the other hand, voluntarism alone does not entail the contractual view, for it does not entail that spouses can negotiate the obligations of marriage or that the obligations be subject to release, only that spouses must agree to them. Voluntarism, in other words, need not extend to the choice of marital obligations and hence need not entail the contractual account. The contractual account depends on denying that there is decisive moral reason for marriage to incorporate certain fixed obligations. Let us turn to the case that there is such reason.
The main theoretical alternatives to the contractual view hold that marital obligations are defined by the purpose of the institution and that spouses cannot alter these institutional obligations (much like the professional moral obligations of a doctor; to become a doctor, one must voluntarily accept the role and its obligations, and one cannot negotiate the content of these obligations). The challenge for institutional views is to defend such a view of marriage, explaining why spouses may not jointly agree to alter obligations associated with marriage. Kant confronted this question, arguing that special marital rights were morally necessary for permissible sex. His account of sexual objectification has influenced a prominent contemporary rival to the contractual view—the new natural law view, which takes procreation as essential to marriage. A second widespread approach focuses solely on love as the defining purpose of marriage.

3.2.1 New Natural Law: Marriage as Procreative Union
Like Kant, the new natural law account of marriage focuses on the permissible exercise of sexual attributes; following Aquinas, it emphasizes the goods of marriage, which new natural lawyers, notably John Finnis (cf. George 2000, Grisez 1993, Lee 2008), identify as reproduction and fides —roughly, marital friendship (see entry on The Natural Law Tradition in Ethics). Marriage is here taken to be the institution uniquely apt for conceiving and rearing children by securing the participation of both parents in an ongoing union. The thought is that there is a distinctive marital good related to sexual capacities, consisting in procreation and fides , and realizable only in marriage. Within marriage, sex may be engaged in for the sake of the marital good. Marital sex need not result in conception to be permissible; it is enough that it is open towards procreation and expresses fides . The view does not entail that it is wrong to take pleasure in sex, for this can be part of the marital good.
However, sex outside marriage (as defined here) cannot be orientated toward the marital good. Furthermore, sexual activity not orientated toward this good—including same-sex activity, masturbation, contracepted sex, sex without marital commitment (even within legal marriage)—is valueless; it does not instantiate any basic good. Furthermore, such activity is impermissible because it violates the basic good of marriage. Marital sex is thought to instantiate the good of marriage. By contrast, non-marital sex is thought to treat sexual capacities instrumentally—using them merely for pleasure. (It is here that the account is influenced by Kant.) Non-marital sex violates the good of marriage by treating sexual capacities in a way contrary to that good. Furthermore, for an agent merely to condone non-marital sex damages his or her relation to the marital good, for even a hypothetical willingness to treat sex instrumentally precludes proper marital commitment (Finnis 1997, 120).
As Finnis emphasizes, one feature of the new natural law account of marriage is that the structure of marriage can be fully explained by its purpose. Marriage is between one man and one woman because this is the unit able to procreate without third-party assistance; permanence is required to give children a lifelong family. Finnis charges, as noted above, that accounts which do not ground marriage in this purpose have no theoretical reason to resist the extension of marriage to polygamy, incest, and bestiality (Finnis 1995). As all non-marital sex fails to instantiate basic goods, there is no way morally to distinguish these different relations.
A further point concerns law: to guide citizens’ judgments and choices towards the relationship in which they can uniquely achieve the marital good, the state should endorse marriage, as understood on this view, and not recognize same-sex relationships as marriages. However, it might be asked whether this is an effective way to guide choice, and whether state resources might be better spent promoting other basic human goods. Moreover, as the argument equally implies a state interest in discouraging contraception, divorce, and extra-marital sex, the focus on same-sex marriage appears arbitrary (Garrett 2008, Macedo 1995). This objection is a specific instance of a more general objection: this account treats sex and the marital good differently than it does the other basic human goods. Not only is less attention paid to promoting those goods legally (and discouraging behavior contrary to them), but the moral principle forbidding action contrary to basic human goods is not consistently applied elsewhere—for example, to eating unhealthily (Garrett 2008).
A second objection attacks the claim that non-marital sex cannot instantiate any basic human goods. This implausibly consigns all non-marital sex (including all contracepted sex) to the same value as anonymous sex, prostitution, or masturbation (Macedo 1995, 282). Plausibly, non-marital sex can instantiate goods such as “pleasure, communication, emotional growth, personal stability, long-term fulfillment” (Corvino 2005, 512), or other basic human goods identified by the new natural law account, such as knowledge, play, and friendship (Garrett 2008; see also Blankschaen 2020).
A third objection is related. The view seems to involve a double standard in permitting infertile opposite-sex couples to marry (Corvino 2005; Macedo 1995). The new natural lawyers have responded that penile-vaginal sex is reproductive in type, even if not in effect, while same-sex activity can never be reproductive in type (Finnis 1997, cf. George 2000, Lee 2008). Reproductive-type sex can be oriented towards procreation even if not procreative in effect. But it is unclear how individuals who know themselves to be infertile can have sex for the reason of procreation (Macedo 1995, Buccola 2005). Ultimately, to differentiate infertile heterosexual couples from same-sex couples, new natural lawyers invoke complementarity between men and women as partners and parents. Thus, the defense of this account of marriage turns on a controversial view of the nature and importance of sexual difference (Finnis 1997, Lee 2008).
A related, influential argument focuses on the definition of marriage. This argues that marriage is necessarily between one man and one woman because it involves a comprehensive union between spouses, a unity of lives, minds, and bodies. Organic bodily union requires being united for a biological purpose, in a procreative-type act (Girgis, et al., 2010). Like the new natural law arguments, this has raised questions as to why only, and all, different-sex couples, even infertile ones, can partake in procreative-type acts, and why bodily union has special significance (Arroyo 2018, Johnson 2013).
While much discussion of new natural law accounts of marriage oscillates between attacking and defending the basis in biological sex difference, some theorists sympathetic to new natural law attempt to avoid the Scylla of rigid biological restrictions and the Charybdis of liberal “plasticity” regarding marriage (Goldstein 2011). Goldstein, for one, offers an account of marriage as a project generated by the basic good of friendship; while this project includes procreation as a core feature, the institution of marriage has, on this account, a compensatory power, meaning that the institution itself can compensate for failures such as inability to procreate. Such an account grounds marriage in the new natural law account of flourishing, but it also allows the extension to same-sex marriage without, according to Goldstein, permitting other forms such as polygamy.
3.2.2 Marriage as Protecting Love
A second widespread (though less unified) institutional approach to marriage appeals to the ideal marital love relationship to define the structure of marriage. This approach, in the work of different philosophers, yields a variety of specific prescriptions, on, for example, whether marital love (or committed romantic love in general) requires sexual difference or sexual exclusivity (Scruton 1986, 305–311, Chapter 11, Halwani 2003, 226–242, Chartier 2016). Some, but not all, proponents explicitly argue that the marital love relationship is an objective good (Scruton 1986, Chapter 11, 356–361, Martin 1993). These views, however, all take the essential feature, and purpose, of marriage to be protecting a sexual love relationship. The thought is that marriage helps to maintain and support a relationship either in itself valuable, or at least valued by the parties to it.
On this approach, the structure of marriage derives from the behavior needed to maintain such a relationship. Thus marriage involves a commitment to act for the relationship as well as to exclude incompatible options—although there is controversy over what specific policies these general commitments entail. To take an uncontroversial example, marriage creates obligations to perform acts which sustain love, such as focusing on the beloved’s good qualities (Landau 2004). More controversially, some philosophers argue that sustaining a love relationship requires sexual exclusivity. The thought is that sexual activity generates intimacy and affection, and that objects of affection and intimacy will likely come into competition, threatening the marital relationship. Another version focuses on the emotional harm, and consequent damage to the relationship, caused by sexual jealousy. Thus, due to the psychological conditions required to maintain romantic love, marriage, as a love-protecting institution, generates obligations to sexual exclusivity (Martin 1993, Martin 1994, Scruton 1986, Chapter 11, 356–361, Steinbock 1986). However, philosophers dispute the psychological conditions needed to maintain romantic love. Some argue that casual extra-marital sex need not create competing relationships or trigger jealousy (Halwani 2003, 235; Wasserstrom 1974). Indeed, some have even argued that extra-marital sex, or greater social tolerance thereof, could strengthen otherwise difficult marriages (Russell 1929, Chapter 16), and some polyamorists (those who engage in multiple sex or love relationships) claim that polyamory allows greater honesty and openness than exclusivity (Emens 2004). Other philosophers have treated sexual fidelity as something of a red herring, shifting focus to other qualities of an ideal relationship such as attentiveness, warmth, and honesty, or a commitment to justice in the relationship (Martin 1993, Kleingeld 1998).
Views understanding marriage as protecting love generate diverse conclusions regarding its obligations. But such views share two crucial assumptions: that marriage has a role to play in creating a commitment to a love relationship, and that such commitments may be efficacious in protecting love (Cave 2003, Landau 2004, Martin 1993, Martin 1994, Mendus 1984, Scruton 1986, 356–361). However, both of these assumptions may be questioned. First, even if commitment can protect a love relationship, why must such a commitment be made through a formal marriage? If it is possible to maintain a long-term romantic relationship outside marriage, the question as to the point of marriage re-emerges: do we really need marriage for love? May not the legal and social supports of marriage, indeed, trap individuals in a loveless marriage or themselves corrode love by associating it with obligation? (Card 1996, Cave 2003; see also Gheaus 2016) Second, can commitment, within or without marriage, really protect romantic love? High divorce rates would seem to suggest not. Of course, even if, as discussed in 3.1, agents cannot control whether they love, they can make a commitment to act in ways protective of love (Landau 2004, Mendus 1984). But this returns us the difficulty, suggested by the preceding paragraph, of knowing how to protect love!
Reflecting the difficulty of generating specific rules to protect love, many such views have understood the ethical content of marriage in terms of virtues (Steinbock 1991, Scruton 1986, Chapter 11, 356–361). The virtue approach analyzes marriage in terms of the dispositions it cultivates, an approach which, by its reference to emotional states, promises to explain the relevance of marriage to love. However, such approaches must explain how marriage fosters virtues (Brake 2012). Some virtue accounts cite the effects of its social status: marriage triggers social reactions which secure spousal privacy and ward off the disruptive attention of outsiders (Scruton 1986, 356–361). Its legal obligations, too, can be understood as Ulysses contracts [ 1 ] : they protect relationships when spontaneous affection wavers, securing agents’ long-term commitments against passing desires. Whether or not such explanations ultimately show that marital status and obligations can play a role in protecting love, the general focus on ideal marital love relationships may be characterized as overly idealistic when contrasted with problems in actual marriages, such as spousal abuse (Card 1996). This last point suggests that moral analysis of marriage cannot be entirely separated from political and social inquiry.
4. The Politics of Marriage
In political philosophy, discussions of marriage law invoke diverse considerations, reflecting the theoretical orientations of contributors to the debate. This discussion will set out the main considerations invoked in arguments concerning the legal structure of marriage.
Marriage is a legal contract, but it has long been recognized to be an anomalous one. Until the 1970s in the U.S., marriage law restricted divorce and defined the terms of marriage on the basis of gender. Marking a shift towards greater alignment of marriage with contractual principles of individualization, marriage law no longer imposes gender-specific obligations, it allows pre-nuptial property agreements, and it permits easier exit through no-fault divorce. But marriage remains (at least in U.S. federal law) an anomalous contract: “there is no written document, each party gives up its right to self-protection, the terms of the contract cannot be re-negotiated, neither party need understand its terms, it must be between two and only two people, and [until 2015, when the US Supreme Court decision in Obergefell v. Hodges established same-sex marriage in the US] these two people must be one man and one woman” (Kymlicka 1991, 88).
Proponents of the contractualization, or privatization, of marriage have argued that marriage should be brought further into line with the contractual paradigm. A default assumption for some liberals, as for libertarians, is that competent adults should be legally permitted to choose the terms of their interaction. In a society characterized by freedom of contract, restrictions on entry to or exit from marriage, or the content of its legal obligations, appear to be an illiberal anomaly. Full contractualization would imply that there should be no law of marriage at all—marriage officiation would be left to religions or private organizations, with the state enforcing whatever private contracts individuals make and otherwise not interfering (Vanderheiden 1999, Sunstein and Thaler 2008, Chartier 2016; for a critique of contractualization, see Chambers 2016). The many legal implications of marriage for benefit entitlements, inheritance, taxation, and so on, can also be seen as a form of state interference in private choice. By conferring these benefits, as well as merely recognizing marriage as a legal status, the state encourages the relationships thereby formalized (Waldron 1988–89, 1149–1152). [ 2 ]
Marriage is the basis for legal discrimination in a number of contexts; such discrimination requires justification, as does the resource allocation involved in providing marital benefits (Cave 2004, Vanderheiden 1999). In the absence of such justification, providing benefits through marriage may treat the unmarried unjustly, as their exclusion from such benefits would then be arbitrary (Card 1996). Thus, there is an onus to provide a rationale justifying such resource allocations and legal discrimination on the basis of marriage, as well as for restricting marriage in ways that other contracts are not restricted.
Before exploring some common rationales, it is worth noting that critics of the social contract model of the state and of freedom of contract have used the example of marriage against contractual principles. First, Marxists have argued that freedom of contract is compatible with exploitation and oppression—and Marxist feminists have taken marriage as a special example, arguing against contractualizing it on these grounds (Pateman 1988, 162–188). Such points, as we will see, suggest the need for rules governing property division on divorce. Second, communitarians have argued that contractual relations are inferior to those characterized by trust and affection—again, using marriage as a special example (Sandel 1982, 31–35, cf. Hegel 1821, §75, §161A). This objection applies not only to contractualizing marriage, but more generally, to treating it as a case for application of principles of justice: the concern is that a rights-based perspective will undermine the morally superior affection between family members, importing considerations of individual desert which alienate family members from their previous unselfish identification with the whole (Sandel 1982, 31–35). However, although marriages are not merely an exchange of rights, spousal rights protect spouses’ interests when affection fails; given the existence of abuse and economic inequality within marriage, these rights are especially important for protecting individuals within, and after, marriage (Kleingeld 1998, Shanley 2004, 3–30, Waldron 1988).
As noted, a rationale must be given for marriage law which explains the restrictions placed on entry and exit, the allocation of resources to marriage, and legal discrimination on the basis of it. The next section will examine gender restrictions on entry; this section will examine reasons for recognizing marriage in law at all, allocating resources to it, and constraining property division on divorce.
A first reason for recognizing marriage should be set aside. This is that the monogamous heterosexual family unit is a natural, pre-political structure which the state must respect in the form in which it finds it (Morse 2006; cf. new natural lawyers, Girgis et al. 2010). But, whatever the natural reproductive unit may be, marriage law, as legislation, is constrained by principles of justice constraining legislation. Within most contemporary political philosophy, the naturalness of a given practice is irrelevant; indeed, in no area other than the family is it proposed that law should follow nature (with the possible exception of laws regarding suicide). Finally, such objections must answer to feminist concerns that excluding the family unit from principles of justice, allowing natural affection to regulate it, has facilitated inequality and abuse within it (see section 5).
Let us then begin with the question of why marriage should be recognized in law at all. One answer is that legal recognition conveys the state’s endorsement, guiding individuals into a valuable form of life (George 2000). A second is that legal recognition is necessary to maintain and protect social support for the institution, a valuable form of life which would otherwise erode (Raz 1986, 162, 392–3; Scruton 1986, 356–361; see discussion in Waldron 1988–89). But this prompts the question as to why this form of life is valuable.
It is sometimes argued that traditions, having stood the test of time, have proved their value. Not only is marriage itself such a tradition, but through its child-rearing role it can pass on other traditions (Sommers 1989, Scruton 1986, 356–361, cf. Devlin 1965, Chapter 4). But many marital traditions—coverture, gender-structured legal duties, marital rape exemptions, inter-racial marriage bans—have been unjust. Tradition provides at best a prima facie reason for legislation which may be overridden by considerations of justice. Further, in a diverse society, there are many competing traditions, amongst which this rationale fails to choose (Garrett 2008).
An account of the value of a particular form of marriage itself (and not just qua tradition) is needed. One thought is that monogamous marriage encourages the sexual self-control needed for health and happiness; another is that it encourages the goods of love and intimacy found in committed relationships. State support for monogamous marriage, by providing incentives to enter marital commitments, thus helps people lead better lives (e.g. Macedo 1995, 286). However, this approach faces objections. First, the explanation in terms of emotional goods underdetermines the institution to be supported: other relationships, such as friendships, embody emotional goods. Second, claims about the value of sexual self-control are controversial; objectors might argue that polygamy, polyamory, or promiscuity are equally good options (see 5.2). There is a further problem with this justification, which speaks to a division within liberal thought. Some liberals embrace neutrality, the view that the state should not base law on controversial judgments about what constitutes valuable living. To such neutral liberals, this class of rationales, which appeal to controversial value judgments about sex and love, must be excluded (Rawls 1997, 779). Some theorists have sought to develop rationales consistent with political liberalism, arguing, for instance, that the intimate dyadic marital relationship protects autonomy (Bennett 2003), or that some form of marriage could be justified by its efficiency in providing benefits (Toop 2019) or its role in protecting diverse caring relationships (Brake 2012), fragile romantic love relationships (Cave 2017), or caregivers and children (Hartley and Watson 2012, Toop 2019; see also May 2016, Wedgwood 2016).
It is widely accepted that the state should protect children. If two-parent families benefit children, incentives to marry may be justified as promoting two-parent families and hence children’s welfare. One benefit of two-parent families is economic: there is a correlation between single motherhood and poverty. Another benefit is emotional: children appear to benefit from having two parents (Galston 1991, 283–288). (Moreover, some argue that gender complementarity in parenting benefits children; but empirical evidence does not seem to support this [Lee 2008, Nussbaum 1999, 205, Manning et al ., 2014].)
One objection to this line of argument is that marriage is an ineffective child anti-poverty plan. For one thing, this account assumes that incentives to marry will lead a significant number of parents who would not otherwise have married to marry. But marriage and child-rearing have increasingly diverged despite incentives to marry. Second, this approach does not address the many children outside marriages and in poor two-parent families. Child poverty could be addressed more efficiently through direct anti-child-poverty programs rather than the indirect strategy of marriage (Cave 2004; Vanderheiden 1999; Young 1995). Moreover, there is controversy over the psychological effects of single parenthood, particularly over the causality underlying certain correlations: for instance, are children of divorce unhappier due to divorce itself, or to the high-conflict marriage preceding it? (Young 1995) Indeed, some authors have recently argued that children might be better protected by legally separating marriage from parenting: freestanding parenting frameworks would be more durable than marriage (which can end in divorce), would protect children outside of marriages, and would accommodate new family forms such as three-parent families (Brennan and Cameron 2016, Shrage 2018; see also Chan and Cutas 2012).
A related, but distinct, line of thought invokes the alleged psychological effects of two-parent families to argue that marriage benefits society by promoting good citizenship and state stability (Galston 1991, 283–288). This depends on the empirical case (as we have seen, a contested one) that children of single parents face psychological and economic hurdles which threaten their capacity to acquire the virtues of citizenship. Moreover, if economic dependence produces power inequality within marriage, then Mill’s ‘school of injustice’ objection applies—an institution teaching injustice is likely to undermine the virtues of citizenship (Okin 1994, Young 1995).
Finally, a rationale for restricting the terms of exit from marriage (but not for supporting it as a form of life) is the protection of women and children following divorce. Women in gender-structured marriages, particularly if they have children, tend to become economically vulnerable. Statistically, married women are more likely than their husbands to work in less well-paid part-time work, or to give up paid work entirely, especially to meet the demands of child-rearing. Thus, following divorce, women are likely to have a reduced standard of living, even to enter poverty. Because these patterns of choice within marriages lead to inequalities between men and women, property division on divorce is a matter of equality or equal opportunity, and so a just law of divorce is essential to gender justice (Okin 1989, Chapters 7 and 8; Rawls 1997, 787–794; Shanley 2004, 3–30; Waldron 1988, and see 5.1). However, it can still be asked why a law recognizing marriage as such should be necessary, as opposed to default rules governing property distribution when such gender-structured relationships end (Sunstein and Thaler 2008, Chambers 2017). Indeed, placing these restrictions only on marriage, as opposed to enacting general default rules, may make marriage less attractive, especially to men, and hence be counter-productive, leaving women more vulnerable.
The preceding two rationales are both weakened by the diminished social role of marriage; changing legal and social norms undermine its effectiveness as a policy tool. In the 20 th century, marriage was beset by a “perfect storm”: the expectation that it should be emotionally fulfilling, women’s liberation, and effective contraception (Coontz 2006, Chapter 16). Legally, exit from marriage has become relatively easy since the ‘no-fault divorce revolution’ of the 1970’s. Moreover, cohabitation and child-rearing increasingly take place outside marriage. This reflects the end of laws against unmarried cohabitation and legal discrimination against children on grounds of ‘illegitimacy’, as well as diminishing social stigmas against such behavior. Given such significant changes, marriage is at best an indirect strategy for achieving goals such as protecting women or children (Cave 2004, Sunstein and Thaler 2008, Vanderheiden 1999).
Some theorists have argued, in the absence of a compelling rationale for marriage law, for abolishing marriage altogether, replacing it with civil unions or domestic partnerships. This line of thought will be taken up in 4.4, after an examination of the debate over same-sex marriage.
Many arguments for same-sex marriage invoke liberal principles of justice such as equal treatment, equal opportunity, and neutrality. Where same-sex marriage is not recognized in law, marriage provides benefits which are denied to same-sex couples on the basis of their orientation; if the function of marriage is the legal recognition of loving, or “voluntary intimate,” relationships, the exclusion of same-sex relationships appears arbitrary and unjustly discriminatory (Wellington 1995, 13). Same-sex relationships are relevantly similar to different-sex relationships recognized as marriages, yet the state denies gays and lesbians access to the benefits of marriage, hence treating them unequally (Mohr 2005, Rajczi 2008, Williams 2011). Further, arguments in support of such discrimination seem to depend on controversial moral claims regarding homosexuality of the sort excluded by neutrality (Wellington 1995, Schaff 2004, Wedgwood 1999, Arroyo 2018).
A political compromise (sometimes proposed in same-sex marriage debates) of restricting marriage to different-sex couples and offering civil unions or domestic partnerships to same-sex couples does not fully answer the arguments for same-sex marriage. To see why such a two-tier solution fails to address the arguments grounded in equal treatment, we must consider what benefits marriage provides. There are tangible benefits such as eligibility for health insurance and pensions, privacy rights, immigration eligibility, and hospital visiting rights (see Mohr 2005, Chapter 3), which could be provided through an alternate status. Crucially, however, there is also the important benefit of legal, and indirectly social, recognition of a relationship as marriage. The status of marriage itself confers legitimacy and invokes social support. A two-tier system would not provide equal treatment because it does not confer on same-sex relationships the status associated with marriage .
In addition, some philosophers have argued that excluding gays and lesbians from marriage is central to gay and lesbian oppression, making them ‘second-class citizens’ and underlying social discrimination against them. Marriage is central to concepts of good citizenship, and so exclusion from it displaces gays and lesbians from full and equal citizenship: “being fit for marriage is intimately bound up with our cultural conception of what it means to be a citizen … because marriage is culturally conceived as playing a uniquely foundational role in sustaining civil society” (Calhoun 2000, 108). From this perspective, the ‘separate-but-equal’ category of civil unions retains the harmful legal symbol of inferiority (Card 2007, Mohr 2005, 89, Calhoun 2000, Chapter 5; cf. Stivers and Valls 2007; for a comprehensive survey of these issues, see Macedo 2015).
However, if marriage is essentially different-sex, excluding same-sex couples is not unequal treatment; same-sex relationships simply do not qualify as marriages. One case that marriage is essentially different-sex invokes linguistic definition: marriage is by definition different-sex, just as a bachelor is by definition an unmarried man (Stainton, cited in Mercier 2001). But this confuses meaning and reference. Past applications of a term need not yield necessary and sufficient criteria for applying it: ‘marriage’, like ‘citizen’, may be extended to new cases without thereby changing its meaning (Mercier 2001). As noted above, appeal to past definition begs the question of what the legal definition should be (Stivers and Valls 2007).
A normative argument for that marriage is essentially different-sex appeals to its purpose: reproduction in a naturally procreative unit (see 3.2.a). But marriage does not require that spouses be able to procreate naturally, or that they intend to do so at all. Further, married couples adopt and reproduce using donated gametes, rather than procreating ‘naturally’. Nor do proponents of this objection to same-sex marriage generally suggest that entry to marriage should be restricted by excluding those unable to procreate without third-party assistance, or not intending to do so.
Indeed, as the existence of intentionally childless married couples suggests, marriage has purposes other than child-rearing—notably, fostering a committed relationship (Mohr 2005, Wellington 1995, Wedgwood 1999). This point suggests a second defense of same-sex marriage: exclusive marital commitments are goods which the state should promote amongst same-sex as well as opposite-sex couples (Macedo 1995). As noted above, such rationales come into tension with liberal neutrality; further controversy regarding them will be discussed below (5.2).
Some arguments against same-sex marriage invoke a precautionary principle urging that changes which might affect child welfare be made with extreme caution. But in light of the data available, Murphy argues that the precautionary principle has been met with regard to harm to children. On his view, parenting is a basic civil right, the restriction of which requires the threat of a certain amount of harm. But social science literature shows that children are neither typically nor seriously harmed by same-sex parenting (see Manning et al ., 2014). Even if two biological parents statistically provide the optimal parenting situation, optimality is too high a standard for permitting parenting. This can be seen if an optimality condition is imagined for other factors, such as education or wealth (Murphy 2011).
A third objection made to same-sex marriage is that its proponents have no principled reason to oppose legally recognizing polygamy (e.g. Finnis 1997; see Corvino 2005). One response differentiates the two by citing harmful effects and unequal status for women found in male-headed polygyny, but not in same-sex marriage (e.g. Wedgwood 1999, Crookston 2014, de Marneffe 2016, Macedo 2015). Another response is to bite the bullet: a liberal state should not choose amongst the various ways (compatible with justice) individuals wish to organize sex and intimacy. Thus, the state should recognize a diversity of marital relationships—including polygamy (Calhoun 2005, Mahoney 2008) or else privatize marriage, relegating it to private contract without special legal recognition or definition (Baltzly 2012).
Finally, some arguments against same-sex marriage rely on judgments that same-sex sexual activity is impermissible. As noted above, the soundness of these arguments aside, neutrality and political liberalism exclude appeal to such contested moral views in justifying law in important matters (Rawls 1997, 779, Schaff 2004, Wedgwood 1999, Arroyo 2018). However, some arguments against same-sex marriage have invoked neutrality, on the grounds that legalizing same-sex marriage would force some citizens to tolerate what they find morally abhorrent (Jordan 1995, and see Beckwith 2013). But this reasoning seems to imply, absurdly, that mixed-race marriage, where that is the subject of controversy, should not be legalized. A rights claim to equal treatment (if such a claim can support same-sex marriage) trumps offense caused to those who disagree; the state is not required to be neutral in matters of justice (Beyer 2002; Boonin 1999; Schaff 2004; see also Barry 2011, Walker 2015).
A number of theorists have argued for the abolition or restructuring of marriage. While same-sex marriage became legally recognized throughout the United States following the Supreme Court decision in Obergefell v Hodges 576 U.S. _ (2015) , some philosophers contend that justice requires further reform. Some have proposed that temporary marriage contracts be made available (Nolan 2016, Shrage 2013) and that legal frameworks for marriage and parenting be separated (Brennan and Cameron 2016, Shrage 2018). A more sweeping view, to be discussed in Section 5, is that marriage is in itself oppressive and unjust, and hence ought to be abolished (Card 1996, Fineman 2004, Chambers 2013, 2017). A second argument for disestablishing or privatizing legal marriage holds that, in the absence of a pressing rationale for marriage law (as discussed in 4.2), the religious or ethical associations of marriage law give reason for abolishing marriage as a legal category. Marriage has religious associations in part responsible for public controversy over same-sex marriage. If marriage is essentially defined by a religious or ethical view of the good, then legal recognition of it arguably violates state neutrality or even religious freedom (Metz 2010, but see Macedo 2015, May 2016, Wedgwood 2016).
There are several reform proposals compatible with the ‘disestablishment’ of marriage. One proposal is full contractualization or privatization, leaving marriage to churches and private organizations. “Marital contractualism” (MC) would relegate spousal agreements to existing contract law, eradicating any special legal marital status or rights. Garrett has defended MC as the default position, arguing that state regulation of contracts between spouses and state expenditures on marriage administration and promotion need justification. On his view, efficiency, equality, diversity, and informed consent favor MC; there is no adequate justification for the costly redistribution of taxpayer funds to the married, or for sustaining social stigma against the unmarried through legal marriage (Garrett 2009, see also Chartier 2016).
But marriage confers rights not available through private contract and which arguably should not be eliminated due to their importance in protecting intimate relationships—such as evidentiary privilege or special eligibility for immigration. A second proposal would retain such rights while abolishing marriage; on this proposal, the state ought to replace civil marriage entirely with a secular status such as civil union or domestic partnership, which could serve the purpose of identifying significant others for benefit entitlements, visiting rights, and so on (March 2010, 2011). This would allow equal treatment of same-sex relationships while reducing controversy, avoiding non-neutrality, and respecting the autonomy of religious organizations by not compelling them to recognize same-sex marriage (Sunstein and Thaler 2008). However, neither solution resolves the conflict between religious autonomy and equality for same-sex relationships. Privatization does not solve this conflict so long as religious organizations are involved in civil society—for example, as employers or benefit providers. The question is whether religious autonomy would allow them, in such roles, to exclude same-sex civil unions from benefits. Such exclusion could be defended as a matter of religious autonomy; but it could also be objected to as unjust discrimination—as it would be if, for example, equal treatment were denied to inter-racial marriages.
Another issue raised by such a reform proposal is how to delimit the relationships entitled to such recognition. Recall the new natural law charge that liberalism entails an objectionable “plasticicty” regarding marriage (3.2.1). One question is whether recognition should be extended to polygamous or polyamorous relationships. Some defenders of same-sex marriage hold that their arguments do not entail recognizing polygamy, due to its oppressive effects on women (Wedgwood 1999). However, some monogamous marriages are also oppressive (March 2011), and egalitarian polygamous or polyamorous relationships, such as a group of three women or three men, exist (Emens 2004). Thus, oppressiveness does not cleanly distinguish monogamous from polygamous relationships. Brooks has sought to show that polygamy is distinctively structurally inegalitarian as one party (usually the husband) can determine who will join the marriage, whereas wives cannot (Brooks 2009). However, this overlooks various possible configurations—if a polygamous “sister wife,” for instance, has the legal right to marry outside the existing marriage, there is no structural inequality (Strauss 2012). Most fundamentally, some authors have urged that a politically liberal state should not prescribe the arrangements in which its competent adult members seek love, sex, and intimacy, so long as they are compatible with justice (Calhoun 2005, March 2011). Some philosophers have argued that polygamists and polyamorous people are unjustly excluded from the benefits of marriage, and that legal recognition of plural marriage - or small groups of friends – can preserve equality (Brake 2012, 2014, Den Otter 2015, Shrage 2016). Finally, the history of racialized stigmatization of polygamy gives reason to consider whether anti-polygamous intuitions rest on just foundations (Denike 2010).
Conservatives also charge that the liberal approach cannot rule out incestuous marriage. While this topic has sparked less debate than polygamy, one defender of the civil-unions-for-all proposal has pointed out that civil union status, as justified on politically liberal grounds, would not connote sexual or romantic involvement. Thus, eligibility of adult family members for this status would not convey state endorsement of incest; whether the state should prohibit or discourage incest is an independent question (March 2010).
A further problem arises with the proposal to replace marriage with civil unions on neutrality grounds. Civil unions, if they carry legal benefits similar to marriage, would still involve legal discrimination (between members of civil unions and those who were not members) requiring justification (for a specific example of this problem in the area of immigration law, see Ferracioli 2016). Depending on how restrictive the entry criteria for civil unions were (for example, whether more than two parties, blood relations, and those not romantically involved could enter) and how extensive the entitlements conferred by such unions were, the state would need to provide reason for this discrimination. In the absence of compelling neutral reasons for such differential treatment, liberty considerations suggest the state should cease providing any special benefits to members of civil unions (or intimate relationships) (Vanderheiden 1999, cf. Sunstein and Thaler 2008). As noted in 4.2, some political liberals have sought to provide rationales showing why a liberal state should support certain relationships; these rationales generate corresponding reform proposals. One approach focuses on protecting economically dependent caregivers; Metz proposes replacing civil marriage with “intimate care-giving unions” which would protect the rights of dependent caregivers (Metz 2010; cf. Hartley and Watson 2012). Another approach holds that caring relationships themselves - whether friendships or romantic relationships - should be recognized as valuable by the politically liberal state, and it should, accordingly, distribute rights supporting them equally; the corresponding reform proposal, “minimal marriage,” would provide rights directly supporting relationships, but not economic benefits, without restriction as to sex or number of parties or the nature of their caring relationship (Brake 2012). This would extend marriage not only to polyamorists, but to asexuals and aromantics, as well as those who choose to build their lives around friendships. A third approach proposes that marital rights and status be replaced by “piecemeal directives” which would regulate the various functional contexts to which marriage law now applies (such as cohabitation and co-parenting) (Chambers 2017); this proposal would avoid designating any relationship type as entitled to special treatment.
Many of the views discussed to this point imply that current marriage law is unjust because it arbitrarily excludes some groups from benefits; it follows, on such views, that marrying is to avail oneself of privileges unjustly extended. This seems to give reason for boycotting the institution, so long as some class of persons is unjustly excluded (Parsons 2008).
Before Obergefell , U.S. law was in patchwork regarding marriages involving at least one transgender person — “trans—marriage,” in Loren Cannon’s term. As a transgender person traveled from state to state, both their legal sex and marital status could change (Cannon 2009, 85). While some raised concerns that the political rationales given for recognizing such marriages (such as the possibility of penile-vaginal intercourse) reaffirmed heteronormative assumptions (Robson 2007), to other theorists, the possibility of trans-marriage itself suggests the instability or incoherence of legal gender categories and gendered restrictions on marriage (Cannon 2009, Almeida 2012).
5. Marriage and Oppression: Gender, Race, and Class
Marriage historically played a central role in women’s oppression, meaning economic and political disempowerment and limitation of opportunities. Until the late 19 th century, the doctrine of coverture (in English and U.S. law) suspended a wife’s legal personality on marriage, ‘covering’ it with that of her husband, removing her rights to own property, make a will, earn her own money, make contracts, or leave her husband, and giving her little recourse against physical abuse. Well into the 20 th century, legislatures continued to impose gendered legal roles within marriage (known as ‘head and master laws’), to exempt rape within marriage from criminal prosecution, and to allow—or impose—professional bars on married women (Coontz 2006, 238; Cronan 1973; Kleingeld 1998). John Stuart Mill compared wives’ condition under coverture to slavery (see section 1); while the late 20 th century U.S. saw gender-neutrality in legal marital responsibilities and an end to the marital rape exemption, criticisms of marriage as oppressive persist. Contemporary feminist attention to marriage is focused on spousal abuse—indeed, some U.S. states still exempt spouses from sexual battery charges (Posner and Silbaugh 1996)—, the gendered division of labor in marriage, and the effects of marriage on women’s economic opportunities and power.
While Mill and Engels saw the establishment of monogamous marriage as an ancient defeat of the female sex, Aquinas, Kant, and many others have seen monogamy as a victory for women, securing for them faithful partners, protection, and material support. So Kant writes that “skepticism on this topic [marriage] is bound to have bad consequences for the whole feminine sex, because this sex would be degraded to a mere means for satisfying the desire of the other sex, which, however, can easily result in boredom and unfaithfulness.—Woman becomes free by marriage; man loses his freedom by it” (Kant 1798, 210–211, [309]). However, as a historical thesis about the origin of marriage, the idea that monogamy provided women with needed material support has been debunked. In early hunting-gathering societies, female foraging likely provided more than male hunting, child-care was arranged communally, and, rather than a single male providing for his female partner, survival required a much larger group (Coontz 2006, 37–38). As a thesis about the protection of women by their male partners, the incidence of rape and violence by male partners themselves must be taken into account (e.g., in the contemporary U.S., Tjaden and Thoennes 2000). And as a thesis about sex difference, evolutionary ‘just-so’ stories purporting to show that women are naturally more monogamous have been challenged by feminist philosophers of biology (Tuana 2004).
Marriage law has also been a tool of racial oppression. The majority of American states at one time prohibited inter-racial marriage; the Supreme Court struck down such laws in 1967 (Wallenstein 2002, 253–254). Anti-miscegenation law did not prevent actual sex and procreation between races, but it excluded women of color and their children from the benefits of marriage. It was also a potent symbol of alleged racial difference. Furthermore, African-American marriage patterns were shaped by slavery. Enslaved persons could not legally marry, and slave couples and their children were frequently separated (Cott 2000). Contemporary philosophers of race argue that marriage is still implicated in systemic racism (Collins 1998). For example, historical conditions and structural racism have led to practices of shared child-rearing in some African-American communities. Some theories of marriage imply that such child-rearing practices are inferior to the marital family. Theorists of racial oppression argue that such practices should be recognized as a valuable alternative, and, moreover, that law which excludes such practices from benefits accorded to marriage may be racially unjust (Vanderheiden 1999; cf. Collins 1998, Card 1996). Immigration law has also made women who are dependent on marriage for their immigration status vulnerable to abuse, particularly those women who are also subject to racism or cultural marginalization (Narayan 1995).
Recent work has also highlighted the contemporary class-based marriage gap in the U.S.: wealthier people are more likely to marry (McClain 2013). This suggests a different link between marriage and oppression: one effect of socioeconomic inequality may be to deprive the worse-off of access to marriage (perhaps because poverty impedes the formation of stable relationships) and the further legal benefits marriage can bring. There is arguably a tension, among egalitarian approaches, between feminist criticisms of marriage as inherently oppressive and egalitarian criticisms of barriers to accessing it (Chambers 2013).
A major theme in feminist political philosophy has been the exclusion of the marital family from justice. Political philosophy has tended to relegate family life to natural hierarchy or affection (Okin 1979, 1989). Historically, this meant that the private sphere of marriage, to which women were confined, was also the zone of state non-interference, so that what happened to women there was not subject to norms of justice. Gradually, law and political philosophy have come to recognize that equal rights and liberties should be upheld within the private sphere as outside it, but many political philosophers still resist applying principles of justice directly within the private sphere. However, feminists argue that gender-structured marriage contributes to, or is even the mainstay of, women’s economic inequality and disempowerment, and that justice must therefore regulate its terms—even, perhaps, to the point of interfering with voluntary marital relations (Okin 1989, Ferguson 2016). At the same time, marriage has been a crucial site of socially valuable care work, which often falls disproportionately on women, and recent feminist work has focused on how the state can support that work more equitably (Metz 2010, Bhandary 2018).
As noted above, one persistent rationale for excluding the family from norms of justice is that its natural relations of affection and trust are superior to merely just relations and likely to be threatened by construing the family in terms of justice (Hegel 1821, §75, §161A; Sandel 1982, 31–35). But abuse within marriage and inequality on dissolution are significant problems, the gravity of which should, according to critics, outweigh these finer virtues; rights within marriage protect spouses when affection fails (Waldron 1988, Okin 1989). Moreover, it is not clear that affection and justice must conflict; a commitment to treating one’s spouse justly could be part of marital love (Kleingeld 1998). Finally, marriage is part of the basic structure of society, and thus, at least within Rawlsian liberalism, is subject to principles of justice. This does not determine, however, how principles of justice should constrain marriage; the default liberal presumption is that marriage, as a voluntary association, should be ordered as spouses choose—so long as these choices do not lead to injustice (Rawls 1997, 792). We will return to this below.
Marriage is a focus of feminist concern due to its effects on women’s life chances. Continuing disadvantage accruing to women in marriage has been widely documented, and in some feminist analyses, undergirds gender inequality (rival accounts place greater emphasis on sexual objectification or workplace discrimination). Wives, even those who work full-time outside the home, perform more housework than husbands—this ‘second shift’ affecting their workplace competitiveness. The social assignment of primary responsibility for childcare to women, combined with the difficulty of combining childcare with paid work, also undermine the workplace competitiveness of women with children (Okin 1989, Chapter 7). The gendered division of labor and the fact that ‘women’s work’ is less well-paid than men’s together make it more likely that married women, rather than their husbands, will downgrade their careers, choose part-time work, or stay home to facilitate child-rearing or when the spouses’ careers conflict. These choices make women “vulnerable by marriage”: economic dependence, and dependence on marriage for benefits such as health insurance, fosters power inequality and makes exit difficult, in turn facilitating abuse (Okin 1989, Chapter 7, Narayan 1995, Card 1996, Brake 2016, Ferguson 2016).
As discussed in 4.2, rationales of equality or equal opportunity are given for addressing economic inequalities arising within marriage through divorce law (Okin 1989, Chapters 7 and 8; Shanley 2004, 3–30, Rawls 1997, 787–794). However, divorce law does not address non-economic sources of power imbalances (such as gender role socialization) within on-going marriages, nor does it address the systemic way in which such inequalities arise. Equal opportunity seems to require changing social norms related to marriage in ways which divorce law does not. First, the gendered division of labor within ongoing marriages is costly for women (Kleingeld 1998). Second, power imbalances within marriage limit girls’ expectations and teach children to accept gendered inequality (Okin 1989, Chapter 7, Okin 1994). Third, anticipation of marriage affects women’s investment in their earning ability before marriage (Okin 1989, Chapter 7). (But for an argument that some hierarchy and inequality in marriage is just, see Landau 2012.)
Such social norms could be addressed through education or through media campaigns promoting the equitable division of housework. Legal measures such as requiring all marital income to be held equally could encourage power equality within marriage (Okin 1989, Chapter 8). However, state interference in on-going marriages arguably conflicts with spouses’ liberties (Rawls 1997, 787–794). This seems to raise a theoretical problem for liberal feminism. Recent liberal feminist approaches to marriage focus on how a just law of marriage can protect women’s interests as well as supporting a fairer distribution of care work, which often falls on women (Metz 2010, Brake 2012, Hartley and Watson 2012, Ferguson 2016, Bhandary 2018; see also reform proposals in 4.4 above).
While many feminists have focused on the reform of marriage, others have argued for its abolition as a legal status (Metz 2010, Chambers 2013, 2017). It is sometimes claimed that marriage is inherently structured by sexist social norms, precluding the possibility of feminist reform — and that marriage also reinforces stigma against the unmarried (Chambers 2017). On such views, abolishing marriage is necessary to reshape social expectations and change patterns of choice accompanying it. For example, legal marriage may encourage women’s economic dependence by enabling and providing incentives for it. Thus, the legal structure of marriage, in combination with social norms, is taken to encourage choices which disempower women relative to men. Moreover, legal recognition of marriage itself endorses an ideal of a central, exclusive love relationship which, on the views of some feminists, encourages women to make disadvantageous choices by inculcating an exaggerated valuation of such relationships—at the expense of women’s other aspirations. Thus, in The Second Sex , feminist philosopher Simone de Beauvoir (1908–86) identified the expectations surrounding marriage as one of the primary means by which women are socialized into a femininity which, in her view, was limiting: marriage “is the destiny traditionally offered to women by society” (de Beauvoir 1949 [1989], 425; see also Okin 1989), leading women to focus on their attractiveness as mates—and not on study, career, or other ambitions. For this reason, some feminists have rejected ideals of romantic, exclusive love relationships, arguing that women should choose non-monogamy or lesbian separatism (Firestone 1970; see also Card 1996). The idea that marriage is essentially tied to such an ideal of romantic love will require further examination in the next section.
Just as some feminists argue that marriage is inherently sexist, so some philosophers of gay, lesbian, bisexual, and transgender oppression argue that it is essentially heterosexist. (Some of these philosophers refer to themselves as queer theorists, reclaiming the word “queer” from its earlier, pejorative usage.) Queer theorists have sought to demonstrate that a wide range of social institutions display heteronormativity, that is, the assumption of heterosexuality and of the gender difference that defines it as a norm. Because queer theorists resist the normativity of gender as well as of heterosexuality, there is an overlap between their critiques of marriage and those of some feminists, especially lesbian feminists. For these critics of heteronormativity, same-sex marriage is undesirable because it would assimilate same-sex relationships to an essentially heterosexual marital ideal: “Queer theorists worry that pursuing marriage rights is assimilationist, because it rests on the view that it would be better for gay and lesbian relationships to be as much like traditional heterosexual intimate relationships as possible” (Calhoun 2000, 113). On this view, extending marriage to same-sex marriage will undermine, rather than achieve, gay and lesbian liberation - and, indeed, further marginalize asexuals, aromantics, polyamorists, and those who choose to build their lives around friendships.
Recall that some arguments for same-sex marriage claim that central, exclusive relationships are valuable, and that same-sex marriage would benefit gays and lesbians by encouraging them to enter such relationships (e.g. Macedo 2005; see 3.3). But critics of heteronormativity, drawing on gay and lesbian experience, have argued that the central, exclusive relationship ideal is a heterosexual paradigm. Such critics note that gays and lesbians often choose relationships which are less possessive and more flexible than monogamous marriage. Instead of recognizing the diverse relationships found in the gay and lesbian community, same-sex marriage would assimilate lesbian and gay relationships into the heterosexual model. While some advocates of same-sex marriage argue that marital status would confer legitimacy on same-sex relationships, these critics argue that the state should not confer legitimacy (and hence, implicitly, illegitimacy) on consensual adult relationships, any more than it should so discriminate between children born in or out of wedlock. Such conferrals of legitimacy are thought to discourage diversity. Moreover, same-sex marriage would expose gays and lesbians to the disadvantages, even evils, of marriage: economic incentives to stay in loveless marriages and reduced exit options which facilitate abuse and violence (Card 1996, 2007, Ettelbrick 1989).
Other philosophers of gay and lesbian oppression have responded in defense of same-sex marriage that it not only serves gay liberation, it is essential to it. Excluding gays and lesbians from marriage marks them as inferior, and so same-sex marriage would decrease stigmas against homosexuality. Further, the costs of same-sex marriage must be weighed with benefits such as healthcare, custody and inheritance rights, and tax and immigration status (Calhoun 2000, Chapter 5, Ferguson 2007, Mayo and Gunderson 2000). Finally, in response to worries about gay and lesbian assimilation, defenders of same-sex marriage have argued that marriage can incorporate diversity, rather than suppressing it. Marriage need not entail monogamy; indeed, it is argued that same-sex marriage could perform the liberatory function of teaching heterosexuals that neither gender roles nor monogamy are essential to love and marriage (Mohr 2005, 69–9, cf. Halwani 2003, Chapter 3; but see Brake 2018 for discussion of whether “subversive weddings” can transform social attitudes if they are not recognized as initiating marriages).
The feminist and queer critiques of marriage as essentially sexist, or essentially heterosexist, face the same objection as do other claims about the essence of marriage. Just because marriage has in the past possessed certain features does not entail that they are inherent to it. Thus, rather than reproducing sexist and heterosexist patterns, same-sex marriage could serve women’s and gay liberation by transforming marriage, even, perhaps, opening the door to recognition of a still wider variety of family forms (Ferguson 2007, Mayo and Gunderson 2000, Calhoun 2005, Brake 2012).
- Abbey, Ruth, and Den Uyl, Douglas, 2001, “The Chief Inducement? The Idea of Marriage As Friendship,” Journal of Applied Philosophy , 18(1): 37–52.
- Almeida, Luís Duarte d’, 2012, “Legal Sex,” Oxford Studies in Philosophy of Law (Volume 2), Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 277–310.
- Altman, Matthew C., 2010, “Kant on Sex and Marriage: The Implications for the Same-Sex Marriage Debate,” Kant-Studien , 101(3): 309–330.
- Arneson, Richard, 2005, “The Meaning of Marriage: State Efforts to Facilitate Friendship, Love, and Childrearing,” San Diego Law Review , 42: 979–1001.
- Arroyo, Christopher, 2018, “Is the Same-sex Marriage Debate Really Just about Marriage?,” Journal of Applied Philosophy , 35(1): 186–203.
- Baltzly, Vaughn Bryan, 2012, “Same-Sex Marriage, Polygamy, and Disestablishment,” Social Theory and Practice , 38(2): 333–362.
- Barry, Peter Brian, 2011, “Same-Sex Marriage and the Charge of Illiberality,” Social Theory and Practice , 37(2): 333–357.
- Beckwith, Francis J., 2013, “Justificatory Liberalism and Same-Sex Marriage,” Ratio Juris , 26(4): 487–509.
- Bennett, Christopher, 2003, “Liberalism, Autonomy, and Conjugal Love,” Res Publica , 9: 285–301.
- Beyer, Jason A., 2002, “Public Dilemmas and Gay Marriage: Contra Jordan,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 33(1): 9–16.
- Bhandary, Asha, 2018, “Arranged Marriage: Could It Contribute to Justice?,” Journal of Political Philosophy , 26(2): 193–215.
- Blankschaen, Kurt, 2020, “Rethinking Same-Sex Sex in Natural Law Theory,” Journal of Applied Philosophy , 37(3): 428–445.
- Boonin, David, 1999, “Same-Sex Marriage and the Argument from Public Disagreement,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 30(2): 251–259.
- Boswell, John, 1994, The Marriage of Likeness: Same-Sex Unions in Pre-Modern Europe , London: HarperCollins.
- Brake, Elizabeth, 2005, “Justice and Virtue in Kant’s Account of Marriage,” Kantian Review , 9: 58–94.
- –––, 2012, Minimizing Marriage: Marriage, Morality, and the Law , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2014, “Recognizing Care: The Case for Friendship and Polyamory,” Syracuse Law and Civic Engagement Journal , 1, [ available online ].
- –––, 2016, “Equality and Non-Hierarchy in Marriage: What Do Feminists Really Want?,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 100–124.
- –––, 2018, “Do Subversive Weddings Challenge Amatonormativity? Polyamorous Weddings and Romantic Love Ideals,” Analize: Journal of Gender and Feminist Studies , 11, [ Brake 2018 available online ].
- Brennan, Samantha, and Bill Cameron, 2016, “Is Marriage Bad for Children? Rethinking the Connection between Having Children, Romantic Love, and Marriage,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 84–99.
- Brooks, Thom, 2009, “The Problem with Polygamy,” Philosophical Topics , 37(2): 109–22.
- Buccola, Nicholas, 2005, “Finding Room for Same-Sex Marriage: Toward a More Inclusive Understanding of a Cultural Institution,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 36(3): 331–343.
- Calhoun, Cheshire, 2000, Feminism, the Family, and the Politics of the Closet: Lesbian and Gay Displacement , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2005, “Who’s Afraid of Polygamous Marriage? Lessons for Same-Sex Marriage Advocacy from the History of Polygamy,” San Diego Law Review , 42: 1023–1042.
- Cannon, Loren, 2009, “Trans-Marriage and the Unacceptability of Same-Sex Marriage Restrictions,” Social Philosophy Today , 25: 75–89.
- Card, Claudia, 1996, “Against Marriage and Motherhood,” Hypatia , 11(3): 1–23.
- –––, 2007, “Gay Divorce: Thoughts on the Legal Regulation of Marriage,” Hypatia , 22(1): 24–38.
- Cave, Eric M., 2003, “Marital Pluralism: Making Marriage Safer for Love,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 34(3): 331–347.
- –––, 2004, “Harm Prevention and the Benefits of Marriage,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 35(2): 233–243.
- –––, 2017, “Liberalism, Civil Marriage, and Amorous Caregiving Dyads,” Journal of Applied Philosophy , 36(1): 50–72.
- Chambers, Clare, 2013, “The Marriage-Free State,” Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , 113 (2): 123–143.
- –––, 2016, “The Limitations of Contract: Regulating Personal Relationships in a Marriage-Free State,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 51–83.
- –––, 2017, Against Marriage: An Egalitarian Defence of the Marriage-Free State , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Chan, Sarah, and Daniela Cutas (eds.), 2012, Families ––Beyond the Nucelar Ideal , New York: Bloomsbury Academic.
- Chartier, Gary, 2016, Public Practice, Private Law: An Essay on Love, Marriage, and the State , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Collins, Patricia Hill, 1998, “It’s All in the Family: Intersections of Gender, Race, and Nation,” Hypatia , 13(3): 62–82.
- Coontz, Stephanie, 2006, Marriage: a History , London: Penguin.
- Corvino, John, 2005, “Homosexuality and the PIB Argument,” Ethics , 115: 501–534.
- Cott, Nancy, 2000, Public Vows: A History of Marriage and the Nation , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Cronan, Sheila, 1973, “Marriage,” in Radical Feminism , ed. Anne Koedt, Ellen Levine, Anita Rapone, New York: Quadrangle, pp.213 –221.
- Crookston, Emily, 2014, “Love and Marriage?,” Journal of Moral Philosophy , 11(4): 267–289.
- De Marneffe, Peter, 2016, “Liberty and Polygamy,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 125–159.
- Den Otter, Ron, 2015, In Defense of Plural Marriage , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Denike, Margaret, 2010, “The Racialization of White Man’s Polygamy,” Hypatia , 25(4): 852–874.
- Devlin, Patrick, 1965, The Enforcement of Morals , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Emens, Elizabeth F., 2004, “Monogamy’s Law: Compulsory Monogamy and Polyamorous Existence,” New York University Review of Law and Social Change , 29: 277–376.
- Ettelbrick, Paula, “Since When is Marriage a Path to Liberation?,” 1989, Out/look: National Lesbian and Gay Quarterly , 6(9): 14–17; reprinted in Andrew Sullivan (ed.), Same-Sex Marriage: Pro and Con , New York: Vintage, 2004, pp. 122–128.
- Ferguson, A., 2007, “Gay Marriage: An American and Feminist Dilemma,” Hypatia , 22(1): 39–57.
- Ferguson, Michaele L., 2016, “Vulnerability by Marriage: Okin’s Radical Feminist Critique of Structural Gender Inequality,” Hypatia (A Journal of Feminist Philosophy), 31(3): 687–703.
- Ferracioli, Luara, 2016, “Family Migration Schemes and Liberal Neutrality: A Dilemma,” Journal of Moral Philosophy , 13(5): 553–575.
- Fineman, Martha, 2004, The Autonomy Myth: A Theory of Dependency , New York: The New Press.
- Finnis, John, 1994, “Law, Morality, and ‘Sexual Orientation’,” Notre Dame Law Review , 69: 1049–1076.
- –––, 1997, “The Good of Marriage and the Morality of Sexual Relations: Some Philosophical and Historical Observations,” American Journal of Jurisprudence , 42: 97–134.
- –––, 2008, “Marriage: A Basic and Exigent Good,” The Monist , 91(3–4): 388–406.
- Firestone, Shulamith, 1970, The Dialectic of Sex: The Case for Feminist Revolution , New York: William Morrow and Co.
- Galston, William, 1991, Liberal Purposes , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Garrett, Jeremy, 2008, “History, Tradition, and the Normative Foundations of Civil Marriage,” The Monist , 91(3–4): 446–474.
- –––, 2008, “Why the Old Sexual Morality of the New Natural Law Undermines Traditional Marriage,” Social Theory and Practice , 34(4): 591–622.
- –––, 2009, “A Prima Facie Case Against Civil Marriage,” Southwest Philosophy Review , 25(1): 41–53.
- George, Robert P., 2000, “‘Same-Sex Marriage’ and ‘Moral Neutrality’,” in Homosexuality and American Public Life , Christopher Wolfe (ed.), Dallas: Spence Publishing Company, pp. 141–153.
- Gheaus, Anca, 2016, “The (Dis)value of Commitment to One’s Spouse,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 204–224.
- Girgis, Sherif, Robert P. George, and Ryan T. Anderson, 2010, “What is Marriage?” Harvard Journal of Law and Public Policy , 34(1): 245–288.
- Goldstein, Joshua D., 2011, “New Natural Law Theory and the Grounds of Marriage,” Social Theory and Practice , 37 (3): 461–482.
- Grisez, Germain, 1993, The Way of the Lord Jesus , vol. 2 Living a Christian Life , Quincy, IL: Franciscan Press.
- Halwani, Raja, 2003, Virtuous Liaisons , Peru, IL: Open Court.
- Hartley, Christie, and Watson, Lori, 2012, “Political Liberalism, Marriage and the Family,” Law and Philosophy , 31(2): 185–212.
- Herman, Barbara, 1993, “Could it be worth thinking about Kant on sex and marriage?,” in A Mind of One’s Own , Louise Antony and Charlotte Witt (eds.), Oxford: Westview Press, pp. 49–67.
- Houlgate, Laurence, 2005, Children’s Rights, State Intervention, Custody and Divorce: Contradictions in Ethics and Family Law , Lewiston, NY: The Mellen Press.
- Johnson, Rebekah, 2013, “Marriage and the Metaphysics of Bodily Union,” Social Theory and Practice , 39(2): 288–312.
- Jordan, Jeff, 1995, “Is It Wrong to Discriminate on the Basis of Homosexuality?,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 26(1): 39–52.
- Kleingeld, Pauline, 1998, “Just Love? Marriage and the Question of Justice,” Social Theory and Practice , 24(2): 261–281.
- Kronqvist, Camilla, 2011, “The Promise That Love Will Last,” Inquiry , 54(6): 650–668.
- Kymlicka, Will, 1991,“Rethinking the Family,” Philosophy and Public Affairs , 20(1): 77–97.
- Landau, Iddo, 2004, “An Argument for Marriage,” Philosophy , 79: 475–481.
- –––, 2012, “Should Marital Relations be Non-Hierarchical?,” Ratio , 25(1): 51–67.
- Lee, Patrick, 2008, “Marriage, Procreation, and Same-Sex Unions,” The Monist , 91(3–4): 422–438.
- Li, Xiaorong, 1995, “Gender Inequality in China and Cultural Relativism,” in Women, Culture and Development: A Study of Human Capabilities , Martha Nussbaum and Jonathan Glovers (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 407–425.
- Macedo, Stephen, 1995, “Homosexuality and the Conservative Mind,” Georgetown Law Review , 84: 261–300.
- –––, 2015, Just Married: Same-Sex Couples, Monogamy & the Future of Marriage , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Mahoney, Jon, 2008, “Liberalism and the Polygamy Question,” Social Philosophy Today , 23: 161–174.
- Manning, W., Fettro, M., and Lamidi, E., 2014, “Child Well-Being in Same-Sex Parent Families: Review of Research Prepared for the American Sociological Association Amicus Brief,” Population Research & Policy Review , 33(4): 485–502.
- March, Andrew F., 2010, “What Lies Beyond Same-Sex Marriage? Marriage, Reproductive Freedom and Future Persons in Liberal Public Justification,” Journal of Applied Philosophy , 27(1): 39–58.
- March, Andrew F., 2011, “Is There a Right to Polygamy? Marriage, Equality, and Subsidizing Families in Liberal Political Justification,” Journal of Moral Philosophy , 8: 246–272.
- Marquis, Don, 2005, “What’s Wrong with Adultery?,” in What’s Wrong? , Graham Oddie and David Boonin (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 231–238.
- Martin, Mike W., 1993, “Love’s Constancy,” Philosophy , 68(263): 63–77.
- –––, 1994, “Adultery and Fidelity,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 25(3): 76–91.
- May, Simon, 2016, “Liberal Neutrality and Civil Marriage,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 9–28.
- Mayo, David J. and Gunderson, Martin, 2000, “The Right to Same-Sex Marriage: A Critique of the Leftist Critique,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 31(3): 326–337.
- McClain, Linda C., 2013, “The Other Marriage Equality Problem,” Boston University Law Review , 93(3): 921–970.
- McMurtry, John, 1972, “Monogamy: A Critique,” The Monist , 56: 587–99.
- Mendus, Susan, 1984, “Marital Faithfulness,” Philosophy , 59: 243–252.
- Mercier, Adèle, 2001, Affidavit , Ontario Superior Court of Justice (Divisional Court), Between Halpern al. (Applicants) and Canada (Attorney General ) et al. (Respondents), Court file 30/2001, 30/2001, Nov. [ available online ]
- Metz, Tamara, 2010, Untying the Knot: Marriage, the State, and the Case for their Divorce , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Mohr, Richard D., 2005, The Long Arc of Justice: Lesbian and Gay Marriage, Equality, and Rights , New York: Columbia University Press.
- Moller, Dan, 2003, “An Argument Against Marriage,” Philosophy , 78(1): 79–91.
- Morse, Jennifer Roback, 2006, “Why Unilateral Divorce Has No Place in a Free Society,” in The Meaning of Marriage , Robert P. George and Jean Bethke Elshtain (eds.), Dallas: Spence Publishing Co, pp. 74–99.
- Moses, Julia (ed.), 2018, Marriage, Law and Modernity: Global Histories , New York: Bloomsbury.
- Murphy, Timothy F., 2011, “Same-Sex Marriage: Not a Threat to Marriage or Children,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 42(3): 288–304.
- Narayan, Uma, 1995, “‘Male-Order’ Brides: Immigrant Women, Domestic Violence and Immigration Law,” Hypatia , 10(1): 104–119.
- –––, 1997, Dislocating Cultures: Identities, Traditions, and Third-World Feminism , Routledge: New York.
- Nolan, Daniel, 2016, “Temporary Marriage,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 180–203.
- –––, forthcoming, “Marriage and its Limits,” Inquiry .
- Nussbaum Martha, 1999, Sex and Social Justice , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Okin, Susan Moller, 1979, Women in Western Political Thought , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- –––, 1989, Justice, Gender, and the Family , New York: Basic Books.
- –––, 1994, “Political Liberalism , Justice, and Gender ,” Ethics , 105(1): 23–43.
- Papadaki, Lina, 2010, “Kantian Marriage and Beyond: Why It Is Worth Thinking About Kant on Marriage,” Hypatia , 25 (2): 276–294.
- Parsons, Kate, 2008, “Subverting the Fellowship of the Wedding Ring,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 39(3): 393–410.
- Pateman, Carole, 1988, The Sexual Contract , Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Posner, Richard, and Silbaugh, Katharine, 1996, A Guide to America’s Sex Laws , Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
- Rajczi, Alex, 2008, “A Populist Argument for Same-Sex Marriage,” The Monist , 91(3–4): 475–505.
- Rawls, John, 1997, “The Idea of Public Reason Revisited,” The University of Chicago Law Review , 64(3): 765–807.
- Raz, Joseph, 1986, The Morality of Freedom , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Robson, Ruthann, 2007, “A Mere Switch or a Fundamental Change? Theorizing Transgender Marriage,” Hypatia , 22 (1): 58–70.
- Sandel, Michael, 1982, Liberalism and the Limits of Justice , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Savulescu, Julian, and Sandberg, Anders, 2008, “Neuroenhancement of Love and Marriage: The Chemicals Between Us,” Neuroethics , 1: 31–44.
- Schaff, Kory, 2004, “Equal Protection and Same-Sex Marriage,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 35(1): 133–147.
- Scruton, Roger, 1986, Sexual Desire , London: The Free Press.
- Shanley, Mary Lyndon, et al ., 2004, Just Marriage , Oxford: Oxford University Press (includes title essay by Shanley and short replies by 13 others).
- Shrage, Laurie, 2013, “Reforming Marriage: A Comparative Approach,” Journal of Applied Philosophy , 30(2): 107–121.
- –––, 2016, “Polygamy, Privacy, and Equality,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 160–179.
- –––, 2018, “Decoupling Marriage and Parenting,” Journal of Applied Philosophy , 35(3): 496–512.
- Sommers, Christina Hoff, 1989, “Philosophers Against the Family,” in Person to Person , George Graham and Hugh LaFollete (eds.), Philadelphia: Temple University Press, pp. 82–105.
- Steinbock, Bonnie, 1986, “Adultery,” QQ: Report from the Center for Philosophy and Public Policy , 6(1): 12–14.
- Sticker, Martin, 2020, “The Case against Different-Sex Marriage in Kant,” Kantian Review , 25(3): 441–464.
- Stivers, Andrew, and Valls, Andrew, 2007, “Same-sex marriage and the regulation of language,” Politics, Philosophy and Economics , 6(2): 237–253.
- Strauss, Gregg, 2012, “Is Polygamy Inherently Unequal?,” Ethics , 122(3): 516–544.
- Sunstein, Cass, and Thaler, Richard, 2008, “Privatizing Marriage,” The Monist , 91(3–4): 377–387.
- Tjaden, Patricia, and Thoennes, Nancy, 2000, “Full Report of the Prevalence, Incidence, and Consequences of Violence Against Women,” Findings from the National Violence Against Women Survey, published by the U. S. Department of Justice, NCJ 183781.
- Toop, Alison, 2019, “Is Marriage Incompatible with Political Liberalism,” Journal of Moral Philosophy , 16(3): 302–326.
- Tuana, Nancy, 2004, “Coming to Understand: Orgasm and the Epistemology of Ignorance,” Hypatia , 19(1): 194–232.
- Vanderheiden, Steve, 1999, “Why the State Should Stay Out of the Wedding Chapel,” Public Affairs Quarterly , 13(2): 175–190.
- Waldron, Jeremy, 1988, “When Justice Replaces Affection: The Need for Rights,” Harvard Journal of Law and Public Policy , 11(3): 625–647.
- –––, 1988–89, “Autonomy and Perfectionism in Raz’s Morality of Freedom ,” Southern California Law Review , 62: 1097–1152.
- Walker, Greg, 2015, “Public Reason Liberalism and Sex-Neutral Marriage A Response to Francis J. Beckwith,” Ratio Juris , 28(4): 486–503.
- Wallenstein, Peter, 2002, Tell the Court I Love My Wife: Race, Marriage, and Law—An American History , New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Wasserstrom, Richard, 1974, “Is Adultery Immoral?,” in Philosophical Forum , 5: 513–528.
- Wedgwood, Ralph, 1999, “The Fundamental Argument for Same-Sex Marriage,” The Journal of Political Philosophy , 7(3): 225–242.
- –––, 2016, “Is Civil Marriage Illiberal?,” in After Marriage: Rethinking Marital Relationships , E. Brake (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 29–50.
- Weitzman, Lenore, 1981, The Marriage Contract , New York: Macmillan.
- Wellington, Adrian Alex, 1995, “Why Liberals Should Support Same Sex Marriage,” Journal of Social Philosophy , 26(3): 5–32.
- Williams, Reginald, 2011, “Same-Sex Marriage and Equality,” Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 14(5): 589–595.
- Wilson, John, 1989, “Can One Promise to Love Another?,” Philosophy , 64: 557–63.
- Young, Iris Marion, 1995, “Mothers, Citizenship, and Independence: A Critique of Pure Family Values,” Ethics , 105: 535–556.
The following works were first published prior to 1950.
- Abelard and Heloise, 2003, The Letters of Abelard and Heloise , Betty Radice (trans.), M. T. Clanchy (rev.), London: Penguin, revised edition.
- Aquinas, Thomas, 1981, Summa Theologiae , English Dominicans (trans.), New York: Christian Classics (reprint of London: Burns, Oates, and Washbourne 1912–36).
- Aristotle, 1984, The Complete Works of Aristotle: The Revised Oxford Translation , Jonathan Barnes (ed.), Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Astell, Mary, 1700, “Reflections upon Marriage,” in Political Writings , Patricia Springborg (ed.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996, pp. 1–80.
- Augustine, 1999, Marriage and Virginity: The Excellence of Marriage, Holy Virginity, The Excellence of Widowhood, Adulterous Marriages, Continence , vol. I/9, Ray Kearney (trans), David Hunter (ed.), John E. Rotelle (series ed.), Hyde Park, New York: New City Press.
- Augustine, 1998, Answer to the Pelagians, II: Marriage and Desire, Answer to the Two Letters of the Pelagians, Answer to Julian , vol. I/24, Roland J. Teske (trans.), John E. Rotelle (series ed.), Hyde Park, New York: New City Press.
- de Beauvoir, Simone, 1949, Le Deuxième sexe , Paris: Gallimard. Translated as The Second Sex , H. M. Parshley (trans.), New York: Vintage, 1972. [Page references to 1989 edition.]
- Engels, Friedrich, 1884 [1972], The Origin of the Family, Private Property, and the State , Eleanor Burke Leacock (ed.), New York: International.
- Hegel, G. W. F., 1995, Elements of the Philosophy of Right , Allen W. Wood (ed.), H. B. Nisbet (trans.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Hobbes, Thomas, 1962, Leviathan , Michael Oakeshott (ed.), New York: Simon and Schuster.
- Kant, Immanuel, 1785 [1991], The Metaphysics of Morals , Mary Gregor (trans.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 1798 [2006], Anthropology from a Pragmatic Point of View , Robert B. Louden (trans., ed.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Kierkegaard, Søren, 1987, Either/Or , 2 vols., Howard V. Hong and Edna H. Hong (trans.), Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Locke, John, 1988, Two Treatises of Government , Peter Laslett (ed.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Mill, John Stuart, 1988, The Subjection of Women , Susan Moller Okin (ed.), Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing Company.
- Marx, Karl, 1848, The Communist Manifesto , in Selected Writings , Lawrence Simon (ed.), Indianapolis: Hackett, 1994, pp. 157–186.
- Plato, 1997, Complete Works , John Cooper (ed.), D. S. Hutchinson (assoc. ed.), Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing Co.
- Rousseau, Jean-Jacques, 1762 [1993], Émile , Barbara Foxley (trans.), P. D. Jimack (intro.), London: J. M. Dent.
- Russell, Bertrand, 1929, Marriage and Morals , New York: Horace Liveright.
- Wollstonecraft, Mary, 1792 [1997], The Vindications: The Rights of Men, The Rights of Woman , D.L. Macdonald and Kathleen Scherf (eds.), Peterborough, ON.: Broadview.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Alternatives to Marriage Project
- 1997 General Accounting Office Report on marriage in U.S. Federal Law
love | Aquinas, Thomas: moral, political, and legal philosophy | Aristotle, General Topics: ethics | Augustine, Saint | Beauvoir, Simone de | civil rights | ethics: natural law tradition | feminist philosophy, interventions: liberal feminism | feminist philosophy, interventions: philosophy of biology | feminist philosophy, interventions: philosophy of law | feminist philosophy, topics: perspectives on reproduction and the family | feminist philosophy, topics: perspectives on trans issues | Hegel, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich: social and political philosophy | homosexuality | Kant, Immanuel: social and political philosophy | Mill, John Stuart: moral and political philosophy | obligations: special | parenthood and procreation | personal relationship goods | Plato: ethics and politics in The Republic | Russell, Bertrand: moral philosophy | sex and sexuality | social institutions | Wollstonecraft, Mary
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Eric Cave, Laurence Houlgate, Ann Levey, Mark Migotti, and Nicole Wyatt for their very helpful comments on drafts of this entry. Thanks also to Tina Strasbourg and Patricia Thornton for research assistance.
Copyright © 2021 by Elizabeth Brake < elizabeth . brake @ rice . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
14.1 What Is Marriage? What Is a Family?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you should be able to:
- Describe society’s current understanding of family
- Recognize changes in marriage and family patterns
- Differentiate between lines of descent and residence
Marriage and family are key structures in many societies. Many of us learn from a young age that finding and joining the right person is a key to happiness and security. We’re told that children need two parents. Many of the tax laws, medical laws, retirement benefit laws, and banking and loan processes seem to favor or assume marriage. Should those assumptions be changed? Is marriage still the foundation of the family and our society?
In 1960, 66 percent of households in America were headed by a married couple. That meant that most children grew up in such households, as did their friends and extended families. Marriage could certainly be seen as the foundation of the culture. By 2010, that number of households headed by married couples had dropped to 45 percent (Luscombe 2014). The approximately 20 percent drop is more than just a statistic; it has significant practical effects. It means that nearly every child in most parts of America is either in or is close to a family that is not headed by a married couple. It means that teachers and counselors and even people who meet children in a restaurant can’t assume they live with two married parents. Some view this decline as a problem with outcomes related to values, crime, financial strength, and mental health. Sociologists may study that viewpoint to determine if it is actually true.
What is marriage? Not even sociologists are able to agree on a single meaning. For our purposes, we’ll define marriage as a legally recognized social contract between two people, traditionally based on a sexual relationship and implying a permanence of the union. In practicing cultural relativism, we should also consider variations, such as whether a legal union is required, whether more than two people can be involved, or whether the marriage is a religious one or a civil one.
Sociologists are interested in the relationship between the institution of marriage and the institution of family because, historically, marriages are what create a family, and families are the most basic social unit upon which society is built. Both marriage and family create status roles that are sanctioned by society.
The question of what constitutes a family may be an even more difficult one to answer; it’s a prime area of debate in family sociology, as well as in politics and religion. Social conservatives tend to define the family in terms of structure with each family member filling a certain role (like father, mother, or child). Sociologists, on the other hand, tend to define family more in terms of the manner in which members relate to one another than on a strict configuration of status roles. Here, we’ll define family as a socially recognized group (usually joined by blood, marriage, cohabitation, or adoption) that forms an emotional connection and serves as an economic unit of society. Sociologists identify different types of families based on how one enters into them. A family of orientation refers to the family into which a person is born. A family of procreation describes one that is formed through marriage. These distinctions have cultural significance related to issues of lineage.
Drawing on two sociological paradigms, the sociological understanding of what constitutes a family can be explained by symbolic interactionism as well as functionalism. These two theories indicate that families are groups in which participants view themselves as family members and act accordingly. In other words, families are groups in which people come together to form a strong primary group connection and maintain emotional ties to one another over a long period of time. Such families may include groups of close friends or teammates. In addition, the functionalist perspective views families as groups that perform vital roles for society—both internally (for the family itself) and externally (for society as a whole). Families provide for one another’s physical, emotional, and social well-being. Parents care for and socialize children. Later in life, adult children often care for elderly parents. While interactionism helps us understand the subjective experience of belonging to a “family,” functionalism illuminates the many purposes of families and their roles in the maintenance of a balanced society (Parsons and Bales 1956). We will go into more detail about how these theories apply to family in the following pages.
Challenges Families Face
People in the United States as a whole are somewhat divided when it comes to determining what does and what does not constitute a family. In a 2010 survey conducted by professors at the University of Indiana, nearly all participants (99.8 percent) agreed that a husband, wife, and children constitute a family. Ninety-two percent stated that a husband and a wife without children still constitute a family. The numbers drop for less traditional structures: unmarried couples with children (83 percent), unmarried couples without children (39.6 percent), gay male couples with children (64 percent), and gay male couples without children (33 percent) (Powell et al. 2010). This survey revealed that children tend to be the key indicator in establishing “family” status: the percentage of individuals who agreed that unmarried couples and gay couples constitute a family nearly doubled when children were added.
The study also revealed that 60 percent of U.S. respondents agreed that if you consider yourself a family, you are a family (a concept that reinforces an interactionist perspective) (Powell 2010). The government, however, is not so flexible in its definition of “family.” The U.S. Census Bureau defines a family as “a group of two people or more (one of whom is the householder) related by birth, marriage, or adoption and residing together” (U.S. Census Bureau 2010). While this structured definition can be used as a means to consistently track family-related patterns over several years, it excludes individuals such as cohabitating unmarried couples. Legality aside, sociologists would argue that the general concept of family is more diverse and less structured than in years past. Society has given more leeway to the design of a family making room for what works for its members (Jayson 2010).
Family is, indeed, a subjective concept, but it is a fairly objective fact that family (whatever one’s concept of it may be) is very important to people in the United States. In a 2010 survey by Pew Research Center in Washington, DC, 76 percent of adults surveyed stated that family is “the most important” element of their life—just one percent said it was “not important” (Pew Research Center 2010). It is also very important to society. President Ronald Reagan notably stated, “The family has always been the cornerstone of American society. Our families nurture, preserve, and pass on to each succeeding generation the values we share and cherish, values that are the foundation of our freedoms” (Lee 2009). While the design of the family may have changed in recent years, the fundamentals of emotional closeness and support are still present. Most responders to the Pew survey stated that their family today is at least as close (45 percent) or closer (40 percent) than the family with which they grew up (Pew Research Center 2010).
As you may have seen in the chapter on Aging and the Elderly, different generations have varying living situations and views on aging. The same goes for living situations with family. The Pew Research Center analyzed living situation of 40-year-olds from different generations. At that age, Millennials indicated that 45 percent of them were not living in a family of their own. In contrast, when Gen Xers and Baby Boomers were about 40 years old (around 2003 and 1987, respectively), an average of 33 percent of them lived outside of a family (Barroso 2020). The dynamic of nearly a 50-50 split between family/non-family for Millennials is very different from a two-third/one third split of Boomers and Gen X.
The data also show that women are having children later in life and that men are much less likely to live in a household with their own children. In 2019, 32 percent of Millennial men were living in a household with their children, compared to 41 percent of Gen X men in 2003 and 44 percent of Boomer men in 1987 (Barroso 2020). Again, the significant drop off in parenting roles likely has an impact on attitudes toward family.
Alongside the debate surrounding what constitutes a family is the question of what people in the United States believe constitutes a marriage. Many religious and social conservatives believe that marriage can only exist between a man and a woman, citing religious scripture and the basics of human reproduction as support. Social liberals and progressives, on the other hand, believe that marriage can exist between two consenting adults—be they a man and a woman, or a woman and a woman—and that it would be discriminatory to deny such a couple the civil, social, and economic benefits of marriage.
Marriage Patterns
With single parenting and cohabitation (when a couple shares a residence but not a marriage) becoming more acceptable in recent years, people may be less motivated to get married. In a recent survey, 39 percent of respondents answered “yes” when asked whether marriage is becoming obsolete (Pew Research Center 2010). The institution of marriage is likely to continue, but some previous patterns of marriage will become outdated as new patterns emerge. In this context, cohabitation contributes to the phenomenon of people getting married for the first time at a later age than was typical in earlier generations (Glezer 1991). Furthermore, marriage will continue to be delayed as more people place education and career ahead of “settling down.”
One Partner or Many?
People in the United States typically equate marriage with monogamy , when someone is married to only one person at a time. In many countries and cultures around the world, however, having one spouse is not the only form of accepted marriage, even if it is the most common. Polygamy , or being married to more than one person at a time, is accepted to varying degrees around the world, with most polygamous societies existing in northern Africa and east Asia (OECD 2019). Instances of polygamy are almost exclusively in the form of a man being married to more than one woman at the same time, rather than a woman being married to more than one man (Altman and Ginat 1996).
While the majority of societies accept polygamy, the majority of people do not practice it. Even in the regions where it is most common, only an average of 11 percent of the population lives in arrangements that include more than one spouse (Kramer 2020). In these relationships, the husbands are often older, wealthy, high-status men (Altman and Ginat 1996). The average plural marriage involves no more than three wives. Negev Bedouin men in Israel, for example, typically have two wives, although it is acceptable to have up to four (Griver 2008). As urbanization increases in these cultures, polygamy is likely to decrease as a result of greater access to mass media, technology, and education (Altman and Ginat 1996).
In the United States, polygamy is illegal. A recent Gallup poll showed that 21 percent of people believe polygamy is morally acceptable, which is a major increase since earlier versions of the same poll. But the poll also found that polygamy was among the least acceptable behaviors considered in the study; for example, polygamy was far less acceptable than consensual sex between teenagers, though it was more acceptable than a married person having an affair (Brenan 2020). The act of entering into marriage while still married to another person is referred to as bigamy and is considered a felony in most states.
Residency and Lines of Descent
When considering one’s lineage, most people in the United States look to both their father’s and mother’s sides. Both paternal and maternal ancestors are considered part of one’s family. This pattern of tracing kinship is called bilateral descent . Note that kinship , or one’s traceable ancestry, can be based on blood or marriage or adoption. Sixty percent of societies, mostly modernized nations, follow a bilateral descent pattern. Unilateral descent (the tracing of kinship through one parent only) is practiced in the other 40 percent of the world’s societies, with high concentration in pastoral cultures (O’Neal 2006).
There are three types of unilateral descent: patrilineal , which follows the father’s line only; matrilineal , which follows the mother’s side only; and ambilineal , which follows either the father’s only or the mother’s side only, depending on the situation. In patrilineal societies, such as those in rural China and India, only males carry on the family surname. This gives males the prestige of permanent family membership while females are seen as only temporary members (Harrell 2001). U.S. society assumes some aspects of patrilineal decent. For instance, most children assume their father’s last name even if the mother retains her birth name.
In matrilineal societies, inheritance and family ties are traced to women. Matrilineal descent is common in Native American societies, notably the Crow and Cherokee tribes. In these societies, children are seen as belonging to the women and, therefore, one’s kinship is traced to one’s mother, grandmother, great grandmother, and so on (Mails 1996). In ambilineal societies, which are most common in Southeast Asian countries, parents may choose to associate their children with the kinship of either the mother or the father. This choice may be based on the desire to follow stronger or more prestigious kinship lines or on cultural customs such as men following their father’s side and women following their mother’s side (Lambert 2009).
Tracing one’s line of descent to one parent rather than the other can be relevant to the issue of residence. In many cultures, newly married couples move in with, or near to, family members. In a patrilocal residence system it is customary for the wife to live with (or near) her husband’s blood relatives (or family of orientation). Patrilocal systems can be traced back thousands of years. In a DNA analysis of 4,600-year-old bones found in Germany, scientists found indicators of patrilocal living arrangements (Haak et al 2008). Patrilocal residence is thought to be disadvantageous to women because it makes them outsiders in the home and community; it also keeps them disconnected from their own blood relatives. In China, where patrilocal and patrilineal customs are common, the written symbols for maternal grandmother ( wáipá ) are separately translated to mean “outsider” and “women” (Cohen 2011).
Similarly, in matrilocal residence systems, where it is customary for the husband to live with his wife’s blood relatives (or her family of orientation), the husband can feel disconnected and can be labeled as an outsider. The Minangkabau people, a matrilocal society that is indigenous to the highlands of West Sumatra in Indonesia, believe that home is the place of women and they give men little power in issues relating to the home or family (Joseph and Najmabadi 2003). Most societies that use patrilocal and patrilineal systems are patriarchal, but very few societies that use matrilocal and matrilineal systems are matriarchal, as family life is often considered an important part of the culture for women, regardless of their power relative to men.
Stages of Family Life
As we’ve established, the concept of family has changed greatly in recent decades. Historically, it was often thought that many families evolved through a series of predictable stages. Developmental or “stage” theories used to play a prominent role in family sociology (Strong and DeVault 1992). Today, however, these models have been criticized for their linear and conventional assumptions as well as for their failure to capture the diversity of family forms. While reviewing some of these once-popular theories, it is important to identify their strengths and weaknesses.
The set of predictable steps and patterns families experience over time is referred to as the family life cycle . One of the first designs of the family life cycle was developed by Paul Glick in 1955. In Glick’s original design, he asserted that most people will grow up, establish families, rear and launch their children, experience an “empty nest” period, and come to the end of their lives. This cycle will then continue with each subsequent generation (Glick 1989). Glick’s colleague, Evelyn Duvall, elaborated on the family life cycle by developing these classic stages of family (Strong and DeVault 1992):
The family life cycle was used to explain the different processes that occur in families over time. Sociologists view each stage as having its own structure with different challenges, achievements, and accomplishments that transition the family from one stage to the next. For example, the problems and challenges that a family experiences in Stage 1 as a married couple with no children are likely much different than those experienced in Stage 5 as a married couple with teenagers. The success of a family can be measured by how well they adapt to these challenges and transition into each stage. While sociologists use the family life cycle to study the dynamics of family over time, consumer and marketing researchers have used it to determine what goods and services families need as they progress through each stage (Murphy and Staples 1979).
As early “stage” theories have been criticized for generalizing family life and not accounting for differences in gender, ethnicity, culture, and lifestyle, less rigid models of the family life cycle have been developed. One example is the family life course , which recognizes the events that occur in the lives of families but views them as parting terms of a fluid course rather than in consecutive stages (Strong and DeVault 1992). This type of model accounts for changes in family development, such as the fact that in today’s society, childbearing does not always occur with marriage. It also sheds light on other shifts in the way family life is practiced. Society’s modern understanding of family rejects rigid “stage” theories and is more accepting of new, fluid models.
Sociology in the Real World
The evolution of television families.
Whether you grew up watching the Huxtables, the Simpsons, the Kardashians, or the Johnsons, most of the drama or comedy you saw involved the relationships, tensions, challenges, and sometimes ridiculousness of family life. You may have also seen a great deal of change. The 1960s was the height of the suburban U.S. nuclear family on television with shows such as The Donna Reed Show and Father Knows Best . While some shows of this era portrayed single parents ( My Three Sons and Bonanza , for instance), the single status almost always resulted from being widowed—not divorced or unwed.
Although family dynamics in real U.S. homes were changing, the expectations for families portrayed on television were not. The United States’ first reality show, An American Family aired on PBS in 1973. The show chronicled Bill and Pat Loud and their children. During the series, the oldest son, Lance, announced to the family that he was gay, and at the series’ conclusion, Bill and Pat decided to divorce. Although the Loud’s union was among the 30 percent of marriages that ended in divorce in 1973, the family was featured on the cover of the March 12 issue of Newsweek with the title “The Broken Family” (Ruoff 2002).
Less traditional family structures in sitcoms gained popularity in the 1980s with shows such as Diff’rent Strokes (a widowed man with two adopted African American sons) and One Day at a Time (a divorced woman with two teenage daughters). Still, traditional families such as those in Family Ties and The Cosby Show dominated the ratings. The late 1980s and the 1990s saw the introduction of the dysfunctional family. Shows such as Roseanne , Married with Children , and The Simpsons portrayed traditional nuclear families, but in a much less flattering light than those from the 1960s did (Museum of Broadcast Communications 2011).
In the early 2000s, the nontraditional family has become somewhat of a tradition in television. While many situation comedies focus on single men and women without children, those that do portray families often stray from the classic structure: they include unmarried and divorced parents, adopted children, gay or lesbian couples, and multigenerational households.
In 2009, ABC emphasized the changes in family dynamics with their choice of title for Modern Family . The show follows an extended family—which is a household that includes at least one parent and child as well as other relatives like grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins—that consists of a divorced and remarried father with one stepchild and his biological adult children, one of whom is in a traditional two-parent household and the other who is a gay man in a committed relationship raising an adopted daughter. Black-ish , which portrays an extended family of African Americans, has at many times dealt with the issue implied by its name: That sometimes what it means to be Black can bring issues of interpretation conflict, especially across generations. For example, the children of the central family have shown interest in “blending in” with their White friends, which brings negative reactions from their grandparents.
Other shows, such as Shameless , interweave family diversity with complex and painful issues such as addiction. The series has a large cast of characters representing different groups, and central to the series are the roles of children, rather than parents, as family leaders. “The families on shows like this one aren’t as idealistic, but they remain relatable,” states television critic Maureen Ryan. “The most successful shows, comedies especially, have families that you can look at and see parts of your family in them” (Respers France 2010).
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Tonja R. Conerly, Kathleen Holmes, Asha Lal Tamang
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Sociology 3e
- Publication date: Jun 3, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/14-1-what-is-marriage-what-is-a-family
© Jan 18, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Election Integrity
- Immigration
Political Thought
- American History
- Conservatism
- Progressivism
International
- Global Politics
- Middle East
Government Spending
- Budget and Spending
Energy & Environment
- Environment
Legal and Judicial
- Crime and Justice
- Second Amendment
- The Constitution
National Security
- Cybersecurity
Domestic Policy
- Government Regulation
- Health Care Reform
Marriage and Family
- Religious Liberty
- International Economies
- Markets and Finance
Marriage: What It Is, Why It Matters, and the Consequences of Redefining It

Key Takeaways
Marriage exists to bring a man and a woman together as husband and wife to be father and mother to any children their union produces.
Government can treat people equally and respect their liberty without redefining marriage.
Redefining marriage would further distance marriage from the needs of children and deny the importance of mothers and fathers.
Select a Section 1 /0
At the heart of the current debates about same-sex marriage are three crucial questions: What is marriage, why does marriage matter for public policy, and what would be the consequences of redefining marriage to exclude sexual complementarity?
Marriage exists to bring a man and a woman together as husband and wife to be father and mother to any children their union produces. It is based on the anthropological truth that men and women are different and complementary, the biological fact that reproduction depends on a man and a woman, and the social reality that children need both a mother and a father. Marriage predates government. It is the fundamental building block of all human civilization. Marriage has public purposes that transcend its private purposes. This is why 41 states, with good reason, affirm that marriage is between a man and a woman.
Government recognizes marriage because it is an institution that benefits society in a way that no other relationship does. Marriage is society’s least restrictive means of ensuring the well-being of children. State recognition of marriage protects children by encouraging men and women to commit to each other and take responsibility for their children. While respecting everyone’s liberty, government rightly recognizes, protects, and promotes marriage as the ideal institution for childbearing and childrearing.
Promoting marriage does not ban any type of relationship: Adults are free to make choices about their relationships, and they do not need government sanction or license to do so. All Americans have the freedom to live as they choose, but no one has a right to redefine marriage for everyone else.
In recent decades, marriage has been weakened by a revisionist view that is more about adults’ desires than children’s needs. This reduces marriage to a system to approve emotional bonds or distribute legal privileges.
Redefining marriage to include same-sex relationships is the culmination of this revisionism, and it would leave emotional intensity as the only thing that sets marriage apart from other bonds. Redefining marriage would further distance marriage from the needs of children and would deny, as a matter of policy, the ideal that a child needs both a mom and a dad. Decades of social science, including the latest studies using large samples and robust research methods, show that children tend to do best when raised by a mother and a father. The confusion resulting from further delinking childbearing from marriage would force the state to intervene more often in family life and expand welfare programs. Redefining marriage would legislate a new principle that marriage is whatever emotional bond the government says it is.
Redefining marriage does not simply expand the existing understanding of marriage. It rejects the anthropological truth that marriage is based on the complementarity of man and woman, the biological fact that reproduction depends on a man and a woman, and the social reality that children need a mother and a father. Redefining marriage to abandon the norm of male–female sexual complementarity would also make other essential characteristics—such as monogamy, exclusivity, and permanency—optional. Marriage cannot do the work that society needs it to do if these norms are further weakened.
Redefining marriage is also a direct and demonstrable threat to religious freedom because it marginalizes those who affirm marriage as the union of a man and a woman. This is already evident in Massachusetts and Washington, D.C., among other locations.
Concern for the common good requires protecting and strengthening the marriage culture by promoting the truth about marriage.
What Is Marriage?
At its most basic level, marriage is about attaching a man and a woman to each other as husband and wife to be father and mother to any children their sexual union produces. When a baby is born, there is always a mother nearby: That is a fact of reproductive biology. The question is whether a father will be involved in the life of that child and, if so, for how long. Marriage increases the odds that a man will be committed to both the children that he helps create and to the woman with whom he does so.
Marriage connects people and goods that otherwise tend to fragment. It helps to connect sex with love, men with women, sex with babies, and babies with moms and dads. [1] Social, cultural, and legal signals and pressures can support or detract from the role of marriage in this regard.
Maggie Gallagher captures this insight with a pithy phrase: “[S]ex makes babies, society needs babies, and children need mothers and fathers.” [2] Connecting sex, babies, and moms and dads is the social function of marriage and helps explain why the government rightly recognizes and addresses this aspect of our social lives. Gallagher develops this idea:
The critical public or “civil” task of marriage is to regulate sexual relationships between men and women in order to reduce the likelihood that children (and their mothers, and society) will face the burdens of fatherlessness, and increase the likelihood that there will be a next generation that will be raised by their mothers and fathers in one family, where both parents are committed to each other and to their children. [3]
Marriage is based on the anthropological truth that men and women are complementary, the biological fact that reproduction depends on a man and a woman, and the social reality that children need a mother and a father.
Marriage is a uniquely comprehensive union. It involves a union of hearts and minds, but also—and distinctively—a bodily union made possible by sexual complementarity. As the act by which a husband and wife make marital love also makes new life, so marriage itself is inherently extended and enriched by family life and calls for all-encompassing commitment that is permanent and exclusive. In short, marriage unites a man and a woman holistically—emotionally and bodily, in acts of conjugal love and in the children such love brings forth—for the whole of life. [4]
Just as the complementarity of a man and a woman is important for the type of union they can form, so too is it important for how they raise children. There is no such thing as “parenting.” There is mothering, and there is fathering, and children do best with both. While men and women are each capable of providing their children with a good upbringing, there are, on average, differences in the ways that mothers and fathers interact with their children and the functional roles that they play.
Dads play particularly important roles in the formation of both their sons and their daughters. As Rutgers University sociologist David Popenoe explains, “The burden of social science evidence supports the idea that gender-differentiated parenting is important for human development and that the contribution of fathers to childrearing is unique and irreplaceable.” [5] Popenoe concludes:
We should disavow the notion that “mommies can make good daddies,” just as we should disavow the popular notion…that “daddies can make good mommies.”… The two sexes are different to the core, and each is necessary—culturally and biologically—for the optimal development of a human being. [6]
Marriage as the union of man and woman is true across cultures, religions, and time. The government recognizes but does not create marriage.
Marriage is the fundamental building block of all human civilization. The government does not create marriage. Marriage is a natural institution that predates government. Society as a whole, not merely any given set of spouses, benefits from marriage. This is because marriage helps to channel procreative love into a stable institution that provides for the orderly bearing and rearing of the next generation.
This understanding of marriage as the union of man and woman is shared by the Jewish, Christian, and Muslim traditions; by ancient Greek and Roman thinkers untouched by these religions; and by various Enlightenment philosophers. It is affirmed by both common and civil law and by ancient Greek and Roman law. Far from having been intended to exclude same-sex relationships, marriage as the union of husband and wife arose in many places, over several centuries, in which same-sex marriage was nowhere on the radar. Indeed, it arose in cultures that had no concept of sexual orientation and in some that fully accepted homoeroticism and even took it for granted. [7]
As with other public policy issues, religious voices on marriage should be welcomed in the public square. Yet one need not appeal to distinctively religious arguments to understand why marriage—as a natural institution—is the union of man and woman.
Marriage has been weakened by a revisionist view of marriage that is more about adults’ desires than children’s needs.
In recent decades, marriage has been weakened by a revisionist view of marriage that is more about adults’ desires than children’s needs. This view reduces marriage primarily to emotional bonds or legal privileges. Redefining marriage represents the culmination of this revisionism and would leave emotional intensity as the only thing that sets marriage apart from other bonds.
However, if marriage were just intense emotional regard, marital norms would make no sense as a principled matter. There is no reason of principle that requires an emotional union to be permanent. Or limited to two persons. Or sexual, much less sexually exclusive (as opposed to “open”). Or inherently oriented to family life and shaped by its demands. Couples might live out these norms where temperament or taste motivated them, but there would be no reason of principle for them to do so and no basis for the law to encourage them to do so.
In other words, if sexual complementarity is optional for marriage, present only where preferred, then almost every other norm that sets marriage apart is optional. Although some supporters of same-sex marriage would disagree, this point can be established by reason and, as documented below, is increasingly confirmed by the rhetoric and arguments used in the campaign to redefine marriage and by the policies that many of its leaders increasingly embrace.
Why Marriage Matters for Policy
Government recognizes marriage because it is an institution that benefits society in a way that no other relationship does.
Virtually every political community has regulated male–female sexual relationships. This is not because government cares about romance as such. Government recognizes male–female sexual relationships because these alone produce new human beings. For highly dependent infants, there is no path to physical, moral, and cultural maturity—no path to personal responsibility—without a long and delicate process of ongoing care and supervision to which mothers and fathers bring unique gifts. Unless children mature, they never will become healthy, upright, productive members of society. Marriage exists to make men and women responsible to each other and to any children that they might have.
Marriage is thus a personal relationship that serves a public purpose in a political community. As the late sociologist James Q. Wilson wrote, “Marriage is a socially arranged solution for the problem of getting people to stay together and care for children that the mere desire for children, and the sex that makes children possible, does not solve.” [8]
Marriage is society’s least restrictive means of ensuring the well-being of children. Marital breakdown weakens civil society and limited government.
Marriage is society’s least restrictive means of ensuring the well-being of children. Government recognition of marriage protects children by incentivizing men and women to commit to each other and take responsibility for their children.
Social science confirms the importance of marriage for children. According to the best available sociological evidence, children fare best on virtually every examined indicator when reared by their wedded biological parents. Studies that control for other factors, including poverty and even genetics, suggest that children reared in intact homes do best on educational achievement, emotional health, familial and sexual development, and delinquency and incarceration. [9]
A study published by the left-leaning research institution Child Trends concluded:
[I]t is not simply the presence of two parents…but the presence of two biological parents that seems to support children’s development. [10]
[R]esearch clearly demonstrates that family structure matters for children, and the family structure that helps children the most is a family headed by two biological parents in a low-conflict marriage. Children in single-parent families, children born to unmarried mothers, and children in stepfamilies or cohabiting relationships face higher risks of poor outcomes.… There is thus value for children in promoting strong, stable marriages between biological parents. [11]
According to another study, “[t]he advantage of marriage appears to exist primarily when the child is the biological offspring of both parents.” [12] Recent literature reviews conducted by the Brookings Institution, the Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs at Princeton University, the Center for Law and Social Policy, and the Institute for American Values corroborate the importance of intact households for children. [13]
These statistics have penetrated American life to such a great extent that even President Barack Obama refers to them as well known:
We know the statistics—that children who grow up without a father are five times more likely to live in poverty and commit crime; nine times more likely to drop out of schools and twenty times more likely to end up in prison. They are more likely to have behavioral problems, or run away from home, or become teenage parents themselves. And the foundations of our community are weaker because of it. [14]
Fathers matter, and marriage helps to connect fathers to mothers and children.
Social science claiming to show that there are “no differences” in outcomes for children raised in same-sex households does not change this reality. In fact, the most recent, sophisticated studies suggest that prior research is inadequate to support the assertion that it makes “no difference” whether a child was raised by same-sex parents. [15] A survey of 59 of the most prominent studies often cited for this claim shows that they drew primarily from small convenience samples that are not appropriate for generalizations to the whole population. [16]
Meanwhile, recent studies using rigorous methods and robust samples confirm that children do better when raised by a married mother and father. These include the New Family Structures Study by Professor Mark Regnerus at the University of Texas–Austin [17] and a report based on Census data recently released in the highly respected journal Demography . [18]
Still, the social science on same-sex parenting is a matter of significant ongoing debate, and it should not dictate choices about marriage. Recent studies using robust methods suggest that there is a lot more to learn about how changing family forms affects children and that social science evidence offers an insufficient basis for redefining marriage.
Marital breakdown costs taxpayers.
Marriage benefits everyone because separating childbearing and childrearing from marriage burdens innocent bystanders: not just children, but the whole community. Often, the community must step in to provide (more or less directly) for their well-being and upbringing. Thus, by encouraging the marriage norms of monogamy, sexual exclusivity, and permanence, the state is strengthening civil society and reducing its own role.
By recognizing marriage, the government supports economic well-being. The benefits of marriage led Professor W. Bradford Wilcox to summarize a study he led as part of the University of Virginia’s National Marriage Project in this way: “The core message…is that the wealth of nations depends in no small part on the health of the family.” [19] The same study suggests that marriage and fertility trends “play an underappreciated and important role in fostering long-term economic growth, the viability of the welfare state, the size and quality of the workforce, and the health of large sectors of the modern economy.” [20]
Given its economic benefits, it is no surprise that the decline of marriage most hurts the least well-off. A leading indicator of whether someone will know poverty or prosperity is whether, growing up, he or she knew the love and security of having a married mother and father. For example, a recent Heritage Foundation report by Robert Rector points out: “Being raised in a married family reduced a child’s probability of living in poverty by about 82 percent.” [21]
The erosion of marriage harms not only the immediate victims, but also society as a whole. A Brookings Institution study found that $229 billion in welfare expenditures between 1970 and 1996 can be attributed to the breakdown of the marriage culture and the resulting exacerbation of social ills: teen pregnancy, poverty, crime, drug abuse, and health problems. [1] A 2008 study found that divorce and unwed childbearing cost taxpayers $112 billion each year, [23] and Utah State University scholar David Schramm has estimated that divorce alone costs local, state, and federal-level government $33 billion each year. [24]
Civil recognition of the marriage union of a man and a woman serves the ends of limited government more effectively, less intrusively, and at less cost than does picking up the pieces from a shattered marriage culture.
Government can treat people equally—and leave them free to live and love as they choose—without redefining marriage.
While respecting everyone’s liberty, government rightly recognizes, protects, and promotes marriage as the ideal institution for childbearing and childrearing. Adults are free to make choices about their relationships without redefining marriage and do not need government sanction or license to do so.
Government is not in the business of affirming our love. Rather, it leaves consenting adults free to live and love as they choose. Contrary to what some say, there is no ban on same-sex marriage. Nothing about it is illegal. In all 50 states, two people of the same sex may choose to live together, choose to join a religious community that blesses their relationship, and choose a workplace offering joint benefits. There is nothing illegal about this.
What is at issue is whether the government will recognize such relationships as marriages—and then force every citizen, house of worship, and business to do so as well. At issue is whether policy will coerce and compel others to recognize and affirm same-sex relationships as marriages. All Americans have the freedom to live as they choose, but they do not have the right to redefine marriage for everyone else.
Appeals to “marriage equality” are good sloganeering, but they exhibit sloppy reasoning. Every law makes distinctions. Equality before the law protects citizens from arbitrary distinctions, from laws that treat them differently for no good reason . To know whether a law makes the right distinctions—whether the lines it draws are justified—one has to know the public purpose of the law and the nature of the good being advanced or protected.
If the law recognized same-sex couples as spouses, would some argue that it fails to respect the equality of citizens in multiple-partner relationships? Are those inclined to such relationships being treated unjustly when their consensual romantic bonds go unrecognized, their children thereby “stigmatized” and their tax filings unprivileged?
This is not hypothetical. In 2009, Newsweek reported that there were over 500,000 polyamorous households in America. [25] Prominent scholars and LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender) activists have called for “marriage equality” for multipartner relationships since at least 2006. [26]
If sexual complementarity is eliminated as an essential characteristic of marriage, then no principle limits civil marriage to monogamous couples.
Supporters of redefinition use the following analogy: Laws defining marriage as a union of a man and a woman are unjust—fail to treat people equally—exactly like laws that prevented interracial marriage. Yet such appeals beg the question of what is essential to marriage. They assume exactly what is in dispute: that gender is as irrelevant as race in state recognition of marriage. However, race has nothing to with marriage, and racist laws kept the races apart. Marriage has everything to do with men and women, husbands and wives, mothers and fathers and children, and that is why principle-based policy has defined marriage as the union of one man and one woman.
Marriage must be color-blind, but it cannot be gender-blind. The color of two people’s skin has nothing to do with what kind of marital bond they have. However, the sexual difference between a man and a woman is central to what marriage is. Men and women regardless of their race can unite in marriage, and children regardless of their race need moms and dads. To acknowledge such facts requires an understanding of what, at an essential level, makes a marriage.
We reap the civil society benefits of marriage only if policy gets marriage right.
The state has an interest in marriage and marital norms because they serve the public good by protecting child well-being, civil society, and limited government. Marriage laws work by embodying and promoting a true vision of marriage, which makes sense of those norms as a coherent whole. There is nothing magical about the word “marriage.” It is not just the legal title of marriage that encourages adherence to marital norms.
What does the work are the social reality of marriage and the intelligibility of its norms. These help to channel behavior. Law affects culture. Culture affects beliefs. Beliefs affect actions. The law teaches, and it will shape not just a handful of marriages, but the public understanding of what marriage is.
Government promotes marriage to make men and women responsible to each other and to any children they might have. Promoting marital norms serves these same ends. The norms of monogamy and sexual exclusivity encourage childbearing within a context that makes it most likely that children will be raised by their mother and father. These norms also help to ensure shared responsibility and commitment between spouses, provide sufficient attention from both a mother and a father to their children, and avoid the sexual and kinship jealousy that might otherwise be present.
The norm of permanency ensures that children will at least be cared for by their mother and father until they reach maturity. It also provides kinship structure for interaction across generations as elderly parents are cared for by their adult children and as grandparents help to care for their grandchildren without the complications of fragmented stepfamilies.
If the law taught a falsehood about marriage, it would make it harder for people to live out the norms of marriage because marital norms make no sense, as matters of principle, if marriage is just intense emotional feeling. No reason of principle requires an emotional union to be permanent or limited to two persons, much less sexually exclusive. Nor should it be inherently oriented to family life and shaped by its demands. This does not mean that a couple could not decide to live out these norms where temperament or taste so motivated them, just that there is no reason of principle to demand that they do so. Legally enshrining this alternate view of marriage would undermine the norms whose link to the common good is the basis for state recognition of marriage in the first place.
Insofar as society weakens the rational foundation for marriage norms, fewer people would live them out, and fewer people would reap the benefits of the marriage institution. This would affect not only spouses, but also the well-being of their children. The concern is not so much that a handful of gay or lesbian couples would be raising children, but that it would be very difficult for the law to send a message that fathers matter when it has redefined marriage to make fathers optional .
This highlights the link between the central questions in this debate: What is marriage, and why does the state promote it? It is not that the state should not achieve its basic purpose while obscuring what marriage is. Rather, it cannot . Only when policy gets the nature of marriage right can a political community reap the civil society benefits of recognizing it.
Finally, support for marriage between a man and a woman is no excuse for animus against those with same-sex attractions or for ignoring the needs of individuals who, for whatever reason, may never marry. They are no less worthy than others of concern and respect. Yet this same diligent concern for the common good requires protecting and strengthening the marriage culture by promoting the truth about marriage.
The Consequences of Redefining Marriage
Redefining marriage would further disconnect childbearing from marriage. That would hurt children, especially the most vulnerable. It would deny as a matter of policy the ideal that children need a mother and a father. Traditional marriage laws reinforce the idea that a married mother and father is the most appropriate environment for rearing children, as the best available social science suggests.
Recognizing same-sex relationships as marriages would legally abolish that ideal. It would deny the significance of both mothering and fathering to children: that boys and girls tend to benefit from fathers and mothers in different ways. Indeed, the law, public schools, and media would teach that mothers and fathers are fully interchangeable and that thinking otherwise is bigoted.
Redefining marriage would diminish the social pressures and incentives for husbands to remain with their wives and biological children and for men and women to marry before having children. Yet the resulting arrangements—parenting by single parents, divorced parents, remarried parents, cohabiting couples, and fragmented families of any kind—are demonstrably worse for children. [27] Redefining marriage would destabilize marriage in ways that are known to hurt children.
Leading LGBT advocates admit that redefining marriage changes its meaning. E. J. Graff celebrates the fact that redefining marriage would change the “institution’s message” so that it would “ever after stand for sexual choice, for cutting the link between sex and diapers.” Enacting same-sex marriage, she argues, “does more than just fit; it announces that marriage has changed shape.” [28] Andrew Sullivan says that marriage has become “primarily a way in which two adults affirm their emotional commitment to one another.” [29]
Government exists to create the conditions under which individuals and freely formed communities can thrive. The most important free community—the one on which all others depend—is the marriage-based family. The conditions for its thriving include the accommodations and pressures that marriage law provides for couples to stay together. Redefining marriage would further erode marital norms, thrusting government further into leading roles for which it is poorly suited: parent and discipliner to the orphaned; provider to the neglected; and arbiter of disputes over custody, paternity, and visitation. As the family weakened, welfare programs and correctional bureaucracies would grow.
Redefining marriage would put into the law the new principle that marriage is whatever emotional bond the government says it is.
Redefining marriage does not simply expand the existing understanding of marriage. It rejects the truth that marriage is based on the complementarity of man and woman, the biological fact that reproduction depends on a man and a woman, and the social reality that children need a mother and a father.
Redefining marriage to include same-sex relationships is not ultimately about expanding the pool of people who are eligible to marry. Redefining marriage is about cementing a new idea of marriage in the law—an idea whose baleful effects conservatives have fought for years. The idea that romantic-emotional union is all that makes a marriage cannot explain or support the stabilizing norms that make marriage fitting for family life. It can only undermine those norms.
Indeed, that undermining already has begun. Disastrous policies such as “no-fault” divorce were also motivated by the idea that a marriage is made by romantic attachment and satisfaction—and comes undone when these fade. Same-sex marriage would require a more formal and final redefinition of marriage as simple romantic companionship, obliterating the meaning that the marriage movement had sought to restore to the institution.
Redefining marriage would weaken monogamy, exclusivity, and permanency—the norms through which marriage benefits society.
Government needs to get marriage policy right because it shapes the norms associated with this most fundamental relationship. Redefining marriage would abandon the norm of male–female sexual complementarity as an essential characteristic of marriage. Making that optional would also make other essential characteristics of marriage—such as monogamy, exclusivity, and permanency—optional. [30] Weakening marital norms and severing the connection of marriage with responsible procreation are the admitted goals of many prominent advocates of redefining marriage.
The Norm of Monogamy. New York University Professor Judith Stacey has expressed hope that redefining marriage would give marriage “varied, creative, and adaptive contours,” leading some to “question the dyadic limitations of Western marriage and seek…small group marriages.” [31] In their statement “Beyond Same-Sex Marriage,” more than 300 “LGBT and allied” scholars and advocates call for legally recognizing sexual relationships involving more than two partners. [32]
University of Calgary Professor Elizabeth Brake thinks that justice requires using legal recognition to “denormalize[] heterosexual monogamy as a way of life” and “rectif[y] past discrimination against homosexuals, bisexuals, polygamists, and care networks.” She supports “minimal marriage,” in which “individuals can have legal marital relationships with more than one person, reciprocally or asymmetrically, themselves determining the sex and number of parties, the type of relationship involved, and which rights and responsibilities to exchange with each.” [33]
In 2009, Newsweek reported that the United States already had over 500,000 polyamorous households. [34] The author concluded:
[P]erhaps the practice is more natural than we think: a response to the challenges of monogamous relationships, whose shortcomings…are clear. Everyone in a relationship wrestles at some point with an eternal question: can one person really satisfy every need? Polyamorists think the answer is obvious—and that it’s only a matter of time before the monogamous world sees there’s more than one way to live and love. [35]
A 2012 article in New York Magazine introduced Americans to “throuple,” a new term akin to a “couple,” but with three people whose “throuplehood is more or less a permanent domestic arrangement. The three men work together, raise dogs together, sleep together, miss one another, collect art together, travel together, bring each other glasses of water, and, in general, exemplify a modern, adult relationship. Except that there are three of them.” [36]
The Norm of Exclusivity. Andrew Sullivan, who has extolled the “spirituality” of “anonymous sex,” also thinks that the “openness” of same-sex unions could enhance the bonds of husbands and wives:
Same-sex unions often incorporate the virtues of friendship more effectively than traditional marriages; and at times, among gay male relationships, the openness of the contract makes it more likely to survive than many heterosexual bonds.… [T]here is more likely to be greater understanding of the need for extramarital outlets between two men than between a man and a woman.… [S]omething of the gay relationship’s necessary honesty, its flexibility, and its equality could undoubtedly help strengthen and inform many heterosexual bonds. [37]
“Openness” and “flexibility” are Sullivan’s euphemisms for sexual infidelity. Similarly, in a New York Times Magazine profile, gay activist Dan Savage encourages spouses to adopt “a more flexible attitude” about allowing each other to seek sex outside their marriage. The New York Times recently reported on a study finding that exclusivity was not the norm among gay partners: “‘With straight people, it’s called affairs or cheating,’ said Colleen Hoff, the study’s principal investigator, ‘but with gay people it does not have such negative connotations.’” [38]
A piece in The Advocate candidly admits where the logic of redefining marriage to include same-sex relationships leads:
Anti-equality right-wingers have long insisted that allowing gays to marry will destroy the sanctity of “traditional marriage,” and, of course, the logical, liberal party-line response has long been “No, it won’t.” But what if—for once—the sanctimonious crazies are right? Could the gay male tradition of open relationships actually alter marriage as we know it? And would that be such a bad thing? [39]
We often protest when homophobes insist that same sex marriage will change marriage for straight people too. But in some ways, they’re right. [40]
Some advocates of redefining marriage embrace the goal of weakening the institution of marriage in these very terms . “[Former President George W.] Bush is correct,” says Victoria Brownworth, “when he states that allowing same-sex couples to marry will weaken the institution of marriage…. It most certainly will do so, and that will make marriage a far better concept than it previously has been.” [41] Professor Ellen Willis celebrates the fact that “conferring the legitimacy of marriage on homosexual relations will introduce an implicit revolt against the institution into its very heart.” [42]
Michelangelo Signorile urges same-sex couples to “demand the right to marry not as a way of adhering to society’s moral codes but rather to debunk a myth and radically alter an archaic institution.” [43] Same-sex couples should “fight for same-sex marriage and its benefits and then, once granted, redefine the institution of marriage completely, because the most subversive action lesbians and gay men can undertake…is to transform the notion of ‘family’ entirely.” [44]
It is no surprise that there is already evidence of this occurring. A federal judge in Utah allowed a legal challenge to anti-bigamy laws. [45] A bill that would allow a child to have three legal parents passed both houses of the California state legislature in 2012 before it was vetoed by the governor, who claimed he wanted “to take more time to consider all of the implications of this change.” [46] The impetus for the bill was a lesbian same-sex relationship in which one partner was impregnated by a man. The child possessed a biological mother and father, but the law recognized the biological mother and her same-sex spouse, a “presumed mother,” as the child’s parents. [47]
Those who believe in monogamy and exclusivity—and the benefits that these bring to orderly procreation and child well-being—should take note.
Redefining marriage threatens religious liberty.
Redefining marriage marginalizes those with traditional views and leads to the erosion of religious liberty. The law and culture will seek to eradicate such views through economic, social, and legal pressure. If marriage is redefined, believing what virtually every human society once believed about marriage—a union of a man and woman ordered to procreation and family life—would be seen increasingly as a malicious prejudice to be driven to the margins of culture. The consequences for religious believers are becoming apparent.
The administrative state may require those who contract with the government, receive governmental monies, or work directly for the state to embrace and promote same-sex marriage even if it violates their religious beliefs. Nondiscrimination law may make even private actors with no legal or financial ties to the government—including businesses and religious organizations—liable to civil suits for refusing to treat same-sex relationships as marriages. Finally, private actors in a culture that is now hostile to traditional views of marriage may discipline, fire, or deny professional certification to those who express support for traditional marriage.
In fact, much of this is already occurring. Heritage Foundation Visiting Fellow Thomas Messner has documented multiple instances in which redefining marriage has already become a nightmare for religious liberty. [48] If marriage is redefined to include same-sex relationships, then those who continue to believe the truth about marriage—that it is by nature a union of a man and a woman—would face three different types of threats to their liberty: the administrative state, nondiscrimination law, and private actors in a culture that is now hostile to traditional views. [49]
After Massachusetts redefined marriage to include same-sex relationships, Catholic Charities of Boston was forced to discontinue its adoption services rather than place children with same-sex couples against its principles. [50] Massachusetts public schools began teaching grade-school students about same-sex marriage, defending their decision because they are “committed to teaching about the world they live in, and in Massachusetts same-sex marriage is legal.” A Massachusetts appellate court ruled that parents have no right to exempt their children from these classes. [51]
The New Mexico Human Rights Commission prosecuted a photographer for declining to photograph a same-sex “commitment ceremony.” Doctors in California were successfully sued for declining to perform an artificial insemination on a woman in a same-sex relationship. Owners of a bed and breakfast in Illinois who declined to rent their facility for a same-sex civil union ceremony and reception were sued for violating the state nondiscrimination law. A Georgia counselor was fired after she referred someone in a same-sex relationship to another counselor. [52] In fact, the Becket Fund for Religious Liberty reports that “over 350 separate state anti-discrimination provisions would likely be triggered by recognition of same-sex marriage.” [53]
The Catholic bishop of Springfield, Illinois, explains how a bill, which was offered in that state’s 2013 legislative session, to redefine marriage while claiming to protect religious liberty was unable to offer meaningful protections:
[It] would not stop the state from obligating the Knights of Columbus to make their halls available for same-sex “weddings.” It would not stop the state from requiring Catholic grade schools to hire teachers who are legally “married” to someone of the same sex. This bill would not protect Catholic hospitals, charities, or colleges, which exclude those so “married” from senior leadership positions…. This “religious freedom” law does nothing at all to protect the consciences of people in business, or who work for the government. We saw the harmful consequences of deceptive titles all too painfully last year when the so-called “Religious Freedom Protection and Civil Union Act” forced Catholic Charities out of foster care and adoption services in Illinois. [54]
In fact, the lack of religious liberty protection seems to be a feature of such bills:
There is no possible way—none whatsoever—for those who believe that marriage is exclusively the union of husband and wife to avoid legal penalties and harsh discriminatory treatment if the bill becomes law. Why should we expect it be otherwise? After all, we would be people who, according to the thinking behind the bill, hold onto an “unfair” view of marriage. The state would have equated our view with bigotry—which it uses the law to marginalize in every way short of criminal punishment. [55]
Georgetown University law professor Chai Feldblum, an appointee to the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, argues that the push to redefine marriage trumps religious liberty concerns:
[F]or all my sympathy for the evangelical Christian couple who may wish to run a bed and breakfast from which they can exclude unmarried, straight couples and all gay couples, this is a point where I believe the “zero-sum” nature of the game inevitably comes into play. And, in making that decision in this zero-sum game, I am convinced society should come down on the side of protecting the liberty of LGBT people. [56]
Indeed, for many supporters of redefining marriage, such infringements on religious liberty are not flaws but virtues of the movement.
The Future of Marriage
Long before the debate about same-sex marriage, there was a debate about marriage. It launched a “marriage movement” to explain why marriage was good both for the men and women who were faithful to its responsibilities and for the children they reared. Over the past decade, a new question emerged: What does society have to lose by redefining marriage to exclude sexual complementarity?
Many citizens are increasingly tempted to think that marriage is simply an intense emotional union, whatever sort of interpersonal relationship consenting adults, whether two or 10 in number, want it to be—sexual or platonic, sexually exclusive or open, temporary or permanent. This leaves marriage with no essential features, no fixed core as a social reality. It is simply whatever consenting adults want it to be.
Yet if marriage has no form and serves no social purpose, how will society protect the needs of children—the prime victim of our non-marital sexual culture—without government growing more intrusive and more expensive?
Marriage exists to bring a man and a woman together as husband and wife to be father and mother to any children their union produces. Marriage benefits everyone because separating the bearing and rearing of children from marriage burdens innocent bystanders: not just children, but the whole community. Without healthy marriages, the community often must step in to provide (more or less directly) for their well-being and upbringing. Thus, by encouraging the norms of marriage—monogamy, sexual exclusivity, and permanence—the state strengthens civil society and reduces its own role.
Government recognizes traditional marriage because it benefits society in a way that no other relationship or institution does. Marriage is society’s least restrictive means of ensuring the well-being of children. State recognition of marriage protects children by encouraging men and women to commit to each other and take responsibility for their children.
The future of this country depends on the future of marriage, and the future of marriage depends on citizens understanding what it is and why it matters and demanding that government policies support, not undermine, true marriage.
Some might appeal to historical inevitability as a reason to avoid answering the question of what marriage is—as if it were an already moot question. However, changes in public opinion are driven by human choice, not by blind historical forces. The question is not what will happen, but what we should do.
—Ryan T. Anderson is William E. Simon Fellow in Religion and a Free Society in the Richard and Helen DeVos Center for Religion and Civil Society at The Heritage Foundation.
[1] John Corvino and Maggie Gallagher, Debating Same-Sex Marriage (Oxford, U.K.: Oxford University Press, 2012), p. 94.
[2] Ibid., p. 116.
[3] Ibid., p. 96.
[4] Sherif Girgis, Ryan T. Anderson, and Robert P. George, What Is Marriage? Man and Woman: A Defense (New York: Encounter Books, 2012).
[5] David Popenoe, Life Without Father: Compelling New Evidence That Fatherhood and Marriage Are Indispensable for the Good of Children and Society (New York: The Free Press, 1996), p. 146.
[6] Ibid., p. 197. See also W. Bradford Wilcox, “Reconcilable Differences: What Social Sciences Show About the Complementarity of the Sexes & Parenting,” Touchstone , November 2005, p. 36.
[7] Girgis et al., What Is Marriage? Man and Woman: A Defense .
[8] James Q. Wilson, The Marriage Problem (New York: HapperCollins Publishers, 2002), p. 41.
[9] For the relevant studies, see Witherspoon Institute, “Marriage and the Public Good: Ten Principles,” August 2008, pp. 9–19, http://www.winst.org/family_marriage_and_democracy/WI_Marriage.pdf (accessed March 4, 2013). “Marriage and the Public Good,” signed by some 70 scholars, corroborates the philosophical case for marriage with extensive evidence from the social sciences about the welfare of children and adults.
[10] Kristin Anderson Moore, Susan M. Jekielek, and Carol Emig, “Marriage from a Child’s Perspective: How Does Family Structure Affect Children, and What Can We Do About It?” Child Trends Research Brief , June 2002, p. 1, http://www.childtrends.org/files/MarriageRB602.pdf (accessed March 4, 2013) (original emphasis).
[11] Ibid., p. 6.
[12] Wendy D. Manning and Kathleen A. Lamb, “Adolescent Well-Being in Cohabiting, Married, and Single-Parent Families,” Journal of Marriage and Family , Vol. 65, No. 4 (November 2003), pp. 876 and 890.
[13] See Sara McLanahan, Elisabeth Donahue, and Ron Haskins, “Introducing the Issue,” Marriage and Child Wellbeing , Vol. 15, No. 2 (Fall 2005), http://futureofchildren.org/futureofchildren/publications/journals/article/index.xml?journalid=37&articleid=103 (accessed March 4, 2013); Mary Parke, “Are Married Parents Really Better for Children?” Center for Law and Social Policy Policy Brief , May 2003, http://www.clasp.org/admin/site/publications_states/files/0086.pdf (accessed March 4, 2013); and W. Bradford Wilcox et al., Why Marriage Matters: Twenty-Six Conclusions from the Social Sciences , 2nd ed. (New York: Institute for American Values, 2005), p. 6, http://americanvalues.org/pdfs/why_marriage_matters2.pdf (accessed March 4, 2013).
[14] Barack Obama, “Obama’s Speech on Fatherhood,” Apostolic Church of God, Chicago, June 15, 2008, http://www.realclearpolitics.com/articles/2008/06/obamas_speech_on_fatherhood.html (accessed March 4, 2013).
[15] See Jason Richwine and Jennifer A. Marshall, “The Regnerus Study: Social Science and New Family Structures Met with Intolerance,” Heritage Foundation Backgrounder No. 2726, October 2, 2012, http://www.heritage.org/research/reports/2012/10/the-regnerus-study-social-science-on-new-family-structures-met-with-intolerance .
[16] Loren Marks, “Same-Sex Parenting and Children’s Outcomes: A Closer Examination of the American Psychological Association’s Brief on Lesbian and Gay Parenting,” Social Science Research , Vol. 41, No. 4 (July 2012), http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0049089X12000580 (accessed March 4, 2013).
[17] See Children from Different Families, http://www.familystructurestudies.com/ (accessed March 4, 2013).
[18] Douglas W. Allen, Catherine Pakaluk, and Joseph Price, “Nontraditional Families and Childhood Progress Through School: A Comment on Rosenfeld,” Demography , November 2012.
[19] Social Trends Institute, “The Sustainable Demographic Dividend: What Do Marriage and Fertility Have to Do with the Economy?” 2011, http://sustaindemographicdividend.org/articles/the-sustainable-demographic (accessed March 4, 2013).
[20] H. Brevy Cannon, “New Report: Falling Birth, Marriage Rates Linked to Global Economic Slowdown,” UVA Today , October 3, 2011, http://www.virginia.edu/uvatoday/newsRelease.php?id=16244 (accessed March 4, 2013).
[21] Robert Rector, “Marriage: America’s Greatest Weapon Against Child Poverty,” Heritage Foundation Special Report No. 117, September 5, 2012, http://www.heritage.org/research/reports/2012/09/marriage-americas-greatest-weapon-against-child-poverty .
[22] Isabel V. Sawhill, “Families at Risk,” in Henry J. Aaron and Robert D. Reischauer, eds., Setting National Priorities: The 2000 Election and Beyond (Washington: Brookings Institution Press, 1999), pp. 97 and 108. See also Witherspoon Institute, “Marriage and the Public Good,” p. 15.
[23] Institute for American Values et al., “The Taxpayer Costs of Divorce and Unwed Childbearing: First-Ever Estimates for the Nation and for All Fifty States,” 2008, http://www.americanvalues.org/pdfs/COFF.pdf (accessed March 6, 2013).
[24] David G. Schramm, “Preliminary Estimates of the Economic Consequences of Divorce,” Utah State University, 2003.
[25] Jessica Bennett, “Only You. And You. And You,” Newsweek , July 28, 2009, http://www.thedailybeast.com/newsweek/2009/07/28/only-you-and-you-and-you.html (accessed March 6, 2013).
[26] Ryan T. Anderson, “Beyond Gay Marriage,” The Weekly Standard , August 17, 2008, http://www.weeklystandard.com/Content/Public/Articles/000/000/012/591cxhia.asp (accessed March 6, 2013).
[27] For the relevant studies, see Witherspoon Institute, “Marriage and the Public Good.” See also Moore et al., “Marriage from a Child’s Perspective,” p. 1; Manning and Lamb, “Adolescent Well-Being in Cohabiting, Married, and Single-Parent Families”; McLanahan et al., “Introducing the Issue”; Parke, “Are Married Parents Really Better for Children?”; and Wilcox et al., Why Marriage Matters , p. 6.
[28] E. J. Graff, “Retying the Knot,” in Andrew Sullivan, ed., Same-Sex Marriage: Pro and Con: A Reader (New York: Vintage Books, 1997), pp. 134, 136, and 137.
[29] Andrew Sullivan, “Introduction,” in Sullivan, ed., Same-Sex Marriage , pp. xvii and xix.
[30] See Girgis et al., What Is Marriage?
[31] See Maggie Gallagher, “(How) Will Gay Marriage Weaken Marriage as a Social Institution: A Reply to Andrew Koppelman,” University of St. Thomas Law Journal , Vol. 2, No. 1 (2004), p. 62, http://ir.stthomas.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1047&context=ustlj (accessed March 6, 2013).
[32] BeyondMarriage.org, “Beyond Same-Sex Marriage: A New Strategic Vision for All Our Families and Relationships,” July 26, 2006, http://beyondmarriage.org/full_statement.html (accessed March 6, 2013).
[33] Elizabeth Brake, “Minimal Marriage: What Political Liberalism Implies for Marriage Law,” Ethics , Vol. 120, No. 2 (January 2010), pp. 302, 303, 323, and 336.
[34] Bennett, “Only You.”
[36] Molly Young, “He & He & He,” New York Magazine , July 29, 2012, http://nymag.com/news/features/sex/2012/benny-morecock-throuple/ (accessed March 6, 2013).
[37] Andrew Sullivan, Virtually Normal: An Argument About Homosexuality (New York: Vintage Books, 1996), pp. 202–203.
[38] Scott James, “Many Successful Gay Marriages Share an Open Secret,” The New York Times , January 28, 2010, http://www.nytimes.com/2010/01/29/us/29sfmetro.html (accessed March 6, 2013).
[39] Ari Karpel, “Monogamish,” The Advocate , July 7, 2011, http://www.advocate.com/Print_Issue/Features/Monogamish/ (accessed March 6, 2013).
[40] Ari Karpel, “Features: Monogamish,” The Advocate , July 7, 2011, http://www.advocate.com/arts-entertainment/features?page=7 (accessed March 7, 2013).
[41] Victoria A. Brownworth, “Something Borrowed, Something Blue: Is Marriage Right for Queers?” in Greg Wharton and Ian Philips, eds., I Do/I Don’t: Queers on Marriage (San Francisco: Suspect Thoughts Press, 2004), pp. 53 and 58–59.
[42] Ellen Willis, “Can Marriage Be Saved? A Forum,” The Nation , July 5, 2004, p. 16, http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-118670288.html (accessed March 6, 2013).
[43] Michelangelo Signorile, “Bridal Wave,” Out , December 1993/January 1994, pp. 68 and 161.
[45] Julia Zebley, “Utah Polygamy Law Challenged in Federal Lawsuit,” Jurist , July 13, 2011, http://jurist.org/paperchase/2011/07/utah-polygamy-law-challenged-in-federal-lawsuit.php (accessed March 6, 2013).
[46] Jim Sanders, “Jerry Brown Vetoes Bill Allowing More Than Two Parents,” The Sacramento Bee , September 30, 2012, http://blogs.sacbee.com/capitolalertlatest/2012/09/jerry-brown-vetoes-bill-allowing-more-than-two-parents.html (accessed March 6, 2013).
[47] For more on this, see Jennifer Roback Morse, “Why California’s Three-Parent Law Was Inevitable,” Witherspoon Institute Public Discourse , September 10, 2012, http://www.thepublicdiscourse.com/2012/09/6197 (accessed March 6, 2013).
[48] Thomas M. Messner, “Same-Sex Marriage and the Threat to Religious Liberty,” Heritage Foundation Backgrounder No. 2201, October 30, 2008, http://www.heritage.org/research/reports/2008/10/same-sex-marriage-and-the-threat-to-religious-liberty ; “Same-Sex Marriage and Threats to Religious Freedom: How Nondiscrimination Laws Factor In,” Heritage Foundation Backgrounder No. 2589, July 29, 2011, http://www.heritage.org/research/reports/2011/07/same-sex-marriage-and-threats-to-religious-freedom-how-nondiscrimination-laws-factor-in ; and “From Culture Wars to Conscience Wars: Emerging Threats to Conscience,” Heritage Foundation Backgrounder No. 2532, April 13, 2011, http://www.heritage.org/research/reports/2011/04/from-culture-wars-to-conscience-wars-emerging-threats-to-conscience .
[49] For more on this, see Messner, “Same-Sex Marriage and the Threat to Religious Liberty.”
[50] Maggie Gallagher, “Banned in Boston,” The Weekly Standard , May 5, 2006, p. 20, http://www.weeklystandard.com/Content/Public/Articles/000/000/012/191kgwgh.asp (accessed March 6, 2013).
[51] For example, see Parker v. Hurley , 514 F.3d 87 (1st Cir. 2008).
[52] Walden v. Centers for Disease Control , Case No. 1:08-cv-02278-JEC, U.S. District Court, Northern District of Georgia, March 18, 2010, http://www.telladf.org/UserDocs/WaldenSJorder.pdf (accessed March 6, 2013).
[53] Becket Fund for Religious Liberty, “Same-Sex Marriage and State Anti-Discrimination Laws,” Issue Brief , January 2009, p. 2, http://www.becketfund.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/Same-Sex-Marriage-and-State-Anti-Discrimination-Laws-with-Appendices.pdf (accessed March 7, 2013). See also Messner, “Same-Sex Marriage and Threats to Religious Freedom,” p. 4.
[54] Thomas John Paprocki, letter to priests, deacons, and pastoral facilitators in the Diocese of Springfield, January 3, 2013, http://www.dio.org/blog/item/326-bishop-paprockis-letter-on-same-sex-marriage.html#sthash.CPXLw6Gt.dpbs (accessed March 6, 2013).
[56] Chai R. Feldblum, “Moral Conflict and Liberty: Gay Rights and Religion,” Brooklyn Law Review , Vol. 72, No. 1 (Fall 2006), p. 119, http://www.brooklaw.edu/~/media/PDF/LawJournals/BLR_PDF/blr_v72i.ashx (accessed March 6, 2013).
Former Visiting Fellow, DeVos Center
Marriage, the union between one man and one woman, and family are the building blocks of all human civilization and the primary institutions of civil society.
Learn more about policies that strengthen marriage and family as cornerstones to a flourishing civil society with Solutions .
COMMENTARY 6 min read
COMMENTARY 3 min read
Subscribe to email updates
© 2024, The Heritage Foundation
Learn Anthropology
No products in the cart.
Username or Email Address
Remember Me Forgot Password?
A link to set a new password will be sent to your email address.
Your personal data will be used to support your experience throughout this website, to manage access to your account, and for other purposes described in our privacy policy .
Get New Password -->
Universality of Marriage
- Last Updated: Sep 10, 2023
Marriage is a social institution existing in all societies but the characteristics vary from culture to culture. Several anthropologists have made an effort to define marriage universally, but none of them have been able to satisfactorily include all of its variations in a single definition.

Different definitions of Marriage
- The concept of legitimacy was central to the definition of marriage put out by early thinkers like Malinowski and Brown. According to Malinowski, a lawful marriage is one that grants the woman’s husband social recognition and the father of her children social recognition. The question of “What marriage was?” was not addressed by this definition, which placed emphasis on legitimacy.
- The first anthropological definition of marriage was published in Notes and Queries (1951), which stated that marriage is a union between a man and woman that ensures the children they have are acknowledged as the legal children of both parents.
- The question arises: What about the human being makes marriage such a ubiquitous social institution in spite of all the restrictions it imposes?
Need for existence of marriage in human society
1. to check chaos that may result because of sexual competition.
- Female humans are capable of mating throughout the year (animal female oestrous cycle is seasonally regulated).
- Sexual dimorphism, which restricts mating in animals, is less pronounced in people.
- In humans, a male’s physical dominance can be resisted by numerical advantage or the use of the mind, although this is not possible in animals.
- If any of these characteristics are left unchecked, they may produce ferocious sexual competition and create anarchy.
- In this case, marriage acts as an institution with a crucial role in controlling mating. This does not mean that only married couples mate. It implies that marriage enables structured mating between partners who are designated by culture.
2. To provide for mother – newborn combinatio n
- Lower apes gave rise to bipedal man. Changes in limb shape, facial features, and brain size resulted from this process of evolution.
- Animal newborn have nearly fully developed brains at birth and can stand up in a matter of minutes or hours. Yet, as brain size increases in humans, there comes a time when giving birth to a child with a fully grown brain may be catastrophic for both the mother and the child.
- The teeth sprout a few months after birth whereas the brain reaches its maximum developmental potential soon before physiological maturation.
- Because of this, a baby’s early years of existence necessitate the mother’s constant protection, which leaves the mother severely handicapped after giving birth.
- This necessitated the association of a male who could take care of the mother-child combination.
- As a result, marriage provides a stable organisation that includes both men and women, ensuring proper security and satisfaction of personal needs such as affection, status, and companionship for both mother and child.
3. To help in the regulation of lines of descent
- The use of descent as a way for one person to claim rights, obligations, privileges, or status in regard to another person (Britannica, 2011).
- Descent has a special impact when succession, inheritance, or residence rights follow kinship lines.
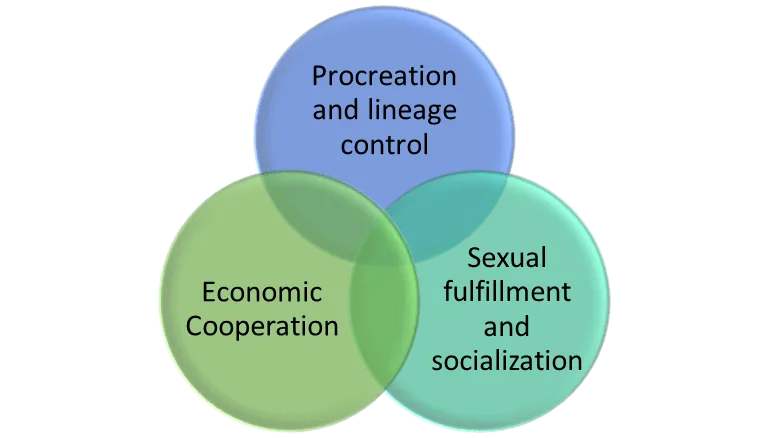
Although there may have been some other options, man chose to establish this organisation. Marriage institution must be a universal aspect of human civilization since these two needs—reducing sexual competition and sustaining the mother-child combination—have been acknowledged by all human communities .
The notions of marriage can alter and adapt, much like any social structures . The idea of marriage is changing significantly in urban settings as socioeconomic opportunities alter and new chances arise for both men and women.
1. Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (2023, February 3). Marriage. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/marriage . Accessed on 16 February 2023.
2. Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (2011, December 5). Descent. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/descent . Accessed on 16 February 2023.
3. Doshi S.L, Jain P.C. (2001). Social Anthropology. Rawat Publications; Jaipur, 2019.
4. Ember Carol, Ember Melvin, Peregrine Peter. (2015). Anthropology. Pearson Education; Noida, 2019.
5. Fussell, E. and Palloni, A. (2004), Persistent marriage regimes in changing times. Journal of Marriage and Family, 66: 1201-1213. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-2445.2004.00087.x . Accessed on 16 February 2023.
6. Hasty, J., Lewis, David G., & Snipes, M. M. (2022). Marriage and Families across cultures. An Introduction to Anthropology. OpenStax; Houston, 2022. https://openstax.org/books/introduction-anthropology/pages/11-4-marriage-and-families-across-cultures . Accessed on 16 February 2023
7. Mair Lucy. (1965). An Introduction to Social Anthropology. Oxford University Press; Oxford, 1972.
8. Why is Marriage Nearly Universal? https://revelpreview.pearson.com/epubs/pearson_ember/OPS/xhtml/ch19_sec_04.xhtml . Accessed on 16 February 2023.

Shefali Sharma is a Research Scholar in the Department of Anthropology at University of Rajasthan. She obtained a prestigious meritorious award by University of Rajasthan in 2022. She also holds qualifications such as UGC – NET. She is a writer by the day and reader by the night and has worked as a content writer for various websites.
Newsletter Updates
Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
I accept the Privacy Policy
Related Posts

Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Your Article Library
Essay on marriage: meaning, functions and forms.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Here is your essay on marriage, it’s meaning, functions and forms!
Introduction :
Marriage and family sociologically signifies the stage of greater social advancement. It is indicative of man’s entry into the world of emotion and feeling, harmony and culture. Long before the institution of marriage developed, man and woman may have lived together, procreated children and died unwept and unsung. Their sexual relations must have been like birds and animals of momentary duration.

Image Courtesy : 2.bp.blogspot.com/–Zyo4IJENYk/TtuIdHcjm-I/AAAAAAAACwQ/Rg89UBiMU0A/s1600/lklk.jpg
Marriage as an institution developed over the time. It may have been accepted as a measure of social discipline and as an expedient to eliminate social stress due to the sex rivalry. The growing sense and sensibility may have necessitated the acceptance of norms for formalising the union between man and woman.
Meaning of Marriage :
Marriage is the most important institution of human society. It is a universal phenomenon. It has been the backbone of human civilisation. Human beings have certain urges like hungers, thirst and sex. Society works out certain rules and regulation for satisfaction of these urges.
The rules and regulations, which deal with regulation of sex life of human beings, are dealt in the marriage institution. We can say that the Marriage is as old as the institution of family. Both these institutions are vital for the society. Family depends upon the Marriage. Marriage regulates sex life of human beings.
Marriage creates new social relationships and reciprocal rights between the spouses. It establishes the rights and the status of the children when they are born. Each society recognises certain procedures for creating such relationship and rights. The society prescribes rules for prohibitions, preferences and prescriptions in deciding marriage. It is this institution through which a man sustains the continuity of his race and attains satisfaction in a socially recognised manner.
Sociologists and anthropologists have given definitions of marriage. Some of the important definitions are given below. Edward Westermark. “Marriage is a relation of one or more men to one or more women which is recognised by custom or law and involves certain rights and duties both in the case of the parties entering the union and in the case of the children born of it.
As B. Malinowski defines, “Marriage is a contract for the production and maintenance of children”.
According H.M. Johnson, “Marriage is a stable relationship in which a man and a woman are socially permitted without loss of standing in community, to have children”.
Ira L. Reiss writes, “Marriage is a socially accepted union of individuals in husband and wife roles, with the key function of legitimating of parenthood”.
William Stephens, the anthropologist, says that marriage is:
(1) A socially legitimate sexual union begun with
(2) A public announcement, undertaken with
(3) Some idea of performance and assumed with a more or less explicit
(4) Marriage contract, which spells out reciprocal obligations between spouses and between spouses and their children.
William J. Goode, the famous family sociologist has tried to combine the two objectives of marriage i.e. to regulate sex life and to recognize the newborn. It was perhaps for this reason that American sociologists came out with the statement that no child should be born without a father.
Although different thinkers have tried to provide definition of marriage, but there is no universally acceptable definition of marriage. There seems to be, however, a consensus that marriage involves several criteria that are found to exist cross-culturally and throughout time. For example, Hindu marriage has three main objectives such as Dharma, Progeny and Sexual Pleasure.
Individual happiness has been given the least importance. It is considered to be sacrament, a spiritual union between a man and a woman in the social status of husband and wife.
In Western countries, marriage is a contract. Personal happiness is given the utmost importance. People enter into matrimonial alliances for the sake of seeking personal happiness. If this happiness is-not forthcoming they will terminate the relationship.
Marriage is thus cultural specific. The rules and regulations differ from one culture to another. We can, however, identify certain basic features of this institution.
(1) A heterosexual union, including at least one male and one female.
(2) The legitimizing or granting of approval to the sexual relationship and the bearing of children without any loss of standing in the community or society.
(3) A public affair rather than a private, personal matter.
(4) A highly institutionalized and patterned mating arrangement.
(5) Rules which determine who can marry whom.
(6) New statuses to man and woman in the shape of husband and wife and father and mother.
(7) Development of personal intimate and affectionate relationships between the spouses and parent and children.
(8) A binding relationship that assumes some performance.
The above discussion helps us to conclude that the boundaries of marriage are not always precise and clearly defined. It is, however, very important institution for the society as it helps in replacement of old and dying population.
Functions of Marriage :
Marriage is an institutionalized relationship within the family system. It fulfills many functions attributed to the family in general. Family functions include basic personality formation, status ascriptions, socialization, tension management, and replacement of members, economic cooperation, reproduction, stabilization of adults, and the like.
Many of these functions, while not requiring marriage for their fulfillment, are enhanced by the marital system”. In fact, evidence suggests marriage to be of great significance for the well-being of the individual. Researchers have shown that compared to the unmarried, married persons are generally happier, healthier, less depressed and disturbed and less prone to premature deaths. Marriage, rather than becoming less important or unimportant, may be increasingly indispensable.
The functions of marriage differ as the structure of marriage differs. ‘For example, where marriage is specially an extension of the kin and extended family system, then procreation, passing on the family name and continuation of property become a basic function. Thus, to not have a child or more specifically, to not have a male child, is sufficient reason to replace the present wife or add a new wife.
Where marriage is based on “free choice,” i.e. parents and kinsmen play no role in selecting the partner, individualistic forces are accorded greater significance. Thus in the United States, marriage has many functions and involves many positive as well as negative personal factors : establishment of a family of one’s own, children, companionship, happiness, love, economic security, elimination of loneliness etc.
The greater the extent to which the perceived needs of marriage are met, and the fewer the alternatives in the replacement of the unmet needs, the greater the likelihood of marriage and the continuation of that marriage. At a personal level, any perceived reason may explain marriage, but at a social level, all societies sanction certain reasons and renounce others.
Forms of Marriage :
Societies evolved mannerism and method for selection of the spouses, according to their peculiar socio-economic and political conditions, and in accordance with their levels of cultural advancement. This explains on the one hand the origin of the various forms, of marriage and on the other the differences in the attitude of societies towards the institution of marriage.
Some have accepted it as purely a contractual arrangement between weds, while others hold it as the sacred union between man, and woman. Forms of marriage vary from society to society. Marriage can be broadly divided into two types, (1) monogamy and (2) polygamy.
1. Monogamy :
Monogamy is that form of marriage in which at a given period of time one man has marital relations with one woman. On the death of the spouse or one of the partners seek divorce then they can establish such relationship with other persons but at a given period of time, one cannot have two or more wives or two or more husbands.
This one to one relationship is the most modern civilized way of living. In most of the societies it is this form, which is found and recognized. It should be noted that on a societal basis, only about 20 per cent of the societies are designated as strictly monogamous, that is, monogamy is the required form.
When monogamy does not achieve stability, certain married persons end their relationship and remarry. Thus, the second spouse, although not existing simultaneously with the first, is sometimes referred to as fitting into a pattern of sequential monogamy, serial monogamy or remarriage.
Advantages:
Keeping in view the advantages of monogamy the world has granted recognition to monogamous form of marriage. The following are its advantages:
1. Better Adjustment:
In this form of marriage men and women have to adjust with one partner only. In this way there is better adjustment between them.
2. Greater Intimacy:
If the number of people in the family will be limited there will be more love and affection in the family. Because of which they will have friendly and deep relations.
3. Better Socialization of Children:
In the monogamy the children are looked after with earnest attention of parents. The development of modes of children will be done nicely. There will be no jealously between the parents for looking after their children.
4. Happy Family:
Family happiness is maintained under monogamy which is completely destroyed in other forms of marriage because of jealousy and other reasons. Thus, in this form of marriage, family is defined as happy family.
5. Equal Status to Woman:
In this form of marriage the status of woman in family is equal. If husband works she looks after the house or both of them work for strengthening the economic condition of the family.
6. Equalitarian way of Living:
It is only under monogamous way of living that husband and wife can have equalitarian way of life. Under this system husband and wife not only share the familial role and obligations but also have joint decisions. The decision making process becomes a joint venture.
7. Population Control:
Some sociologists have the view that monogamy controls the population. Because of one wife children in the family will be limited.
8. Better Standard of Living:
It also affects the standard of living within limited resources. One can manage easily to live a better life. It helps in the development of independent personality without much constraint and pressure.
9. Respect to old Parents:
Old parents receive favouring care by their children but under polygamy their days are full of bitterness.
10. Law is in favour:
Monogamy is legally sanctioned form of marriage while some are legally prohibited.
11. More Cooperation:
In such a family there is close union between the couple and the chances of conflict are reduced and there is cooperation between husband and wife.
12. Stability:
It is more stable form of marriage. There is better division of property after the death of parents.
Disadvantages :
1. Adjustment:
Monogamy is a marriage between one husband and one wife. So if the partner is not of choice then life loses its charm. They have to adjust between themselves but now-a-days divorce is the answer to their problem.
2. Monopoly:
According to Sumner and Keller, “Monogamy is monopoly.” Wherever there is monopoly, there is bound to be both ‘ins and outs’.
3. Childlessness:
Some inpatients can’t have kids or some barren cannot have kids. If one of the partners has some problem couples cannot have children. They have to suffer from childlessness.
4. Economic Factors:
Marriage in monogamy does not play part of income. They have to depend upon their own occupation for living. If they are poor they will remain poor. So monogamy effects the economic condition of man and woman.
5. Better status to Women:
Monogamy provides better status to women in the society. They are counted equal to men. Some people do not like this form of marriage.
6. Adultery:
When they do not get partner of their own choice they start sexual relations with other people. This also leads to the problem of prostitution.
2. Polygamy :
Distinguished from monogamy is polygamy. Polygamy refer to the marriage of several or many. Polygamy is the form of marriage in which one man marries two or more women or one woman marries two or more men or a number of men many a number of women. According to F.N. Balasara, “The forms of marriage in which there is plurality of partners is called polygamy”.
Polygamy, like other forms of marriage is highly regulated and normatively controlled. It is likely to be supported by the attitudes and values of both the sexes. Polygamy itself has many forms and variations. Polygamy is of three types: (i) Polygyny, (ii) Polyandry and (iii) Group marriage.
Let us now discuss forms of polygamy in details,
(i) Polygyny:
Polygyny is a form of marriage in which a man has more than one .wife at a time. In other words it is a form of marriage in which one man marries more than one woman at a given time. It is the prevalent form of marriage among the tribes, Polygyny also appears to be the privilege of the wealthy, in many African societies the rich usually have more than one wife.
This type of marriage is found in Ghana, Nigeria, Kenya and Uganda. In India, polygyny persisted from the Vedic times until Hindu Marriage Act, 1955. Now polygyny is visible among many tribes of India.
Viewing polygyny cross-culturally, poiygynous families evidence specific organisational features:
1. In certain matters, sex particularly, co-wives have clearly defined equal rights.
2. Each wife is set up in a separate establishment.
3. The senior wife is given special powers and privileges.
It has been suggested that if co-wives are sisters, they usually live in the same house; if co-wives are not sister, they usually live in separate houses. It is believed that sibling can better tolerate, suppress and live with a situation of sexual rivalry than can non-siblings.
Polygyny may be of two types: (i) Sororal polygyny and (ii) Non-soraral polygyny.
Sororal polygyny is one in which all the wives are sisters. Non-sororal polygyny means the marriage of one man with many women who are not sisters.
Causes of Polygyny :
1. Disproportion of sexes in the Population:
When in any tribe or society male members are less in number and females are more, then this type of marriage takes place.
2. Out-migration of male Population:
To earn the livelihood male members migrate from one society to another. This way there is a decrease in the number of males than females and polygyny takes place.
3. Hypergamy:
Hypergamy also gives rise to polygyny. Under this system the parents of lower castes or classes want to improve their social status by marrying their daughters in the higher caste or classes.
4. Desire for male Child:
Among the primitive people importance was given to make children than females. Thus man was free to have as many marriages as he liked on the ground to get male children.
5. Social Status:
In some societies number of wives represented greater authority and status.
Particularly the leaders of primitive society increased number of wives in order to prove their superiority. A single marriage was considered a sign of poverty. So where marriage is taken as sign of prestige and prosperity the custom of polygyny is natural.
6. Economic Reason:
Where the people of the poor families were unable to find suitable husbands for their daughters they started marrying their daughters to rich married males.
7. Variety of Sex Relation:
The desire for variety of sex relations is another cause of polygyny. The sexual instincts become dull by more familiarity. It is stimulated by novelty.
8. Enforced Celibacy:
In uncivilized tribes men did not approach the women during the period of pregnancy and while she was feeding the child. Thus long period of enforced celibacy gave birth to second marriage.
9. More Children:
In uncivilized society more children were needed for agriculture, war and status recognition. Moreover, in some tribes the birth rate was low and death rate was high. In such tribes polygyny was followed to obtain more children.
10. Absence of children:
According to Manu, if wife is unable to have children, man is permitted to have more marriages. He further says if a wife takes her husband then he should live with her one year and take another wife.
11. Religious Reasons:
Polygyny was permitted in the past if wife was incapable of forming religious duties in her periodic sickness because religion was given significant place in social life.
12. Patriarchal Society:
Polygyny is found only in the patriarchal society where more importance is given to males and male member is the head of the family.
Advantages :
(1) Better status of children:
In polygyny children enjoy better status. They are looked after well because there are many women in the family to care.
(2) Rapid growth of Population:
In those societies where population is very less and birth rate is almost zero, for those societies polygyny is best suited, as it increases the population at faster rate.
(3) Importance of Males:
In polygyny males occupy higher status. More importance is given to husband by several wives.
(4) Division of Work:
In polygyny there are several wives. Therefore, there is a proper division of work at home.
(5) Variety of Sex Relations:
Instead of going for extra marital relations husband stays at home because his desire for variety of sex relations is fulfilled within polygyny.
(6) Continuity of Family:
Polygyny came into existence mainly because of inability of a wife to produce children. Polygyny provides continuity to the family tree. In absence of one wife other women in the family produce children.
Disadvantage :
1. Lower status of Women:
In this form of marriage women have very low status; they are regarded as an object of pleasure for their husbands. They generally do not have a right to take decisions about their welfare; they have to depend upon their husband for fulfillment of their basic needs.
2. Jealousy as stated by Shakespeare:
“Woman thy name is jealousy”. When several wives have to share one husband, there is bound to be jealousy among co-wives. Jealousy leads to inefficiency in their work. They are not able to socialize their children in a proper manner in such atmosphere.
3. Low Economic Status:
Polygyny increases economic burden on the family because in many cases only husband is the bread winner and whole of the family is dependent on him.
4. Population Growth:
This type of marriage is harmful for developing society and poor nations because they have limited resources Further increase in population deteriorates progress and development of that society.
5. Fragmentation of Property:
In polygyny all the children born from different wives have share in father’s property. Jealousy among mothers leads to property conflicts among children as a result property is divided and income per capita decreases.
6. Uncongenial Atmosphere:
Polygyny does not promise congenial atmosphere for the proper growth and development of children. There is lack of affection among the members. As such families have large number of members. They fail to provide proper attention to all of them. This gives rise to many immoral practices in the society.
(ii) Polyandry :
It is a form of marriage in which one woman has more than one husband at a given time. According to K.M. Kapadia, Polyandry is a form of union in which a woman has more than one husband at a time or in which brothers share a wife or wives in common. This type marriage is prevalent in few places such as tribes of Malaya and some tribes of India like Toda, Khasi and Kota etc. Polyandry is of two types:
(i) Fraternal Polyandry and
(ii) Non-Fratemai Polyandry.
(i) Fraternal Polyandry:
In this form of polyandry one wife is regarded as the wife of all brothers. All the brothers in a family share the same woman as their wife. The children are treated as the offspring of the eldest brother, it is found in some Indian tribes like Toda and Khasis. This type of marriage was popular in Ceylon (Srilanka at present).
(ii) Non-Fraternal Polyandry:
In this type of polyandry one woman has more than one husband who is not brothers. They belong to different families. The wife cohabits with husbands in turn. In case of Fraternal Polyandry, the wife lives in the family of her husbands, while in case of non-fraternal polyandry, the wife continues to stay in the family of her mother. This type of polyandry is found among Nayars of Kerala.
Causes of Polyandry :
1. Lesser number of Women:
According to Westermark, when the number of women is lesser than the number of males in a society, polyandry is found. For example, among Todas of Nilgiri. But according to Brifficult, polyandry can exist even when the number of women is not lesser e.g. in Tibet, Sikkim and Laddakh polyandry is found even though there is not much disparity in the number of men and women.
2. Infanticide:
In some tribal societies female infanticide is present; as a result these female population is less than male population. Further males do not enjoy good status. Therefore, one female is married to a group of brothers and polyandry exists.
3. Matrilineal System:
Just in contrast to above noted point, it has also been argued that polyandry exists in matrilineal system where one woman can have relationship with more than one man and the children instead of getting the name of father are known by mother’s name.
4. Poverty:
Polyandry exists in such areas where there is scarcity of natural resources. It is for this reason many men support one woman and her children.
5. Bride Price:
In societies where there is bridge price, polyandry exists. Brothers pay for one bride who becomes wife of all of them.
6. Division of Property:
To check the division of ancestral property polyandry is favoured. When all the brothers have one wife then the question of division of property does not arise.
7. Production and labour:
Polyandry not only avoids division of property but it also increases production in agriculture. All the brothers work together because they have to support only one family. Thus production and income increases, further there is no expenditure with regard to labour because all the husbands contribute their share of work.
8. Social Custom:
Polyandry exists in some societies mainly because of customs and traditions of that particular society. Generally, polyandry is found in such areas which are situated far away from modern developed areas.
(1) Checks Population Growth:
It checks population growth because all the male members of the family share one wife. As a result population does not increase at that rapid rate, the way in which it occurs in polygyny Therefore, it limits the size of the family.
(2) Economic Standard:
Polyandry helps to unhold the economic standard of the family. It strengthens the economic position of the family because all the members work for the improvement of the family.
(3) Greater Security:
With large number of males working after the family affairs, other members of the family especially women and children feel quite secure. Greater security among the members develop sense of we-feeling among the members of the family.
(4) Property is kept Intact:
In polyandry family does not get divided. The property of the family is held jointly and thus it is kept intact.
(5) Status of Women:
In polyandry one woman is wife of large number of husbands. As a result she gets attention of all the members and thus enjoys a good status in the family. She feels quite secure because in the absence of one husband other males are there to fulfill her basic needs.
Disadvantages:
(1) Jealousy:
When all the men have to share one woman, family quarrels and tensions are ought to be there. Husbands feel jealous of one another which adversely effect congenial atmosphere of the family.
(2) Lack of Model:
When children have large number of fathers they fail to select appropriate model for themselves. This adversely effects their personality configuration.
(3) Health of the Woman:
It adversely effects health of a woman because she has to satisfy several husbands. It not only has negative effect on the physical health but also on mental health of the woman.
(4) Sterility:
According to biologists if the same woman cohabits with several men, it may lead to sterility, further lack of sex gratification give rise to extra-marital relationship of husbands.
(5) Status of Men:
In matrilineal system where polyandry is found husbands do not enjoy high status. They do not give their name to the children.
(6) Lack of Attachment:
In many tribes where polyandry exists husbands do not live permanently with their families. They are visiting husband who visit the family for a specific period. They do not get love and affection of their children because children feel unattached to their fathers.
(7) Less Population:
This form of marriage decreases population growth. In some tribal societies where polyandry continues to exist may get extinct after a gap of few years.
(8) Loose Morality:
This is another outcome of this practice.
(iii) Group Marriage :
Group marriage is that type of marriage in which a group of men marry a group of women. Each man of male group is considered to be the husband of every woman of female group. Similarly, every woman is the wife of every man of male group. Pair bonded or Multilateral marriage are the substitute term for group marriages.
This form of marriage is found among some tribes of New Guinea and Africa. In India group marriage is practised by the Toda Tribe of Nilgiri Hills. Except on an experimental basis it is an extremely rare occurrence and may never have existed as a viable form of marriage for any society in the world.
The Oneida community of New York State has been frequently cited as an example of group marriage experiment. It involved economic and sexual sharing based on spiritual and religious principles. Like most group marriage on record, its time span was limited. Rarely do they endure beyond one or two generations.
Levirate and Sororate:
(i) Levirate:
In levirate the wife marries the brother of the dead husband. If a man dies, his wife marries the brother of her dead husband. Marriage of the widow with the dead husband’s elder brother is called Senior Levirate. But when she marries to the younger brother of the dead husband, it is called Junior Levirate.
(ii) Sororate:
In Sororate the husband marries the sister of his wife. Sororate is again divided into two types namely restricted Sororate and simultaneous Sororate. In restricted sororate, after the death of one’s wife, the man marries the sister of his wife. In simultaneous sororate, the sister of one’s wife automatically becomes his wife.
Concubinage:
Concubinage is a state of living together as husband and wife without being married. It is .cohabitation with one or more women who are distinct from wife or wives. Concubinage is sometimes recognised by various societies as an accepted institution. A concubine has a lower social status than that of a wife. The children of a concubine enjoy a lower status in the society.
Related Articles:
- Forms of Marriage: Polyandry, Polygyny and Monogamy
- Hindu Marriage: Aims, Ideals and Types
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Marriage Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on marriage.
In general, marriage can be described as a bond/commitment between a man and a woman. Also, this bond is strongly connected with love, tolerance, support, and harmony. Also, creating a family means to enter a new stage of social advancement. Marriages help in founding the new relationship between females and males. Also, this is thought to be the highest as well as the most important Institution in our society. The marriage essay is a guide to what constitutes a marriage in India.

Whenever we think about marriage, the first thing that comes to our mind is the long-lasting relationship. Also, for everyone, marriage is one of the most important decisions in their life. Because you are choosing to live your whole life with that 1 person. Thus, when people decide to get married, they think of having a lovely family, dedicating their life together, and raising their children together. The circle of humankind is like that only.
Read 500 Words Essay on Dowry System
As it is seen with other experiences as well, the experience of marriage can be successful or unsuccessful. If truth to be held, there is no secret to a successful marriage. It is all about finding the person and enjoying all the differences and imperfections, thereby making your life smooth. So, a good marriage is something that is supposed to be created by two loving people. Thus, it does not happen from time to time. Researchers believe that married people are less depressed and more happy as compared to unmarried people.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Concepts of Marriage
There is no theoretical concept of marriage. Because for everyone these concepts will keep on changing. But there are some basic concepts which are common in every marriage. These concepts are children, communication , problem-solving , and influences. Here, children may be the most considerable issue. Because many think that having a child is a stressful thing. While others do not believe it. But one thing is sure that having children will change the couple’s life. Now there is someone else besides them whose responsibilities and duties are to be done by the parents.
Another concept in marriage is problem-solving where it is important to realize that you can live on your own every day. Thus, it is important to find solutions to some misunderstandings together. This is one of the essential parts of a marriage. Communication also plays a huge role in marriage. Thus, the couple should act friends, in fact, be,t friends. There should be no secret between the couple and no one should hide anything. So, both persons should do what they feel comfortable. It is not necessary to think that marriage is difficult and thus it makes you feel busy and unhappy all the time.
Marriage is like a huge painting where you brush your movements and create your own love story.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Women
Marriage Essay Examples
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Women , Marriage , Love , Life , Family , Children , Social Issues , Relationships
Published: 04/05/2021
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Marriage is a term that signifies an agreed union or vow between two consenting adults who signified intentions of living together within the conditions stipulated in their religious, civic, or cultural affinities. As could be deduced, since people come from diverse cultural, ethnic, racial and religious orientations, the beliefs and value systems incorporated within the matrimonial vow or ceremony differs accordingly. For one’s personal understanding and perspective, marriage is conceptualized as one of the sacraments of the Catholic Church that unites man and woman from the time of the matrimony until their demise – or the famous words: until death which is the only rational and justified reason for the dissolution of this sacrament.
This was therefore accurately corroborated in the following definition as shown in the Vatican Archives, the sacrament of matrimony was described as “the matrimonial covenant, by which a man and a woman establish between themselves a partnership of the whole of life, is by its nature ordered toward the good of the spouses and the procreation and education of offspring; this covenant between baptized persons has been raised by Christ the Lord to the dignity of a sacrament” (Vatican: The Holy See, n.d., par. 1). Therefore, it is confirmed from the definition, that the essential ingredients for marriage include union between a man and a woman, the whole life time frame, for the purpose of the betterment of the spouses, for the procreation of children, as wel as for raising and educating children. Likewise, it was clearly stipulated that the union should be between two baptized persons.
In this regard, to be married means being able to withstand the challenges and trials encountered by the spouses. This includes staying by the side of a spouse in times of health and in times of illness; in good times, as well as in bad times; in times of poverty or in times of good wealth; and most especially in enduring the ups and downs of raising children, in the process. Being married during bad times mean finding solutions to problems together. The real challenge to the marriage comes in trials and difficulties when partners’ abilities to withstand adversities are aptly tested. Usually, problems in marriage, such as financial, emotional, social (third-parties), family or relatives, and even work, need to be resolved together. If one partner assumes sole responsibility and accountability for looking solutions to these dilemmas, there are tendencies for greater pressures and anxieties for the spouse who is burdened with the insurmountable tasks.
Likewise, to be married means acknowledging that there are roles and responsibilities to be undertaken, as spouses; and eventually, as parents. In decision making processes, there must be consensus of both partner, as well as those of the children, when needed, to resolve matters and issues pertaining to them.
Also, to be married means accepting the person who one loved and who one agreed to love for the rest of their lives – despite shortcomings, mistakes and errors that were committed within the union. However, part of the role and responsibilities of each spouse is to provide constructive criticisms to each partner and provide ways for correcting mistakes and for improvement. To emphasize, being married does not necessarily mean that one or both of the spouses would become subservient to the other, to the extent that personal and professional growth would be stunted and sacrificed. Ways and means should be offered and provided to make needed changes and transformations that would make the union better.
The secret of being happily married, therefore, is retaining the respect, love, and admiration for each other and allowing each spouse to growth in ways which would benefit their union and that of the well-being of their children.
Reference List
Vatican: The Holy See, n.d.. Part Two: The Celebration of the Chrisian Mystery. [Online] Available at: http://www.vatican.va/archive/ccc_css/archive/catechism/p2s2c3a7.htm[Accessed 6 May 2013].

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 1857
This paper is created by writer with
ID 251326339
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Meter research papers, john deere case studies, vietnam war course work, iraq course work, starbucks course work, parenting course work, industrialization course work, sculpture course work, award course work, athletes course work, telephone no literature review examples, racism in us essay sample, htc corporation report examples, individual cultural diversity issue and its relevance to workplace dynamics essay sample, kant case study example, koppen climate classification system essay examples, free book review about steve jobs, chief characteristics of postmodernism as described by lyotard and jameson essay samples, essay on following are the influences on business buyers, example of research paper on consumer models and and understanding of the manager 039 s problems, good example of research paper on effect of communication on interpersonal relations, good research paper on leadership interview project, berkleys position essay, good essay about decision analysis, good example of healthcare ethics essay, creative writing on social justice leader, marketing essays examples, laminar and turbulent pipe flow report, article review on chinese art and literature, quot essays, almon essays, scholars essays, air quality essays, proposals essays, new kind essays, third world countries essays, tourism sector essays, hacking essays, higher learning essays, institutions of higher learning essays, pertaining essays, headaches essays, rights movement essays.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
344 Marriage Essay Topics & Examples
Whether you’re writing about unconventional, traditional, or arranged marriage, essay topics can be pretty handy. Consider some original ideas gathered by our experts and discuss divorce, weddings, and family in your paper.
🏆 Best Marriage Essay Examples & Topics
👍 good marriage essay topics, 💡 simple topics about marriage, ⭐ interesting research topics about marriage, 🔍 good research topics about marriage, 📌 most interesting marriage topics to write about, ❓ marriage research questions.
- Christian vs. Muslim Marriages Comparison and Contrast A wedding is a civil or religious ceremony conducted in the presence of the family and friends of the bride and groom, to celebrate the beginning of their marriage.
- Marriage in the Importance of Being Earnest: Analysis Although Algernon’s view on love and marriage is not known during the conversation with his butler, we get to know his thoughts on the subject in a monologue where he claims that marriage is an […]
- Concept of Representation of Marriage According to Louise, her marriage is fulfilling, yet emotionally, she is in a cage of inherent oppression. Moreover, Bertha alludes to the fact that she has never loved her husband in the romantic way except […]
- Early Marriage Advantages In addition to this, there is a positive correlation between marriage and the increased mental and physical well being of an individual.
- Marriage in A Midsummer Night’s Dream The main theme of the play revolves around the marriage between Thesus, the Duke of Athens, and the Queen of Amazons called Hippolyta, as well as the events that surround the married couple.
- The Pros and Cons of Gay Marriage Counteracting the argument that prohibition of gay marriage appears similar to discrimination is the idea that marriage, in the traditional understanding of the word, is the union of necessarily different sexes, a man and a […]
- Early Marriage and Its Impact on Education Given the significant impacts that early marriage has had on education, this paper builds on the available recent research to establish the extent of early marriage and its impacts on the lives of children.
- Statement for Marriage and Family Therapist Applicant My personal experience in marriage, long-term work with families within the framework of my occupational duties, and the desire to help people through life’s difficulties motivate me to become a Marriage and Family Therapist.
- Why Gay Marriage Should Not Be Legal Therefore, because marriage is a consecrated unification of a male and a female, ready to sacrifice all that is at their disposal for the continuation of the human species and societal values, I believe all […]
- Women, Friendships, Marriage in Lynn Nottage’s “Poof!” Maybe Loureen and Florence treat their problems a little differently depending on the fact of having children or the degree to which the husband’s attitude can be tolerated. The general opinion about women and their […]
- Argument for Gay Marriages Enacting laws that recognize gay marriages would be beneficial to the society in the sense that it promotes equal rights among members of the society.
- The Future of Marriage Although today marriage is still a significant stage in the personal life and family is discussed as the fundamental factor for the social development, the role of marriage declines, the rate of divorces increases, and […]
- Qualities of Successful Marriages Faith makes great differences in marriage and this is why it is very important to share your individual beliefs and values with the partner prior to marriage in order to understand each other and plan […]
- Marriage is Outdated and no Longer Suits Modern Lifestyles and Attitudes They do not perceive the essence of entering in to marriage when they can accomplish most of the above mentioned issues outside marriage.
- Arguments against Young Marriage and Their Rebuttal For the most part, these arguments point at the current social flaws and the need to address them. Instead, such experience is acquired in the course of social interactions, which young people are engaged into […]
- Marriage and Adultery Laws of Emperor Augustus The laws were enacted to deal with marriage avoidance, the preference for childless unions, marriage of lower class women by the Roman elite, and adultery, all of which threatened the continuity of the Roman aristocracy.
- The Marriage Traditions of Wolof Culture These include the role that marriage plays in the family formation in the Wolof society, what the economic background of the plural marriages is, and which traditions describe the marriage ceremony of the Wolof culture.
- The Marriage of Heaven and Hell The contraries used by the poet in “The Marriage of Heaven and Hell” are the backbone of this poem. The structure of “The Marriage of Heaven and Hell” is the first feature of the contraries […]
- Marriage and Family Challenges As a rule, one of the principal reasons for a difficult adaptation is the initially inflated requirements of one of the spouses or even both of them.
- How to Have a Happy Marriage In life, although a number of strategies of enhancing happiness in life exist, it is important for all individuals to note that, success of these strategies depends on the commitment levels in spouses hence, the […]
- Marriage in the Postmodern Society Circa 900BC, the world only knew one type of marriage, at least the Judeo-Christian history, which is the best documented type that indicates that marriage was between a man and a woman with the option […]
- Christian Marriage Rituals From the ancient times, parents of both the bride and groom were the primary parties to the marriage covenant. According to the biblical times, marriage was a legal covenant between the parents of the bride […]
- Marriage Relationships in “The Snows of Kilimanjaro” by Hemingway Harry and his wife, Helen, are stranded in Mount Kilimanjaro and their interactions reveal that their rocky relationship is a result of a mixture of frustration, incorrect decisions, getting married for wrong reasons, and unreciprocated […]
- Islamic Marriage and Divorce The family being the basic unit of a society which is also a principle in the Islamic society its genesis is the relationship between a husband and a wife.
- Absolute Gender Equality in a Marriage Despite the fact that the principles of gender equality in marriage will clearly affect not only the relationships between a husband and a wife but also the roles of the spouses considerably, it is bound […]
- Marriage Differences in Botswana The body part discusses the history of life and marriage, marriage now, marriage in the book, the similarities and differences of life and marriage in the book and real life.
- Premarital Cohabitation’s Impact on Marriage Though premarital cohabitation used to be linked to an increased probability to a divorce.recent studies confirm that cohabitation enhances the power of a marriage.
- Interracial Marriage in the 1950s The central problem was that the period was characterized by racial segregation laws that did not allow people of a different race to attend the same restaurants, cinemas, and other public places. Moreover, parents often […]
- From Collectivism to Individualism in Marriage A marriage that is established on a collectivist ideal tends to be focused more on the interests of the in-group more than self interests.
- Marriage in “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin News about the death of her husband arises and owing to her heart problem, carefulness is vital for the one to deliver the news to her.
- Interracial Marriage in the United Arab Emirates One of the main problems is the population ratio of the country. The increased presence of foreign wives in the country can create an appearance that the identity of the country changed.
- Traditional Marriage and Love Marriage Comparison In this paper, the pros and cons of love marriage and traditional marriage will be discussed to clarify which one is a better or just more appropriate option for modern people.
- Marriage and Family: Life Experience When we got married, a man was perceived to be the head of the family, and in his absence the wife was expected to guide the family.
- Cultural Traditions: Arranged vs. Autonomous Marriage Given the aforementioned reasons, this is possible to convince people that pre-arranged marriages can be admitted as culturally permissible, and the concept of cultural relativism is an objective tool.
- Interracial Marriage Explained Secondly, an interracial marriage promotes the general acceptance of people from a different race in the new society or community and also promotes the appreciation of other people’s values in the new community and their […]
- Cultural Differences in Arranged Marriages All the expenses of the marriage are taken care of by the parents of the couple. The reason why arranged marriages are encouraged among the Hindus is that there is utmost respect compared to marriages […]
- Marriage in the Bible According to the book of genesis 1:28, after creating a man and a woman, God bestowed them with blessings and told them to “…be fruitful, and multiply, and replenish the earth, and subdue it: and […]
- The Marriage in Norway in the 1800s The paper reviews the tendencies of matrimonial and reproduction life in Norway in the 19th century. The research study is based on the academic peer-reviewed article that analyzes marriage in the country in the 1800s.
- Factors Influencing Perception on Same-sex marriage in the American Society The protagonists and antagonists of this marriage institution have always clashed over the tenet of the same-sex marriage against the moral standards of the society.
- The Benefits of Marriage This essay aims to identify the benefits of marriage, compare the level of happiness between married couples and cohabitors and analyze the conditions that contribute to the marriage advantage.
- Marriage in the Modern World For instance, there is no common agreement over the number of parties required in a marriage; who should select partners for marriage; whether or not the rearing of children is the core idea of marriage; […]
- American vs. Asian Marriages This is mandatory for both the grooms and the brides who are believed to yield complete fun in the marriage and traditionalisms of it.
- Marriage and Family Therapy Even though she is the one instigating therapy, she is suggesting that the therapist speaks to Leon and not her. This case, the problems is Marceline’s indecision and lack of set goals of what she […]
- Marriage in The Yellow Wallpaper She has failed to recognize that she is the driver of her own life, and blame should not be put on man. Therefore, she is not able to work her creativity and ends up drawing […]
- American Marriage in transition Nevertheless, the Great Depression and the two World Wars drove women from homes into the labor market, and this had a major effect on the roles and expectations of both husbands and wives within the […]
- Process Philosophy’s Impact on Marriage and Education The growth in the popularity of gay marriages in America provides evidence of the impact of process philosophy on government policies.
- Marianne Weber’s Views on Marriage Traditionally, the role of a husband was that of a breadwinner and a patriarch of the family, whereas a wife’s duties were to take care of their children and keep the family hearth.
- Benefits of Remarriage for Happy Life Remarriage allows a person to find love and comfort from the other partner. When a person chooses to be remarried, they would likely accumulate their financial sources to focus their economic development with the partner.
- Love, Marriage, and Divorce He weighs the possible outcomes, and mostly, these were negative elements such as discrimination of his side of the family who are expected to wait only for food and drink during the wedding, other wedding […]
- Interracial Marriage and Emirati Identity Issues According to the Federal National Council, the prevalence of interracial marriages in the UAE is threatening Emirati women, in terms of their ability to be married by a fellow Emirati man.
- Let Me Not to the Marriage of Two Minds by William Shakespeare The reader can interpret starting lines as the response to the question of the priest in the wedding ceremony about the reasons preventing the couple from getting married The structure of the phrase “Let me […]
- Marriage Vs. Living Together: Pros and Cons Marriage is simply a ceremony that was imagined and enacted by man in order to signify the decision of a man and a woman to live together in a forever sense of the word.
- Marriage and Family Problems as Social Issues Sociology as a discipline has an extremely wide range of interests and it is next to impossible even to enumerate them, however the issue that has always been of the utmost importance for the sociological […]
- Making Marriage Work The aim of the governor in using state funds to reduce the number of divorce cases is compulsory because it becomes obligatory for individuals to know each other, be able to come up with conclusive […]
- The Concept of Same Sex Marriage and Child Adoption It is as a result of this approach that an individual sexual orientation cannot be used to limit them from adopting children least it is proven beyond doubt that the relationship will be harmful to […]
- Marriage in Saudi Arabia The elders of the prospective bride propagated marriage in Saudi Arabia, and afterward, it was the responsibility of either the groom or the groom’s parents to propose to her father.
- Child Marriages in Modern India The practice of child marriages among the Shaikh and the Rajasthan community at large has been exacerbated by the government’s reluctance in preventing it and to make the matter worst, it seems to be very […]
- Unforgiveness in Marriages and Families I think true forgiveness in the context of marital or familial relationships cannot be achieved without a complete understanding of the causes of the transgression and the reasons behind one’s inability to forgive.
- Marriage Types and Their Critical Components Increasingly, variations have also encompassed how one of the traditional expectations of marriage, that is, siring children, is construed and whether spouses are of the same or different sexes.
- Comparison of Marriage in Elizabethan Times and in “Othello” The man was believed to be the head of the family, and he had the legal right to punish his wife.
- Taqiya and Mut’ah in Islam: The Legal Status of Mut’ah Marriage in Indonesia It is essentially a temporary contract marriage, in which a man and a woman agree to assume the roles of husband and wife for a limited period.
- Arranged Marriages in India According to Bertolani, marriage in Indian society is strictly arranged by the parents of potential marriage partners and does not necessarily have to involve love. Thus, arranged marriage in the context of Indian society is […]
- Effects of Mastectomy on Marriage This is because the husband has to deal with the fact that his wife has one breast. The husband is affected by his wife’s condition of a missing breast.
- The Role of Marriage on the Example of Two Plays The plays Waiting for Godot and A Long Day’s Journey into Night indirectly imply the topic of the marriage’s role and how it impacts the individuals.
- How Is Marriage Related to Health? We can only surmise how marriage is related to health, but those who have been through a lot of problems and hassles as a result of bad marriages, literally know what marriage can bring to […]
- Domestic Violence in Marriage and Family While there are enormous reports of intimate partner homicides, murders, rapes, and assaults, it is important to note that victims of all this violence find it very difficult to explain the matter and incidents to […]
- Five Filters of Communication in Marriage It is therefore important for a couple to be careful and aware of these filters in order to ensure that the message received is the actual message intended to be conveyed.
- Biblical Marriage and Divorce – Religious Studies The outstanding fact is that the Bible discourages the practice. Divorce is harmful to both society and the Church.
- Social Issues: Arranged Marriages Even though research has shown that some arranged marriages result in loving and stable relationships, I think it is important to give individuals the freedom to choose their partners and decide whether they are prepared […]
- Assessing in the Field of Marriage and Family Therapy Through assessment, the family therapist can influence the outcome of the conversations in a consultative meeting between the troubled individual and the therapist.
- Genograms Role in Family and Marriage In my second marriage, the major challenge was to find a unified approach to my son and the children of my new partner.
- Importance of Communication in Marriage Marriage is the first step in establishing a family and the kind of communication that exists between the partners determines the kind of family that they will establish.
- Marriage and Alternative Family Arrangements In the selection of the marriage partners, individuals are required to adhere to the rules of endogamy as well as the rules of exogamy.
- Marriage Decline as a Social Problem in the US To discuss the social illness of declining marriages in the US, the incorporated is the social constructionist perspective. The origins of the constructionism can be traced back to the attempts to establish the nature of […]
- Arranged Marriages are Less Successful This research aims to establish the reasons why arranged marriages are less successful when compared to love unions in the realms of commitment, passion, intimacy, and marital satisfaction.
- Common Sexual Problems Experienced During a Marriage Dissatisfaction with the relationship, a lack of shared activities, old age, poor health, and daily stress also contribute to a decrease in sexual satisfaction in a marriage.
- Marriage Decline Among Black Americans The marriage rate in the United States of America has generally declined in the current decade. Incarceration of the African American community has played a significant role in promoting their marriage decline for decades.
- Life in Marriage or Single Life? However, in recent decades, the world has begun to actively change, society has become more inclusive, and more and more people who refuse to marry for different beliefs have begun to appear.
- Privacy in Marriage: Rights Violations While this approach differs from the notion of the Living Constitution, which holds that the constitution should be read in the context of current times and political identities, even if such interpretation is at odds […]
- The Importance of Marriage Education In such cases, the importance of attending marriage education is highlighted, the usefulness and importance of which is to provide knowledge not only about the marriage union but also in general about interaction and proper […]
- Women in Marriage & Sex, Abortion, and Birth Control The historical period chosen is from the eighteenth to the twentieth century to demonstrate the advancement of social structures for women.
- Creating a Survey About an Institution of Marriage If I were to create a poll or a survey, I would want to study the institution of marriage from the viewpoint of people who have gotten a divorce at least once.
- Family Behaviors, Inequality, and Outside Childbearing Marriage The gap between the poor and the rich is widening in the US, making the American dream impossible for many people, especially children and families.
- The Meaning of Marriage: A Comparison of Articles In addition to the titles of academic journals and articles, it is possible to determine which field of science an article belongs to from its content, the language used, and the focus of the study.
- The Love and Marriage Relationship Analysis This shows that the researcher was determined to obtain accurate results from the subjects with the least, and that is the strength of the research.
- Institution of Marriage: The Sociological Perspectives However, sociological studies played a pivotal role in defining the main tendencies of marriage as a social institute development from the end of World War II to the current realities.
- Same-Sex Marriages and Equality Some oppose gay marriage on religious grounds and others- on an individual or group basis, but some tussle against the inequitable portrayal of gay marriage with zeal, such as Senator Dianne Feinstein.
- Newlyweds’ Optimistic Forecasts of Their Marriage The first instrument used was the Quality of Marriage Index, a six-item scale requiring partners to describe the level of their agreement and disagreements regarding their marriage in general.
- The Supreme Court Decision on the Right to Same-Sex Marriage The decision of the Supreme Court on the constitutional right of citizens to same-sex marriage is a significant event in the history of the development of modern democratic society.
- “Do Student Loans Delay Marriage?”: Participants, Measures, and Results The purpose of this article is to discover: the relationship between student loan debt and marriage in young adulthood; whether or not the relationship differs for women and men; if this relationship becomes weak over […]
- Aspects of Marriage and Family Life At the time of Colonial America, during the consequent period of the emerging modern family, and after the formation of the contemporary family, the situation of this institution differed drastically.
- Institution of Marriage in China Marriage is one of the oldest social institutions that regulate interpersonal and sexual relations, a society recognized by the union between spouses to create a family, giving rise to a married couple’s mutual rights and […]
- How Marriage Affected the Economic Status of Women On the other hand, in Twelfth Night, written in the early XVIIth century, the reader is shown the more romantic side of a marital union.
- Institution of Marriage and Its History Due to the nature and intentions of marriage, numerous definitions and viewpoints have emerged that continue to dictate what the institution ought to be.
- The Church’s Attitude Toward Homosexual Marriage Erickson Millard claims that Jesus’s teaching about the permanence of marriage is based on the fact that: God made humanity as male and female and pronounced them to be one.
- Future of Marriage: Non-Monogamy, People’s Needs in Marriage Another condition explaining the likelihood of the shift in the meaning and form of this institution is the fact that some of the values underpinning it remain intact.
- Marriage in Muslim Cultures and America In the Muslim religion, which is most widespread in the Arabian countries and among the Arabian people, marriage is perceived differently than in the American culture.
- Girls Not Brides Organization’s Commitment to Eliminate the Forced Child Marriage Graca Machel, and Archbishop Desmond Tutu are the champions of Girls Not Bride, and they advocate to end child marriage in our society.
- Gay Marriage Should Be Repealed The institution of marriage has changed dramatically within the first two decades of the 21st century due to the gradual acceptance of gay marriage.
- Interracial Marriages in “Like Mexicans” by Gary Soto Therefore, Soto’s decision to marry a Japanese woman should encourage Mexican people to change their negative attitude towards other ethnic groups and practice interracial marriages.
- COVID-19: How Race, Gender and Marriage Contribute to Humanity A study by Landivar et al.about the effect of the virus on gender and marriage in the US reveals that the pandemic has worsened gender inequality in employment.
- “Social Attitudes Regarding Same-Sex Marriage and LGBT…” by Hatzenbuehler It relates to the fact that the scientists failed to articulate a research question in the proper form. However, it is possible to mention that the two hypotheses mitigate the adverse effect of the lacking […]
- Cuban Americans Views on Marriage The representatives of different racial and ethnic groups tend to share dissimilar views regarding marriage, parenting, and divorce that are based on their cultural traditions and beliefs.
- Specific Communication Styles That Make for Happy Marriages The next style of communication is submissive, characterized by a desire to please other people, and avoid conflicts by all means.
- Does Marriage Bring Happiness?: Based on “The Story of an Hour” In this case, marriage is not a union of the loved ones but is a social obligation where a wife is a subject of a husband.Mr. Millard’s family seemed a perfect example of the social […]
- The Defense of Marriage Act: LGBTQ + Community One of the milestones in the development of the struggle of members of the LGBTQ + community for their rights in the United States is the adoption of the Defense of Marriage Act.
- Marriage and Divorce: Problems of Couples This seems to be the same stand that is taken by Paul in regards to the position of the man and the woman in the marriage, where the man seems to be the sole determinant […]
- Legalization of the Same-Sex Marriage: Advantages In this particular section, I would like to find out by which percent the economy of different countries will grow when the government legalizes homosexuality due to the excess expenses that it uses in buying […]
- Controversies Surrounding the Topic of Same-Sex Marriage In particular, the emergence of same-sex relations is the sign of the deinstitutionalization of the concept of marriage in society. The changes that occurred at the beginning of the 90s of the past century were […]
- The Gay Marriages: Ethical and Economic Perspectives Among the key ethical dilemmas that are related to the issue in question, the conflict between religious beliefs and the necessity to provide the aforementioned services, the issue regarding the company’s needs v.its duty to […]
- Marriage and Crime Reduction: Is There a Relationship? It is clear that marriage plays an integral role in reducing crime through a shift of priorities that are family centered and the transition to adulthood.
- California’s Proposition 8 on Same-Sex Marriages However, in other states, obtaining the right for same sex marriages is only one of a series of the issues that have arisen since much controversy as the U.S.same sex marriages movement rose in the […]
- “Why Marriages Succeed or Fail”: The “Bang” or “Whimper?” As mentioned above, it is common for people to assume that if something is wrong in a close relationship between a wife and a husband, there is a profound and apparent conflict to blame.
- Stephanie Doe: Misyar Marriage as Human Trafficking in Saudi Arabia In this article, the author seeks to highlight how the practice of temporary marriages by the wealthy in Saudi Arabia, commonly known as misyar, is a form of human trafficking.
- The Opinion of Americans on Whether Gay Marriage Should Be Allowed or Not Based on the political nature of the population, 43% of the democrats think, American society supports gay marriages and only 18% of the republicans hold the same view.
- “Why Marriages Fail” by Anne Roiphe It is a productive way to end the essay because people are reassured that in every situation there is a way out and it all depends on the individuals and their want to work things […]
- Millennials Say Marriage Ideal but Parenthood the Priority However, it is still believed that the joy of giving birth to a child is one of the greatest joys in life.
- Doomed Marriage in “The Girls in Their Summer Dresses” by Irwin Shaw The most common answer to this question is that these people love each other. The article The Girls in Their Summer Dresses testifies to the fact that marriage is doomed.
- Sexuality, Marriage, Gay Rights The supremacy of law and protection of people right lie in the heart of the protection of the freedom of personality.”Part of the basis of democratic government in the United States is a system of […]
- Cross-Border Marriages Between Japan and China: Reasons and Results Besides, the statistics of Japanese men and women dissatisfied with their marriages is humbling; consequently, determined to find a more gratifying alternative, men are engaged in cross-border marriage enterprise.
- Same-Sex Marriage Policy & Social Impact Reflection Creation of public policies and laws are significantly influenced by the diversity in culture forcing the government to engage with the society when developing policies.
- Same‐Sex Couples, Families, and Marriage The article under consideration is a systematic review of the recent scientific literature that addresses the range of issues that same-sex couples face and the peculiarities of their inner structure.
- Marriage Premium for Professional Athletes Researchers in the sphere of the labor economy agree that there is a connection between marital status and the number of wages earned by men.
- Polygamy in Islam: Marriage Issues Thus, the faith of people in their prophet is also the basis and rationale for the practice of polygamy. The fact that Islam views marriage as a sacred act of goodness and mutual help is […]
- “How I Met Your Mother”: Ideas of Marriage The central relationship throughout the series is Marshall and Lily’s marriage, with its ups and downs, individual quirks, and their influence on each other.
- Woman’s Position in Marriage: Similarities in History With time she began to see the creeping figures in the pattern of the wallpapers in the room; with an absence of any physical and mental activity, her anxiety began to increase and resulted in […]
- For Richer (Not for Poorer): The Inequality Crisis of Marriage An example of a factual claim made by the writer is where she states that the number of marriages in the United States dropped by 5% from the year 2009 to 2010.
- In Defense of Marriage Act 1996 As the editorial holds, the power of the law is lower than that of the congress and therefore its application on the subject of marriage is like depriving the congress of its powers of regulating […]
- Effect of Same-Sex Marriage on the Legal Structure of Gender in All Marriages Despite the fact that the current article does not address the gender roles in the family, parallels can be drawn showing that in no way the institutionalization of same-sex marriage can have an effect on […]
- Gender, Love and Sexuality: Healthy Marriage Formation Parties in marriage must have trust in each other because it is a basis for the growth of their union. Parties in a marriage need to be romantic as it harnesses love and loyalty.
- Same Sex Marriages: Definition and Main Problems In essence, the opposition of same sex marriages practically comes out of the use of the word “marriage”; such that, same sex couples enjoy the same rights as partners from contemporary marriages.
- Emotionally Focused Therapy Effectiveness in the Instituion of Marriage The suitability of the elements of the methodology determines the appropriateness. They indicate the main themes of the study and provide a beginning for the reader to understand the problem that is being researched and […]
- Marriage and Mothering Challenges In the modern world, the institution of marriage and the issue of motherhood have experienced challenges due to changes in perception.
- Interventions in Institution of Marriage Analysis This paper helps to understand the principles of evaluation research, the effectiveness of the intervention selected for settling marital discord and the use of evidence elicited in the research analysis for the purpose of enhancing […]
- The Case Against Gay Marriage The Constitutional protection to equal rights under the law has been invoked over and over again to try and afford homosexuals “equal right” to the social institution of marriage and to social security when one […]
- Conflict and Marriage Satisfaction To manage solving differences effectively, individuals in a marriage relationship should learn the thinking and positive and negative behaviors of their partners and have a positive perception towards these partners. This leads to unresolved conflicts […]
- Marriage and Physical Well-Being The dissolution of a marriage combined with the poor quality of the marriage leading up to the divorce is associated with the decline of both mental and physical health resulting in the increased use of […]
- Cohabitation Before Marriage One of the many disadvantages of cohabiting is that in this condition, you are never sure of your partner’s next move.
- Irony of Marriages in an Indian Set Up On the contrary, it is a belief, which can well be attributed to the rigidity of an Indian cultural norm that forces its followers to believe that the institution of marriage is indeed a handiwork […]
- Marriage and Family Systems: Western Society and Kadara of Nigeria The institution of marriage in the modern culture holds a distinct development over the years. In these cultures, marriage is negotiated by the parents of the betrothed.
- Re-Thinking Homosexual Marriage in Rational and Ethical Fashion We demonstrate that the way out of the hysterical debate is to consider soberly the basis for supporting the ordinary family as the basic unit of society and protector of the next generation.
- Gay Marriage and Bible: Differences From Heterosexual Practice When respected the bonds of marriage leads to the good not only of the couple and their children, but also to the good of society as a whole.
- Gay Marriage: Evaluation Argument The basic theme of the article was to present advocacy of gay marriage and a thorough presentation of arguments in favor of the legalization of gay marriages.
- Definition of Marriage. Reward of Marriage For many years, social scientists have argued on the reward of marriage due to the distinctiveness of the populace who get married and stay married. As a result, the definition of marriage can be broadened […]
- Same Sex Marriage Morality: Discussion Patterson further concluded that as long as the homosexual parents could let their children understand the real scenario, there is a strong indication that children could very well accept and love their parents even though […]
- Do Young Couples Marriages Always End in Divorce? The reasons for the failure of the marriage is supposed to stem from the immaturity of the parties involved and the ill preparedness of the couple to deal with the changes that married life brings […]
- Sex and Marriage Relations Analysis The problem of the modern married couples is that the notion of sex became the dominant in the relations and the faithfulness in the family is not in honor now.
- Temporary Marriage in Lebanon: Pros and Cons Supporters of temporary marriage in Lebanon argue that, since the union does not involve use of force, it cannot be termed as a violation of the right of women.
- The Concept of Marriage: Discussion They control their language and behavior and this is a prime example of symbolic interactionism that is instrumental in the institution of marriage.
- Marriage Rates in Oklahoma and Illinois This essay dwells much in the states of Illinois and Oklahoma and the differences and the reasons for this differences will make up the body of this discussion. Marriage rate differs a lot in the […]
- Interracial Marriage: History and Future Developments Sigler in- “Civil rights in America: 1500 to the present” is of the opinion that the civil rights of the citizens of America is helpful to make and end to the racial segregation in America.”Politics […]
- Civil Union: Legal Recognition of Same-Sex Couples’ Marriages Once the readers are influenced by the argument it is assumed that they would move a social memorandum in favor of the argument and insist the authority to grant the gay couples the status of […]
- Arranged Marriages: A Critical Analysis While discussing the points in favor of arranged marriage, the writer does not seem to have taken a stand in favor yet he has provided evidence to show that arranged marriage is an outlet for […]
- Inter Caste Marriages and Mixed Identity They do not experience the practices of a particular religion due to which they are perturbed when other children know and talk about their religion and its practices with a sense of pride and belonging.
- Christians Holy Orders and Marriage To a great level the society itself is constitutive of the symbol, and is thus vital in calling forward the gifts of the occupation in which each individual is well-known and established in each sacrament […]
- Marriage and Family: Women as Love Experts and Victims As evidenced in the case of Roberta, it is essential for women to continually reiterate emotions of love at regular intervals, in the absence of which she begins to lose faith in the very basics […]
- Views on Marriage and Family Throughout Chinese History in Relation to Religion The cost of having a kid in China is going up tremendously; especially since about a few years back due to the rapid development in China as they have only recently opened their market to […]
- Successful Marriage Conditions Research indicates that the success of long-term relationships is related both to intrinsic aspects of the relationship, such as liking one’s partner as a person, and to factors that are extrinsic to the relationship, such […]
- The Definition of Marriage The Sexual Revolution that took place in the 1960s caused sex to brazenly slip out of the boundaries of marriage. S, same-sex marriage is legal only in the states of Iowa and Massachusetts.
- Advocacy Plan for Forced Marriage in Sudanese Tradition This situation is a violation of human rights, and its high rate denotes that it is necessary to take specific actions to solve the problem. The information above means that it is necessary to address […]
- The Effects of Social Media on Marriage in the UAE
- Marriage in Contemporary America
- Marriage Lawsuit in the State of Florida
- Gender Role Attitudes and Expectations for Marriage
- First and Second Marriages: Psychological Perspective
- Happiness: Health, Marriage, and Success
- Gay Marriage: Societal Suicide
- Early Arranged Marriages in Indonesia
- Child Marriage in Egypt: Changing Public Attitudes
- Same-Sex Marriage Discriminatory Law in Alabama
- Family, Marriage, and Parenting Concepts Nowadays
- Marriage and Divorce Statistics in the United States
- “The Case For Same Sex Marriage” Video by Savino
- The Rejection of Marriage and Social Stability
- Family Life Cycle: The Institution of Marriage
- Marriage Expectations in Newlyweds
- Marriage Stages: Mother and Daughter’s Interview
- Marriage Process in Saudi Culture
- Advices for a Happy Marriage Life
- Marriage: The Good, the Bad, and the Greedy
- Same-Sex Marriage Legalization and Public Attitude
- Same-Sex Marriage National Legalization
- Long-Lasting Marriage and Its Psychology
- Marriage: Economic, Social and Political Meanings
- Interfaith Marriages in Islamic Views
- Child Marriage in Egypt as a Social Problem
- Arranged Marriage and Its Ethical Dilemma
- The Smart Stepfamily Marriage
- Gay Marriage and Its Social Acceptance in the US
- Relations and Social Distance in Kinship and Marriage
- Infidelity in Sexual Relationships and Marriage
- Same-Sex Marriage as a Positive Tendency Nowadays
- American Marriage Trends and Government Measures
- Same-Sex Marriage Representation in American Media
- Relationship and Marriage Coaching
- Marriage and Family Class Ideas
- Marriage and Politics in 3500 BC-1600 AD
- Marriage Peculiarities in the United Arab Emirates
- Marriage Life in the Film “The World of Apu”
- Does Marriage and Relationship Education Work?
- High Marriage Costs in the United Arab Emirates
- Marriage in the New Millennium
- Homosexual Marriage: Causes of Debates
- Interpersonal Communication Issues in the Marriage
- Marriage in the Films: The Mirror Has Two Faces and Sunrise
- Cohabiting Before Marriage: Reasons and Benefits
- Weddings, Marriage, and Money in the UAE
- Physical Health Problems in Marriage
- Marriage in the United Arab Emirates
- Tthe Defense of Marriage
- Sociology: Marriage and Reasons Why People Get Married
- The Changing Landscape of Love and Marriage
- Asian American Women and Marriage
- Legalizing Gay Marriage in the US
- The Miseries of Enforced Marriage
- “Gay Marriages” by Michael Nava and Robert Dawidoff
- Fairy Tale Marriages Are Not Real
- Marriage as Depicted in Soloveitchik’s Typology of Human Nature
- Why Do Conservatives Disagree on the Topic of Marriage Equality?
- Same-Sex Marriage in the United States of America
- Legalization of Same-Sex Marriage in San Francisco
- Family and Marriage Therapy
- Boundaries in Marriage: A Healthy Marital Association
- Gay Marriage’s Social and Religious Debates
- Interracial Marriages in the US
- Marriage and Family Therapy in Connecticut
- Interview of a Marriage and Family Therapist
- Gay Marriage in The UK
- Marriage and Love are Incompatible
- Marriage & Family Therapy
- Legalization of the Same Sex Marriage in California
- Constitutional Amendment that Allows Same-sex Marriage
- Gay Marriage: Debating the Ethics, Religion, and Culture Analytical
- Marriage and Family Counselling
- Effect of Stress on Relations and Marriage
- The Problems of Marriage and Divorce
- The Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA)
- Homosexuals’ Right to Marry
- Conservative Views on Same-Sex Marriage Campaigns
- The Effectiveness of Marriage Conflict Resolution Programs in the USA
- Self-Expansion and Marriage
- The Government Should Sanction Marriages of Same Sex Couples
- Millennials Say Marriage is Ideal but Parenthood is the Priority
- The Effect of Marriage on Crime Rate
- Current Trends Affecting Marriage and Family Formation in Asia
- Effects of Same Sex Marriage to the Society
- Gay Marriages and US Constitution
- The Issue of Gay Marriages: Meaning, Importance and Cons
- Legalizing Gay Marriage
- Incest – How Did Society’s View on Consanguineous Marriage Change Throughout History and Science Development and Why
- Naked Marriage and Chinese Society Research
- Marriage in Early Modern Europe
- Gay Marriage, Same-Sex Parenting, And America’s Children
- The Nature of Aristocratic Marriage and Family in the Mid-Heian Period
- Gay Couples’ Right to Marriage
- Human Behavior: How Five General Perspectives Affect Marriage
- Marriage and the Limits of Contract
- Defending Gay Marriage
- Relation of Gay Marriage to the Definition of Marriage
- Marriage Concerns in Al-Khobar City
- Concepts of Gay Marriage
- The Idea of Marriage: Why So Eager?
- Effects of the Social, Economic and Technological Change on Marriage
- Defense of Marriage Act
- Medieval Introduction to the Basic Principles of Marriage Sovereignty
- The Ethics of Early Marriages in the American Society
- Gay Marriage: Culture, Religion, and Society
- Gay Marriages in New York
- Should Same Sex Marriage Be Legal?
- Why Gay Marriages Should Not Be Legalized?
- Interracial Marriage in the U.S.
- Gay Marriage as a Civil Rights Issue
- Low Income Marriage and Divorce VS. High Level of Income Marriage and Divorce
- Role of Marriage/Family & Singlehood
- Anti-same-sex Marriage Laws and Amendments Violate the Constitutional Guarantees of Equality for all Citizens of the United States
- Arguments for Supporting Same-Sex Marriage
- Interracial Marriages and Relationships in Asian American Communities in the US
- Same-sex Couples and Marriage: Causes and Claims
- Children in Interracial Marriages
- Gay Marriage and Parenting
- Feelings about Marriage and Family Life
- The Women’s Career Role in the Institution of Marriage
- Should Gay Marriages Be Allowed?
- The Importance of Premarital Counseling Before Marriage
- Reasons of the High Homosexual Marriage Rate
- Marriage systems of the Gikuyu and San Communities
- Gay Marriage and Decision Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court
- Cohabitation: Is It Wrong?
- Arguments for Gay Marriages
- Opposition to the Legalization of Same Sex Marriage
- Marriage and Family Imagery in the Cinematography
- Religious, Governmental and Social Views on Same-Sex Marriage
- The Changes that has Occurred in Transpacific Vietnamese Marriages
- Love and Marriage during the Era of Mao in Communist China
- Gay Marriages: Why Not Legalize Them?
- 19th Century Norms of Marriage
- Should We Allow Gay Marriages as Civil Unions?
- Same-Sex Marriage: Sociopolitical
- Cohabitation vs. Marriage
- Marriage Equality: Same-Sex Marriage
- Monogamy as an Acceptable System of Marriage in America
- Must gay marriage to be legal?
- Gay Marriage in the U.S.
- Marriage as a Basic and Universal Social Institute
- Concepts why marriage matters
- Gay marriage and homosexuality
- Problems in Marriage – The Weakening of Families
- Pre Marriage Counseling: One Year Before Getting Married
- Same Sex Marriages Impact on the Children Social Growth
- Gay Marriage Legalization
- The Effect of Divorce on a Person After Long Marriage
- Rebuilding Families and Marriage in America’s Society
- Problems in Marriage: Is Divorce the Only Option?
- Sex Marriage: Personal Opinion
- What Are Factors Aid Determining Societal Norms Marriage Family?
- Who Did First Love Marriage in the World?
- How Does Marriage Affect Physical and Psychological Health?
- How Has Same-Sex Marriage Decision of Supreme Court Impacted Lives?
- What Are the Stages of Marriage?
- How Does the Perspective of Gay Marriage?
- Why Should Couples Not Live Together Before Marriage?
- How Do Cohabitation and Marriage Effects Childhood Well?
- What Are the Types of Marriage?
- How Do Legal Constraints Affect Marriage and Family Formations?
- How Has Marriage Changed Over the Last 30 Years?
- Can a Marriage Survive Different Political Views?
- Why Do People Stop Fighting for Their Marriage?
- How Does Same-Sex Marriage Affect Decreasing Population Growth?
- Why Do Men Change After Marriage?
- Why Married Couples Drift Apart After Marriage?
- Why Was Marriage Originally Created?
- How Does Same-Sex Marriage Affects Society?
- What Does the Bible Say About Marriage?
- What Do the Parental Pressures Affect Your Own Desire for Marriage?
- How Did the Utopian Communities Challenge Existing Ideas About Property and Marriage?
- How Does Infidelity Affect the Marriage and Family?
- How Was Marriage Back in the 1800s?
- Why Should Couples Live Together Before Marriage?
- How Does Infertility Effects Marriage?
- How Does Interracial Marriage Affect Children?
- How Similar Are Cohabitation and Marriage?
- How Far Would You Agree That Marriage Is Based on Social Class?
- When Marriage Loses Its Value?
- What Benefits Are There of Marriage Today?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 344 Marriage Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/marriage-essay-topics/
"344 Marriage Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/marriage-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '344 Marriage Essay Topics & Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "344 Marriage Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/marriage-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "344 Marriage Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/marriage-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "344 Marriage Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/marriage-essay-topics/.
- Family Titles
- Relationship Research Ideas
- Friendship Essay Ideas
- Wedding Research Topics
- Arranged Marriage Questions
- Bisexual Essay Titles
- Adultery Essay Ideas
- Demography Paper Topics
- Constitution Research Ideas
- Divorce Research Ideas
- Family Problems Questions
- Gender Discrimination Research Topics
- Happiness Research Ideas
- Same Sex Marriage Questions
- Women’s Role Essay Topics
The Phantasms of Judith Butler
In a new book, the influential theorist tries to indict gender-critical feminists.

J udith Butler, for many years a professor of rhetoric and comparative literature at UC Berkeley, might be among the most influential intellectuals alive today. Even if you have never heard of them (Butler identifies as nonbinary and uses they / them pronouns), you are living in their world, in which babies are “assigned” male or female at birth, and performativity is, at least on campus, an ordinary English word. Butler’s breakout 1990 book, Gender Trouble , argued that biological sex, like gender, is socially constructed, with its physical manifestations mattering only to the degree society assigns them meaning. The book is required reading in just about every women’s-, gender-, or sexuality-studies department. Butler has won a raft of international honors and been burned in effigy as a witch in Brazil. How many thinkers can say as much?
A few decades ago, Butler was probably as famous outside academia for their impenetrable jargon-ridden prose as for anything they were trying to say. In 1998, they won first prize in the annual Bad Writing Contest run by Philosophy and Literature , an academic journal. The next year, the philosopher Martha Nussbaum published a coruscating takedown , “The Professor of Parody,” in The New Republic , in which she argued that Butler had licensed a whole generation of feminist academics to blather incomprehensibly about semantics while ignoring the real-life global oppression of women. In the 1999 preface to a new edition of Gender Trouble , Butler struck back by attacking “parochial standards of transparency” and comparing critics to Richard Nixon, who would notoriously begin statements full of lies and self-excuses with the phrase “Let me make one thing perfectly clear.” Maybe the criticism stuck with Butler, though, because little by little, their nonspecialist writing has become more readable as they’ve ventured into current topics such as Donald Trump and Israel-Palestine (Butler’s view: The October 7 Hamas attack on Israel, which included the murder, rape, and mass kidnapping of civilian women, was a legitimate “act of armed resistance.”) Butler also began publishing in The Guardian , The Nation , and other venues. Who’s Afraid of Gender? , Butler’s first book for a nonacademic readership, is not particularly well written, and it’s quite repetitious (a whole paragraph is repeated, along with many, many phrases and ideas). But it’s not difficult. In fact, it’s all too simple.
The central idea of Who’s Afraid of Gender? is that fascism is gaining strength around the world, and that its weapon is what Butler calls the “phantasm of gender,” which they describe as a confused and irrational bundle of fears that displaces real dangers onto imaginary ones. Instead of facing up to the problems of, for example, war, declining living standards, environmental damage, and climate change, right-wing leaders whip up hysteria about threats to patriarchy, traditional families, and heterosexuality. And it works, Butler argues: “Circulating the phantasm of ‘gender’ is also one way for existing powers—states, churches, political movements—to frighten people to come back into their ranks, to accept censorship, and to externalize their fear and hatred onto vulnerable communities.” Viktor Orbán, Giorgia Meloni, Vladimir Putin, even Pope Francis—all inveigh against “gender.”

In the United States, this politicized use of the word gender itself has not caught on as it has in much of the world, where, as an English word for which many languages have no equivalent, it is often used to attack feminism and LGBTQ rights as foreign imports. Still, as Butler notes, America’s Christian fundamentalists and far-right Republicans are fervently in the anti-gender vanguard, whether or not these groups actually use the word gender .
Butler is obviously correct that the authoritarian right sets itself against feminism and modern sexual rights and freedom. This is nothing new, although being reminded of it is good. But is the gender phantasm as crucial to the global far right as Butler claims? Butler has little to say about the appeal of nationalism and community, insistence on ethnic purity, opposition to immigration, anxiety over economic and social stresses, fear of middle-class-status loss, hatred of “elites.” If I had to say why Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán is so popular, it would be less his invocation of the gender phantasm and more his ruthless determination to keep immigrants out, especially Muslim ones, along with his delivery of massive social services to families in an attempt to raise the birth rate. He neatly combines anti-feminist rhetoric about women’s duty to produce more Hungarians with policies that aim to make it easier for mothers to hold jobs, which is, however tacitly, feminist.
Similarly, Trump’s Christian-right supporters see this adjudicated rapist as a bulwark against sexual libertinism, but he also has a following among young men who admire him as libertine in chief and among people of every stripe who think he’ll somehow make them richer. I don’t disagree with Butler that the gender phantasm is part of the mix—some people, such as the QAnon followers who think Hillary Clinton is orchestrating child-abuse rings and the Moms for Liberty intent on purging school libraries, have clearly lost their minds. Butler mentions international organizations, such as the World Congress of Families, that seek to return us to the 1950s, or maybe the 1850s. But is obsession with “gender” really the primary motive behind current right-wing movements? And why is it so hard to trust that the noise around “gender” might actually be indicative of people’s real feelings, and not just the demagogue-fomented distraction Butler asserts it is? Their theory sounds a lot like an imposed false consciousness: You think you’re upset about Drag Queen Story Hour, but really you’re being distracted from deeper worries about unemployment or climate destruction. Instead of proving that “gender” is a crucial part of what motivates popular support for right-wing authoritarianism, Butler simply asserts that it is, and then ties it all up with a bow called “fascism.”
F ascism is a word that Butler admits is not perfect but then goes on to use repeatedly. I’m sure I’ve used it myself as a shorthand when I’m writing quickly, but it’s a bit manipulative. As used by Butler and much of the left, it covers way too many different issues and suggests that if you aren’t on board with the Butlerian worldview on every single one of them, a brown shirt must surely be hanging in your closet. As they define it—“fascist passions or political trends are those which seek to strip people of the basic rights they require to live”—most societies for most of history have been fascist, including, for long stretches, our own. That definition is so broad and so vague as to be useless. You might even say that “fascism” functions as a kind of phantasm, frightening people into accepting views wholesale without examining them individually. It’s a kind of guilt by association—like comparing critics of your prose to Nixon.
The chapter of Who’s Afraid of Gender? that is most relevant for American and British readers is probably the one about the women, many of them British, whom opponents call “TERFs” (trans-exclusionary radical feminists), but who call themselves “gender-critical feminists.” It’s a clunky, confusing label, and Butler spends a lot of time attacking it. About the substance of gender-critical-feminist arguments, they have much less to say. They discuss only two authors at any length, the philosopher Kathleen Stock and J. K. Rowling. Butler does not engage with their writing in any detail—they do not quote even one sentence from Stock’s Material Girls: Why Reality Matters for Feminism , a serious book that has been much discussed, or indeed from any other gender-crit work, except for some writing from Rowling, including her essay in which she describes domestic violence at the hands of her first husband, an accusation he admits to in part. (Butler finds Rowling’s concern about male violence excessive.) In essence, Butler accuses gender-crits of “phantasmatic” anxieties. They dismiss, with that invocation of a “phantasm,” apprehension about the presence of trans women in women’s single-sex spaces, (as well as, gender-crits would add, biological men falsely claiming to be trans in order to gain access to same), concerns for biologically female athletes who feel cheated out of scholarships and trophies, and the slight a biological woman might experience by being referred to as a “menstruator.”
Read: The worst argument for youth transition
Butler wants to dismiss gender-crits as fascist-adjacent: Indeed, in an interview , they compare Stock and Rowling to Putin and the pope. Unfortunately for Butler, many of the major figures in the movement are liberals and leftists, many are lesbians, and many, such as Joan Smith and Julie Bindel, have a long history of fighting misogyny and male violence.
It does seem odd that Butler, for whom everything about the body is socially produced, would be so uninterested in exploring the ways that trans identity is itself socially produced, at least in part—by, for example, homophobia and misogyny and the hypersexualization of young girls, by social media and online life, by the increasing popularity of cosmetic surgery, by the libertarian-individualist presumption that you can be whatever you want. Butler seems to suggest that being trans is being your authentic self, but what is authenticity? In every other context, Butler works to demolish the idea of the eternal human—everything is contingent—except for when it comes to being transgender. There, the individual, and only the individual, knows themself.
Like the gender phantasm, brandishing the word fascism functions much like the stance that trans activists have taken of insisting that their positions are not up for debate. That approach worked pretty well for a while. I can't tell you how many left and liberal people I know who keep quiet about their doubts because they fear being ostracized professionally or socially. Nobody wants to be accused of putting trans people's lives in danger, and, after all, don't we all want, as the slogan goes, to “Be Kind”? This self-imposed silence is a tiny problem compared with what trans people go through. The trouble is that, in the long run, the demand for self-suppression fuels reaction. Polls show declining support for various trans demands for acceptance . People don’t like being forced by social pressure to deny what they think of as the reality of sex and gender.
Butler calls for a coalition of allies to combat the gender phantasm. That would be a very good thing, but they’re preaching to the choir. They cite the civil-rights activist and singer Bernice Johnson Reagon’s call for “difficult coalitions” but forget that coalitions necessarily involve compromise and choosing your battles, not just accusing people of sharing the views of fascists if they don’t believe, for example, that a man can have a baby or that people should be able to change their gender just by filling out a form. Why would gender-critical feminists join such a movement?
Butler seems to want their opponents to simply cave. It could happen. Maybe 10 or 20 years from now, gender-critical feminism will seem as silly as opposition to same-sex marriage does today—a moral panic over what will be by then perfectly harmless, normal life. Then again, it could go the other way: In 10 or 20 years, the present moment might seem like a parenthesis in the long history of an overwhelmingly sexually dimorphic species. So here’s a thought: What if instead of trying to suppress the questioning of skeptics, we admit we don’t have many answers? What if, instead, we had a conversation? After all, isn’t that what philosophy is all about?
When you buy a book using a link on this page, we receive a commission. Thank you for supporting The Atlantic.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Who Is Leo Varadkar?
Mr. Varadkar, who said on Wednesday that he would step down as Ireland’s prime minister, has had a career of firsts. His resignation came as a surprise.

By Matthew Mpoke Bigg
Reporting from London
When Leo Varadkar said on Wednesday that he was resigning as Ireland’s prime minister , the surprise announcement ended a chapter in the career of a politician who has twice led the country, but whose party faces a struggle in elections next year.
As Mr. Varadkar ascended to the role in 2017, his identity — as the country’s first openly gay leader and its first with South Asian heritage — was viewed as evidence of Ireland’s rapid modernization. At 38, he was also its youngest leader.
Mr. Varadkar was born in Dublin to an Irish mother and a father born in India. Before embarking on a career in politics, he trained as a doctor. During a referendum campaign in 2015 on the legalization of same-sex marriage , Mr. Varadkar, who at the time was health minister , announced that he was gay, a measure credited with bolstering the “Yes” vote.
By the time he became prime minister, or taoiseach, Mr. Varadkar’s party, Fine Gael, had been in power for six years and was facing a crisis over domestic policy, including issues like health, education and housing. In an election in 2020, the party slumped to third place and formed a coalition with its rival center-right party, Fianna Fáil, and with the Green Party to hold onto power.
As part of the coalition deal, Mr. Varadkar resigned as leader and was succeeded by Micheál Martin, the leader of Fianna Fáil. After a stint as deputy prime minister, Mr. Varadkar returned to the top job in December 2022.
Speaking in Dublin with cabinet members behind him on Wednesday, Mr. Varadkar trumpeted what he described as his government’s achievements on domestic issues and singled out moves to enshrine personal rights.
“I am proud that we have made the country a more equal and more modern place when it comes to the rights of children, the L.G.B.T. community, equality for women and their bodily autonomy,” he said.
At the same time, he acknowledged that his decision to step down would come as a surprise to many. Explaining his rationale, he said that there was “never a right time to resign high office,” but that he was “not the best person for the job anymore.”
This month, voters rejected two proposed changes to the Constitution that would have removed language about women’s duties being in the home and broadened the definition of family beyond marriage.
Mr. Varadkar appeared to allude to the setbacks for his government in his remarks on Wednesday, saying: “There are areas in which we have been much less successful and some in which we have sadly gone backward.”
In recent months, Mr. Varadkar has been a vociferous critic of Israel for its conduct in its war against Hamas in Gaza, an issue that he raised with President Biden at the White House on Sunday during the Irish leader’s St. Patrick’s Day visit to the United States. Critics have argued that Mr. Varadkar’s blunt-spoken manner was at times jarring.
His resignation does not mean that an election must immediately take place. But an election that is due to take place next year appears to be an uphill battle for his party, not least because of the relative weakness of the coalition agreement by which Mr. Varadkar returned to the top office.
Matthew Mpoke Bigg is a correspondent covering international news. He previously worked as a reporter, editor and bureau chief for Reuters and did postings in Nairobi, Abidjan, Atlanta, Jakarta and Accra. More about Matthew Mpoke Bigg

COMMENTS
marriage, a legally and socially sanctioned union, usually between a man and a woman, that is regulated by laws, rules, customs, beliefs, and attitudes that prescribe the rights and duties of the partners and accords status to their offspring (if any). The universality of marriage within different societies and cultures is attributed to the ...
Marriage is a legally recognized union between two individuals that comes with legal rights, responsibilities, and obligations. It is usually formalized through a wedding ceremony or a legal process. In a marriage, couples typically obtain a marriage license and have their union solemnized by a marriage officiant.
Abstract. In the article, we argue that as a moral reality, marriage is the union of a man and a woman who make a permanent and exclusive commitment to each other of the type that is naturally fulfilled by bearing and rearing children together, and renewed by acts that constitute the behavioral part of the process of reproduction.
Marriage by definition is "the legal union of a man and a woman as husband and wife.". Americans statistically fail in a marriage, (According to Susan Estrich)"with more than half of all marriages ending in divorce, families are not what they used to be. In modern marriages, one of the partners will get married to the other for the wrong ...
Marriage and Domestic Partnership. First published Sat Jul 11, 2009; substantive revision Wed Jul 14, 2021. Marriage, a prominent institution regulating sex, reproduction, and family life, is a route into classical philosophical issues such as the good and the scope of individual choice, as well as itself raising distinctive philosophical ...
Definition Essay On Marriage 843 Words | 4 Pages. Marriage by definition is "the legal union of a man and a woman as husband and wife." Americans statistically fail in a marriage, (According to Susan Estrich)"with more than half of all marriages ending in divorce, families are not what they used to be. In modern marriages, one of the ...
Marriage is the legal or formal recognition of union between two people. Marriage symbolizes the love of two people until death do them part. Marriage is a risk people take despite the various odds against it. People get married for a variety of reasons because of religious beliefs, societal pressure, and obligations.
Marriage and family are key structures in many societies. Many of us learn from a young age that finding and joining the right person is a key to happiness and security. We're told that children need two parents. Many of the tax laws, medical laws, retirement benefit laws, and banking and loan processes seem to favor or assume marriage.
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognised union between people called spouses.It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children (if any), and between them and their in-laws. It is nearly a cultural universal, but the definition of marriage varies between cultures and religions, and over time.
Marriage is very common among societies. Depending on the culture, the definition and the type of marriages differ. According to Encyclopedia Britannica, "Marriage is a physical, legal and moral union between man and woman in complete community life for the establishment of a family(2013)."A broader definition of marriage is that it's ritually and socially recognized union between people ...
So, what is marriage? Some might say the definition of marriage is a promise, a vow to stay with the person you love. Some might even say that marriage is the graveyard of love. In fact, we cannot give a correct definition of marriage. Marriage has changed a lot throughout seventy-five years of history.
Marriage is a relationship that bind of a spouse in formal event and registered by law as to declare a husband and wife. Marriage is key to form a family into larger as a basic unit in social system. Marriage also bind of the emotional relationship where both spouse are sharing their life together as to form a family.
Marriage is based on the truth that men and women are complementary, the biological fact that reproduction depends on a man and a woman, and the reality that children need a mother and a father.
Marriage is a phenomenon that has existed throughout human history and appears in a variety of literatures including sociology, anthropology, cultural studies and legal studies among others. It is a phenomenon that has evolved through different definitions that attempt to fit the concept in particular circumstances.
Universality of Marriage. Marriage is a social institution existing in all societies but the characteristics vary from culture to culture. Several anthropologists have made an effort to define marriage universally, but none of them have been able to satisfactorily include all of its variations in a single definition.
Marriage is an institutionalized relationship within the family system. It fulfills many functions attributed to the family in general. Family functions include basic personality formation, status ascriptions, socialization, tension management, and replacement of members, economic cooperation, reproduction, stabilization of adults, and the like.
500+ Words Essay on Marriage. In general, marriage can be described as a bond/commitment between a man and a woman. Also, this bond is strongly connected with love, tolerance, support, and harmony. Also, creating a family means to enter a new stage of social advancement. Marriages help in founding the new relationship between females and males.
Marriage is a term that signifies an agreed union or vow between two consenting adults who signified intentions of living together within the conditions stipulated in their religious, civic, or cultural affinities. As could be deduced, since people come from diverse cultural, ethnic, racial and religious orientations, the beliefs and value ...
By definition, marriage is "the legal union of a man and a woman as husband and wife" (Webster's Dictionary). Most people claim that they want their marriage to last a lifetime. Because over half of all marriages in the United States end in a divorce, most people lack the understanding of what it takes to stay married.
344 Marriage Essay Topics & Examples. Updated: Feb 29th, 2024. 26 min. Whether you're writing about unconventional, traditional, or arranged marriage, essay topics can be pretty handy. Consider some original ideas gathered by our experts and discuss divorce, weddings, and family in your paper. We will write.
Marriage is the economic and sexual union between two or more people. Many people marry for love, economic reasons, and simply just to start a family. Many cultures throughout the world partake in different types of marriage such as monogamy, polygamy, cousin marriages, arranged marriages, and group marriages.
The classic legal definition of marriage can be found in Hyde v Hyde and Woodmansee, [ 3] where Lord Penzance defined marriage as the 'voluntary union for life of one man and one woman, to the exclusion of all others'. [ 4] This has been enshrined in the Matrimonial Causes Act (MCA) 1973 s.11 (c), where a marriage is void when the parties ...
Butler does not engage with their writing in any detail—they do not quote even one sentence from Stock's Material Girls: Why Reality Matters for Feminism, a serious book that has been much ...
Definition Essay: Defining Marriage. Defining Marriage Tensions between religious communities and the Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender (LGBT) community are at an all-time high. Bryan Cones and the United Conference of Catholic Bishops lead those whose religious beliefs mandate marriage must exist only between one man and one woman.
Mr. Varadkar, who said on Wednesday that he would step down as Ireland's prime minister, has had a career of firsts. His resignation came as a surprise. Prime Minister Leo Varadkar of Ireland ...